A New Benchmark for the Appropriate Evaluation of RTL Code Optimization
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: A New Benchmark for the Appropriate Evaluation of RTL Code Optimization- ArXiv ID: 2601.01765
- Date: 2026-01-05
- Authors: Yao Lu, Shang Liu, Hangan Zhou, Wenji Fang, Qijun Zhang, Zhiyao Xie
📝 Abstract
The rapid progress of artificial intelligence increasingly relies on efficient integrated circuit (IC) design. Recent studies have explored the use of large language models (LLMs) for generating Register Transfer Level (RTL) code, but existing benchmarks mainly evaluate syntactic correctness rather than optimization quality in terms of power, performance, and area (PPA). This work introduces RTL-OPT, a benchmark for assessing the capability of LLMs in RTL optimization. RTL-OPT contains 36 handcrafted digital designs that cover diverse implementation categories including combinational logic, pipelined datapaths, finite state machines, and memory interfaces. Each task provides a pair of RTL codes, a suboptimal version and a human-optimized reference that reflects industry-proven optimization patterns not captured by conventional synthesis tools. Furthermore, RTL-OPT integrates an automated evaluation framework to verify functional correctness and quantify PPA improvements, enabling standardized and meaningful assessment of generative models for hardware design optimization.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **New Benchmark Proposal:** While existing benchmarks focus on artificial problems in evaluating RTL code optimization, RTL-OPT provides a variety of real-world optimization patterns that reflect actual circuit design challenges. This allows for more accurate evaluations of how LLMs improve RTL codes. 2. **Impact of Synthesis Process:** The synthesis tool used, compile modes, and clock period constraints significantly affect the final PPA results of RTL code. RTL-OPT is designed to evaluate LLM performance across various synthesis configurations. 3. **Real Improvement Verification:** Existing benchmarks often fail to reflect real improvements in RTL code due to artificial inefficiencies. In contrast, RTL-OPT captures actual design challenges, enabling a more precise assessment of how well LLMs can optimize RTL codes.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
In recent years, the adoption of large language models (LLMs) in the agile design of ICs has emerged as a promising research direction . Especially, many recent works develop customized LLMs to directly generate IC designs in the format of Register-Transfer Level (RTL) code, such as Verilog.
Benchmarking RTL Code Generation. The RTL design is the starting point of digital IC design implementation and requires significant human efforts and expertise. LLM-assisted RTL code generation techniques aim to relieve engineers from the tedious RTL coding process. To enable a fair comparison among different LLMs’ capabilities in RTL generation, high-quality benchmarks become necessary. Representative benchmarks on RTL code generation include VerilogEval and RTLLM , VerilogEval v2 , RTLLM 2.0 , CVDP , and others .
Difficulty in Evaluating RTL Optimization. However, the aforementioned benchmarks primarily focus on the correctness of RTL code generation, without explicitly evaluating the optimization of IC design’s ultimate qualities in terms of power, performance, and area (PPA). The RTL code will be synthesized into ultimate circuit implementations using synthesis tools, which will apply extensive logic optimizations when converting RTL code into implementations. Thus, PPA results depend on both the RTL code quality and the downstream synthesis process. As we will point out in this paper, this tight interplay makes benchmarking RTL optimization particularly challenging, sometimes even misleading.
 />
/>
 />
/>
Benchmarking RTL Code Optimization. Constructing a high-quality benchmark for RTL optimization is inherently challenging due to the severe scarcity of open-source circuit designs, which are valuable IPs for semiconductor companies. Most recently, some LLM works start to target generating more optimized RTL code, which is expected to yield better ultimate chip quality in PPA. These works are all evaluated on the only relevant benchmark , which provides suboptimal RTL codes for LLMs to improve. However, our study indicates that this benchmark falls short in several aspects: 1) Unrealistic designs: many suboptimal RTL codes in this benchmark are overly contrived and fail to capture real inefficiencies in practice; 2) Oversimplified synthesis setup: reliance on weak synthesis tools such as Yosys leads to results that are sensitive to superficial RTL code changes and poorly aligned with industrial-grade flows; 3) Insufficient evaluation: its assessments focus only on area-related metrics, while neglecting power and timing. Such evaluation metric neglects the ubiquitous trade-offs in a typical IC design process.
In this work, we first inspect the existing works on RTL optimization and rethink a key question: how to benchmark the optimization of RTL code appropriately?1 We carefully inspect existing works and downstream synthesis flows. This study reveals that evaluating RTL optimization is non-trivial and may easily lead to misleading conclusions. Specifically, whether one RTL code is superior (i.e., more optimized) to the other strongly depends on the synthesis tool and setup. Many “optimized” RTL codes indicated by the prior work turn out to be the same or even worse than their “suboptimal” RTL counterparts when different, typically more advanced, synthesis options are adopted.
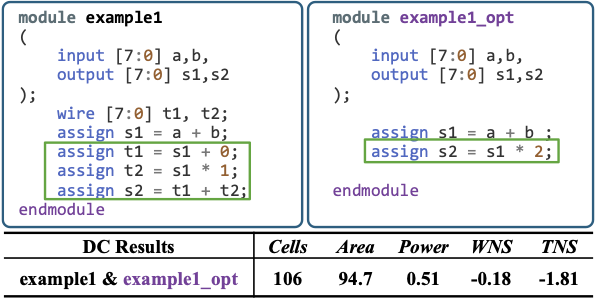
Figure 1 highlight a common flaw in designs:
its RTL pairs are based on unrealistic transformations that do not
address true optimization challenges in hardware design.
These contrived suboptimal examples exhibit
unnecessary inefficiencies, such as redundant computations and
superfluous arithmetic operations, which are unlikely to occur in
practice. Synthesis tools can easily optimize these contrived patterns,
leading to evaluations that may overstate the effectiveness of LLMs in
improving RTL quality. The optimized version (example1_opt)
implements the logic directly by computing s1 = a + b and then
deriving the output as s2 = s1 * 2. In contrast, the suboptimal
version (example1) introduces contrived and unnecessary steps: it
first computes s1 = a + b, then redundantly adds 0 and multiplies by 1
to produce intermediate wires t1 and t2, before summing them into
s2. Such constructions are unnatural and would rarely appear in
practical RTL coding, making the benchmark examples unrealistic.
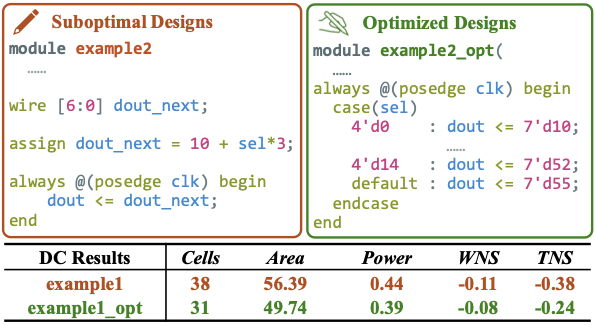
Figure 2 shows an example from RTL-OPT, the
detailed analysis are in
Section 3.2.
 style="width:100.0%" />
style="width:100.0%" />
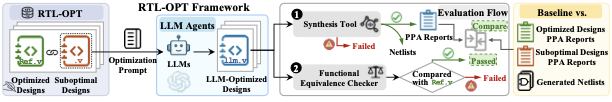
Based on our aforementioned observations, we propose a new benchmark, RTL-OPT, specifically designed to evaluate LLMs’ ability in RTL design optimization systematically. RTL-OPT consists of 36 handcrafted RTL optimization tasks targeting PPA qualities. A key distinguishing feature is that it provides a collection of diverse and realistic optimization patterns, such as bit-width optimization, precomputation and LUT conversion, operator strength reduction, control simplification, resource sharing, and state encoding optimization, all derived from proven industry practices. These patterns capture transformations that truly matter for RTL optimization and remain effective even under advanced synthesis. It sets RTL-OPT apart from prior works that often lacked real optimization impact. As illustrated in Figure 4, each RTL-OPT task provides a pair of RTL codes: a deliberately designed suboptimal (to-be-optimized) version and an optimized version serving as the golden reference. LLMs take the suboptimal code as input and attempts to generate a more optimized RTL code while preserving design functionality. Specifically, RTL-OPT provides: a set of 36 handcrafted tasks, ensuring comprehensive and representative coverage of real-world design challenges; an integrated evaluation framework (Figure 4), which automatically verifies functional correctness and compares the ultimate PPA of LLM-optimized designs against the designer-optimized golden reference.
Rethinking the RTL Code Optimization
In this section, we present a comprehensive study examining both existing benchmarks for RTL code optimization and our proposed RTL-OPT benchmark across multiple synthesis configurations. This study reveals the inherent limitations of relying solely on overly contrived design examples in conventional benchmarks.
Impact of Synthesis Process on RTL Evaluation
According to our study, we point out that the evaluation of RTL optimization (i.e., judging which RTL code leads to better PPA) is not a straightforward task. One primary reason is that the ultimate design quality also depends on the synthesis process. Differences in synthesis tools, optimization modes, and timing constraints can all significantly affect whether and how structural differences in RTL code are reflected in the final implementation.
Effect of Synthesis Tool. Different tools adopt distinct optimization strategies and heuristics. Commercial tools such as Synopsys Design Compiler (DC) typically perform more aggressive and sophisticated optimizations, while open-source tools like Yosys provide a weaker alternative valued in academic research. As a result, the same pair of RTL codes may exhibit different levels of quality differentiation depending on the synthesis tool used.
Effect of Compile Mode. Commercial tools support multiple
compilation modes with varying optimization aggressiveness. More
advanced modes (e.g., compile_ultra in DC) tend to aggressively
restructure logic, which can obscure fine-grained RTL differences.
Effect of Clock Period Constraints. The target clock period also shapes synthesis behavior. Tight constraints often lead to aggressive timing-driven optimizations, while relaxed constraints may reduce differentiation between RTL variants. Choosing a realistic and consistent timing target is important for fair and interpretable evaluation of RTL code.
Inspection of Existing Benchmark
The existing benchmark provides multiple pairs of suboptimal and human-optimized RTL designs, along with additional RTL code generated by their LLM-based optimization experiments. Surprisingly, our study reveals that: 1) Both the human-optimized RTL designs and the LLM-optimized RTL designs from often fail to outperform their corresponding suboptimal counterparts after synthesis. In many cases, they are essentially the same or even worse, particularly when advanced synthesis options are applied. 2) We observe clearly different impacts on ultimate PPAs between different synthesis tools: commercial tool DC with strong optimization capabilities tend to eliminate the differences between suboptimal and optimized RTL, while open-source Yosys often exaggerates them. Together, these results suggest that the existing benchmark does not reliably reflect true improvements in RTL code.
The evaluation results of existing benchmarks
are shown in Table [tab:measure1]
and [tab:measure2]. We carefully
inspect and evaluate all 43 pairs of RTL code2 from the whole
benchmark released in . Specifically,
Table [tab:measure1] compares each pair of
suboptimal and human-optimized designs, both from the original
benchmark. We evaluate whether the human-optimized reference is
actually better, worse, or the same compared with its suboptimal RTL
counterpart after synthesis3. In addition, there may exist a
“trade-off” result in the PPA comparison, indicating improvement in one
PPA metric while degradation in the other. As for Yosys, similar to
prior works, we only compare the number of cells. In
Table [tab:measure1], only 13
human-optimized RTL out of 43 cases are better than their
suboptimal counterparts with compile_ultra. This number rises to 16
with compile and further to 24 with Yosys. Many human-optimized RTLs
are no better than suboptimal RTL, particularly with advanced
synthesis options. It validates that
commercial tools can eliminate many contrived inefficiencies, while
open-source tools often retain them, highlighting a clear
discrepancy.
We also extend our evaluation under different clock constraints by
setting a tighter timing target of clock period = 0.1ns. The
corresponding results are shown as the
gray entries in
Table [tab:measure1]. When using the same
synthesis modes (i.e., compile or compile_ultra), using a tighter
timing constraint leads to slightly more cases with PPA trade-offs and
even less actually better RTL code.
Table [tab:measure2] further compares
LLM-optimized designs with suboptimal designs directly released by
prior work . In Table [tab:measure2], for both GPT-4.0 and
model proposed by , only 3 LLM-optimized RTL out of 12 cases are
actually better than their suboptimal counterparts with
compile_ultra. The number rises to 5 out of 12 with compile. In
summary, many LLM-optimized RTLs turn out to be no better than
suboptimal RTL, especially with advanced synthesis options.
It indicates that under strict synthesis
flows, the benchmark shows limited effectiveness.
Same Inspection of Our Benchmark
In Table [tab:measure1], we also evaluate our
proposed benchmark, RTL-OPT, using the same setup. According to
Table [tab:measure1], 35 out of 36
human-optimized RTL codes in RTL-OPT are better when compile_ultra
is adopted, and 33 out of 36 for Yosys. In
Table [tab:measure1], with a tight timing
constraint, 23 cases remain better while 13 result in PPA trade-offs,
with no cases achieving the same ultimate PPA. Compared to the previous
benchmark , RTL-OPT shows significant improvements in evaluating RTL
designs.
This clear validation of RTL-OPT’s benchmark quality arises from its design philosophy: it provides genuinely suboptimal RTL implementations with meaningful room for improvement, rather than contrived inefficiencies that synthesis tools can remove.
RTL-OPT Benchmark
In this section, we present RTL-OPT, a benchmark designed for evaluating RTL code optimization with LLMs. RTL-OPT provides realistic suboptimal and optimized RTL pairs handcrafted by experts, ensuring genuine inefficiencies and meaningful golden references. Covering diverse design types and evaluated with both commercial and open-source tools, it offers a robust and practical resource for advancing RTL optimization research.
Benchmark Description
The RTL-OPT consists of 36 RTL design optimization tasks. Each task provides a pair of RTL codes: a suboptimal version and a corresponding designer-optimized version, implementing the same functionality. All designs are manually written by hardware engineers to reflect realistic coding styles and optimization practices, with the optimized RTL serving as the golden reference for human-optimized PPA quality. The suboptimal RTL is not arbitrarily degraded; it represents a valid, functionally correct design that omits specific optimization opportunities. This setup creates meaningful optimization gaps and practical scenarios encountered in the semiconductor industry.
The 36 provided design tasks cover a variety of design types, including arithmetic units, control logic, finite state machines (FSMs), and pipelined datapaths. These designs vary in size and complexity, with logic area ranging from 14 to 20K cells and synthesized area ranging from 15 to 19K $`\mu m^2`$. This diversity ensures that the benchmark is representative of practical RTL design tasks.
Table [tab:general] summarizes the average PPA metrics of RTL-OPT provided suboptimal and optimized designs across 36 benchmarks. The results include synthesis and evaluation using both commercial DC and open-source Yosys tools. From the table, it is evident that the suboptimal designs exhibit significantly higher PPA values compared to the optimized designs. These results indicate that the suboptimal designs have substantial room for improvement even under DC, highlighting the effectiveness of RTL-OPT as a benchmark for optimizing the PPA of RTL code in LLMs.
RTL-OPT is fully open-sourced and provides the following artifacts to support benchmarking the RTL optimization capabilities of LLMs: (1) 36 carefully designed RTL code pairs; (2) Corresponding synthesized netlists from commercial synthesis tools; (3) Detailed PPA reports from electronic design automation (EDA) tools for both suboptimal and optimized designs; (4) A complete toolchain flow, including standard-cell library, scripts for synthesis, simulation, and functional verification, which can also verify the correctness of the rewritten code by LLMs.
RTL-OPT Analysis: Optimization Patterns
The optimization patterns, which provide optimization opportunities, are derived from proven industry-standard RTL coding practices that have a direct impact on the quality of logic synthesis. These patterns represent how specific RTL-level modifications ultimately affect downstream synthesis outcomes. The key optimization pattern types in the RTL-OPT benchmark are summarized as follows:
-
Bit-width Optimization: Reducing register and wire widths where full precision is not necessary, optimizing both area and power consumption.
-
Precomputation & LUT Conversion: Replacing runtime arithmetic operations with precomputed lookup tables to eliminate complex logic units.
-
Operator Strength Reduction: Substituting high-cost operators with simpler equivalents through bit manipulation.
-
Control Simplification: Flattening nested finite state machines (FSMs) or reducing unnecessary states, streamlining control logic, and improving both area and timing.
-
Resource Sharing: Consolidating duplicate logic across different cycles to maximize hardware resource efficiency.
-
State Encoding Optimization: Selecting optimal state encoding schemes (One-hot, Gray, Binary) based on state count to balance power, area, and timing.
By integrating optimization patterns across a diverse range of RTL designs, RTL-OPT generates its realistic yet challenging benchmark for LLM-assisted RTL code optimization: enhancing PPA metrics of optimized code while maintaining functional correctness.
To illustrate these optimization patterns, we provide one simple code example from the RTL-OPT in Figure 2. This example compares suboptimal and optimized RTL implementations within a specific pattern category, accompanied by discussions on the structural changes and the quantitative improvements observed in downstream PPA metrics.
Example: This example in
Figure 2 demonstrates the optimization pattern
of precomputation & LUT conversion, where real-time arithmetic
operations are replaced with precomputed values. In the suboptimal
design, the output is dynamically calculated using the sel input,
requiring multiplication at each clock cycle. The optimized design
replaces this operation with a case statement that directly assigns
precomputed values based on the selection. This optimization results in
a 14% reduction in area and a 12% decrease in power consumption by
eliminating arithmetic operations and reducing signal toggling.
Evaluation Methodology and Tools
RTL-OPT provides a complete evaluation flow to assess LLMs’ optimization capabilities by measuring the PPA of synthesized RTL code. This is achieved through a combination of synthesis, functionality verification, and PPA evaluation, all performed using industry-standard EDA tools.
Synthesis Process
The logic synthesis process converts the initial RTL code into gate-level netlists, based on which the PPA metrics can be quantitatively evaluated. In this work, we mainly employ DC for the synthesis of the RTL-OPT benchmark, given its established effectiveness in industrial design flows. DC demonstrates superior capabilities in identifying inefficient RTL constructs and optimizing them into more efficient circuit implementations, thereby minimizing sensitivity to the initial code quality.
When benchmark quality is insufficient, DC tends to synthesize both the suboptimal and optimized RTL codes into functionally equivalent gate-level netlists, resulting in identical PPA outcomes. This behavior reflects the limited optimization opportunities offered by low-quality benchmarks. Conversely, open-source synthesis tools such as Yosys , which provide less aggressive optimization, may still produce differing PPA results for such code pairs, potentially overstating the effectiveness of certain code transformations. For completeness, we also provide synthesis results obtained using Yosys to support broader comparative analyses.
The synthesis process also involves the use of a technology library, or cell library, which is a collection of pre-characterized standard cells such as logic gates, flip-flops, and other fundamental components. These cells are designed to meet specific PPA constraints. While we use Nangate45 in our evaluation, other libraries could also be used, though they typically require a license. The choice of library significantly impacts the RTL optimization process, as it defines the available cells and their performance characteristics, ultimately influencing the design’s efficiency.
Functional Equivalance Verification
After successful synthesis, the RTL code is ensured to be free of syntax errors, as it can be correctly transformed into a gate-level netlist. Following synthesis, functional verification is essential to ensure that the optimization steps have not introduced errors. This verification is primarily conducted using Synopsys Formality , which performs functional equivalence checking by rigorously comparing the LLM-optimized RTL against the golden reference to ensure behavioral consistency. However, for optimizations involving timing adjustments, such as pipelining, additional dynamic verification is required. This is performed using Synopsys VCS , which employs comprehensive testbenches to validate the design’s behavior under various operating conditions.
This combined approach ensures both logical equivalence and operational reliability of the optimized design. A design is considered functionally valid only if it passes both formal equivalence checking and dynamic verification for timing-critical optimizations.
PPA Metrics and Trade-offs in Optimization
To evaluate the quality of the synthesized designs, we analyze them from three aspects: Power, Performance, and Area:
Power: Total power reported by the synthesis tool, including dynamic and leakage components.
Performance: Timing quality measured by Worst Negative Slack (WNS) and Total Negative Slack (TNS).
Area: Physical implementation cost characterized by silicon area and cell count.
Trade-offs widely exist in these PPA metrics. For instance, optimizing for power may increase area, while minimizing area could compromise power efficiency. A key challenge in RTL optimization is managing these competing goals to achieve an optimal balance based on design constraints.
Experiments
This section presents the experiments conducted to evaluate the optimization capabilities of different LLMs on the RTL-OPT benchmark. We compare the performance of several LLMs, including GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-2.5, Deepseek V3, and Deepseek R1, in optimizing RTL code. The focus of the experiments is on assessing the optimization in terms of PPA metrics, as well as the functional correctness of the optimized designs. The results show that the two Deepseek models demonstrate stronger optimization ability than the other evaluated LLMs.
Summary of Benchmarking Results
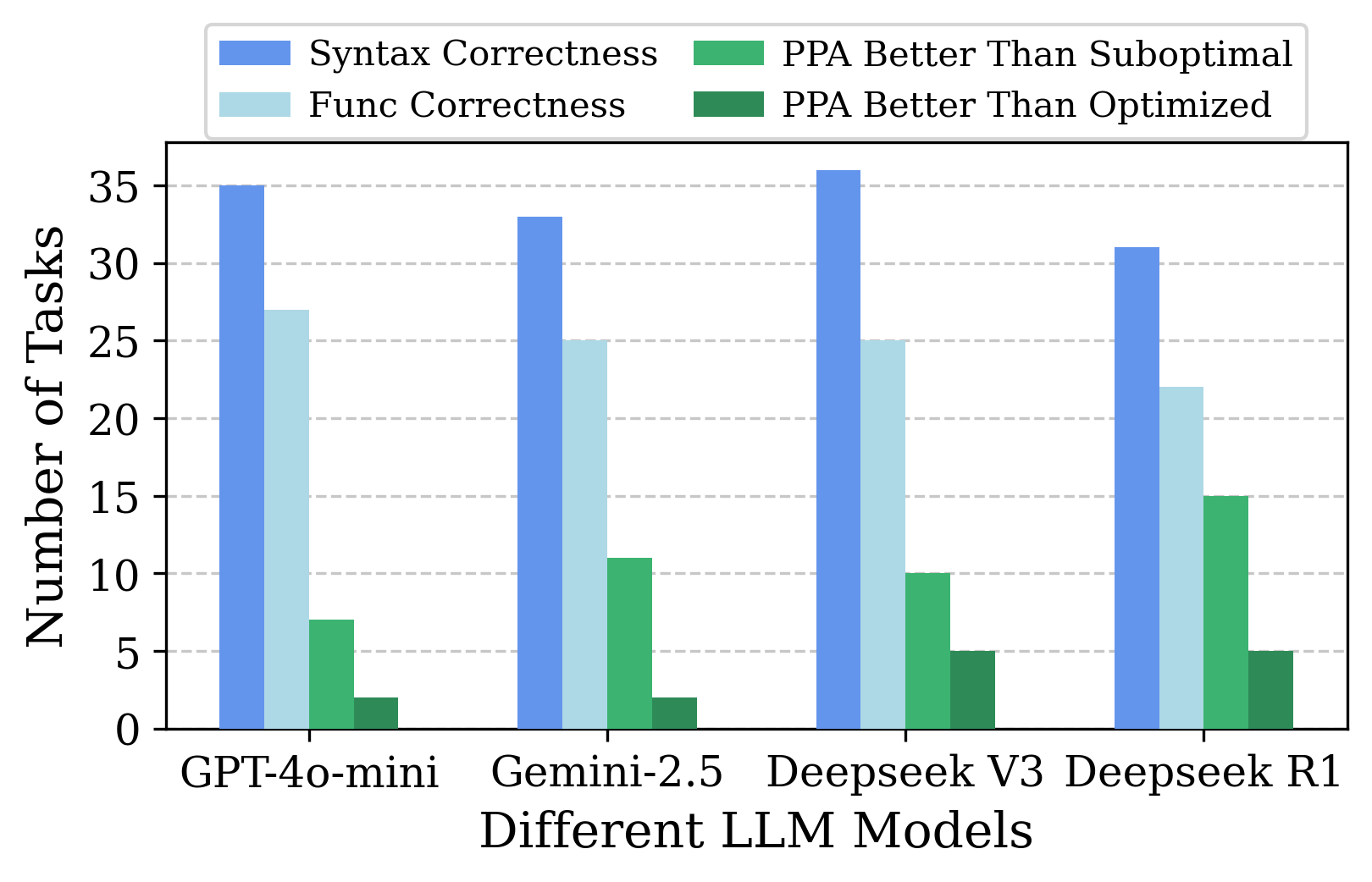
Figure 5 shows a summary of benchmarking results of the four evaluated LLMs. It reveals the syntax correctness, functionality correctness, and post-optimization PPA quality performance of the various LLMs. The overall results highlight that: There is still significant room for LLM to improve in RTL optimization compared to human designers. Our benchmark is designed to be realistic, providing a set of challenging tasks that reflect the complexities encountered in real-world hardware design.
Notably, the overall performance of all LLMs is not very good, reflecting the challenges in our RTL-OPT benchmark. Many LLMs have over 10 optimized cases failed to maintain functionality correctness. Deepseek R1 can successfully optimize about 15 suboptimal designs, and can outperform our human designers’ solution for around 5 designs.
When comparing these 4 LLMs, Deepseek R1 generally outperforms the other models in terms of PPA. However, Deepseek R1 also exhibits a higher rate of functional discrepancies compared to the other models. In contrast, models such as GPT-4o-mini and Gemini-2.5, while maintaining high syntax correctness, achieved fewer improvements in PPA. It implies that their optimization strategies are either more conservative or lack effective optimizations.
Detailed Benchmarking Results
One observation from the evaluation results in Figure 5 is the trade-off between optimization and functionality. While Deepseek R1 showed the most significant improvements in PPA, it was also the most prone to introducing functional errors. In contrast, GPT-4o-mini and Gemini-2.5 exhibited a more balanced approach, optimizing PPA while maintaining syntax correctness. This indicates that Deepseek R1’s aggressive optimization, though effective, tends to increase error, especially in designs with complex timing or control logic. Conversely, GPT-4o-mini and Gemini-2.5, while less aggressive, maintained functional correctness and achieved meaningful PPA improvements.
For example, in the sub_32bit, Deepseek R1 achieved a 9% reduction in
area and a 13% reduction in power, but it also resulted in functional
discrepancies. This suggests that Deepseek R1’s aggressive optimization
approach, while effective in improving PPA, may also increase the
likelihood of errors, particularly in designs with complex timing or
control logic.
Table [tab:exp] summarize the evaluated PPA performance of each LLM-optimized design and compare it with the provided suboptimal RTL and optimized RTL (golden reference). Green cells indicate that the PPA is better than the suboptimal RTL, and bold green cells indicate that the PPA surpasses the optimized RTL. The table also shows the functional correctness after verification (Func column), with and representing the verification results. indicates that the corresponding design contains syntax errors and fails to pass DC synthesis.
For the experimental results, we summarize the performance of four LLMs across syntax correctness, functional correctness, and PPA improvement. 1) GPT-4o-mini achieves good correctness, with a syntax correctness rate of 97.2% and functional correctness of 75%. Though only 19.4% of its generated code achieving better PPA than the suboptimal version. 2) Similarly, Gemini-2.5 exhibited the same trend as GPT-4o-mini: relatively high functional correctness but low performance in PPA optimization. 3) For Deepseek V3, it gets the highest syntax correctness of 100%, and the same functional correctness of 69.4% with Gemini-2.5. It achieved a balanced performance across all metrics. 4) In contrast, Deepseek R1, with a syntax correctness rate of 86.1% and functional correctness of 61.1%, produced 41.7% of the code with better PPA than the suboptimal version, and 13.9% better than designer solutions, despite its lower functional correctness.
Beyond quantitative results, we also randomly inspected 40 cases where LLM-optimized designs passed syntax checks but failed functional verification. We observed three main failure modes: control logic inconsistencies (e.g., incorrect Boolean conditions in comparators), overly aggressive pipelining (e.g., violating latency requirements in FSMs), and improper resource sharing (e.g., stale data due to register reuse). These results highlight that LLM errors often stem from subtle design semantics rather than surface-level syntax issues.
Conclusions
In this paper, we introduce RTL-OPT, a benchmark for RTL code optimization aimed at enhancing IC design quality. RTL-OPT includes 36 handcrafted digital IC designs, each with suboptimal and optimized RTL code, enabling the assessment of LLM-generated RTL. An integrated evaluation framework verifies functional correctness and quantifies PPA improvements, providing a standardized method for evaluating generative AI models in hardware design. RTL-OPT has significant potential to influence AI-assisted IC design by offering valuable insights and fostering advancements.
Full PPA Quality Comparison of RTL-OPT
Due to space limitations, we move the full PPA evaluation results to the appendix. This section provides the complete comparison between the suboptimal and optimized RTL designs in RTL-OPT. Both Synopsys Design Compiler and Yosys are used for synthesis and evaluation. As PPA inherently involves trade-offs, smaller values indicate better design quality. These results complement the main text by presenting full numerical evidence under different synthesis constraints.
Results under DC Compile_ultra, 1 ns
Table [tab:result_1] reports the full PPA metrics of all 36 RTL-OPT designs when synthesized using Synopsys DC with a relaxed 1ns clock period on the “compile ultra” setting. Both suboptimal and optimized RTL codes are evaluated, enabling direct comparison. This setting highlights how expert-optimized RTL consistently achieves superior power, performance, and area outcomes compared to the suboptimal versions, demonstrating the reliability of RTL-OPT for benchmarking.
Results under DC Compile, 0.1 ns
Table [tab:result_2] presents the full PPA metrics for the same 36 designs under a more aggressive 0.1ns clock period constraint. Compared to the 1ns setting, these results illustrate sharper trade-offs among PPA metrics, where aggressive timing optimization can sometimes increase power or area. Nevertheless, the optimized RTL consistently outperforms the suboptimal RTL, reaffirming that RTL-OPT reflects realistic and meaningful optimization challenges.
PPA and Functional Correctness of LLM-Optimized Designs
Due to space limitations, the detailed experimental results are moved to the appendix. They report PPA quality and functional correctness for all designs optimized by GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-2.5, Deepseek V3, and Deepseek R1, using the RTL-OPT benchmark.
Table [tab:exp] and [tab:exp5] summarize the evaluated PPA performance of each LLM-optimized design and compare it with the provided suboptimal RTL and optimized RTL (golden reference). Green cells indicate that the PPA is better than the suboptimal RTL, and bold green cells indicate that the PPA surpasses the optimized RTL (golden reference). The table also shows the functional correctness after verification (Func column), with and representing the verification results. indicates that the corresponding design contains syntax errors and fails to pass DC synthesis.
PPA and Functional Correctness of LLM-Optimized Designs (DC Compile, 1 ns)
Table [tab:exp5] summarizes the PPA results and functional correctness checks for designs optimized by GPT-4o-mini, Gemini-2.5, Deepseek V3, and Deepseek R1 on the RTL-OPT benchmark. All evaluations are conducted under DC compile with 0.1ns clock period. This supplements Table [tab:exp], which uses a more relaxed timing setup.
Reproduction of Existing Benchmark with Multiple Synthesis Flows
Reproduction of Designs with Multiple Synthesis Flows
Table [tab:exp6] provides reproduction results for 14 designs originally optimized by . Both the baseline (original) and expert-optimized versions are evaluated using our unified flow, across three synthesis settings: Yosys, DC compile (0.1ns), and DC compile ultra (1ns). This ensures fair comparisons across benchmarks and demonstrates the effectiveness of our pipeline in capturing prior work.
Reproduction of GPT-Optimized Designs
Table [tab:exp7] and Table [tab:exp8] provide the PPA reproduction of designs optimized by GPT-based methods and own optimization strategies, respectively. These results help evaluate the generalizability of our flow when applied to designs outside the RTL-OPT benchmark and provide fair comparisons across different optimization methodologies. The same three synthesis settings are used (Yosys, DC compile 0.1ns, and DC compile ultra 1ns), under our unified evaluation flow.
Detailed LLM Evaluation Results and Statistical Analysis
We re-run each LLM evaluation 5 times on RTL-OPT (36 designs), using the same prompt template to ensure consistency. For each run, we recorded the: (1) Syntax correctness; (2) Func correctness; (3) PPA better than suboptimal; (4) PPA better than optimized. The experimental results for 6 different LLMs (including two open-source LLMs) are summarized below.
We summarize statistical results and conduct paired t-tests on two representative LLM pairs: Gmini vs. DS-R1 and LLaMA vs. Qwen. We will include the complete mean ± $`\sigma`$ and paired t-tests results in this appendix when updating the camera-ready version.
Syntax Correctness (N out of 36)
Functional Correctness (N out of 36)
PPA >Suboptimal (N out of 36)
PPA >Optimized (N out of 36)
Comparison: GPT-4o vs. DS-R1
Comparison: LLaMA vs. Qwen
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)




A Note of Gratitude
The copyright of this content belongs to the respective researchers. We deeply appreciate their hard work and contribution to the advancement of human civilization.-
Please note that the pioneering work did not claim their designs as a standard benchmark, and we appreciate their open-source contributions. ↩︎
-
As shown in Table [tab:measure1], paper of and SymRTLO are different subsets of the Benchmark . We only successfully synthesized 43 cases out of the 54 pairs of RTL code from the benchmark . For the others, we synthesized 12 out of 14 pairs and 13 out of 16 pairs, respectively. These synthesis failures in the original benchmarks are mainly caused by Verilog syntax errors. ↩︎
-
The details of the synthesis process, tools, and PPA metrics used for evaluating are provided in Section 3.3. ↩︎