AI Research Archive
KOINEU is a research analysis platform that summarizes and explains AI and machine learning papers in an accessible format.
Latest Research


A Categorical Theory of Patches

On monoids of monotone injective partial selfmaps of $L_ntimes_{operatorname{lex}}mathbb{Z}$ with co-finite domains and images

SOFA: An Extensible Logical Optimizer for UDF-heavy Dataflows

Evaluating the Impact of SDC on the GMRES Iterative Solver

Implementing and reasoning about hash-consed data structures in Coq
Editor's Pick
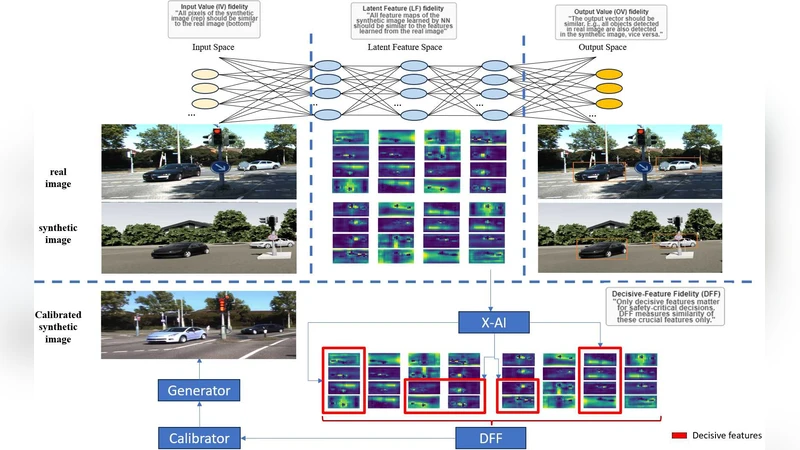
Quantifying Fidelity: A Decisive Feature Approach to Comparing Synthetic and Real Imagery

경험 재생에서 깊은 망각과 얕은 망각의 비대칭: 작은 버퍼는 특징 공간을 유지하지만 분류 경계는 왜곡한다
ESPADA: Execution Speedup via Semantics Aware Demonstration Data Downsampling for Imitation Learning
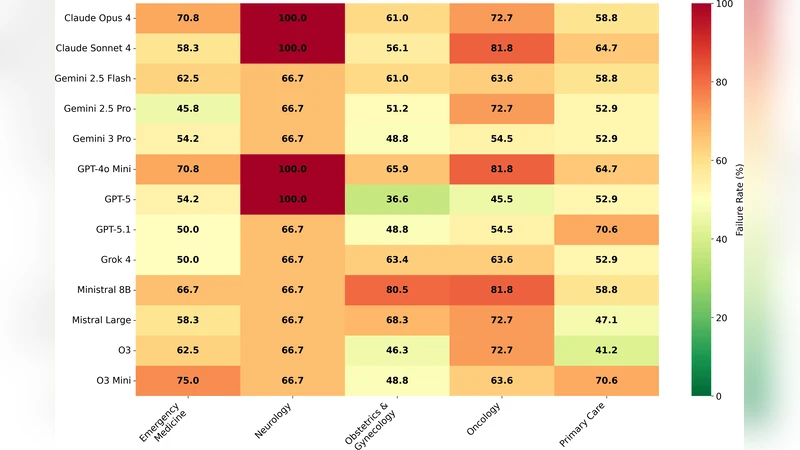
A Women's Health Benchmark for Large Language Models
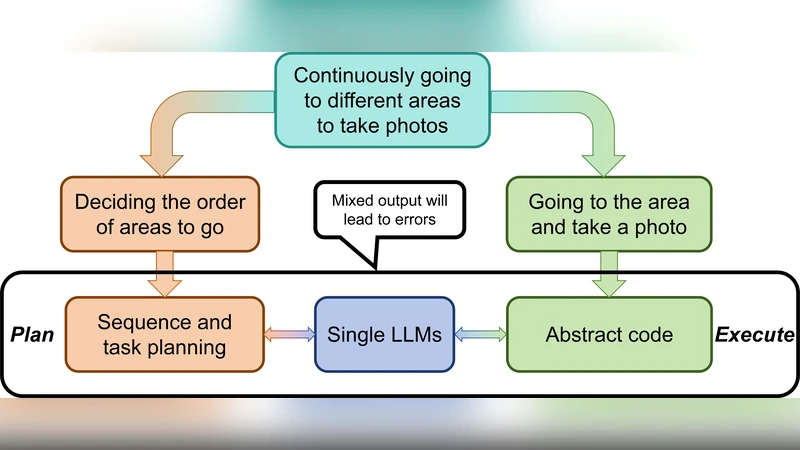
Chat with UAV -- Human-UAV Interaction Based on Large Language Models

How to Tame Your LLM: Semantic Collapse in Continuous Systems
Information Theory
1,601 Papers
Artificial Intelligence
1,580 Papers
Cryptography and Security
1,290 Papers
Data Structures and Algorithms
1,258 Papers
Networking
1,126 Papers
Discrete Mathematics
1,039 Papers
Distributed Computing
981 Papers
Logic in Computer Science
972 Papers
Software Engineering
935 Papers
Machine Learning
932 Papers
Computers and Society
915 Papers
Computational Complexity
861 Papers
Latest in Computer Science
VIEW ALL →
A Categorical Theory of Patches

Evaluating the Impact of SDC on the GMRES Iterative Solver

Implementing and reasoning about hash-consed data structures in Coq

Category-Theoretic Quantitative Compositional Distributional Models of Natural Language Semantics

Toward a structure theory for Lorenzen dialogue games
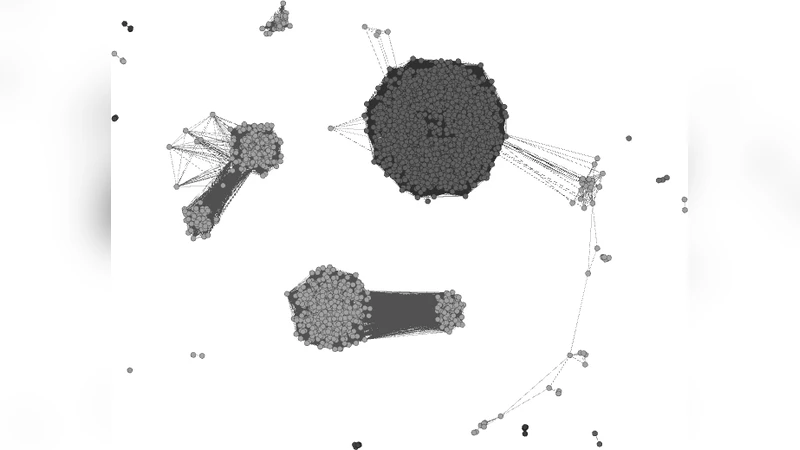
Tracking and Characterizing Botnets Using Automatically Generated Domains

Borel and Hausdorff Hierarchies in Topological Spaces of Choquet Games and Their Effectivization

On the Structure of Bispecial Sturmian Words

An Axiomatization for Quantum Processes to Unifying Quantum and Classical Computing

Toward Security Verification against Inference Attacks on Data Trees
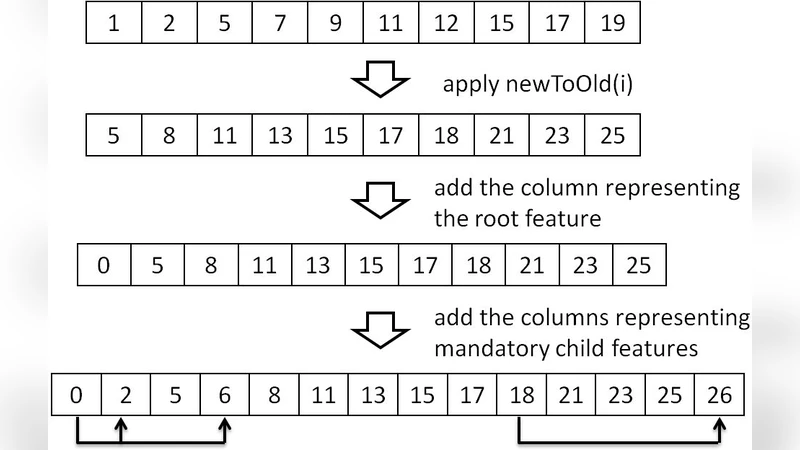
Improving CASA Runtime Performance by Exploiting Basic Feature Model Analysis

Worst-Case Analysis of Webers Algorithm
High Energy Astrophysics
4,296 Papers
Cosmology
1,434 Papers
Computational Physics
1,379 Papers
Physics and Society
1,070 Papers
Solar and Stellar Astrophysics
988 Papers
Astrophysics of Galaxies
980 Papers
Data Analysis (Physics)
976 Papers
Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics
834 Papers
Nonlinear Systems
771 Papers
Statistical Mechanics
730 Papers
Planetary Astrophysics
689 Papers
Geophysics
684 Papers
Latest in Physics
VIEW ALL →
Electric dipole polarizability of alkaline-Earth-metal atoms from perturbed relativistic coupled-cluster theory with triples
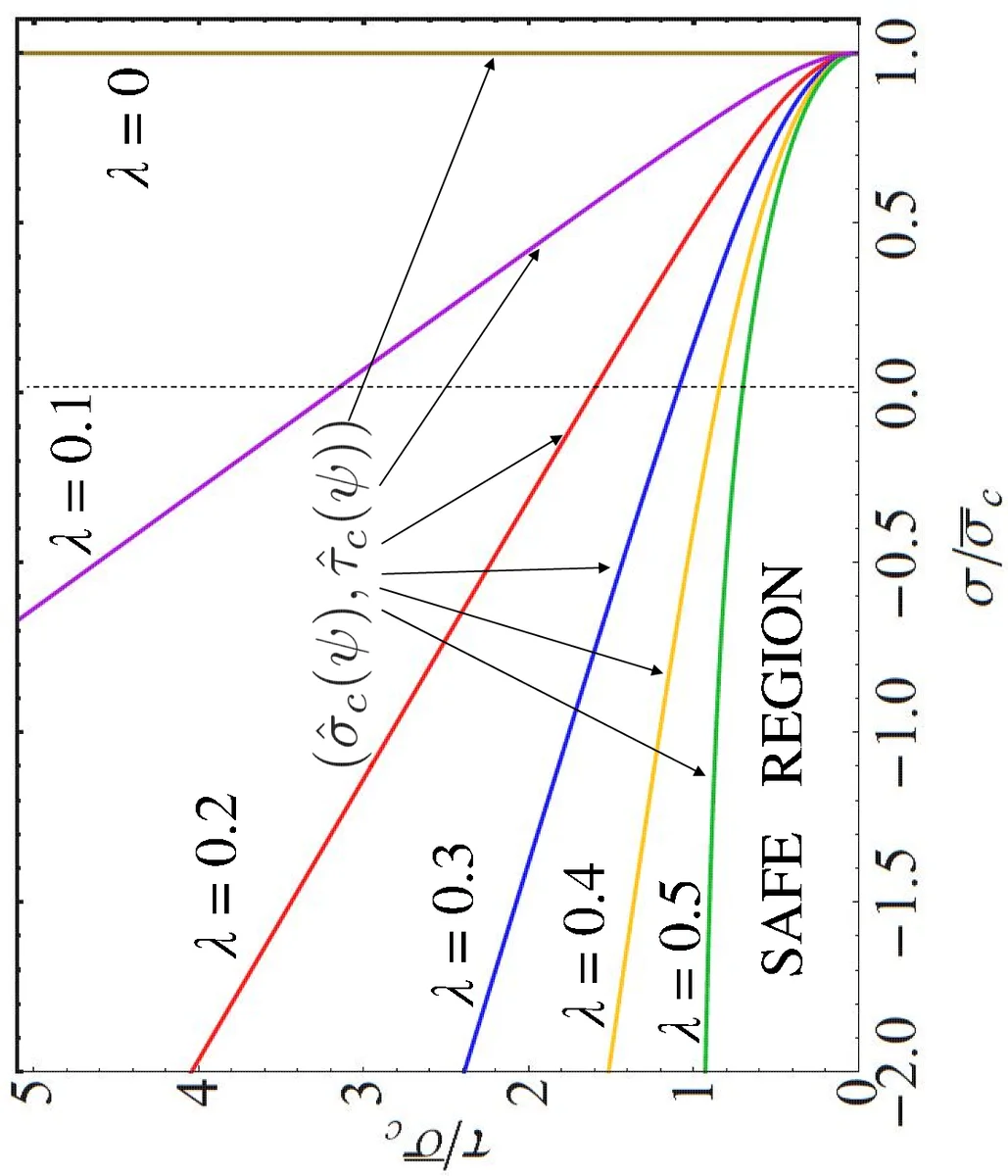
Application of a linear elastic - brittle interface model to the crack initiation and propagation at fibre-matrix interface under biaxial transverse loads

Source identities and kernel functions for deformed (quantum) Ruijsenaars models
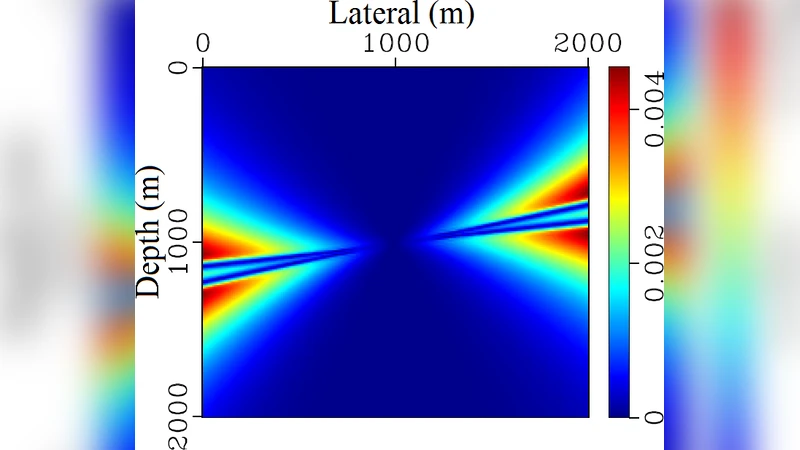
Efficient traveltime solution of the acoustic TI eikonal equation
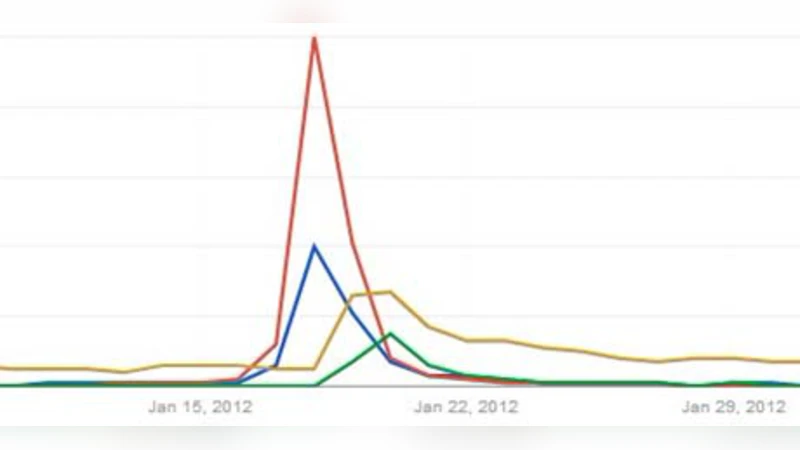
Event Evolution Tracking from Streaming Social Posts
Pegasus: A New Hybrid-Kinetic Particle-in-Cell Code for Astrophysical Plasma Dynamics
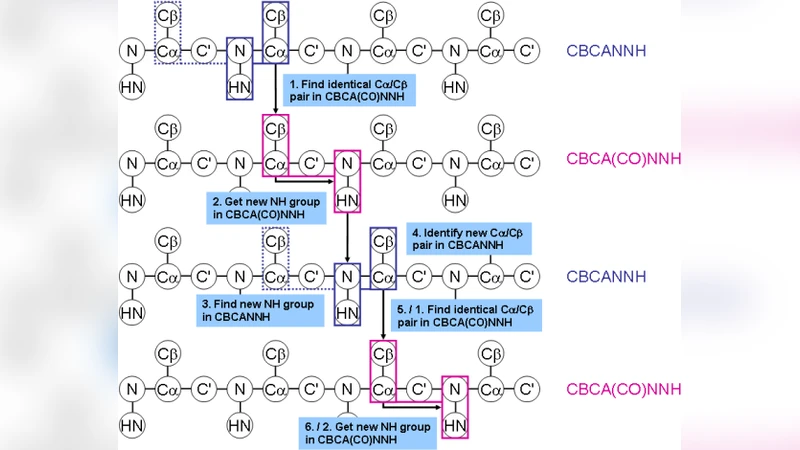
Computational Assignment of Chemical Shifts for Protein Residues

Dimensionality reduction and spectral properties of multilayer networks
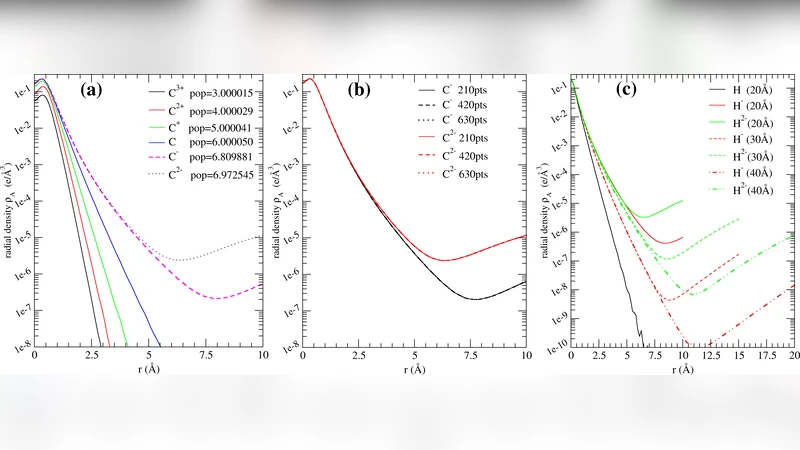
Revealing Relationships among Relevant Climate Variables with Information Theory

Reflections on the direct detection of particle dark matter
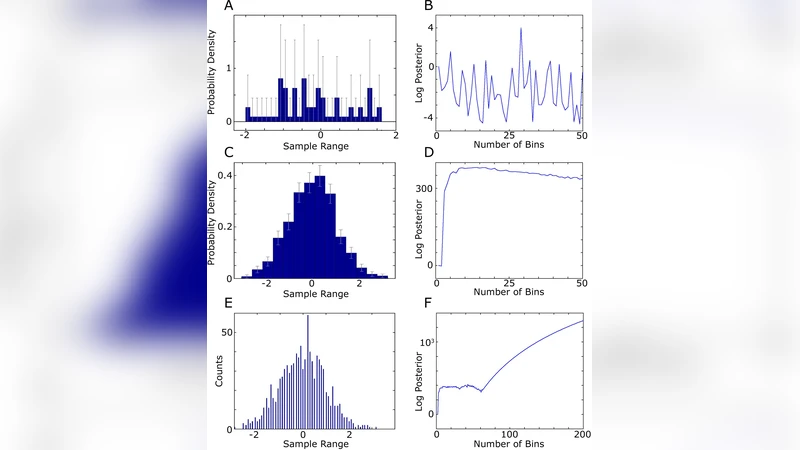
Models and Simulations in Material Science: Two Cases Without Error Bars
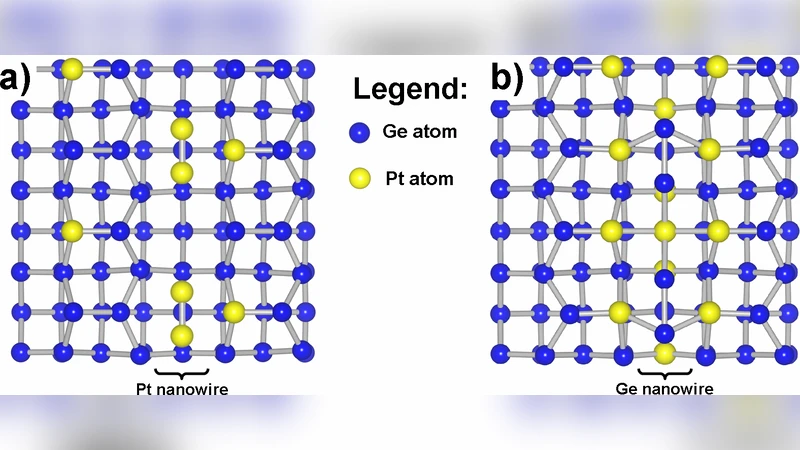
Extending Hirshfeld-I to bulk and periodic materials
Information Theory
1,599 Papers
Mathematical Physics
611 Papers
Mathematical Physics
610 Papers
Combinatorics
593 Papers
Category Theory
538 Papers
K-Theory and Homology
428 Papers
General Topology
365 Papers
Optimization and Control
345 Papers
Algebraic Topology
326 Papers
Mathematical Statistics
309 Papers
Probability
302 Papers
Metric Geometry
288 Papers
Latest in Mathematics
VIEW ALL →
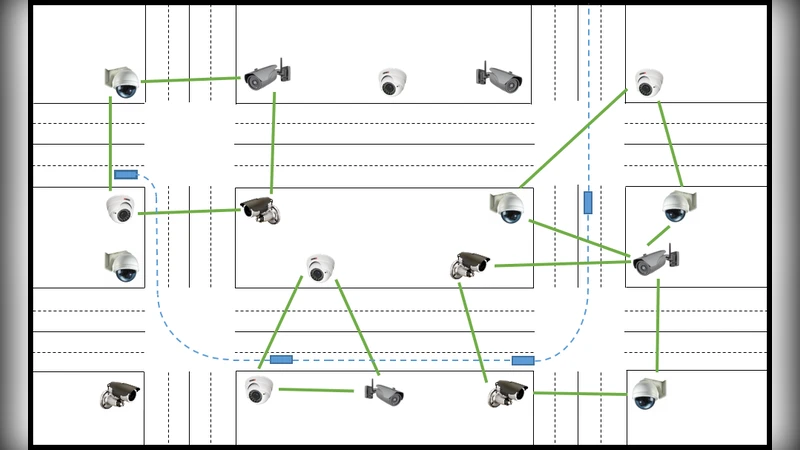
Mixed Human-Robot Team Surveillance

A Categorical Theory of Patches

On monoids of monotone injective partial selfmaps of $L_ntimes_{operatorname{lex}}mathbb{Z}$ with co-finite domains and images

Category-Theoretic Quantitative Compositional Distributional Models of Natural Language Semantics

On Lobachevskys trigonometric formulae

Source identities and kernel functions for deformed (quantum) Ruijsenaars models

Worst-Case Analysis of Webers Algorithm

Analysis of Load Balancing in Large Heterogeneous Processor Sharing Systems

Dimensionality reduction and spectral properties of multilayer networks

The non-Urysohn number of a topological space

Ferromagnetic Potts Model: Refined #BIS-hardness and Related Results

On the Communication Complexity of Secure Computation
Quantitative Methods
536 Papers
Biomolecules
482 Papers
Molecular Networks
444 Papers
Populations and Evolution
351 Papers
Neuroscience
336 Papers
Genomics
288 Papers
Cell Behavior
240 Papers
Subcellular Processes
235 Papers
Tissues and Organs
207 Papers
Other Quantitative Biology
178 Papers
Latest in Medical & Biology
VIEW ALL →
Kernelizations for the hybridization number problem on multiple nonbinary trees
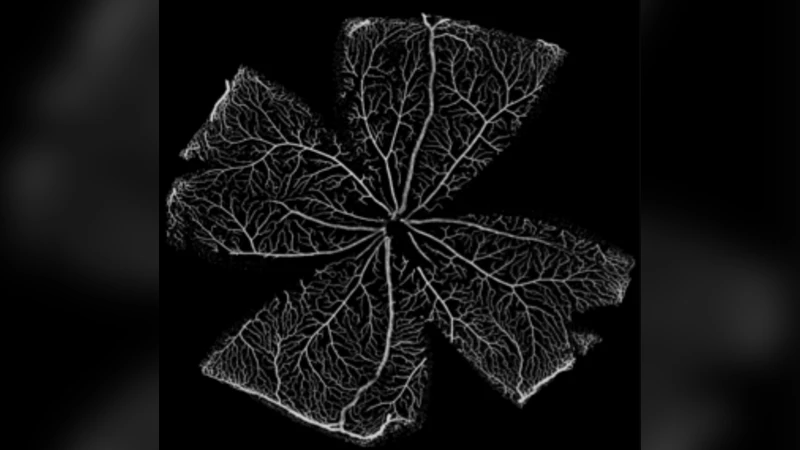
Computer simulations reveal complex distribution of haemodynamic forces in a mouse retina model of angiogenesis

Efficient coding of spectrotemporal binaural sounds leads to emergence of the auditory space representation

Computational Assignment of Chemical Shifts for Protein Residues
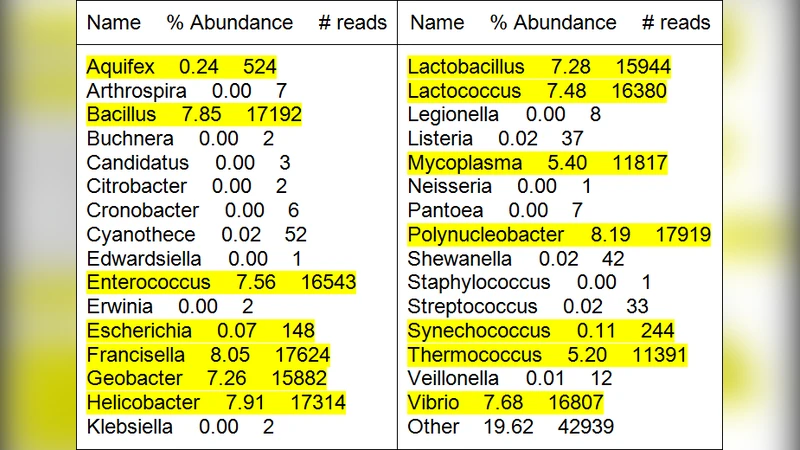
MCUIUC -- A New Framework for Metagenomic Read Compression

Parameter identification problems in the modelling of cell motility

Evolving functional network properties and synchronizability during human epileptic seizures

Modeling and Simulation of the Effects of Cyclic Loading on Articular Cartilage Lesion Formation

Dimension Reduction of Large AND-NOT Network Models

Estimating Functions of Distributions Defined over Spaces of Unknown Size
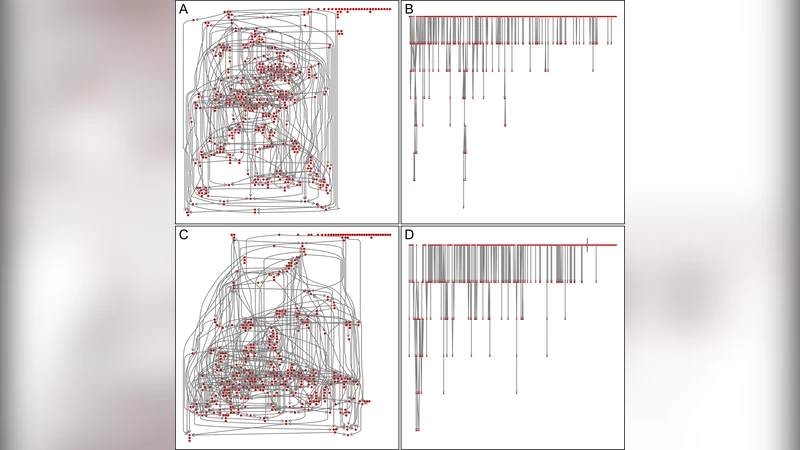
Probabilistic generation of random networks taking into account information on motifs occurrence
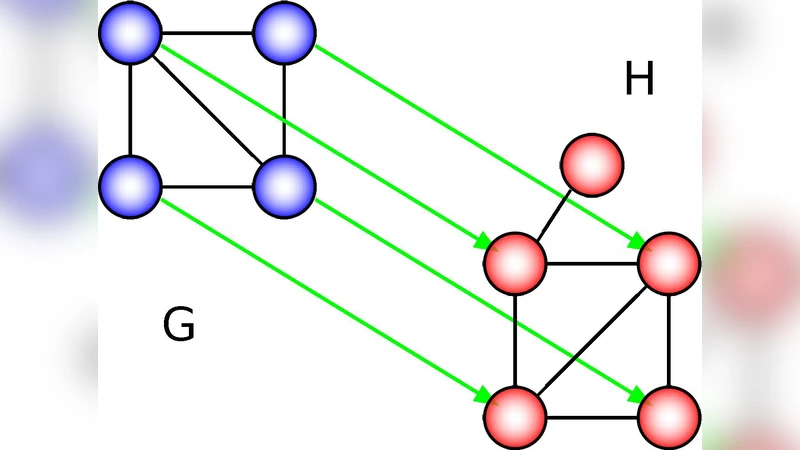
MAGNA: Maximizing Accuracy in Global Network Alignment
Methodology (Stats)
578 Papers
Applications
537 Papers
Machine Learning (Stats)
514 Papers
Statistical Computing
311 Papers
Statistical Theory
304 Papers
Other Statistics
61 Papers
Latest in Statistics
VIEW ALL →
Shape from Texture using Locally Scaled Point Processes

Fast Training of Effective Multi-class Boosting Using Coordinate Descent Optimization

Bayesian Discovery of Threat Networks

Gradient Hard Thresholding Pursuit for Sparsity-Constrained Optimization

Learning Reputation in an Authorship Network

Estimating Functions of Distributions Defined over Spaces of Unknown Size

Smoothed Analysis of Tensor Decompositions

A Bayesian Network View on Acoustic Model-Based Techniques for Robust Speech Recognition

Retrieval of Experiments with Sequential Dirichlet Process Mixtures in Model Space

Waste Not, Want Not: Why Rarefying Microbiome Data is Inadmissible
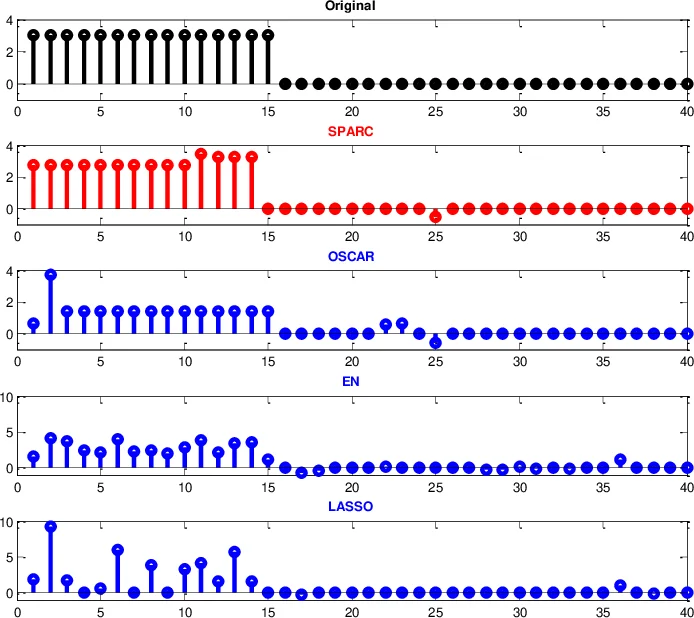
A novel sparsity and clustering regularization

A maximum entropy model for opinions in social groups
Latest in Engineering
VIEW ALL →
Machine Speech Chain with One-shot Speaker Adaptation
TickTalk -- Timing API for Dynamically Federated Cyber-Physical Systems
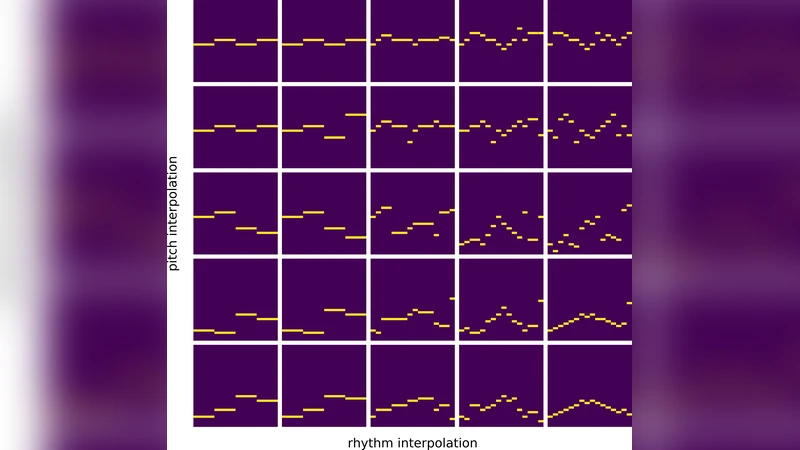
Deep Music Analogy Via Latent Representation Disentanglement
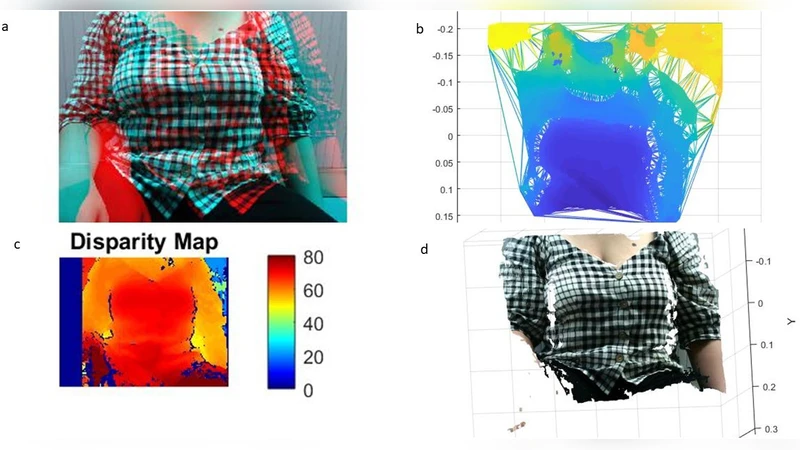
A low-cost real-time 3D imaging system for contactless asthma observation
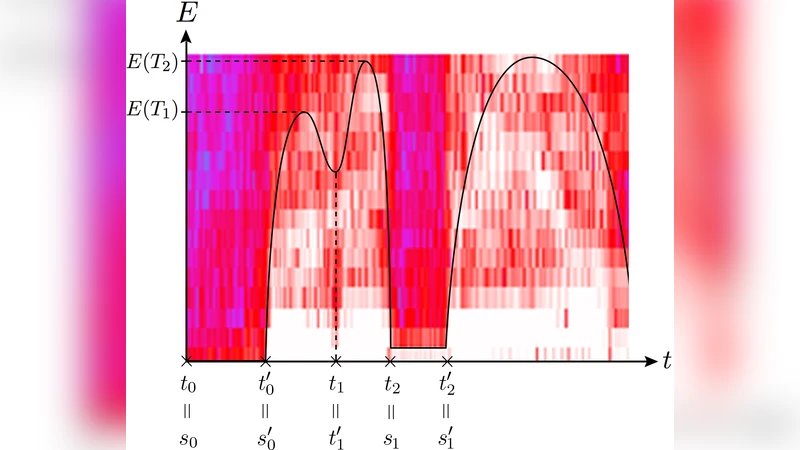
Automatic Conflict Detection in Police Body-Worn Audio

EXTD: Extremely Tiny Face Detector via Iterative Filter Reuse
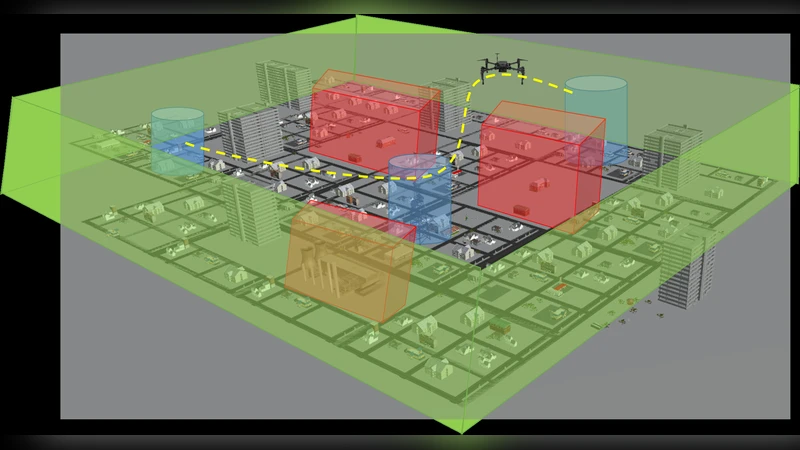
Fixed-time Control under Spatiotemporal and Input Constraints: A Quadratic Program Based Approach

On Opacity Verification for Discrete-Event Systems
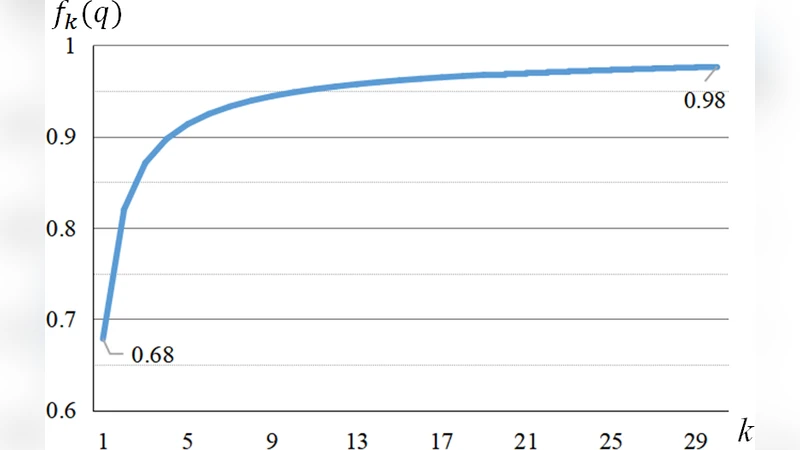
Essence Knowledge Distillation for Speech Recognition
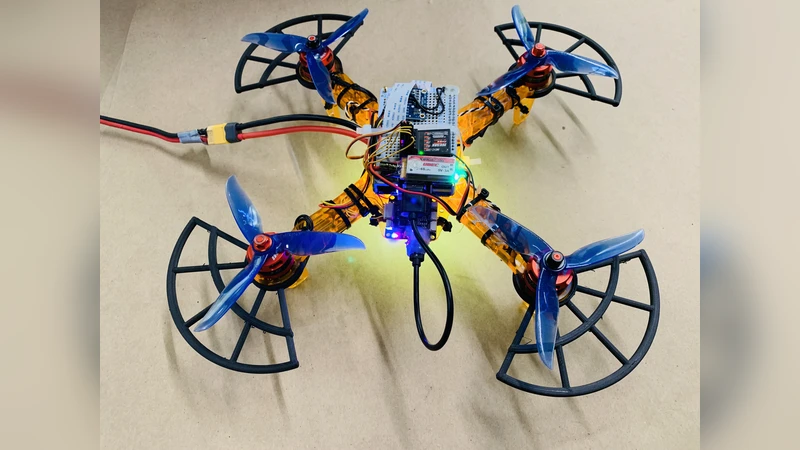

Advanced Autonomy on a Low-Cost Educational Drone Platform
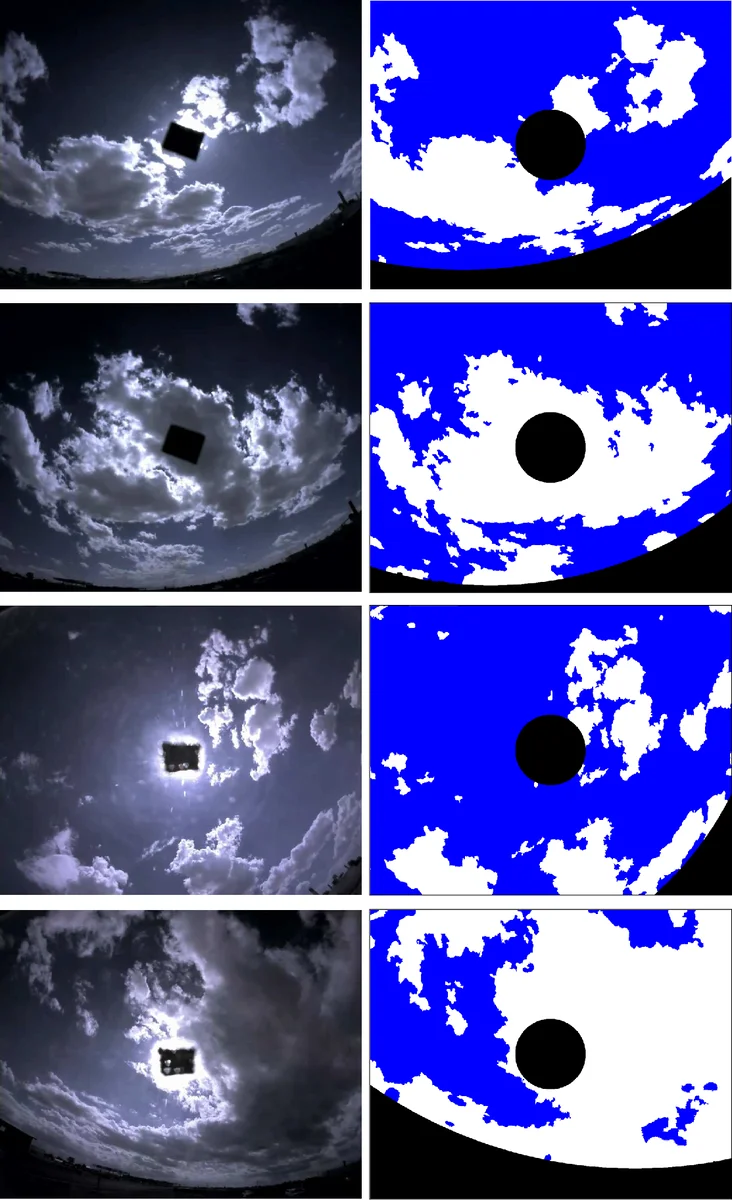
A Conditional Random Field Model for Context Aware Cloud Detection in Sky Images