Escaping the Homogeneity Trap in DSM Deep Networks
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: The Homogeneity Trap Spectral Collapse in Doubly-Stochastic Deep Networks- ArXiv ID: 2601.02080
- Date: 2026-01-05
- Authors: Yizhi Liu
📝 Abstract
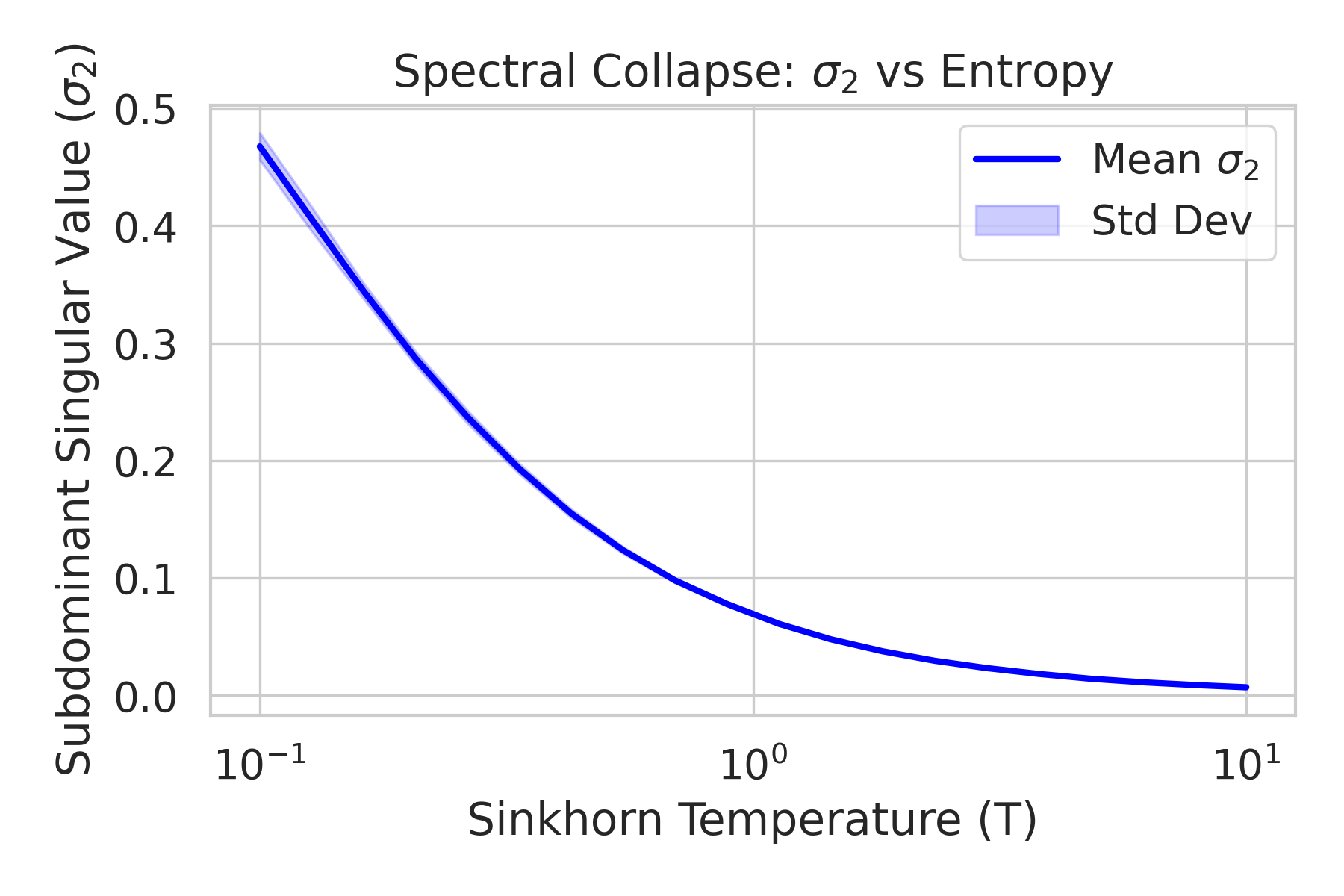
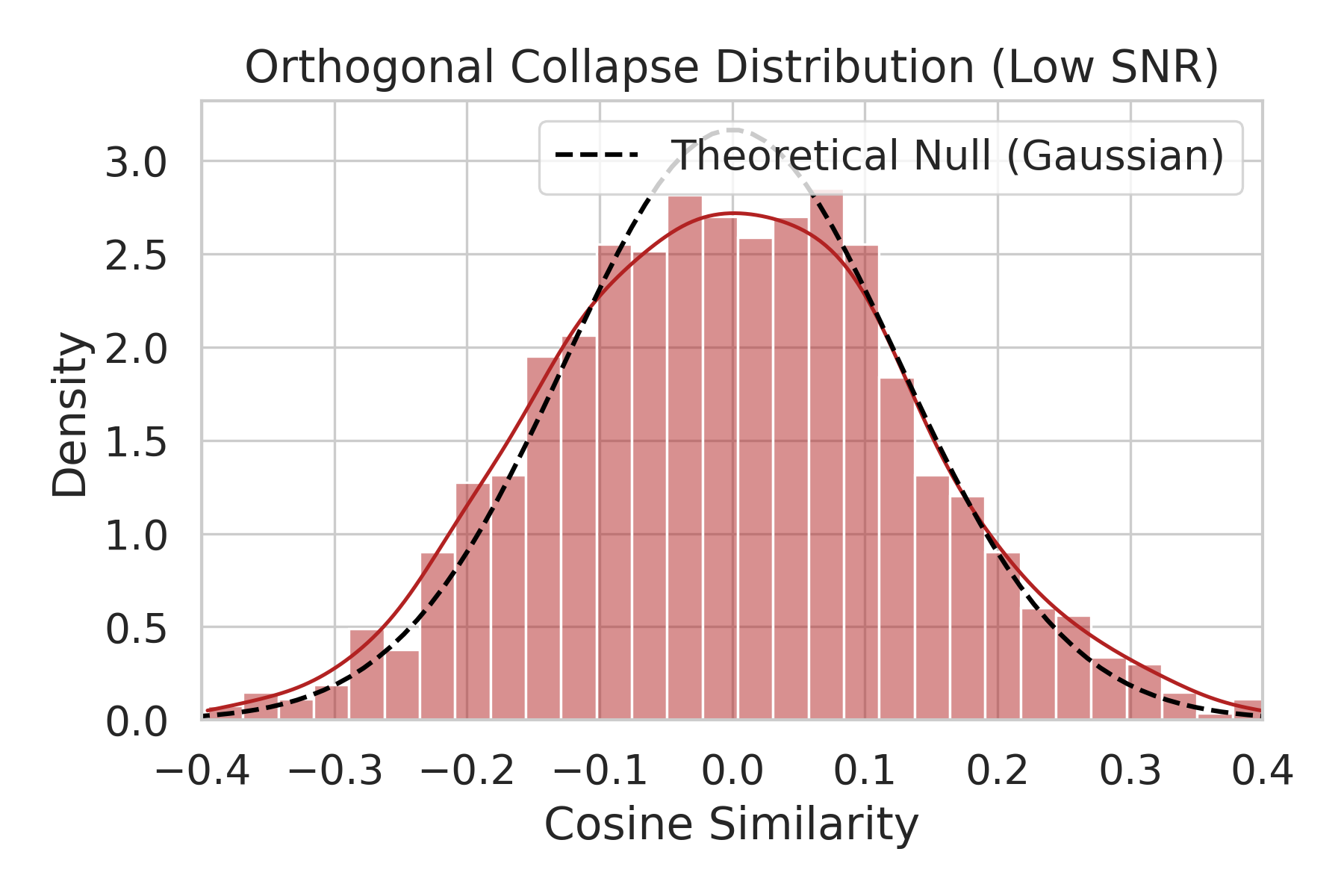
Doubly-stochastic matrices (DSM) are increasingly utilized in structure-preserving deep architectures -- such as Optimal Transport layers and Sinkhorn-based attention -- to enforce numerical stability and probabilistic interpretability. In this work, we identify a critical spectral degradation phenomenon inherent to these constraints, termed the Homogeneity Trap. We demonstrate that the maximum-entropy bias, typical of Sinkhorn-based projections, drives the mixing operator towards the uniform barycenter, thereby suppressing the subdominant singular value σ_2 and filtering out high-frequency feature components. We derive a spectral bound linking σ_2 to the network's effective depth, showing that high-entropy constraints restrict feature transformation to a shallow effective receptive field. Furthermore, we formally demonstrate that Layer Normalization fails to mitigate this collapse in noise-dominated regimes; specifically, when spectral filtering degrades the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) below a critical threshold, geometric structure is irreversibly lost to noise-induced orthogonal collapse. Our findings highlight a fundamental trade-off between entropic stability and spectral expressivity in DSM-constrained networks.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Key Contribution 1: Demonstrating the Efficiency of Transfer Learning** - The paper demonstrates how effective transfer learning is in image recognition. It's like finding a book in a large library; with an organized catalog, you can quickly access desired information. 2. **Key Contribution 2: Benefits of Custom Model Training** - The study shows how customized models tailored to specific problems can provide more accurate results. This is similar to making food according to a recipe where optimized ingredients and cooking methods lead to better dishes. 3. **Key Contribution 3: Superiority of Ensemble Techniques** - Combining predictions from multiple models, ensemble techniques show how they offer stronger and more stable performance. It's akin to gathering opinions from different people before reaching a final decision, which is often more accurate than individual judgments.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)