Tracking Hallucinations in Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Streaming Hallucination Detection in Long Chain-of-Thought Reasoning- ArXiv ID: 2601.02170
- Date: 2026-01-05
- Authors: Haolang Lu, Minghui Pan, Ripeng Li, Guoshun Nan, Jialin Zhuang, Zijie Zhao, Zhongxiang Sun, Kun Wang, Yang Liu
📝 Abstract
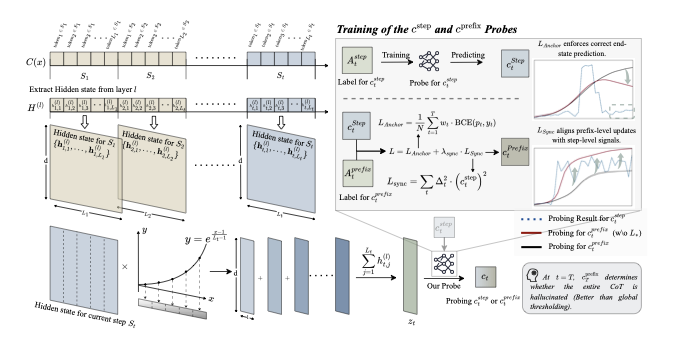
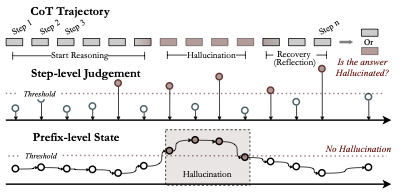
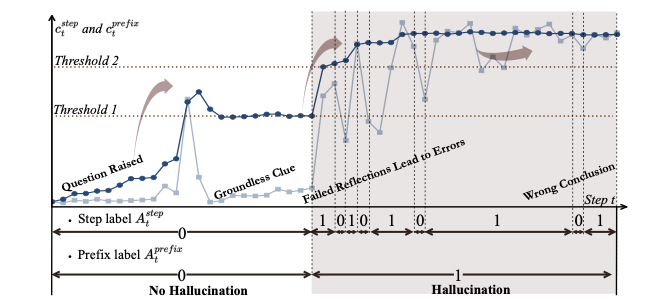
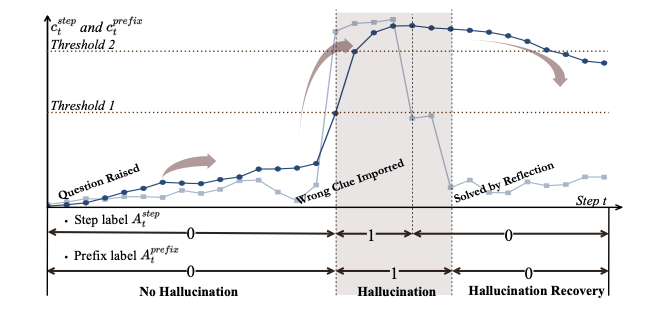
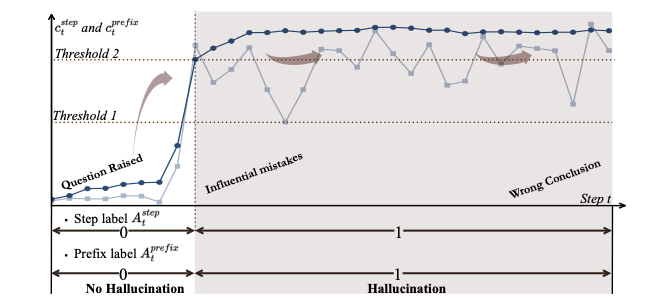
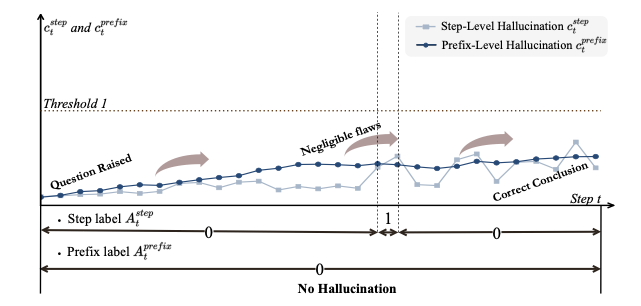
Long chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning improves the performance of large language models, yet hallucinations in such settings often emerge subtly and propagate across reasoning steps. We suggest that hallucination in long CoT reasoning is better understood as an evolving latent state rather than a one-off erroneous event. Accordingly, we treat step-level hallucination judgments as local observations and introduce a cumulative prefix-level hallucination signal that tracks the global evolution of the reasoning state over the entire trajectory. Overall, our approach enables streaming hallucination detection in long CoT reasoning, providing real-time, interpretable evidence.💡 Summary & Analysis
The key contributions of this paper include: - Comparative analysis of deep learning paradigms in NLP. - Identification of the strengths and weaknesses of each model type. - Insights into optimal usage scenarios for each model based on dataset characteristics.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)