Graphs in Memory Myth or Reality?
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Does Memory Need Graphs? A Unified Framework and Empirical Analysis for Long-Term Dialog Memory- ArXiv ID: 2601.01280
- Date: 2026-01-03
- Authors: Sen Hu, Yuxiang Wei, Jiaxin Ran, Zhiyuan Yao, Xueran Han, Huacan Wang, Ronghao Chen, Lei Zou
📝 Abstract
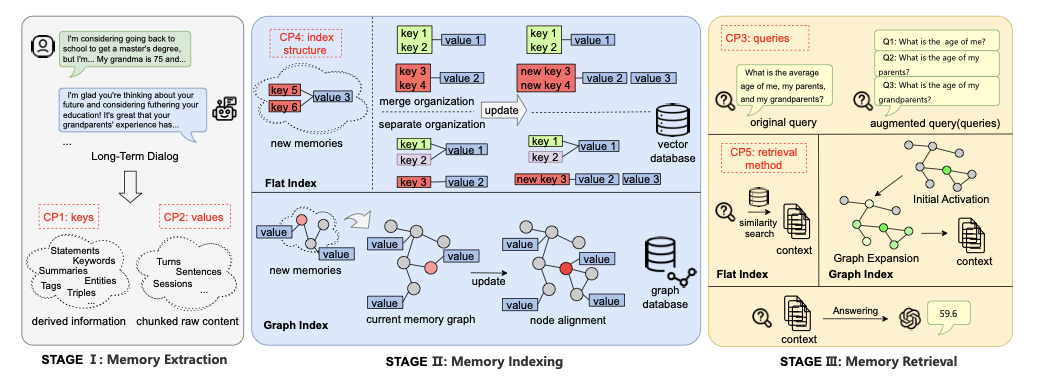
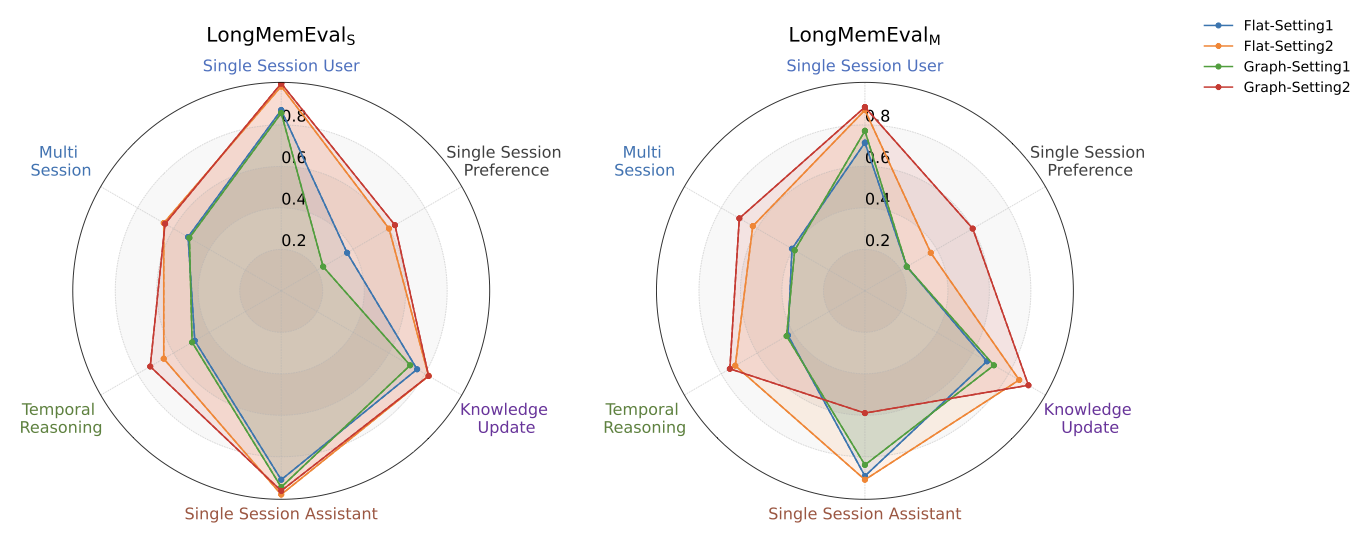
Graph structures are increasingly used in dialog memory systems, but empirical findings on their effectiveness remain inconsistent, making it unclear which design choices truly matter. We present an experimental, system-oriented analysis of long-term dialog memory architectures. We introduce a unified framework that decomposes dialog memory systems into core components and supports both graph-based and non-graph approaches. Under this framework, we conduct controlled, stage-wise experiments on LongMemEval and HaluMem, comparing common design choices in memory representation, organization, maintenance, and retrieval. Our results show that many performance differences are driven by foundational system settings rather than specific architectural innovations. Based on these findings, we identify stable and reliable strong baselines for future dialog memory research.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1: Custom Model vs Transfer Learning** - The study clearly illustrates the pros and cons of building a model from scratch versus using transfer learning, akin to comparing making dinner from fresh ingredients with buying pre-made meals. 2. **Contribution 2: Impact of Fine-Tuning** - Adding fine-tuning after transfer learning significantly improved performance across different datasets, similar to upgrading an existing bicycle by fitting new tires for better speed. 3. **Contribution 3: Evaluation of Generalization Ability** - The models were tested on various datasets to assess their generalization abilities, much like experimenting with the same recipe using different ingredients.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)