Quantization Quandary Does It Halt LLM Self-Explanations?
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Can Large Language Models Still Explain Themselves? Investigating the Impact of Quantization on Self-Explanations- ArXiv ID: 2601.00282
- Date: 2026-01-01
- Authors: Qianli Wang, Nils Feldhus, Pepa Atanasova, Fedor Splitt, Simon Ostermann, Sebastian Möller, Vera Schmitt
📝 Abstract
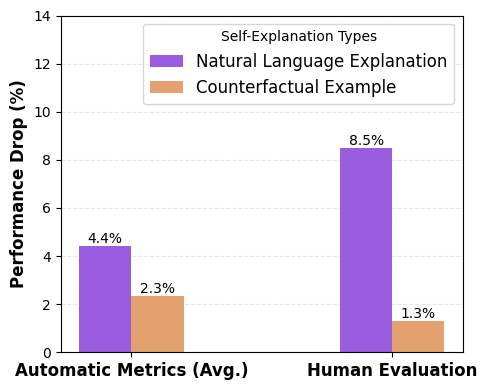
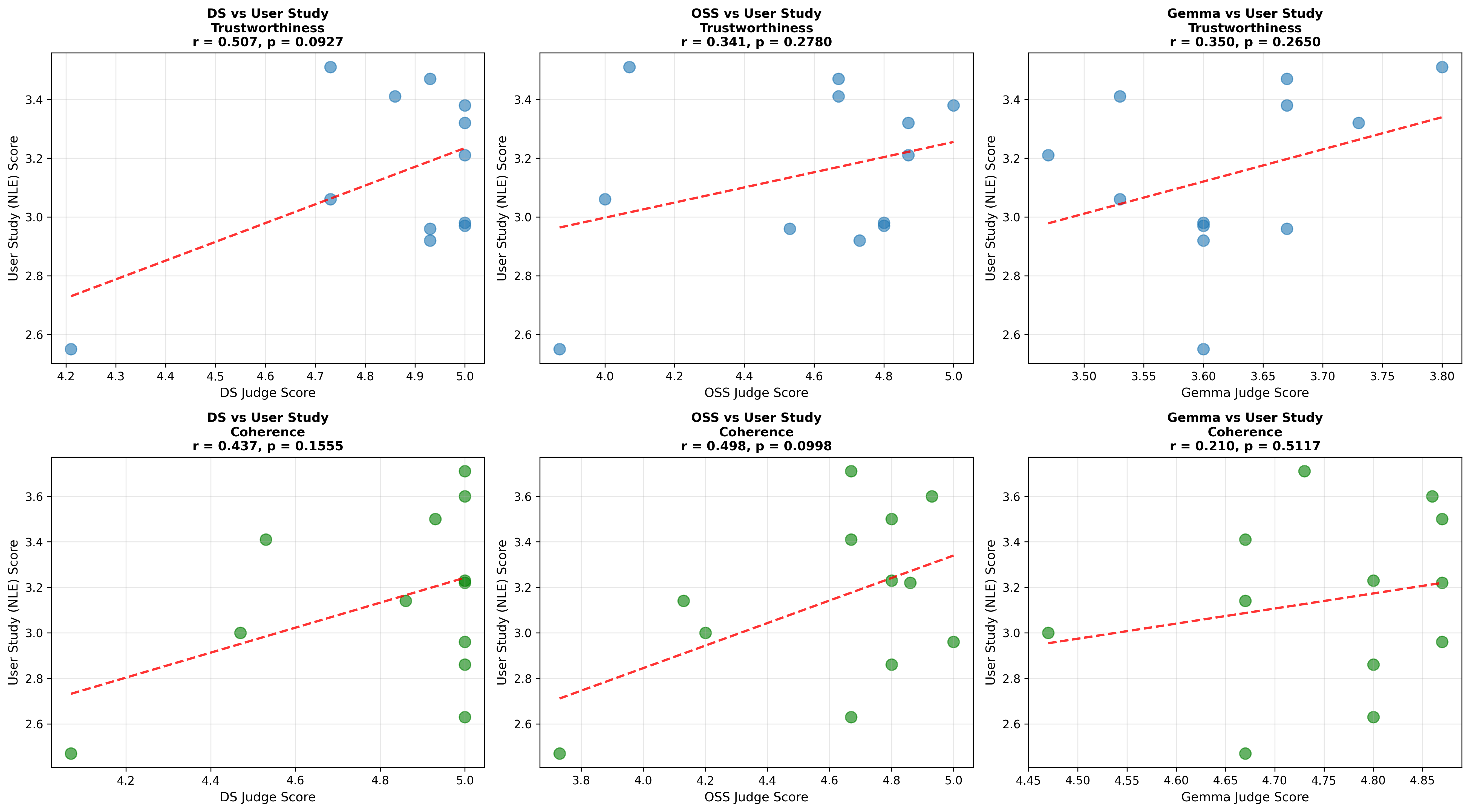
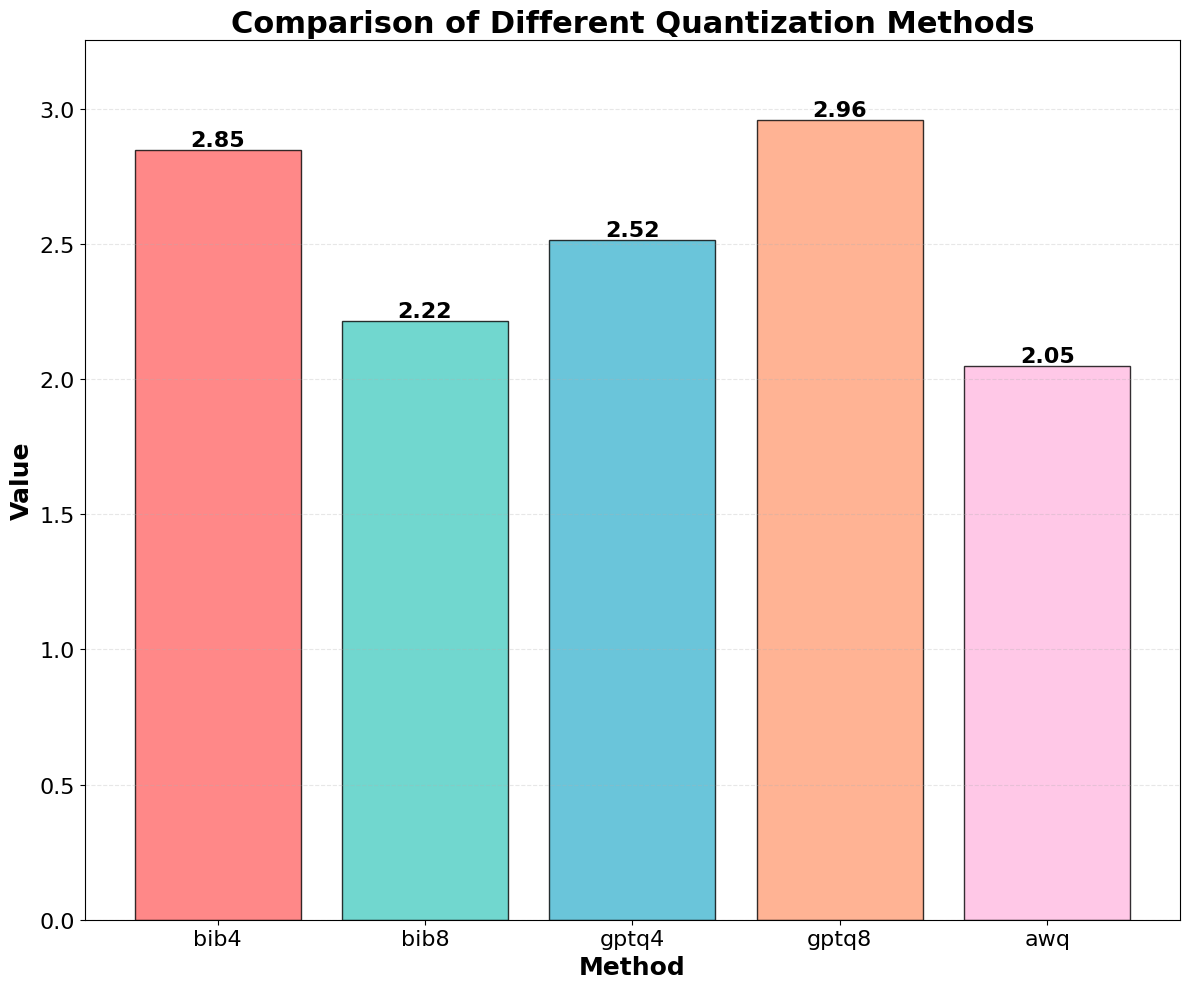
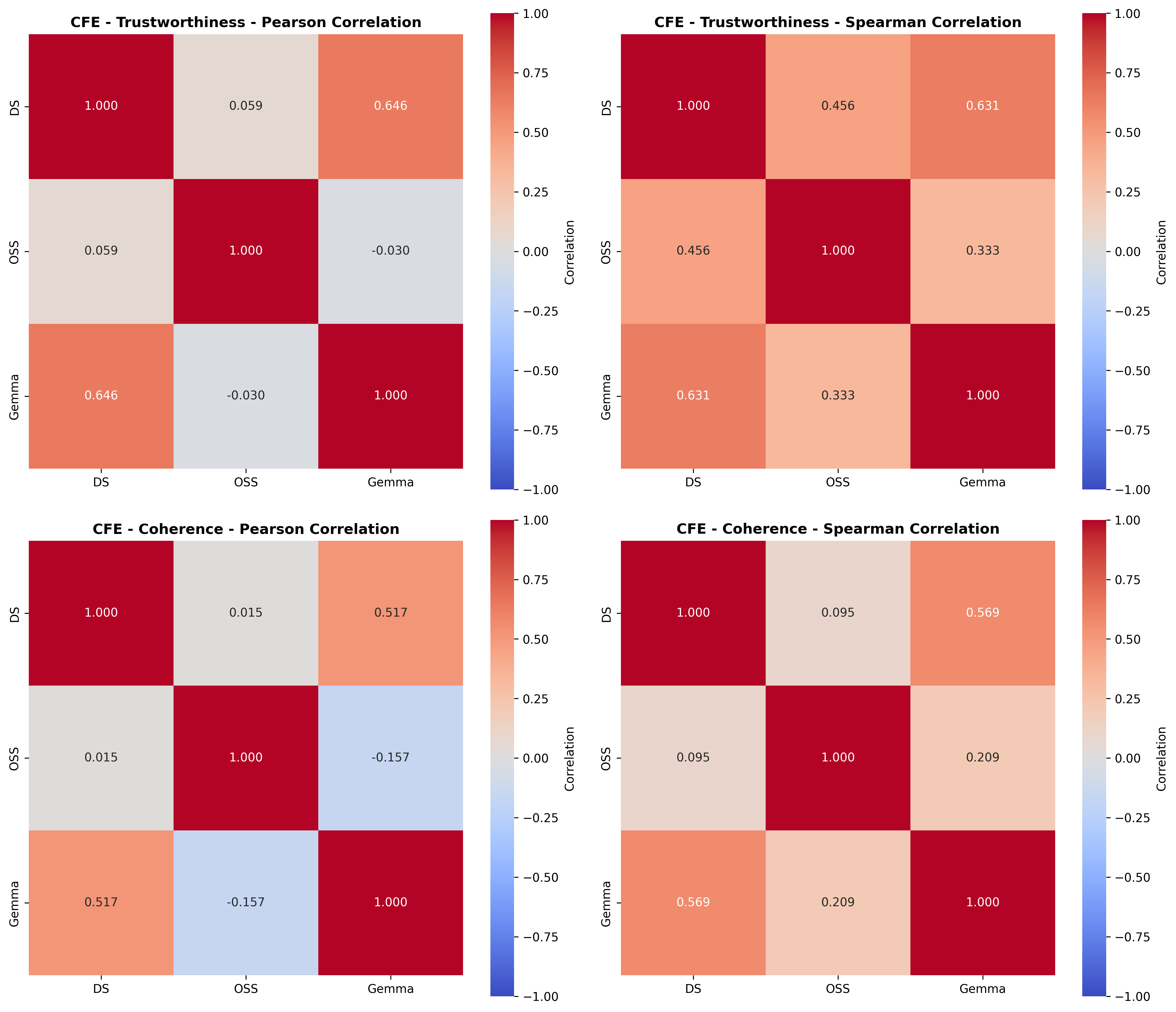
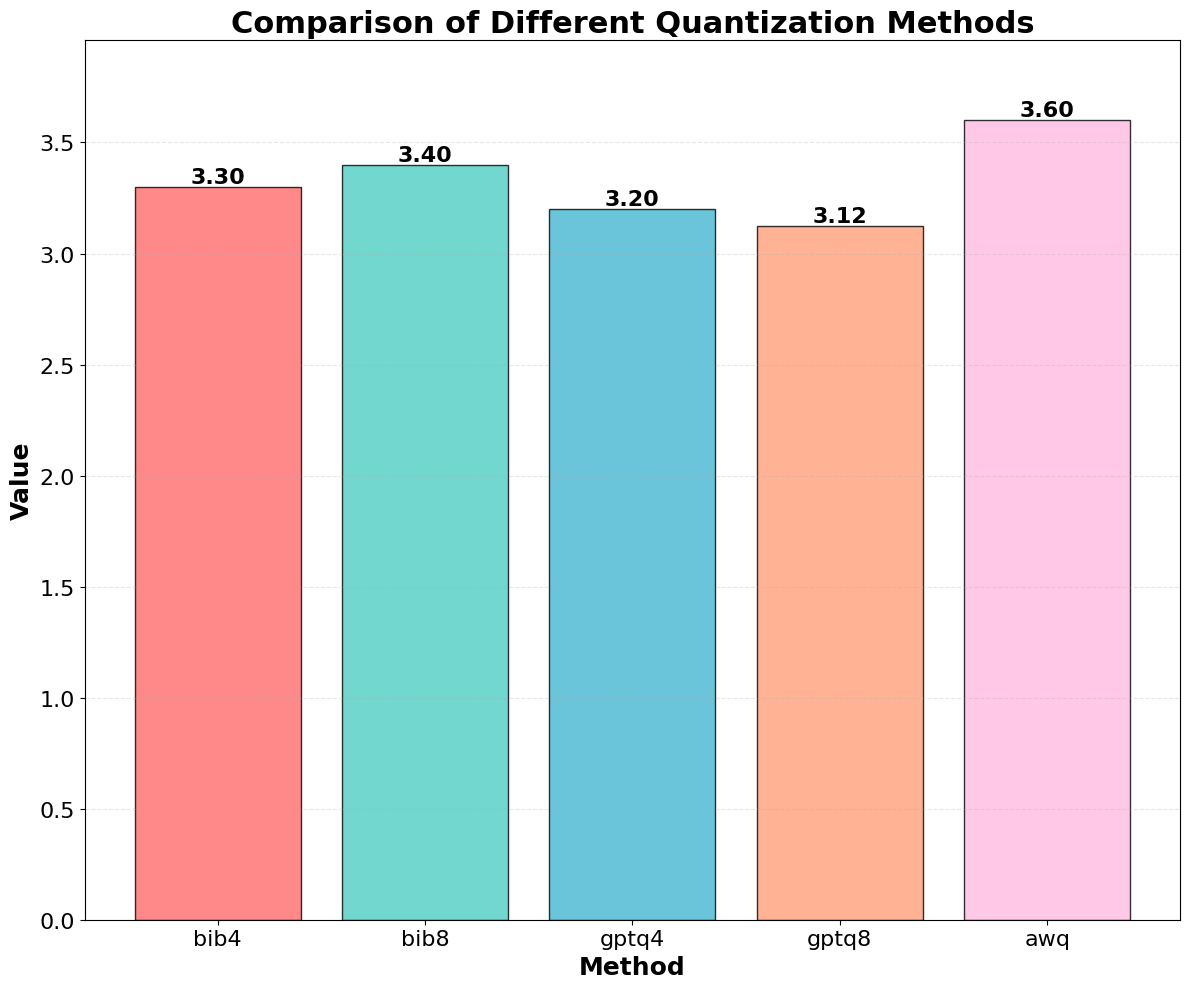
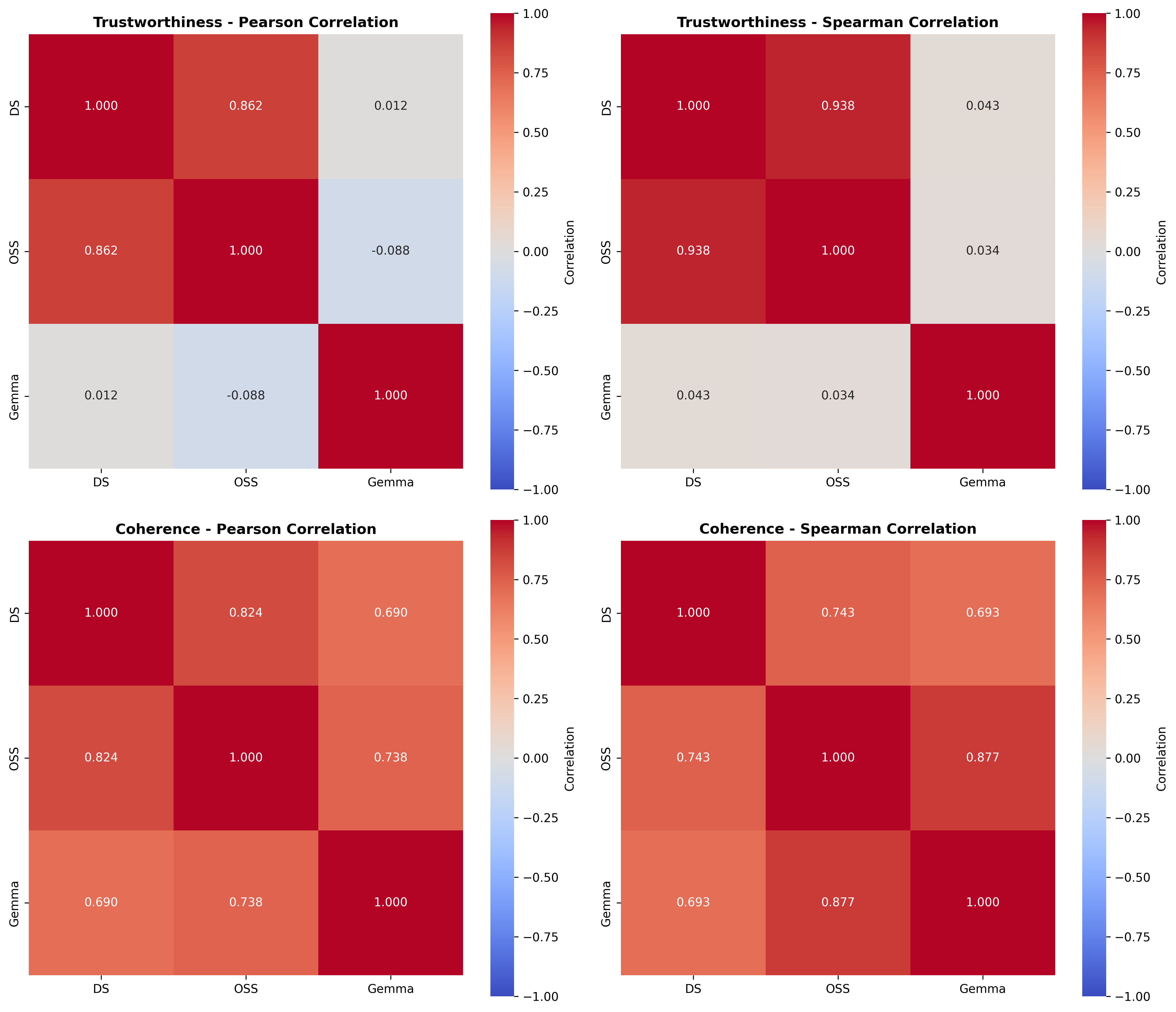
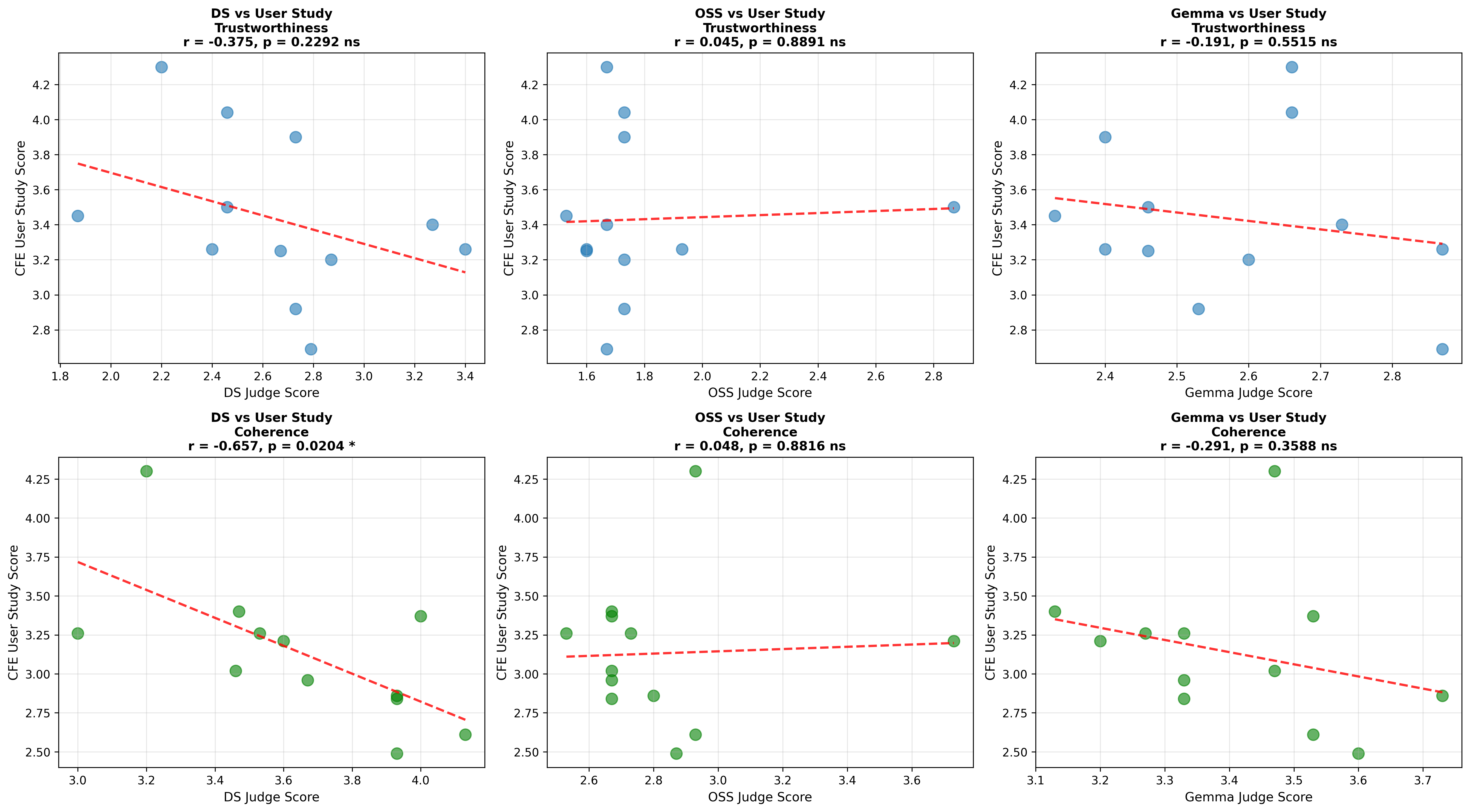
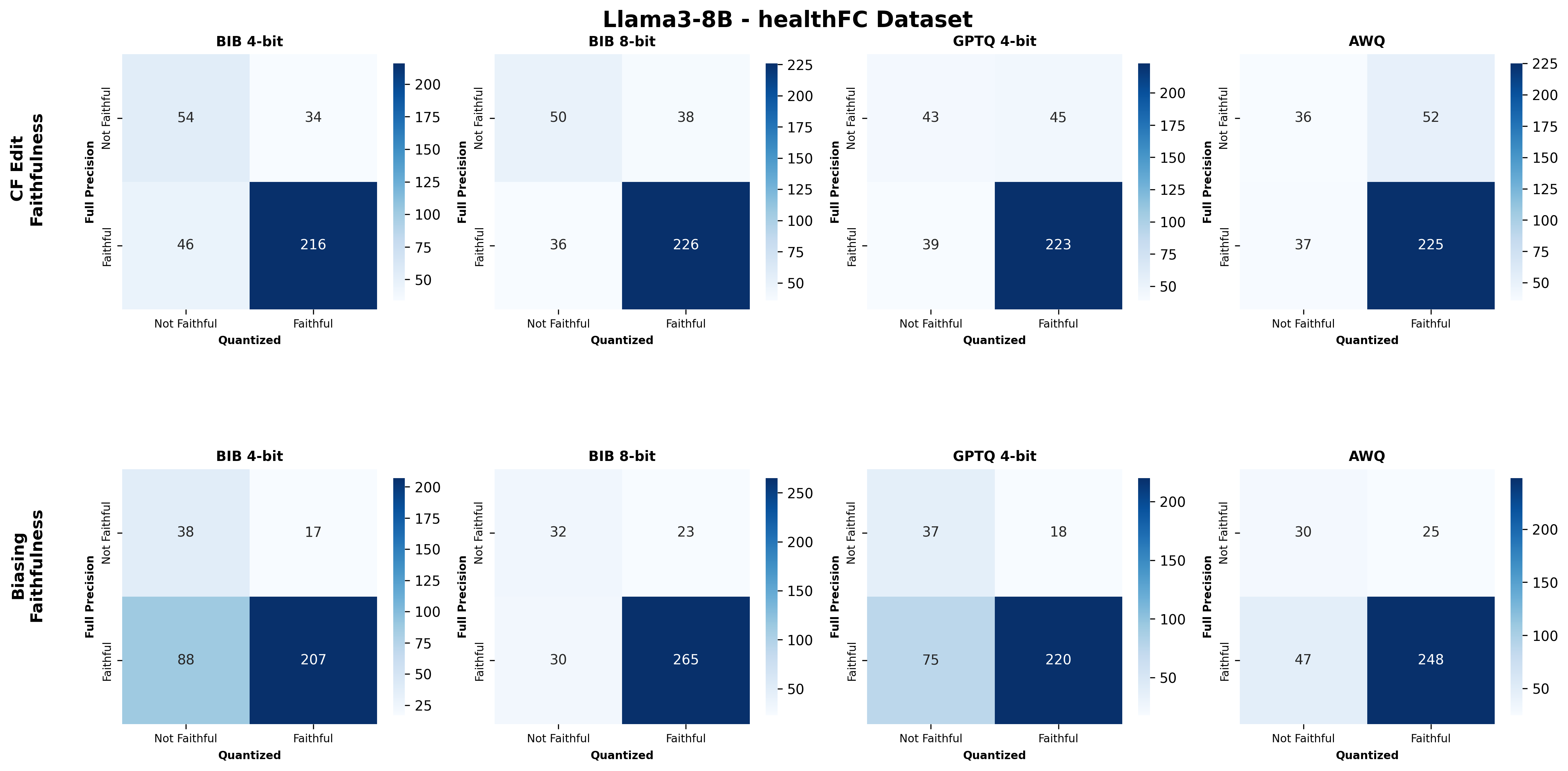
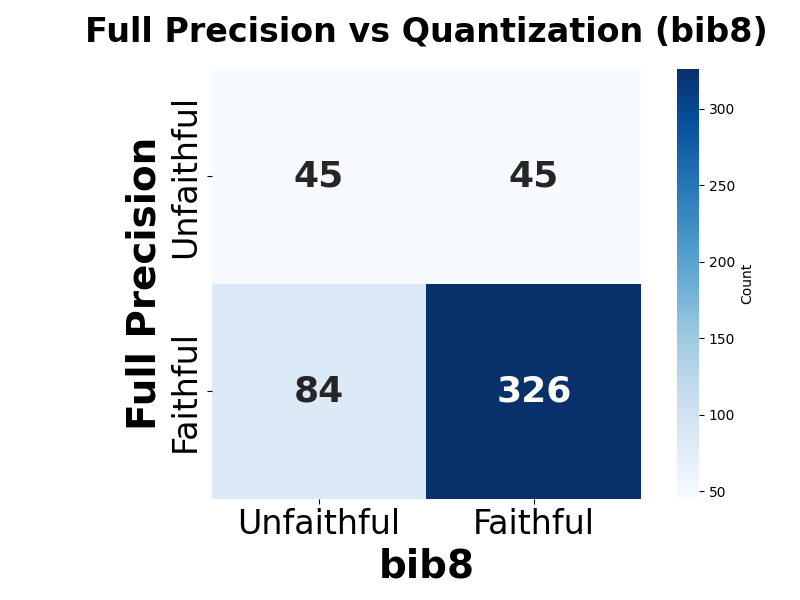
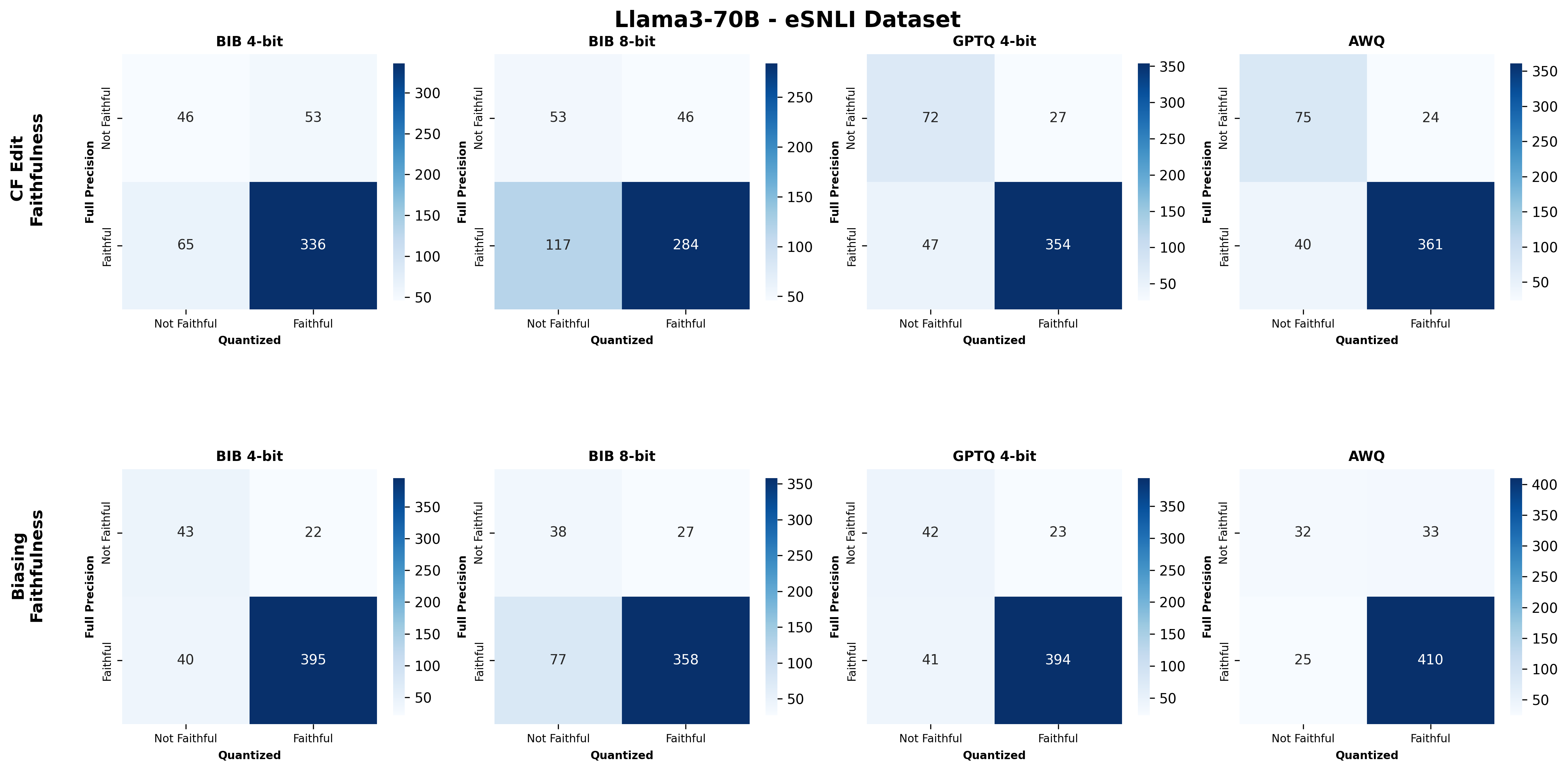
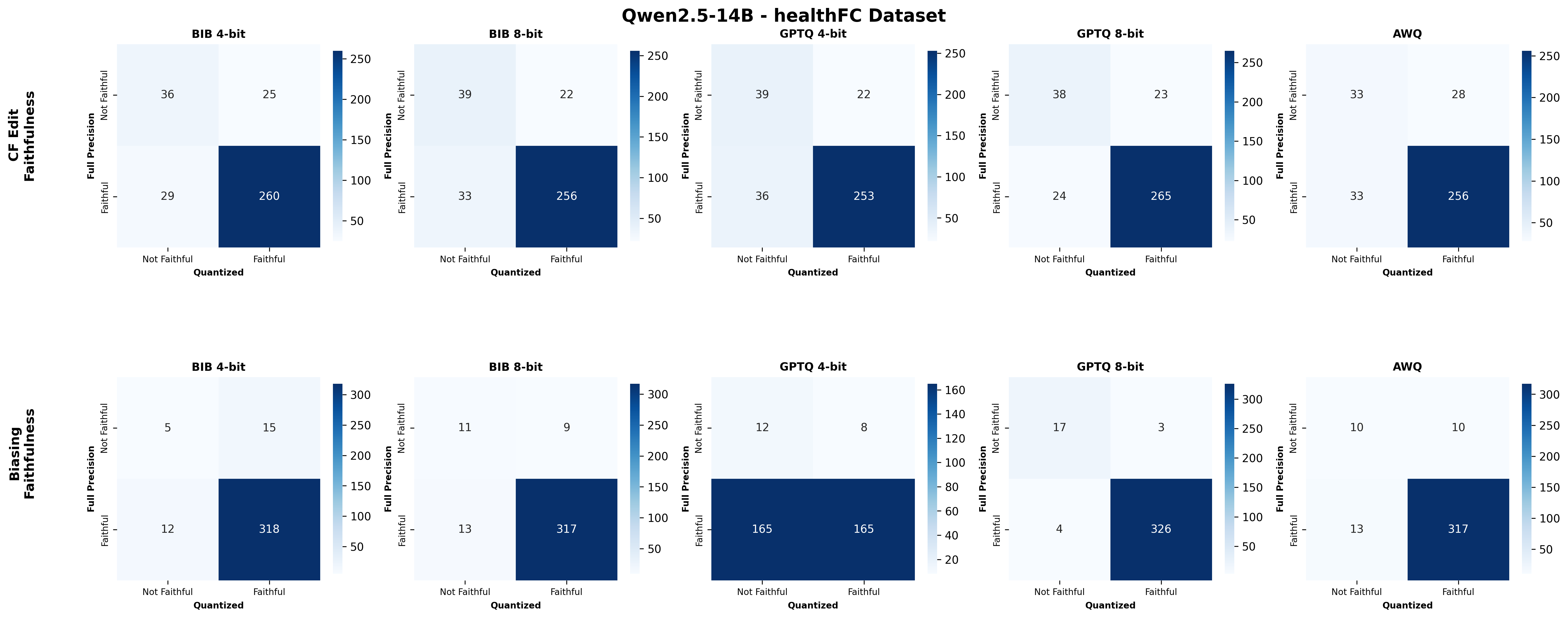
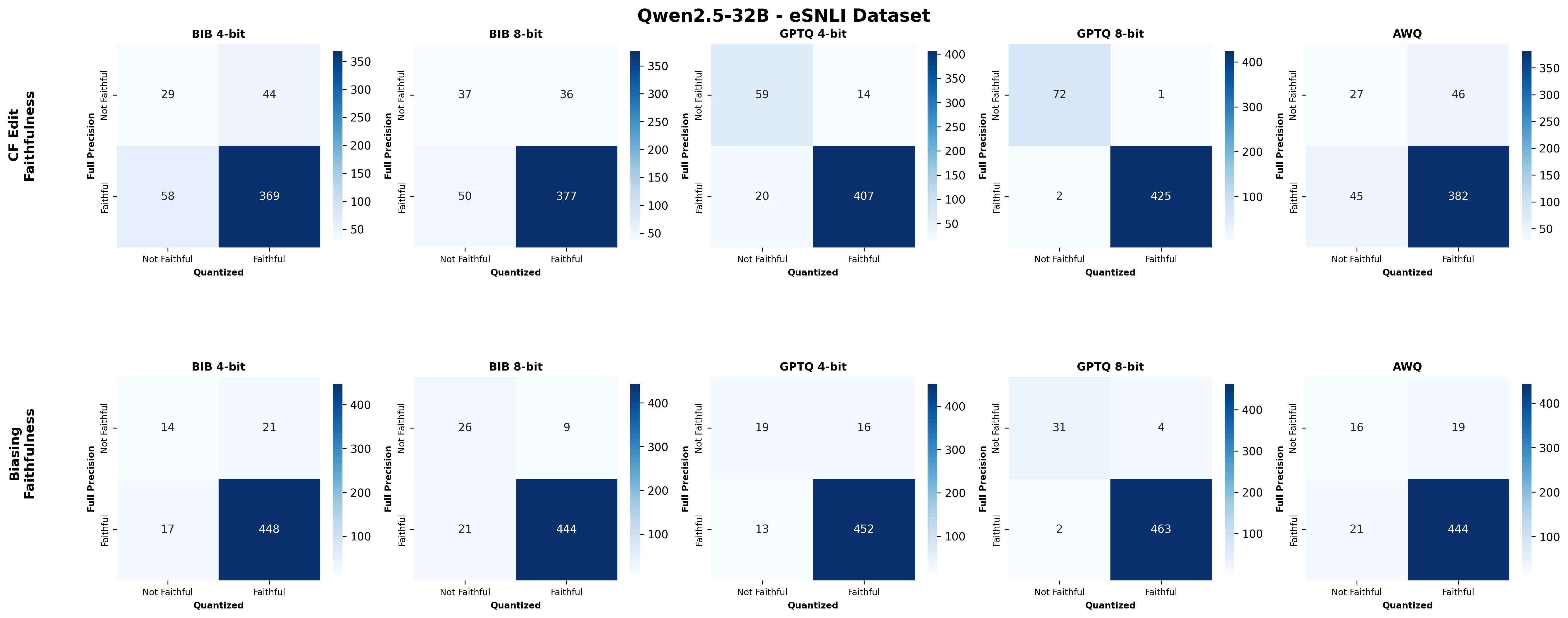
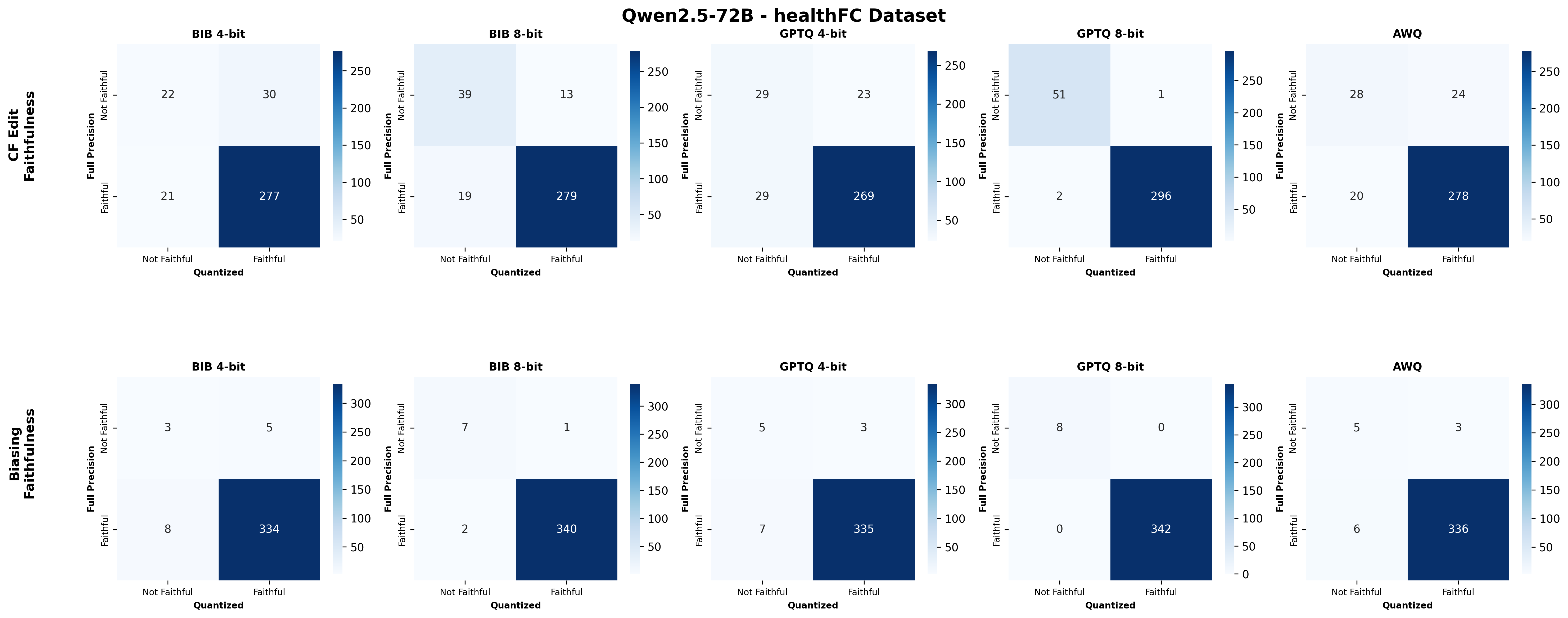
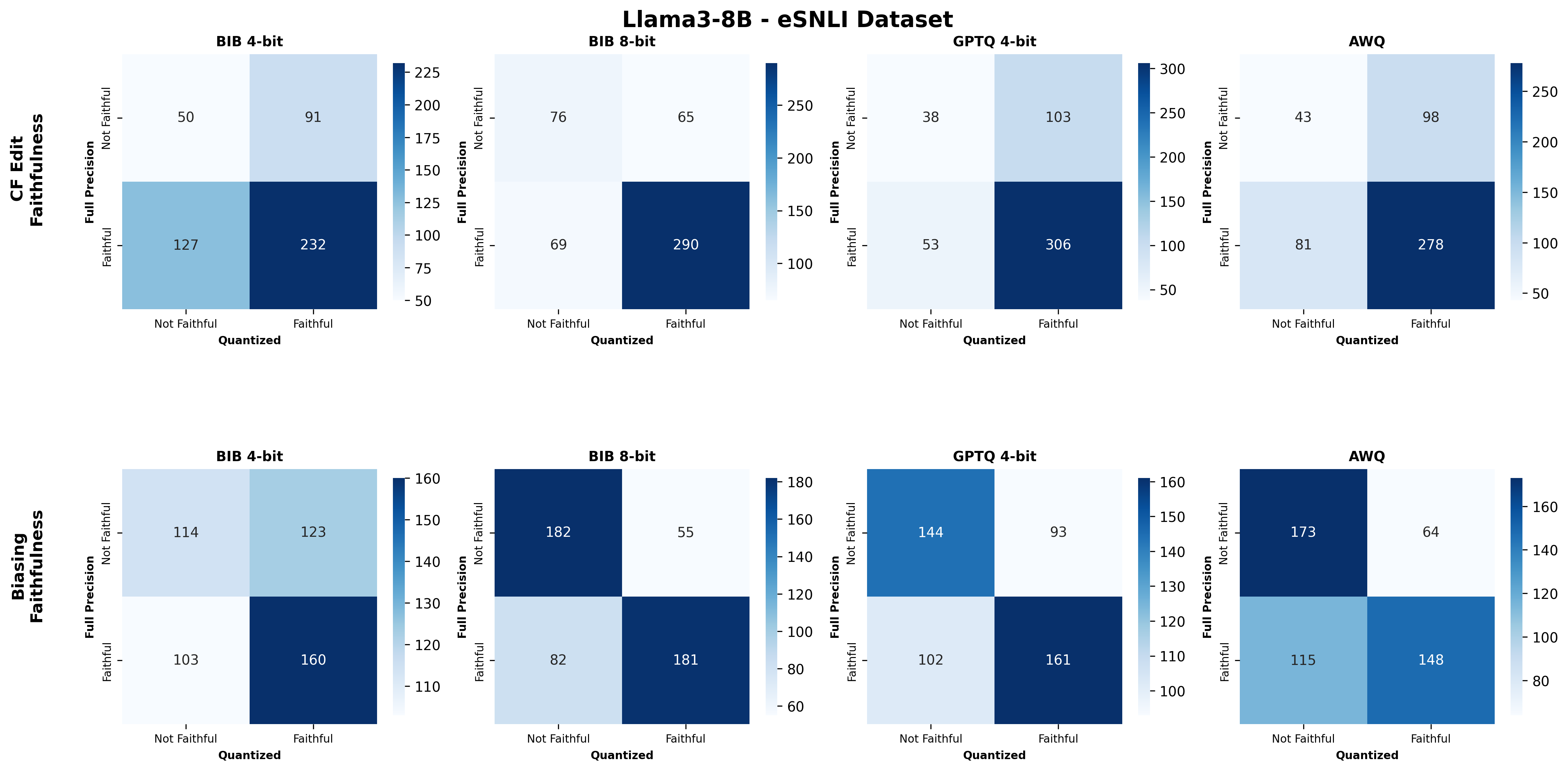
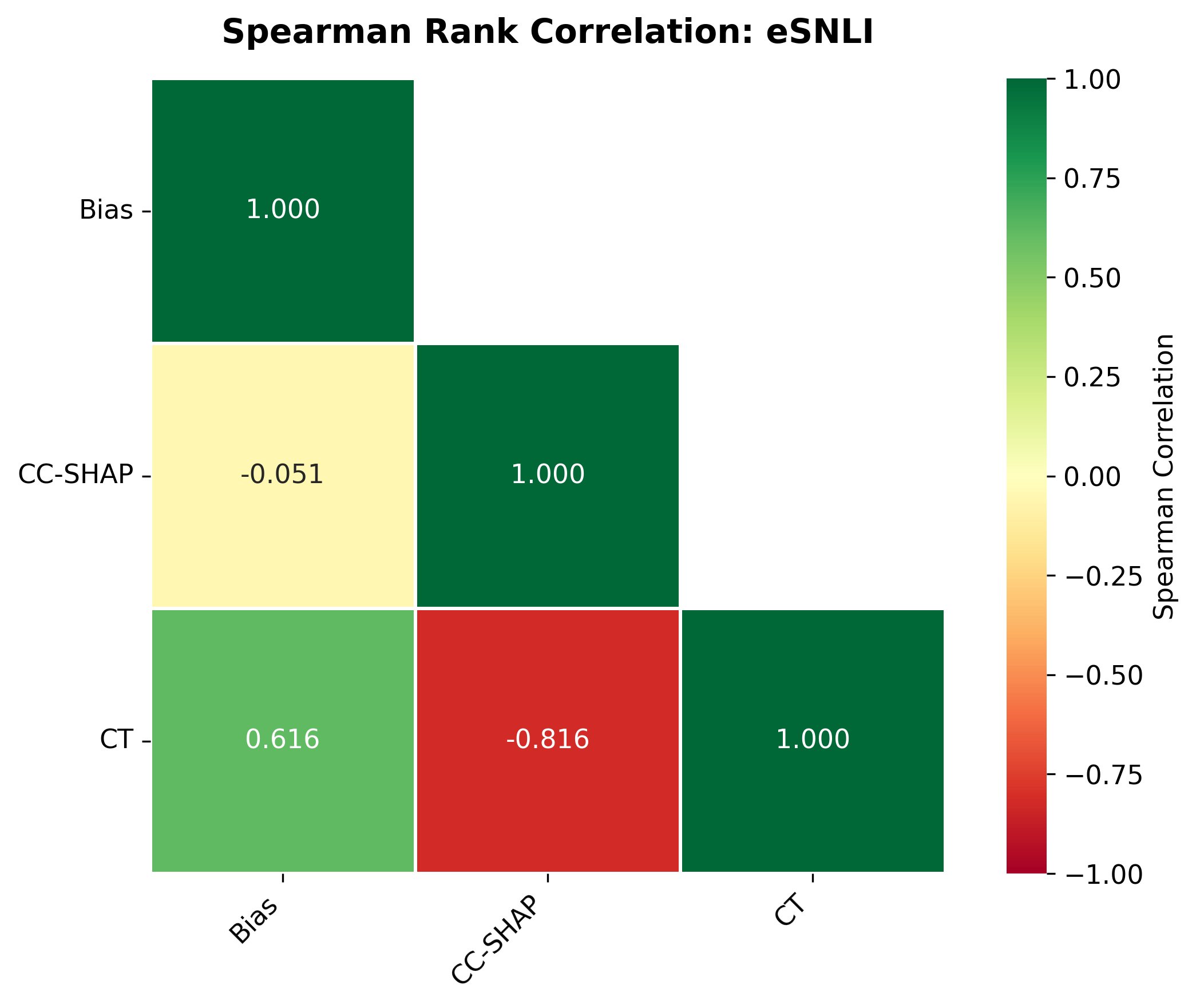
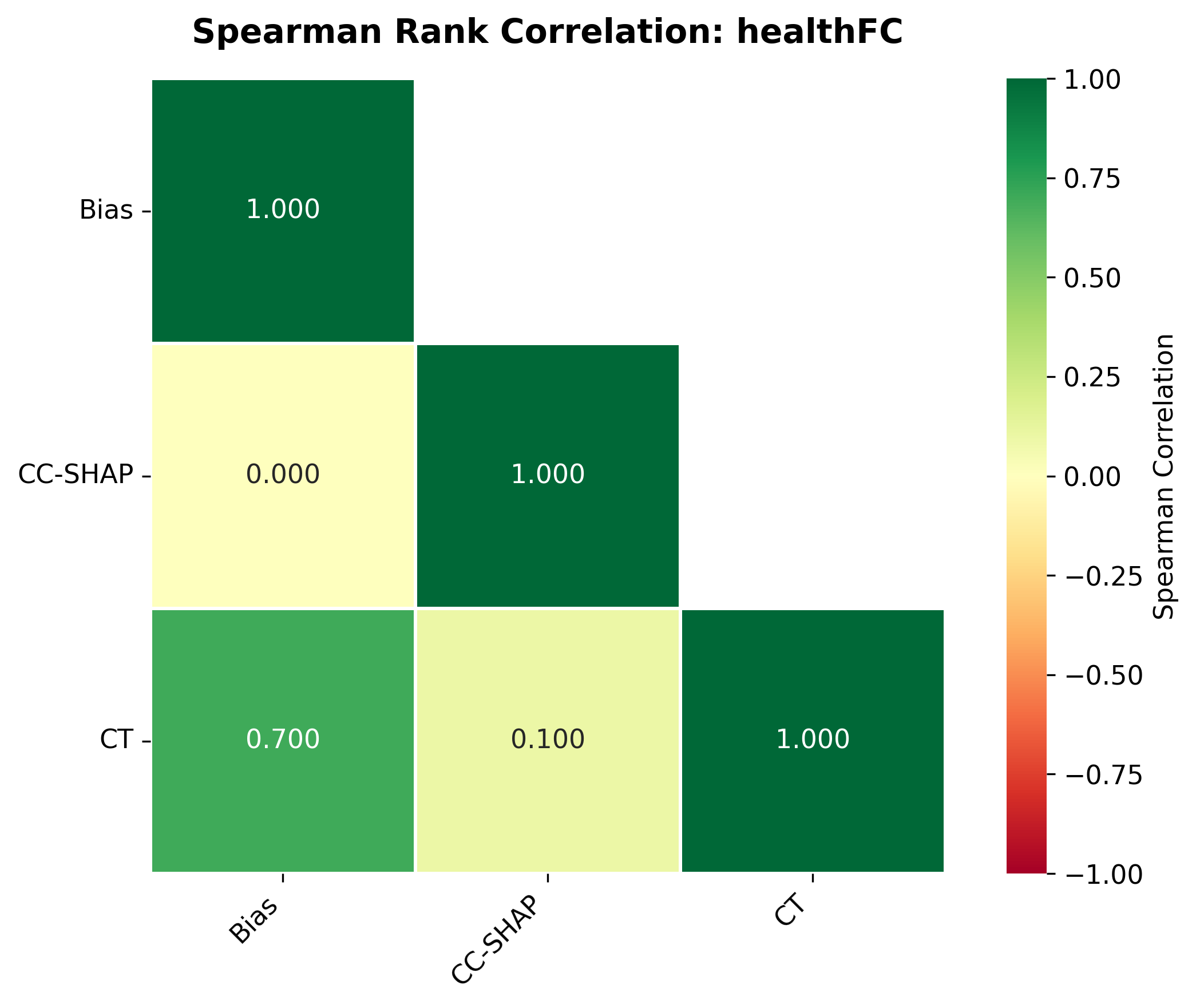
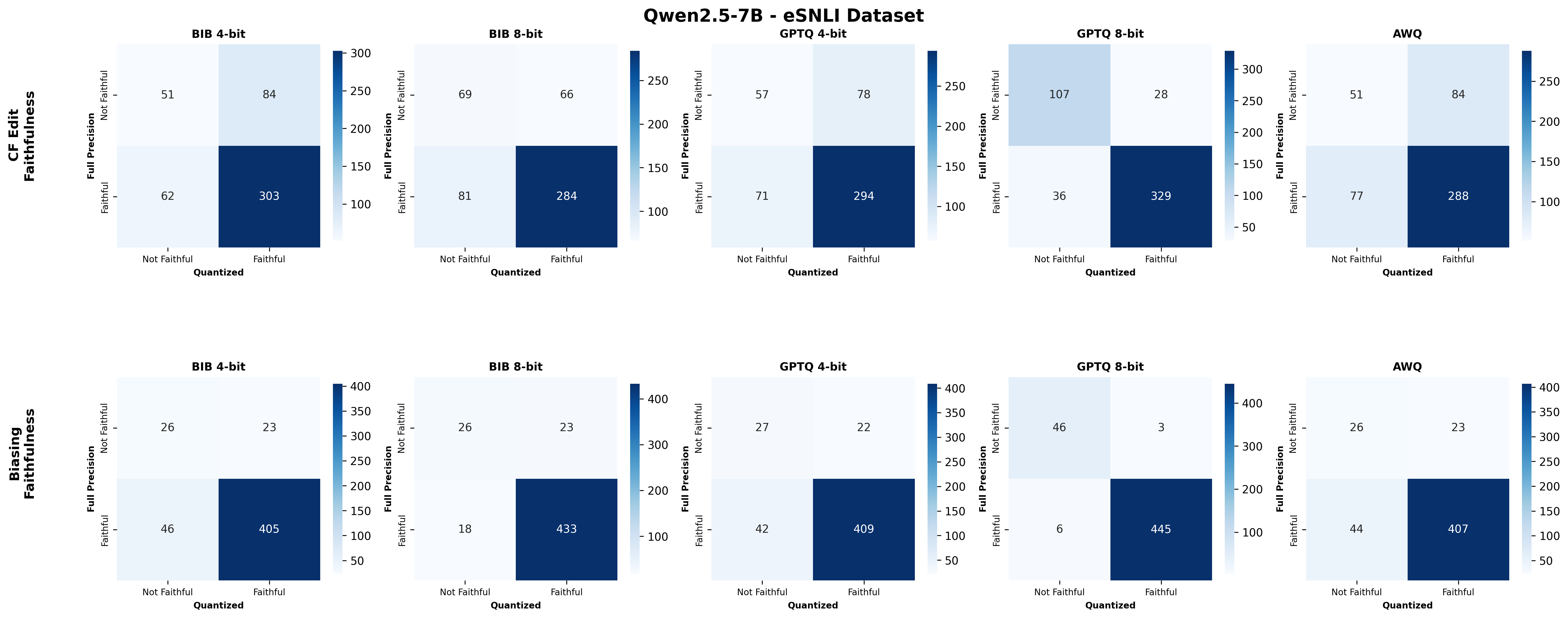
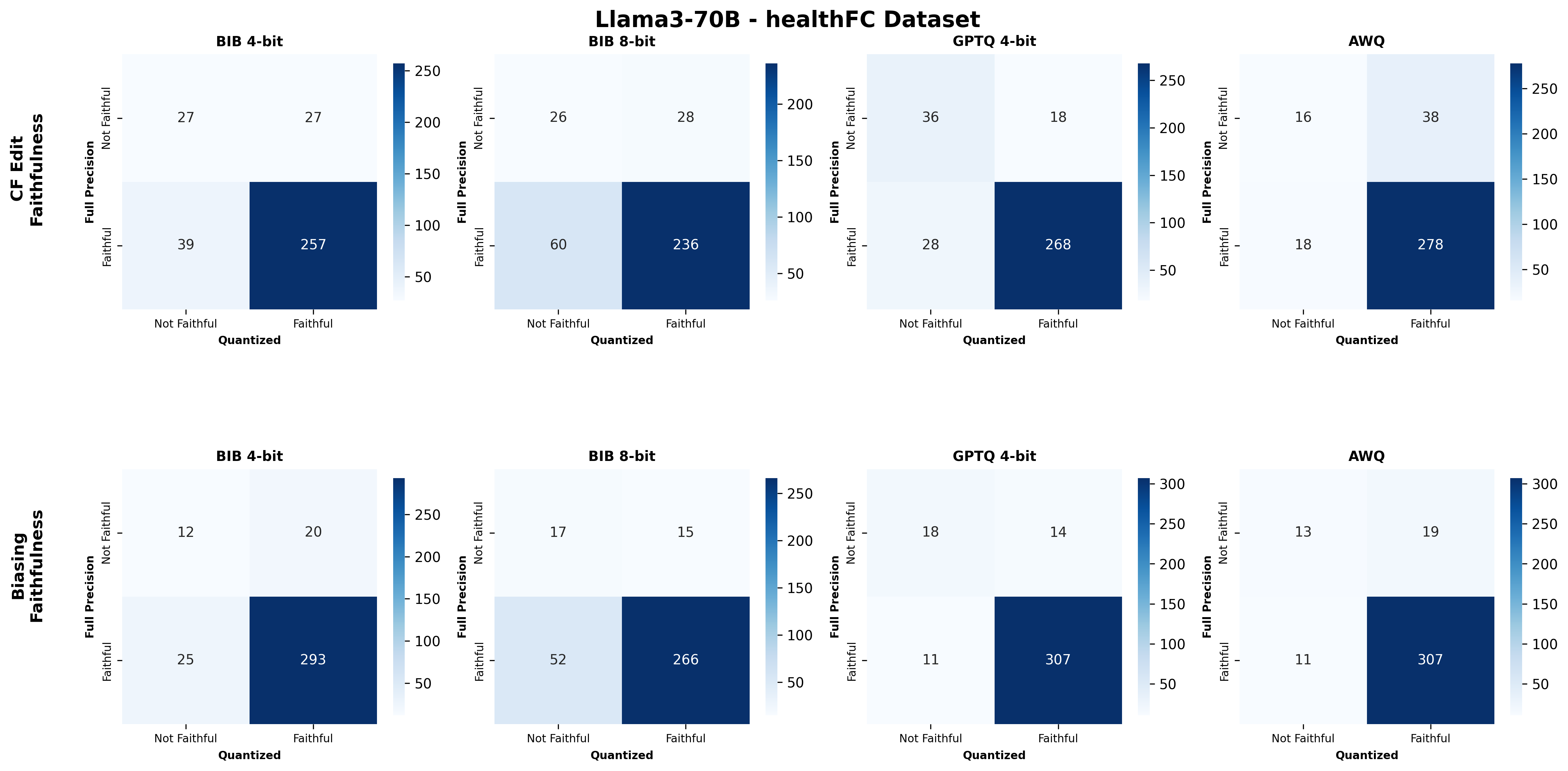
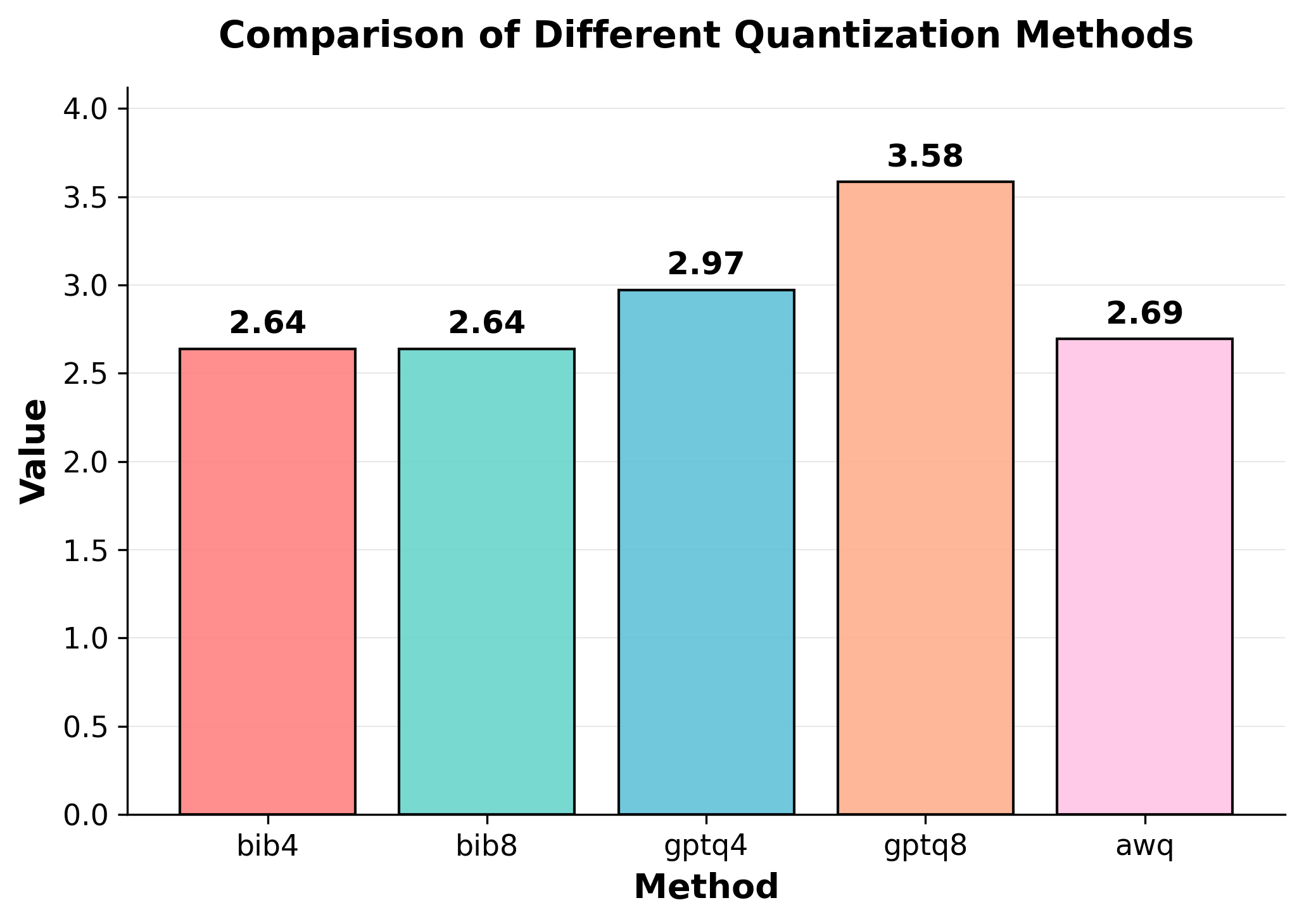
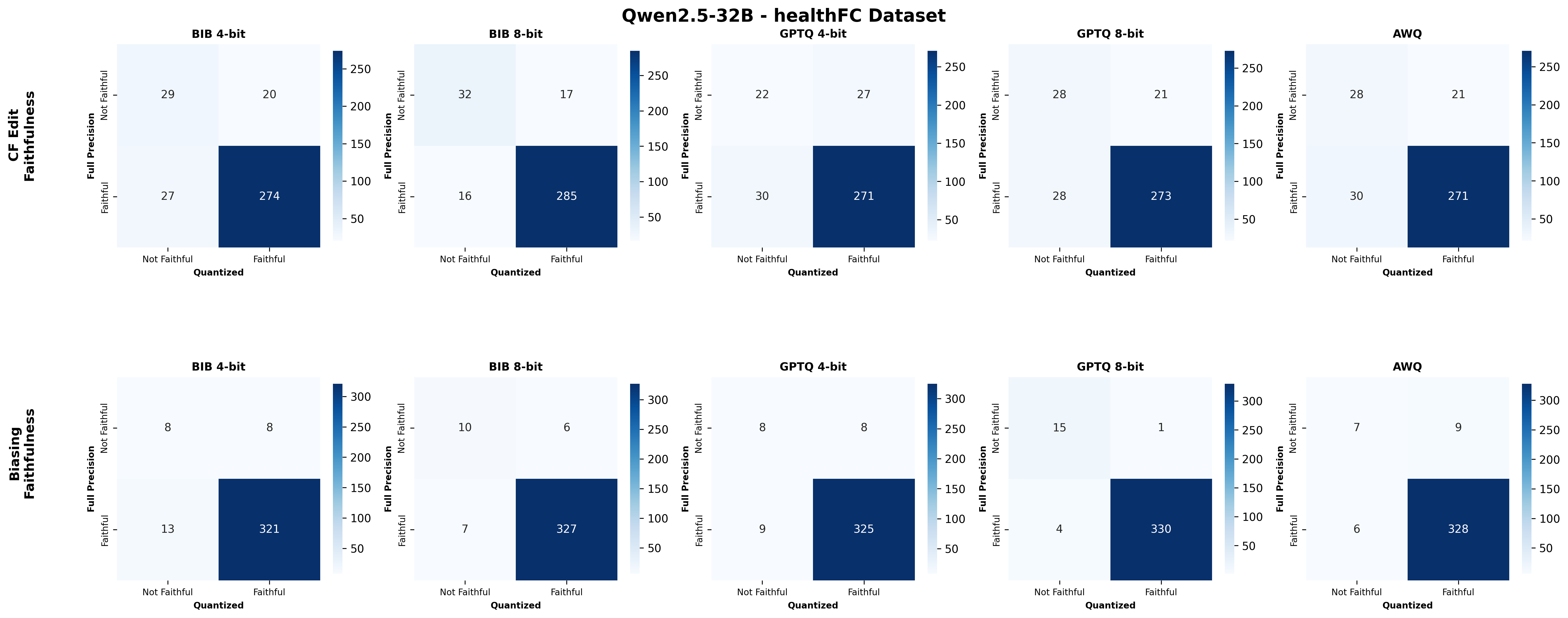
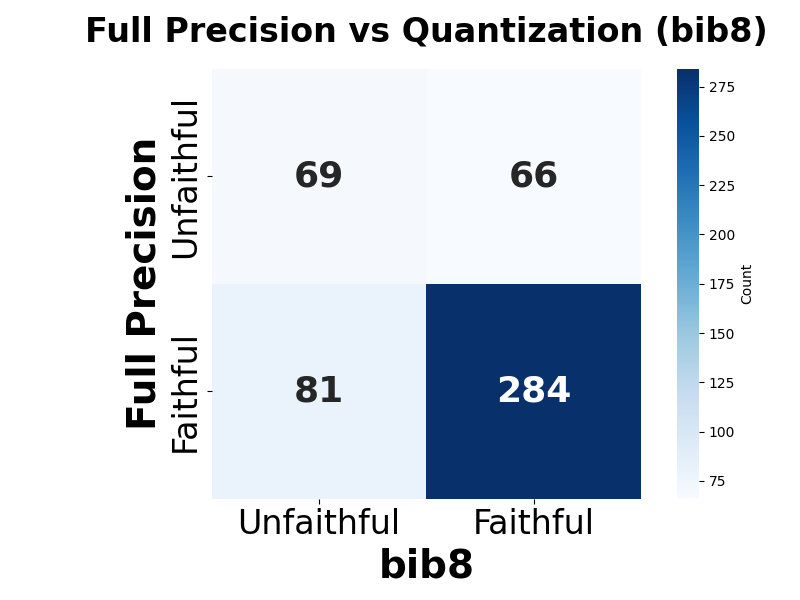
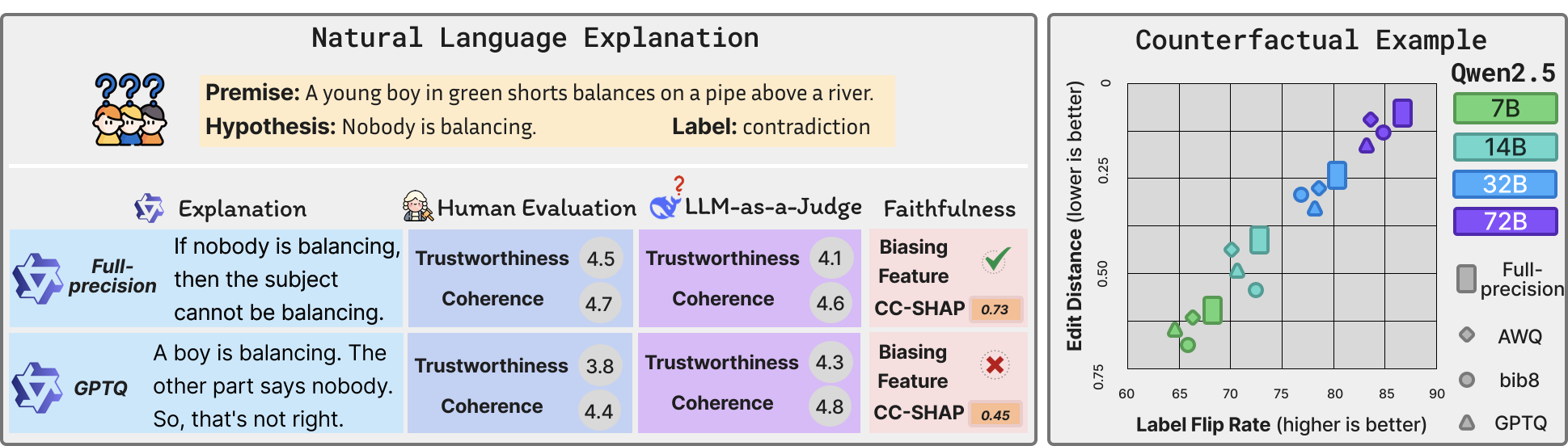
Quantization is widely used to accelerate inference and streamline the deployment of large language models (LLMs), yet its effects on self-explanations (SEs) remain unexplored. SEs, generated by LLMs to justify their own outputs, require reasoning about the model's own decision-making process, a capability that may exhibit particular sensitivity to quantization. As SEs are increasingly relied upon for transparency in high-stakes applications, understanding whether and to what extent quantization degrades SE quality and faithfulness is critical. To address this gap, we examine two types of SEs: natural language explanations (NLEs) and counterfactual examples, generated by LLMs quantized using three common techniques at distinct bit widths. Our findings indicate that quantization typically leads to moderate declines in both SE quality (up to 4.4\%) and faithfulness (up to 2.38\%). The user study further demonstrates that quantization diminishes both the coherence and trustworthiness of SEs (up to 8.5\%). Compared to smaller models, larger models show limited resilience to quantization in terms of SE quality but better maintain faithfulness. Moreover, no quantization technique consistently excels across task accuracy, SE quality, and faithfulness. Given that quantization's impact varies by context, we recommend validating SE quality for specific use cases, especially for NLEs, which show greater sensitivity. Nonetheless, the relatively minor deterioration in SE quality and faithfulness does not undermine quantization's effectiveness as a model compression technique.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Improving Deep Learning Model Performance:** The core of deep learning technology is the ability of models to automatically learn patterns from data. This study highlights how transformer models like BERT can be effective in various NLP tasks. 2. **Importance of Hyperparameters:** Hyperparameters are used to adjust how a model learns. The research shows that specific settings can improve accuracy, but at the cost of increased computational expenses. 3. **Differences Across Datasets and Task Types:** Different NLP tasks have distinct characteristics. Therefore, what works well for one task might not be effective for another.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)