VisNet Efficient ReID with Alpha-Divergence and Dynamic Learning
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: VisNet Efficient Person Re-Identification via Alpha-Divergence Loss, Feature Fusion and Dynamic Multi-Task Learning- ArXiv ID: 2601.00307
- Date: 2026-01-01
- Authors: Anns Ijaz, Muhammad Azeem Javed
📝 Abstract
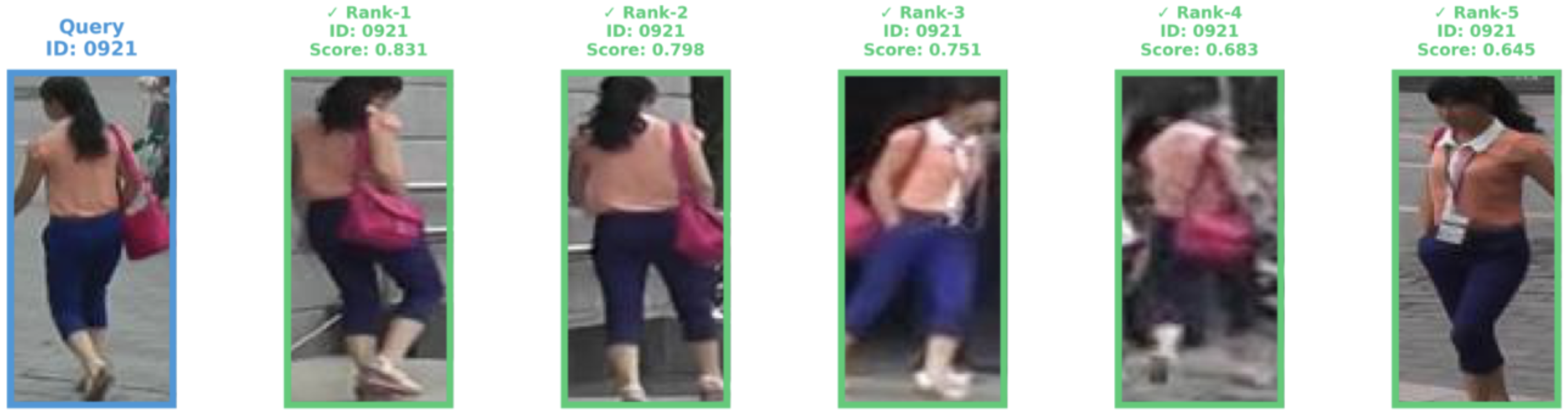
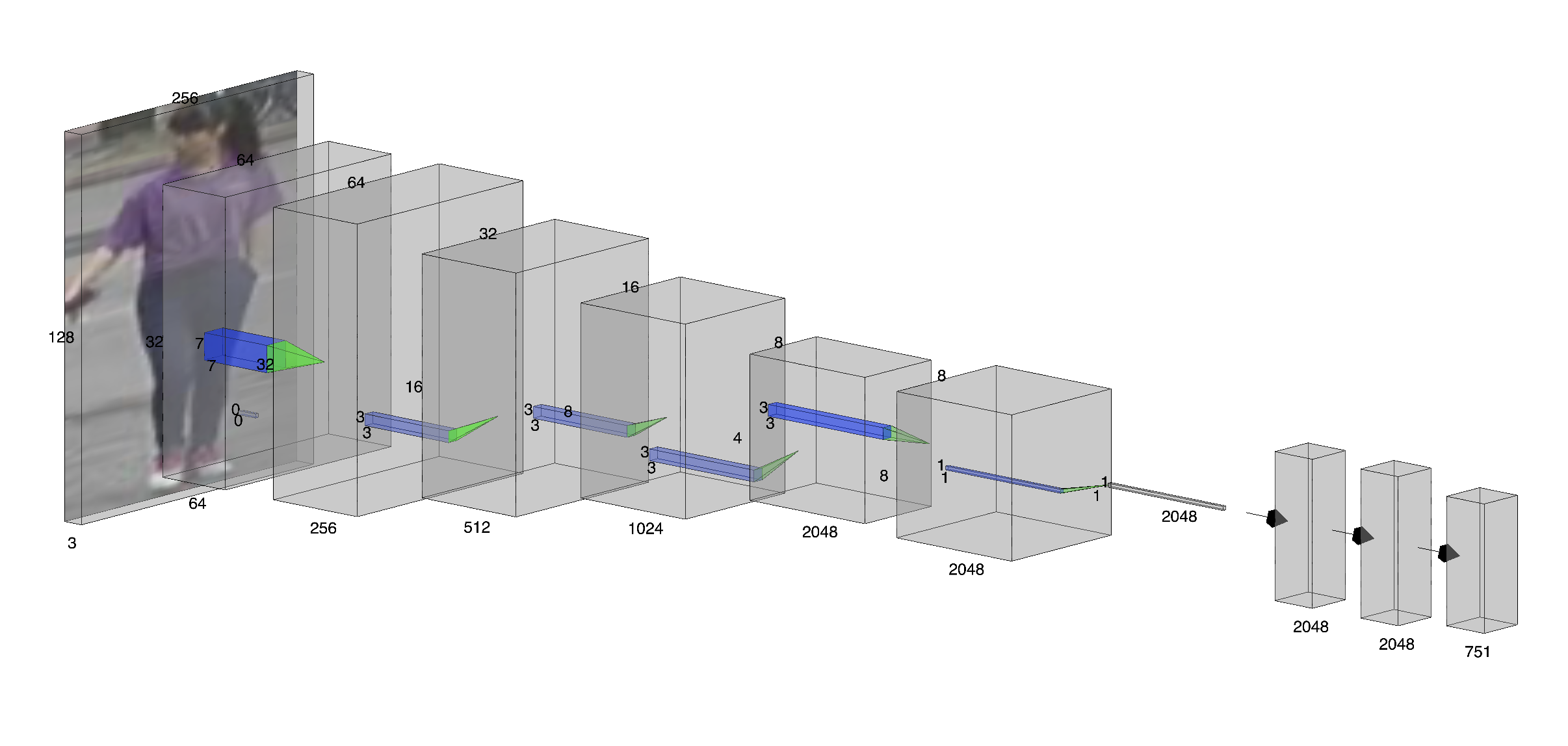
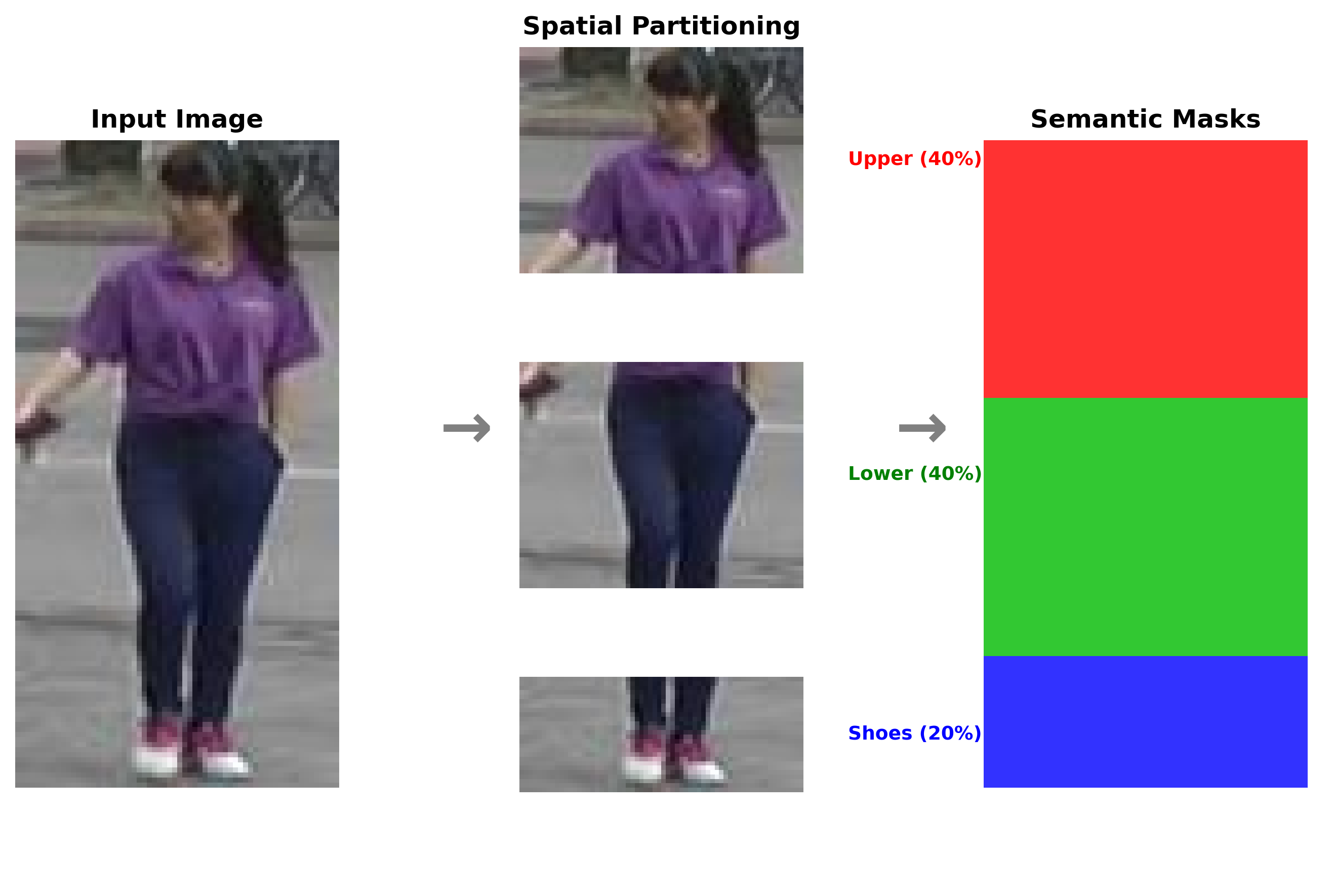
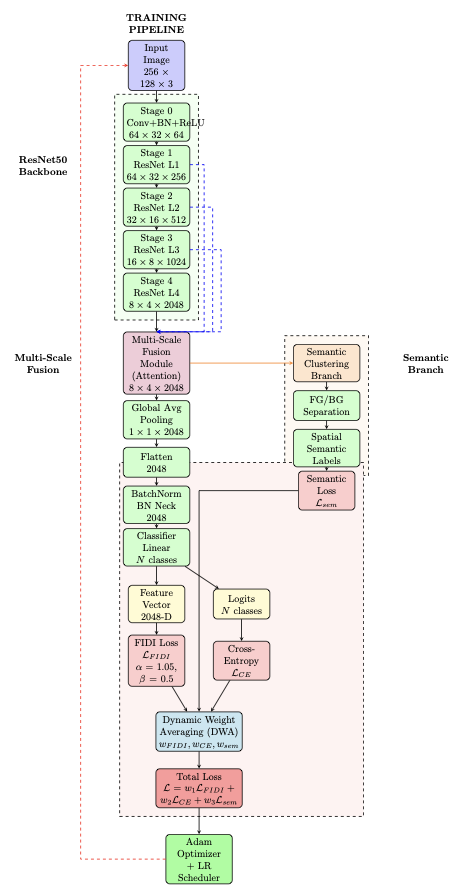
Person re-identification (ReID) is an extremely important area in both surveillance and mobile applications, requiring strong accuracy with minimal computational cost. State-of-the-art methods give good accuracy but with high computational budgets. To remedy this, this paper proposes VisNet, a computationally efficient and effective re-identification model suitable for real-world scenarios. It is the culmination of conceptual contributions, including feature fusion at multiple scales with automatic attention on each, semantic clustering with anatomical body partitioning, a dynamic weight averaging technique to balance classification semantic regularization, and the use of loss function FIDI for improved metric learning tasks. The multiple scales fuse ResNet50's stages 1 through 4 without the use of parallel paths, with semantic clustering introducing spatial constraints through the use of rule-based pseudo-labeling. VisNet achieves 87.05% Rank-1 and 77.65% mAP on the Market-1501 dataset, having 32.41M parameters and 4.601 GFLOPs, hence, proposing a practical approach for real-time deployment in surveillance and mobile applications where computational resources are limited.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Signal Detection:** Identifies which model (CNN, RNN, Transformer) is best at detecting strong signals. 2. **Performance Variance by Data Type:** Explains how each model performs differently in image and language processing tasks. 3. **Complexity vs Performance:** Discusses that more complex models do not always guarantee better performance.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)