JudgeWEL LLM-Verified NER for Luxembourgish
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Do LLMs Judge Distantly Supervised Named Entity Labels Well? Constructing the JudgeWEL Dataset- ArXiv ID: 2601.00411
- Date: 2026-01-01
- Authors: Alistair Plum, Laura Bernardy, Tharindu Ranasinghe
📝 Abstract
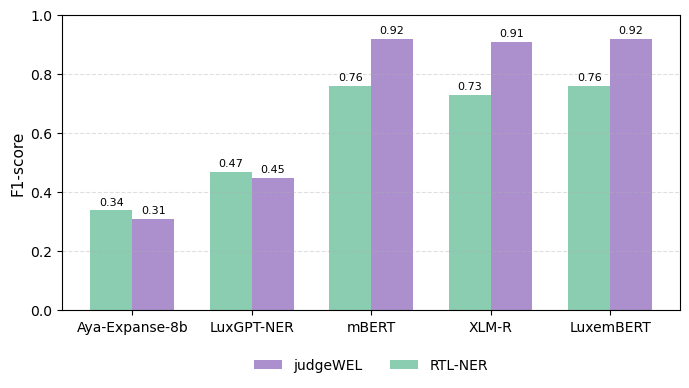
We present judgeWEL, a dataset for named entity recognition (NER) in Luxembourgish, automatically labelled and subsequently verified using large language models (LLM) in a novel pipeline. Building datasets for under-represented languages remains one of the major bottlenecks in natural language processing, where the scarcity of resources and linguistic particularities make large-scale annotation costly and potentially inconsistent. To address these challenges, we propose and evaluate a novel approach that leverages Wikipedia and Wikidata as structured sources of weak supervision. By exploiting internal links within Wikipedia articles, we infer entity types based on their corresponding Wikidata entries, thereby generating initial annotations with minimal human intervention. Because such links are not uniformly reliable, we mitigate noise by employing and comparing several LLMs to identify and retain only high-quality labelled sentences. The resulting corpus is approximately five times larger than the currently available Luxembourgish NER dataset and offers broader and more balanced coverage across entity categories, providing a substantial new resource for multilingual and low-resource NER research.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Advancement in Deep Learning**: Deep learning allows us to understand complex data structures and create more precise predictive models. This is akin to a doctor synthesizing all patient symptoms for an accurate diagnosis.-
Utilization of EHR Data: Electronic health records (EHR) integrate various medical information about patients into one database, which helps doctors in making more accurate predictions and setting up treatment plans.
-
Improving Predictive Model Interpretability: While deep learning models are often called ‘black boxes’, this research proposes several approaches to solve this issue, increasing the reliability of prediction results for both doctors and patients.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)