Encyclo-K Dynamic Knowledge Assessment for LLMs
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Encyclo-K Evaluating LLMs with Dynamically Composed Knowledge Statements- ArXiv ID: 2512.24867
- Date: 2025-12-31
- Authors: Yiming Liang, Yizhi Li, Yantao Du, Ge Zhang, Jiayi Zhou, Yuchen Wu, Yinzhu Piao, Denghui Cao, Tong Sun, Ziniu Li, Li Du, Bo Lei, Jiaheng Liu, Chenghua Lin, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Wenhao Huang, Jiajun Zhang
📝 Abstract
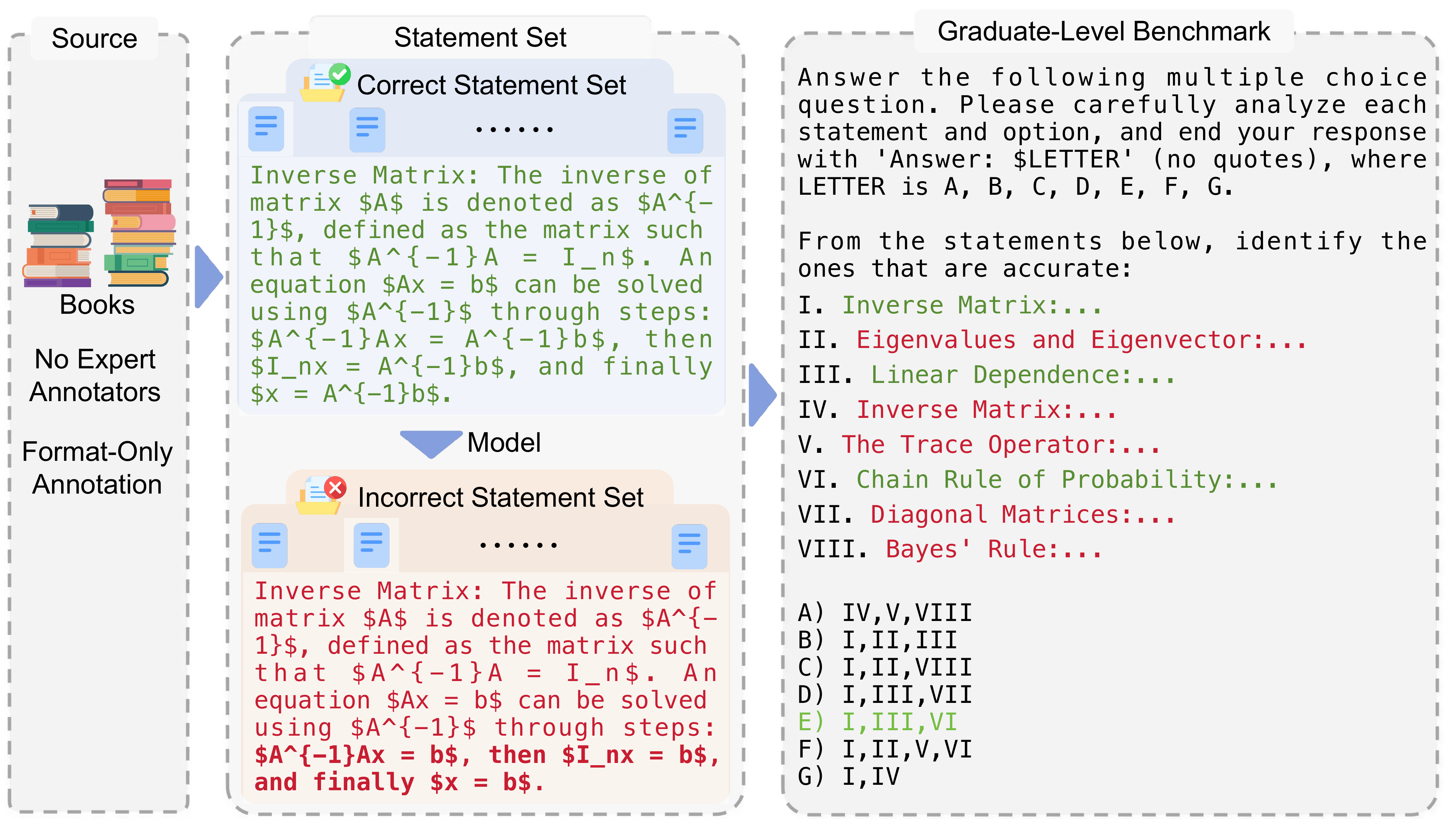
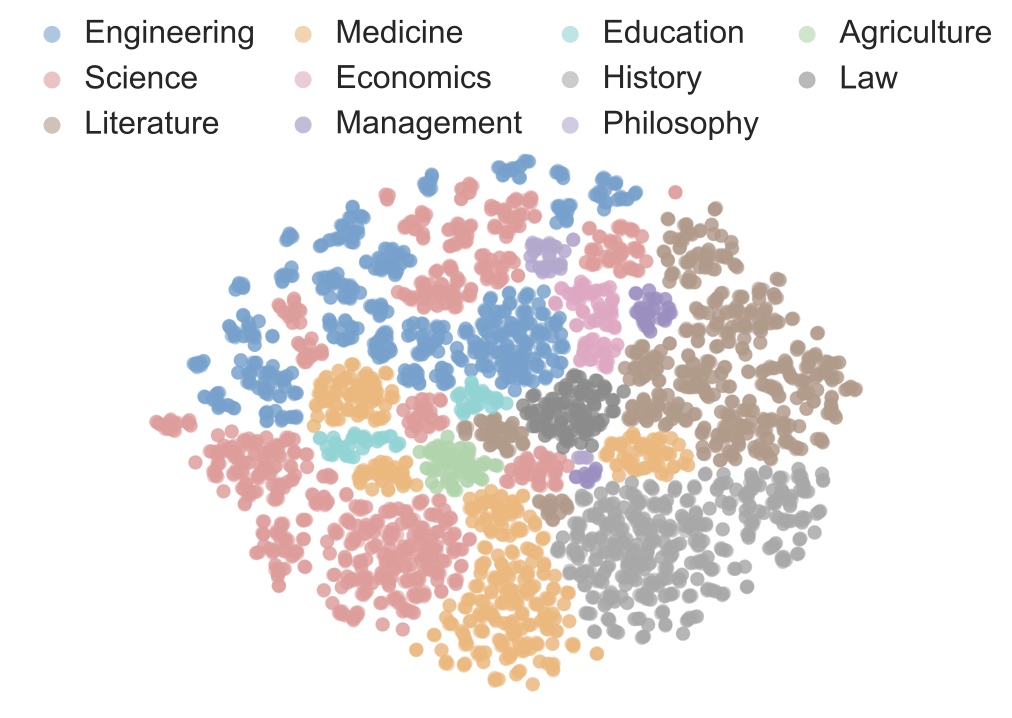
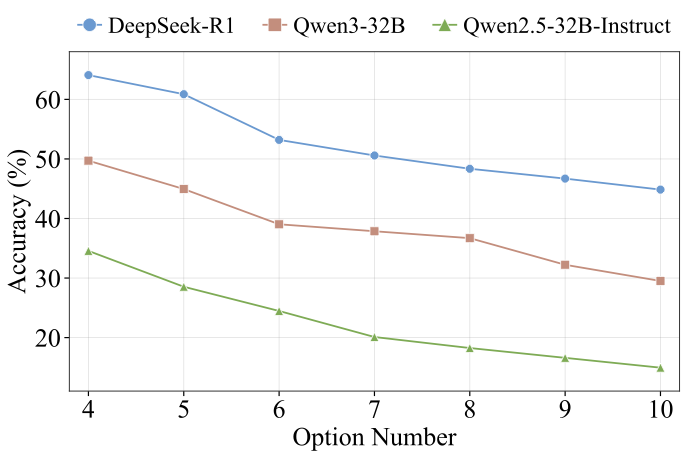
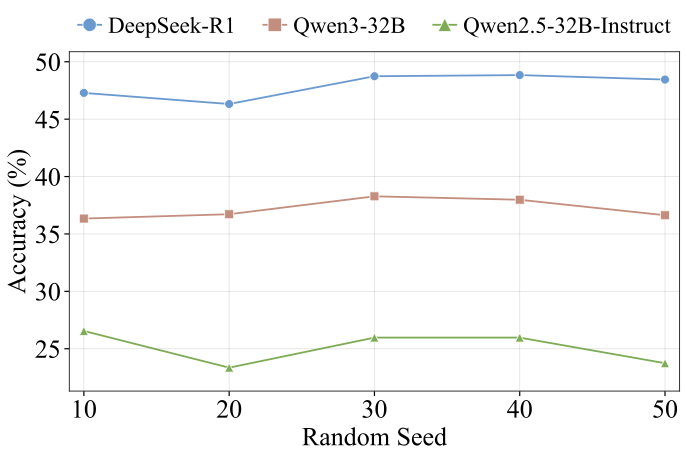
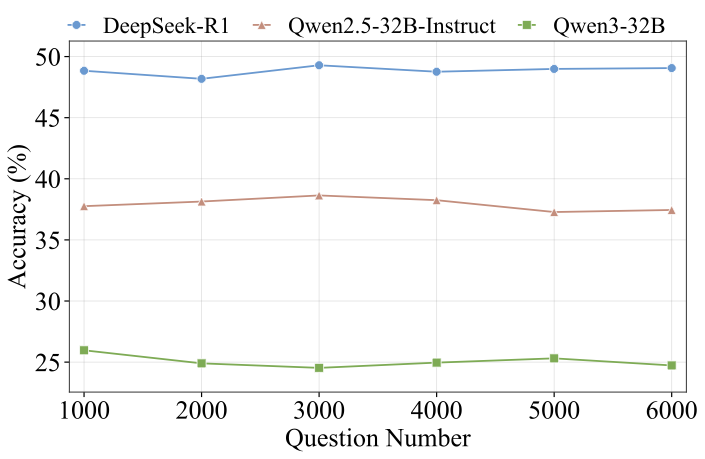
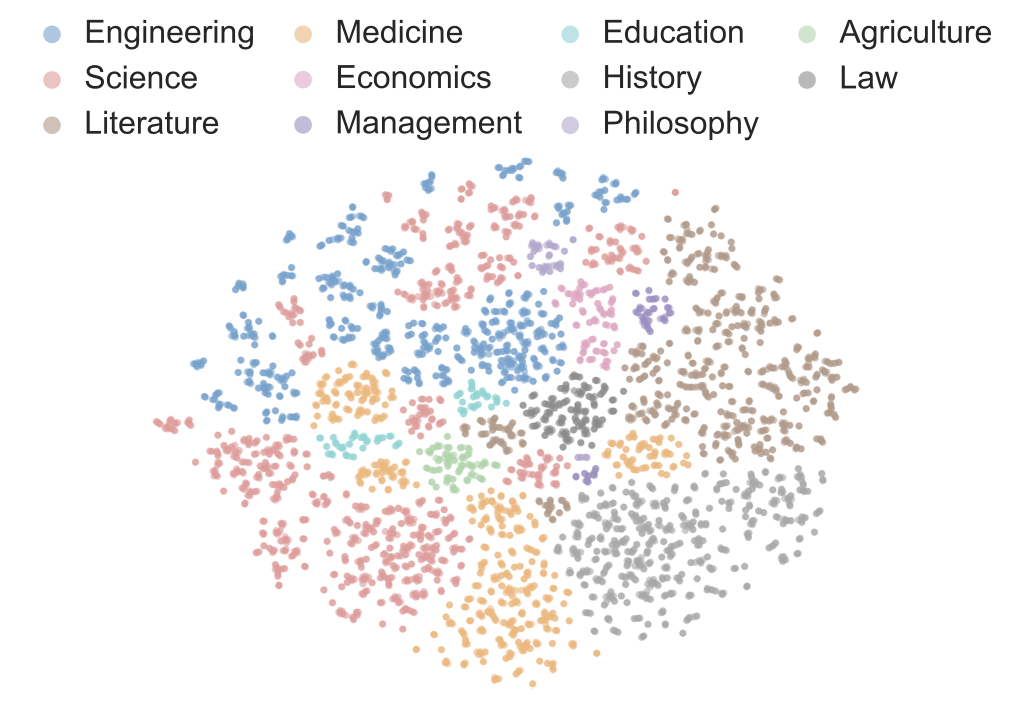
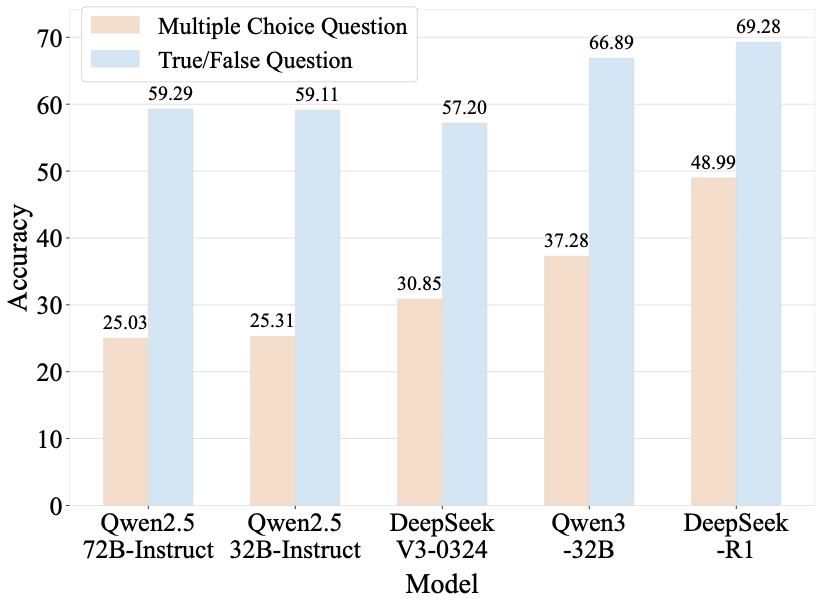
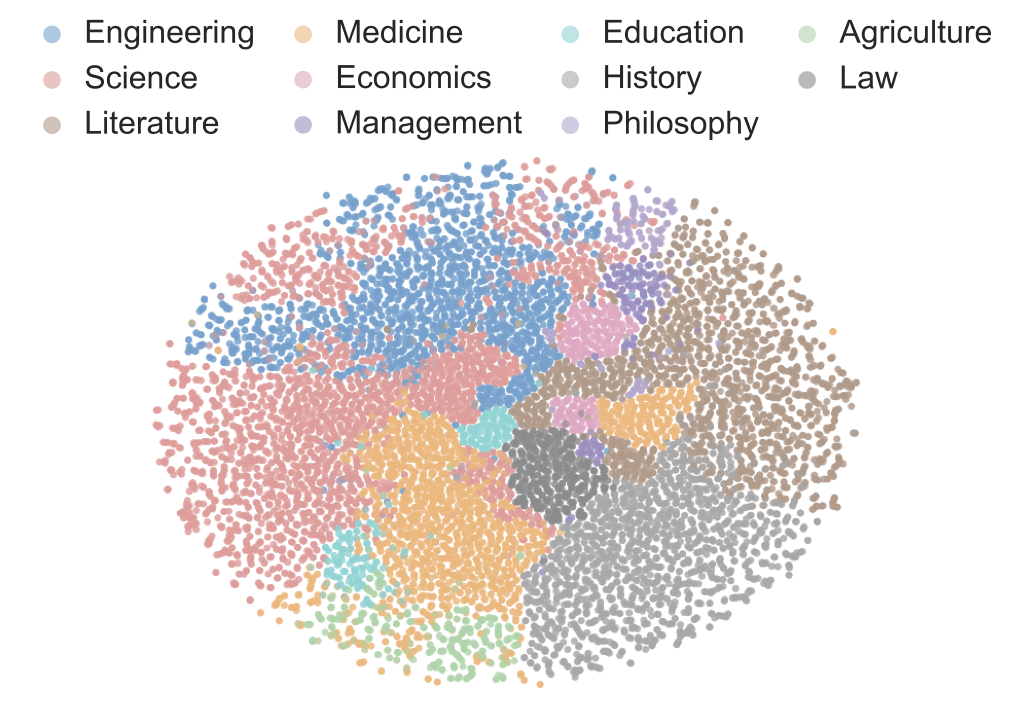
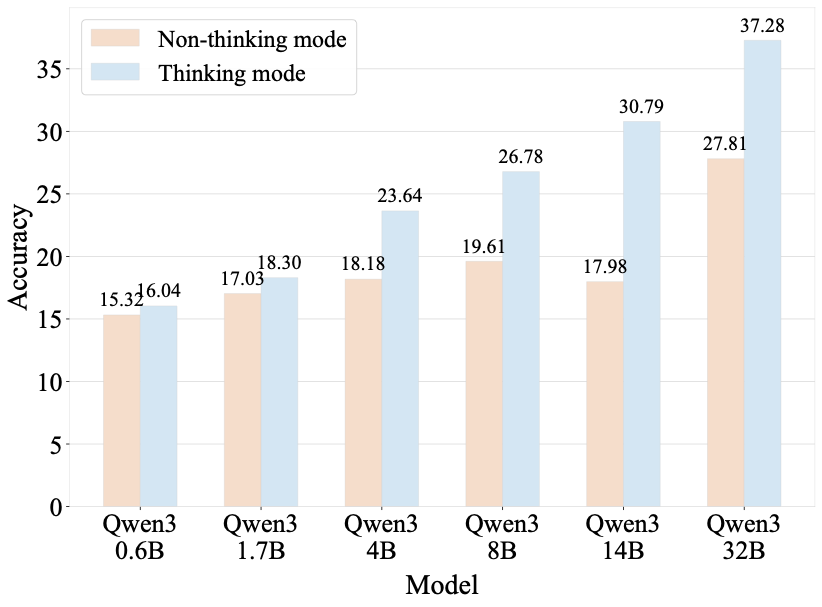
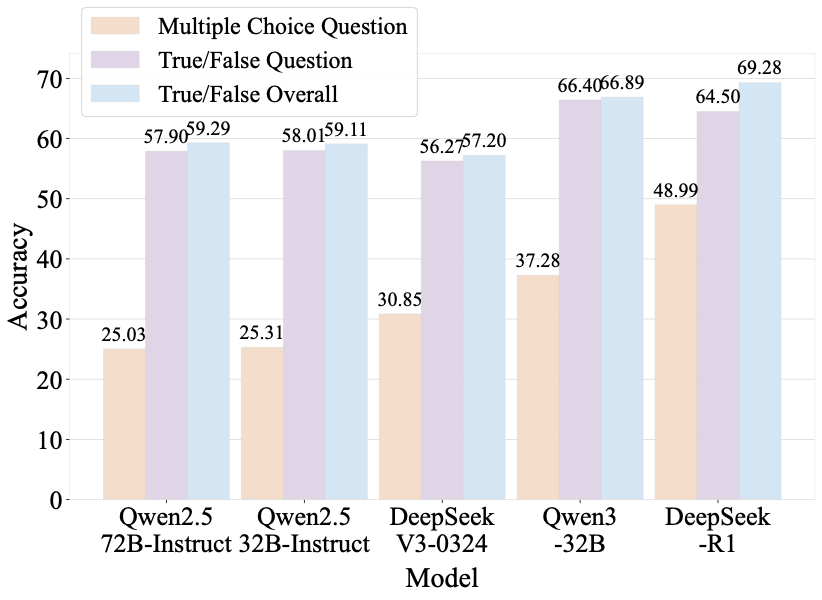
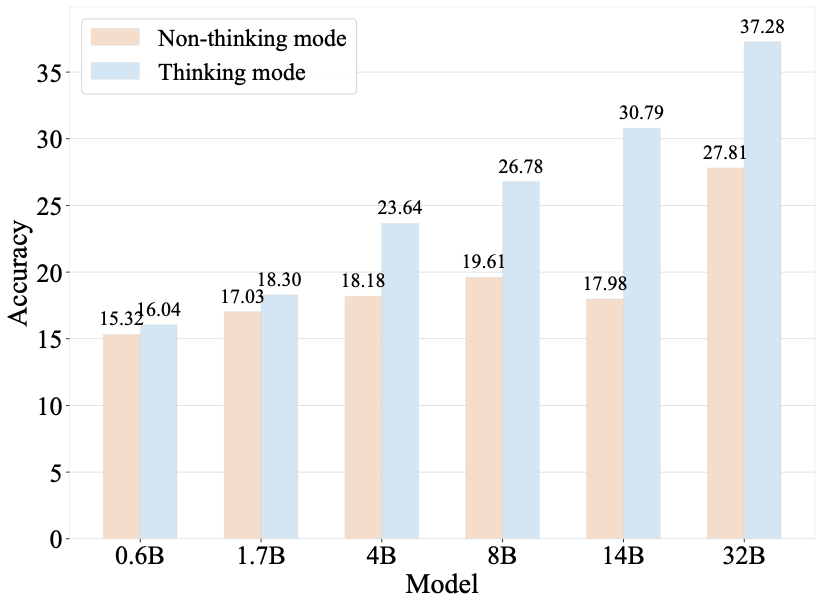
Benchmarks play a crucial role in tracking the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and identifying their capability boundaries. However, existing benchmarks predominantly curate questions at the question level, suffering from three fundamental limitations: vulnerability to data contamination, restriction to single-knowledge-point assessment, and reliance on costly domain expert annotation. We propose Encyclo-K, a statement-based benchmark that rethinks benchmark construction from the ground up. Our key insight is that knowledge statements, not questions, can serve as the unit of curation, and questions can then be constructed from them. We extract standalone knowledge statements from authoritative textbooks and dynamically compose them into evaluation questions through random sampling at test time. This design directly addresses all three limitations: the combinatorial space is too vast to memorize, and model rankings remain stable across dynamically generated question sets, enabling reliable periodic dataset refresh; each question aggregates 8-10 statements for comprehensive multi-knowledge assessment; annotators only verify formatting compliance without requiring domain expertise, substantially reducing annotation costs. Experiments on over 50 LLMs demonstrate that Encyclo-K poses substantial challenges with strong discriminative power. Even the top-performing OpenAI-GPT-5.1 achieves only 62.07% accuracy, and model performance displays a clear gradient distribution--reasoning models span from 16.04% to 62.07%, while chat models range from 9.71% to 50.40%. These results validate the challenges introduced by dynamic evaluation and multi-statement comprehensive understanding. These findings establish Encyclo-K as a scalable framework for dynamic evaluation of LLMs' comprehensive understanding over multiple fine-grained disciplinary knowledge statements.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1:** Clearly demonstrates how deep learning models work in sentiment analysis. - **Metaphor:** This is akin to finding the method that accurately judges whether a movie review is positive or negative.-
Contribution 2: Analyzes performance differences between LSTM, GRU, and BERT architectures.
- Metaphor: These models are like different race cars in the sentiment analysis championship. Understanding which model arrives first and why is crucial.
-
Contribution 3: Evaluates generalization ability by comparing performances across various datasets.
- Metaphor: This is similar to testing multiple cooking recipes to see which yields the most delicious result when applied to different types of food.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)