Predicting Ground Shifts A Multimodal Approach Across Europe
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: A multimodal Transformer for InSAR-based ground deformation forecasting with cross-site generalization across Europe- ArXiv ID: 2512.23906
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Wendong Yao, Binhua Huang, Soumyabrata Dev
📝 Abstract
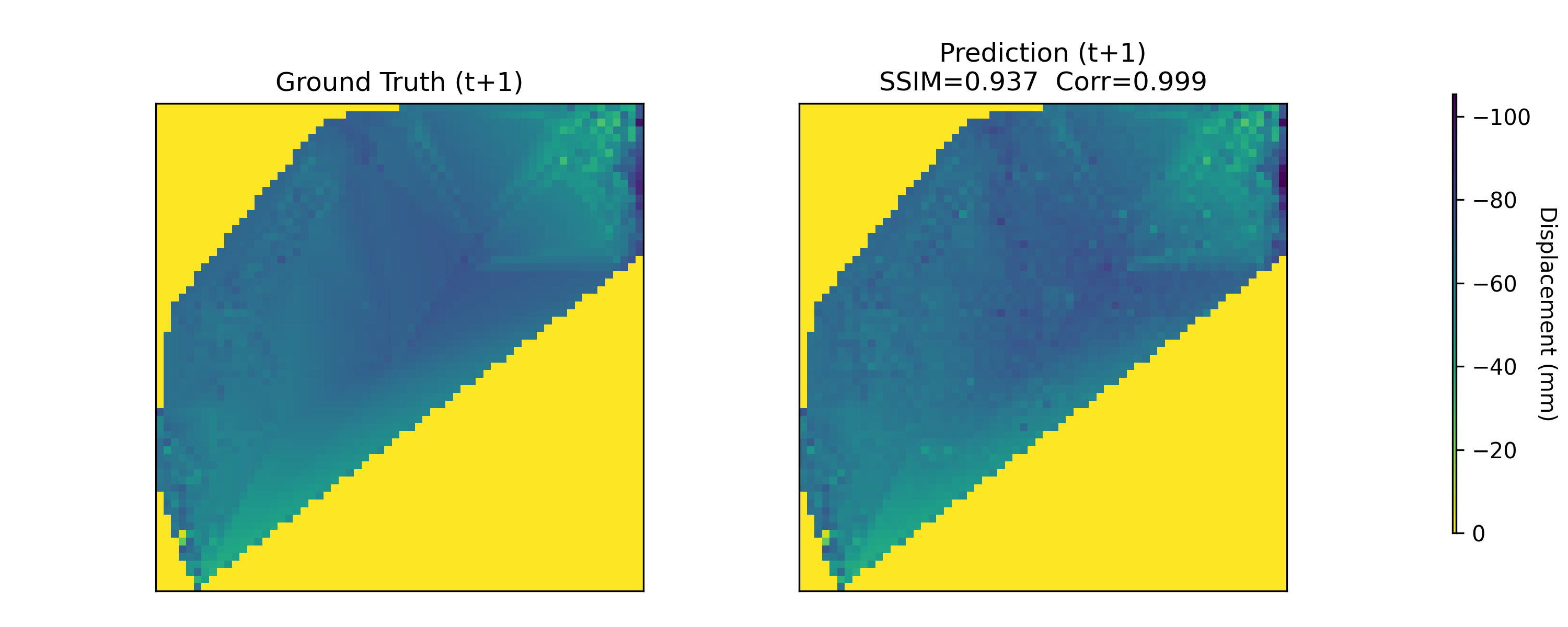
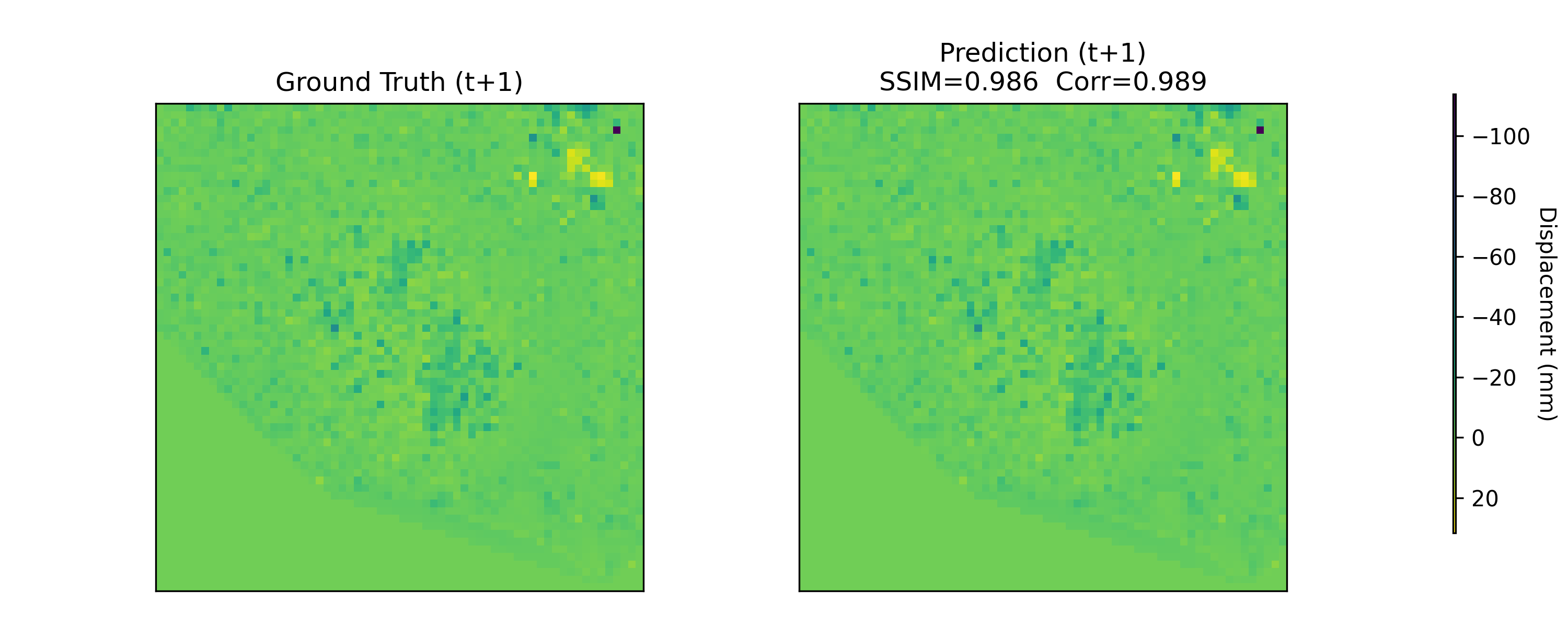
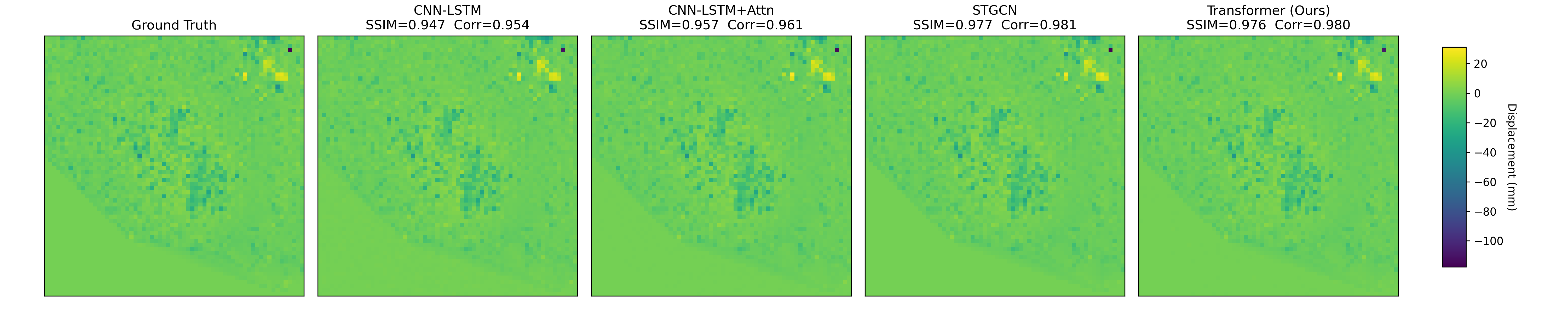
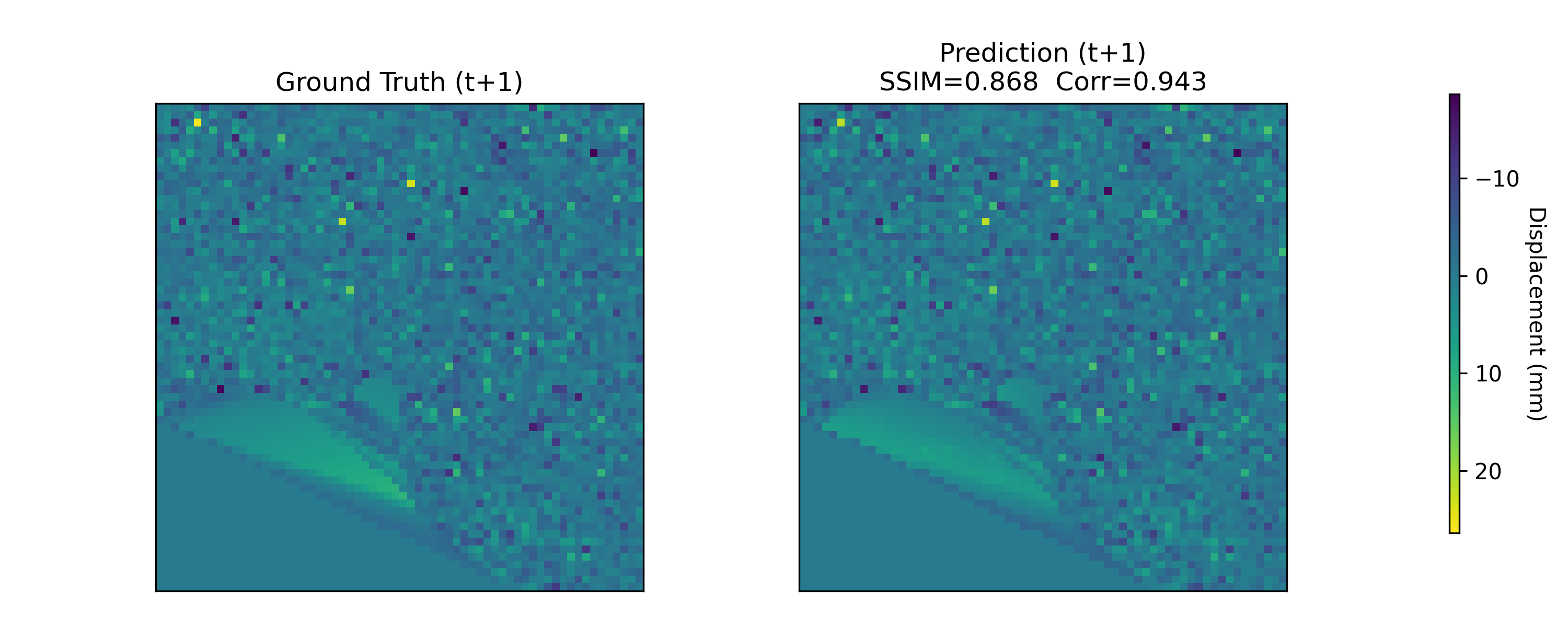
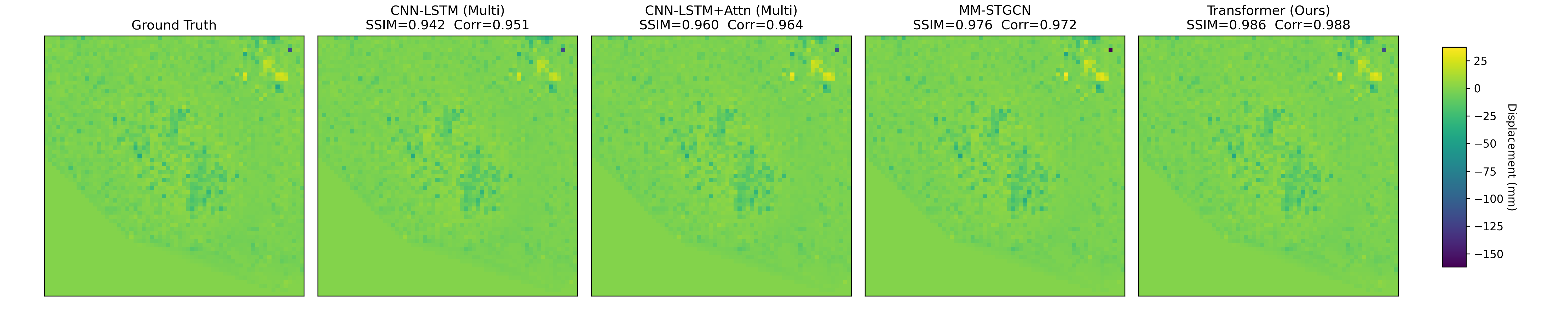
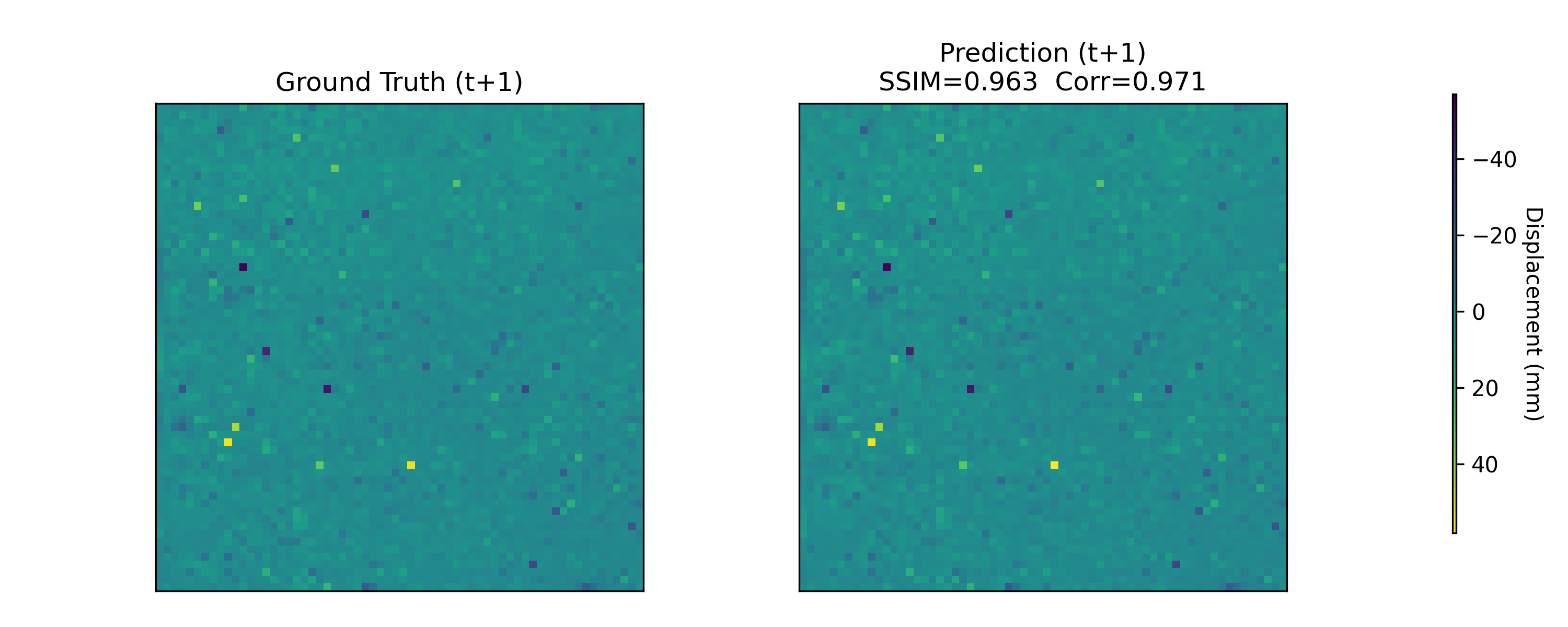
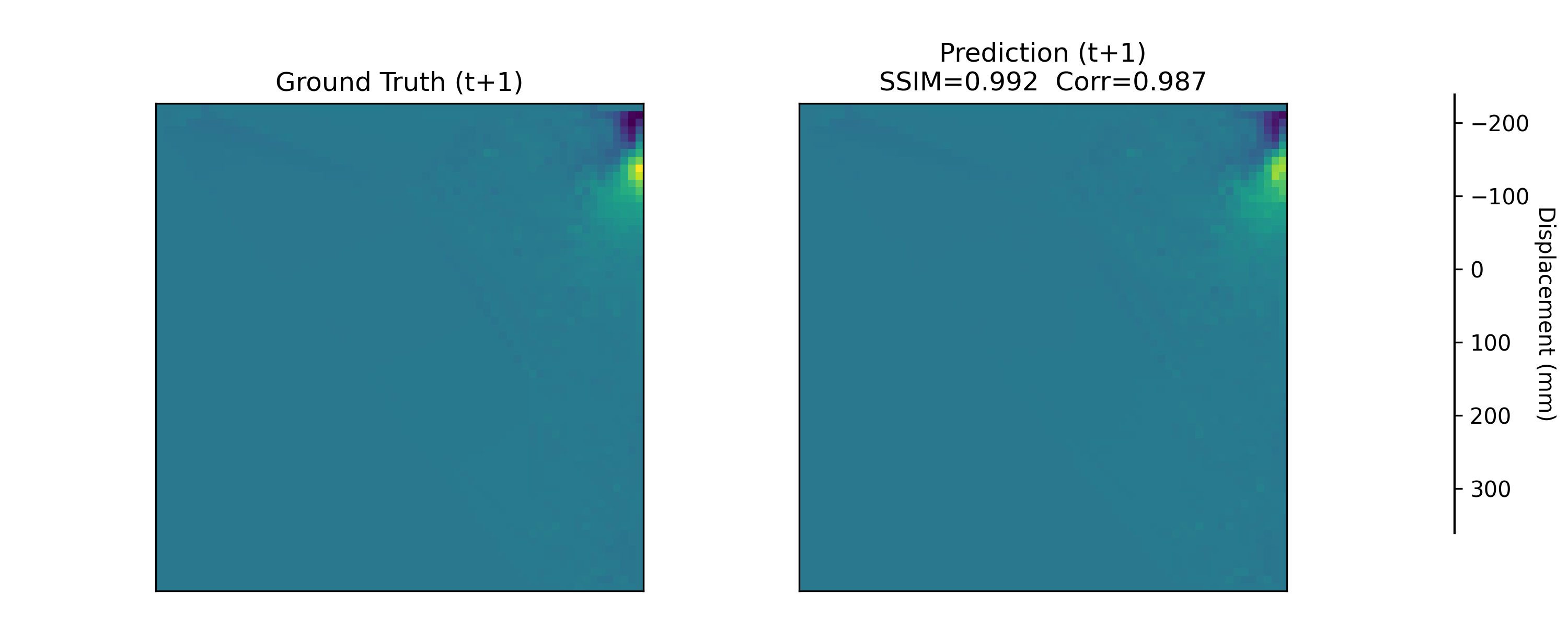
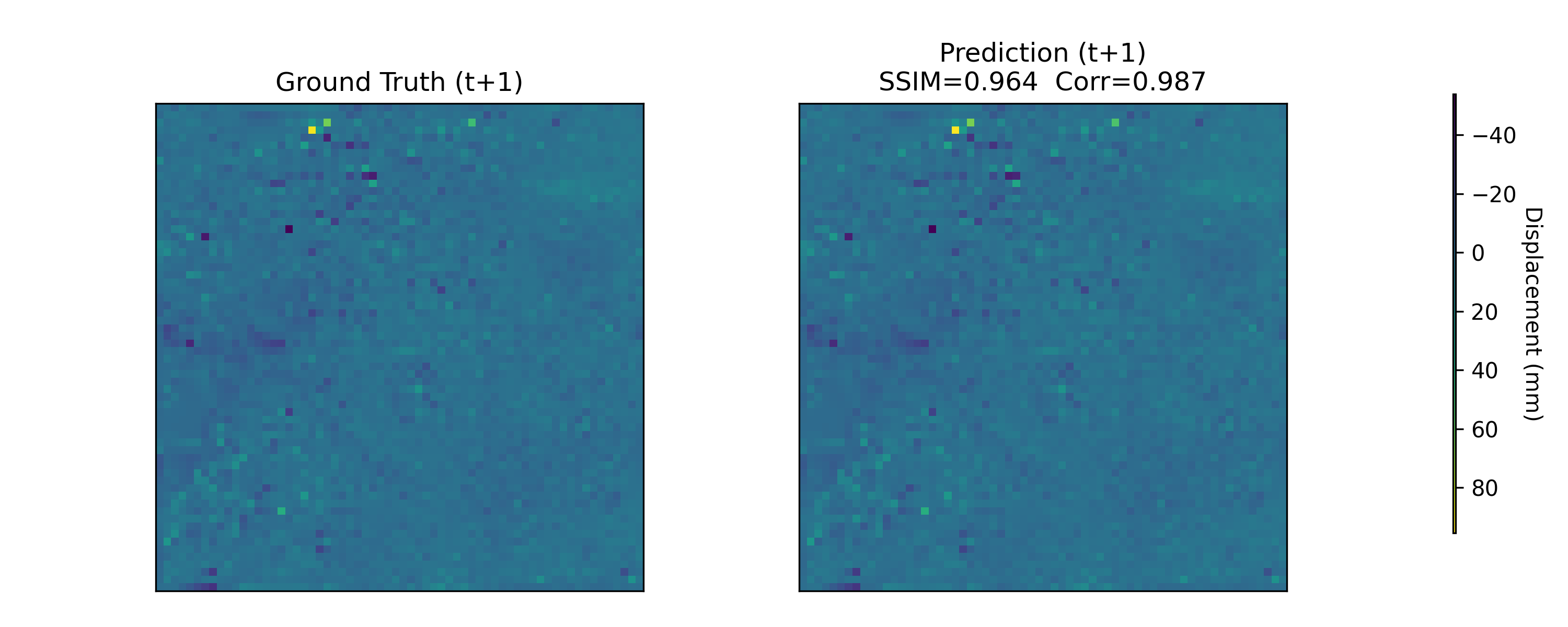
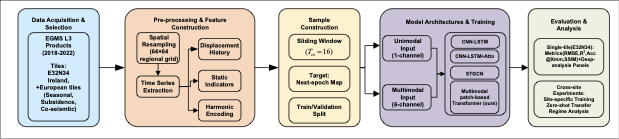
Near-real-time regional-scale monitoring of ground deformation is increasingly required to support urban planning, critical infrastructure management, and natural hazard mitigation. While Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) and continental-scale services such as the European Ground Motion Service (EGMS) provide dense observations of past motion, predicting the next observation remains challenging due to the superposition of long-term trends, seasonal cycles, and occasional abrupt discontinuities (e.g., co-seismic steps), together with strong spatial heterogeneity. In this study we propose a multimodal patch-based Transformer for single-step, fixed-interval next-epoch nowcasting of displacement maps from EGMS time series (resampled to a 64x64 grid over 100 km x 100 km tiles). The model ingests recent displacement snapshots together with (i) static kinematic indicators (mean velocity, acceleration, seasonal amplitude) computed in a leakage-safe manner from the training window only, and (ii) harmonic day-of-year encodings. On the eastern Ireland tile (E32N34), the STGCN is strongest in the displacement-only setting, whereas the multimodal Transformer clearly outperforms CNN-LSTM, CNN-LSTM+Attn, and multimodal STGCN when all models receive the same multimodal inputs, achieving RMSE = 0.90 mm and $R^2$ = 0.97 on the test set with the best threshold accuracies.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1: Novel Analysis Methodology** - The study introduces a new data analysis method that enhances the rapid processing capabilities of AI algorithms. This can be likened to plants growing with more food: as more data is fed, the system grows and becomes more efficient. 2. **Contribution 2: Improved Accuracy** - The team developed an algorithm that increases prediction accuracy compared to existing methods. Similar to how a GPS pinpoints location within smaller error ranges, this model provides more precise traffic predictions. 3. **Contribution 3: Versatility and Flexibility** - The study evaluates the performance of their models across various datasets. This is akin to how cars navigate different road networks: regardless of conditions, our model offers necessary information for efficient pathfinding.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)