MeLeMaD Meta Learning for Malware Detection
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: MeLeMaD Adaptive Malware Detection via Chunk-wise Feature Selection and Meta-Learning- ArXiv ID: 2512.23987
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Ajvad Haneef K, Karan Kuwar Singh, Madhu Kumar S D
📝 Abstract
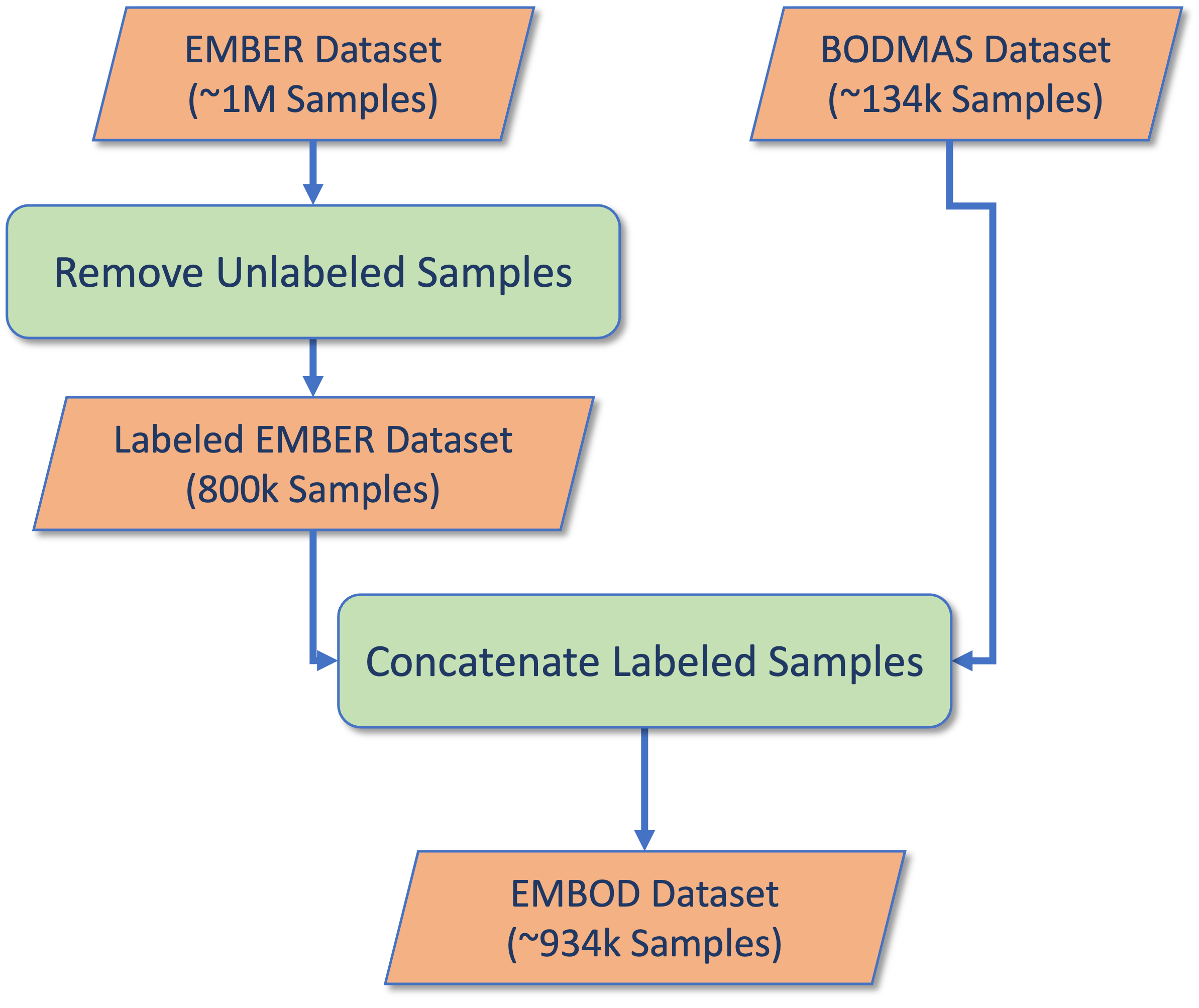
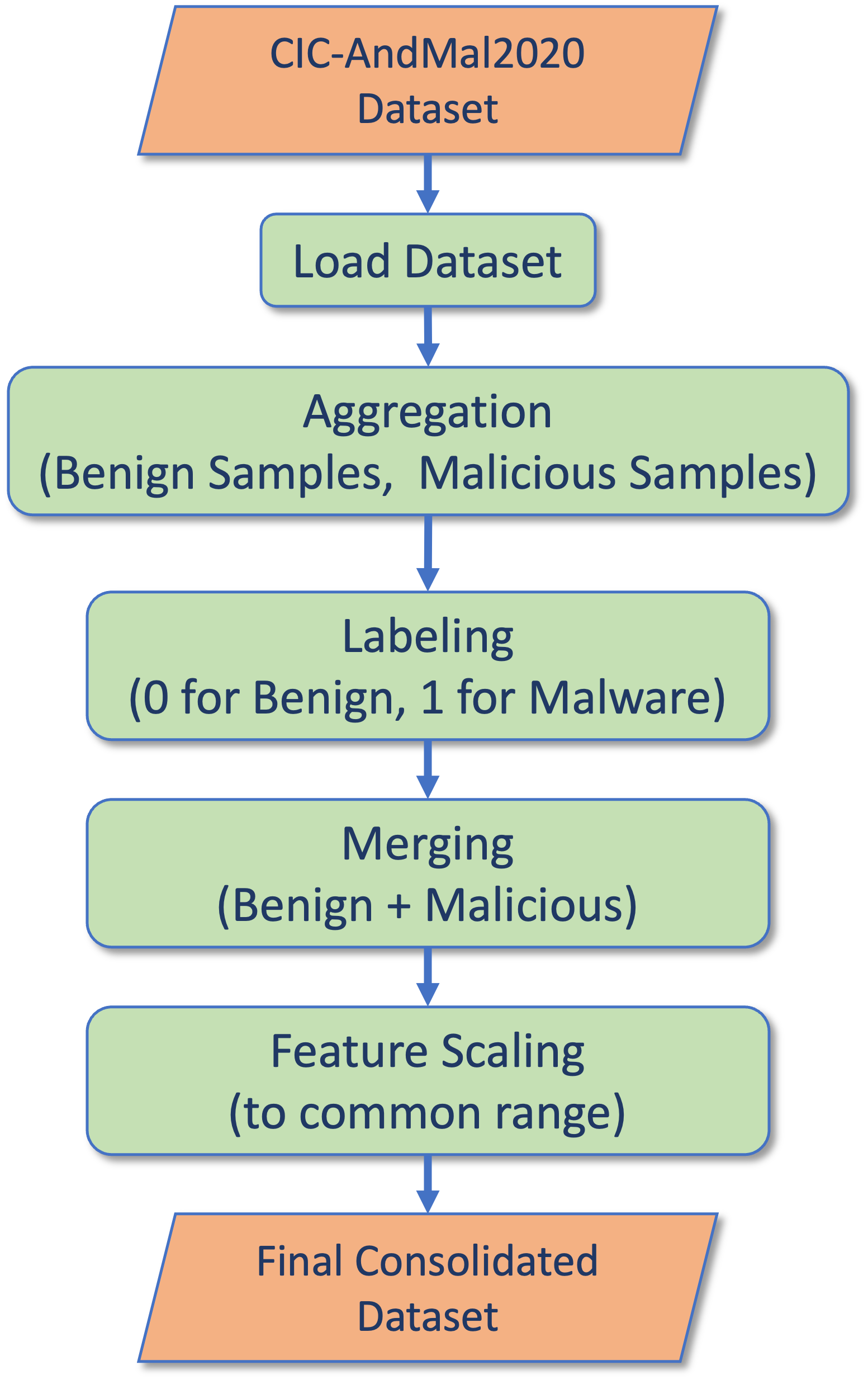
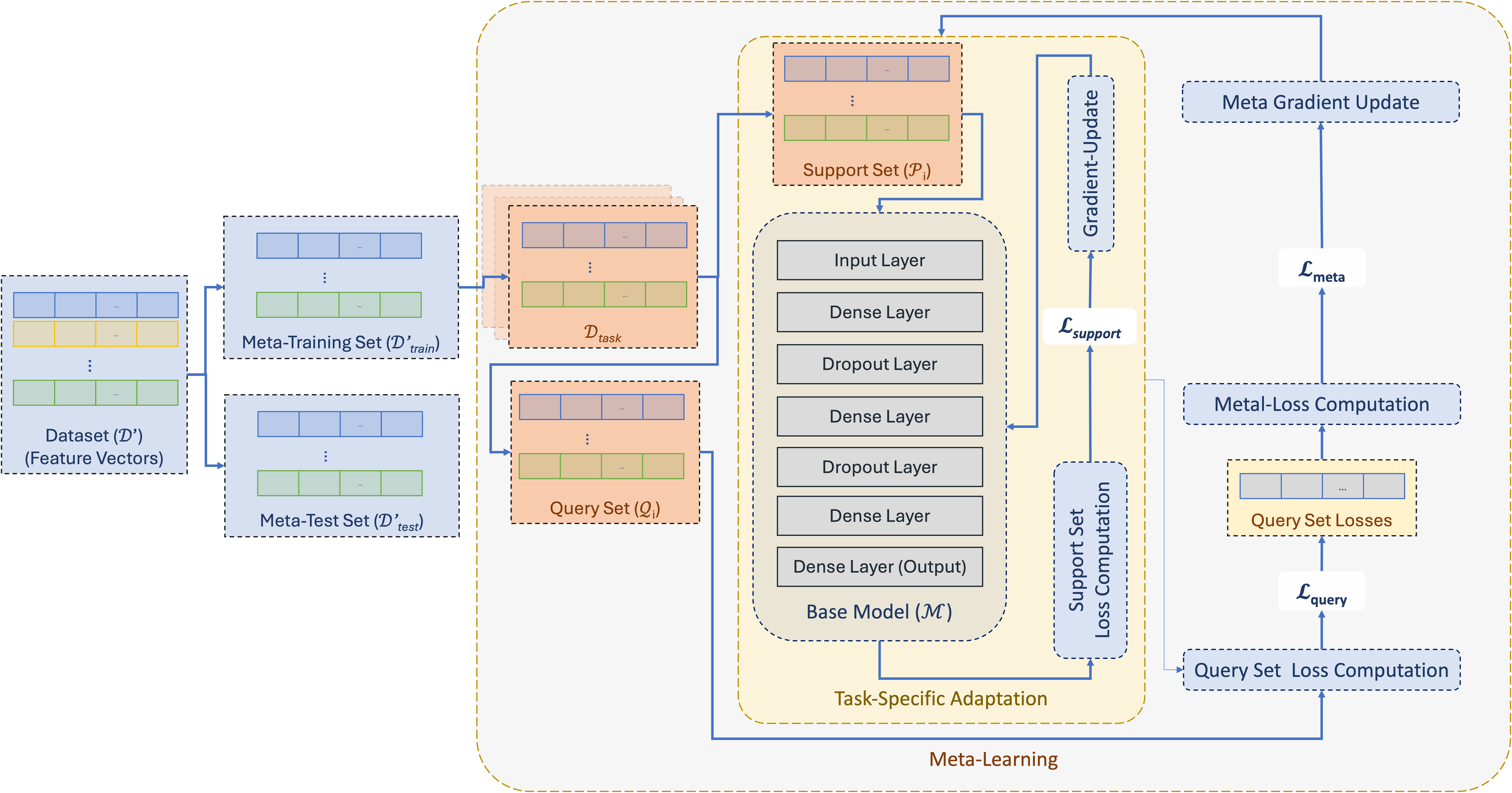
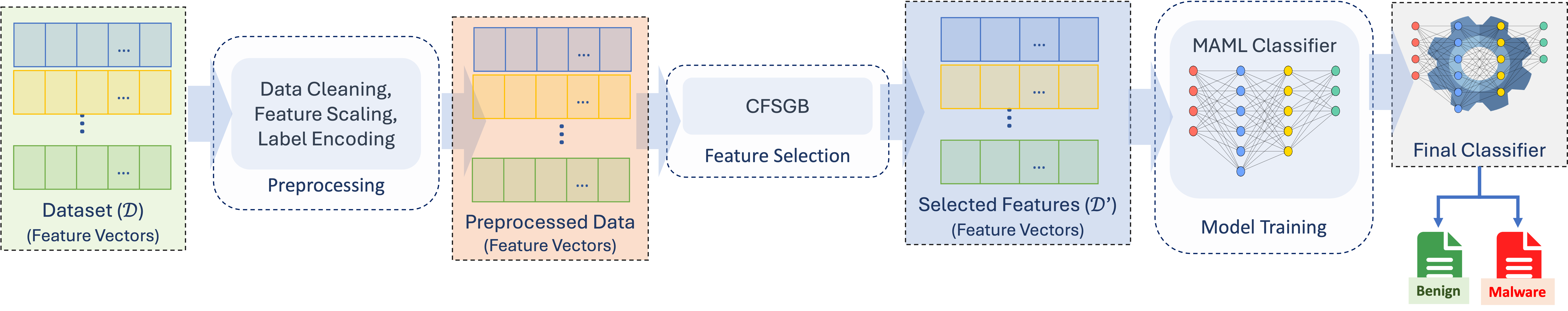
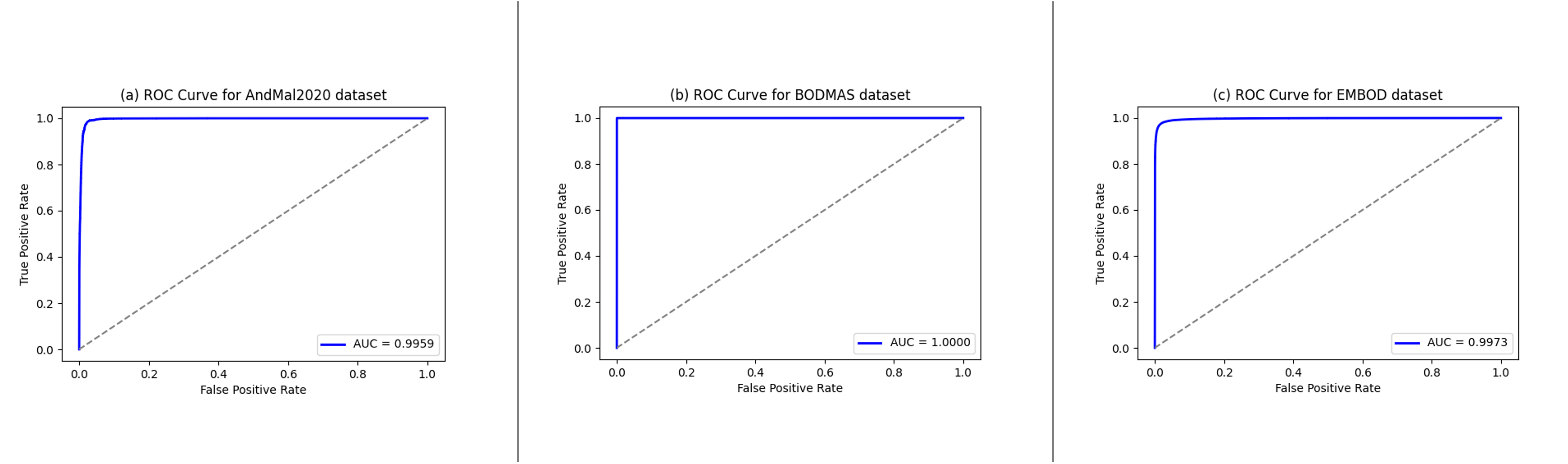
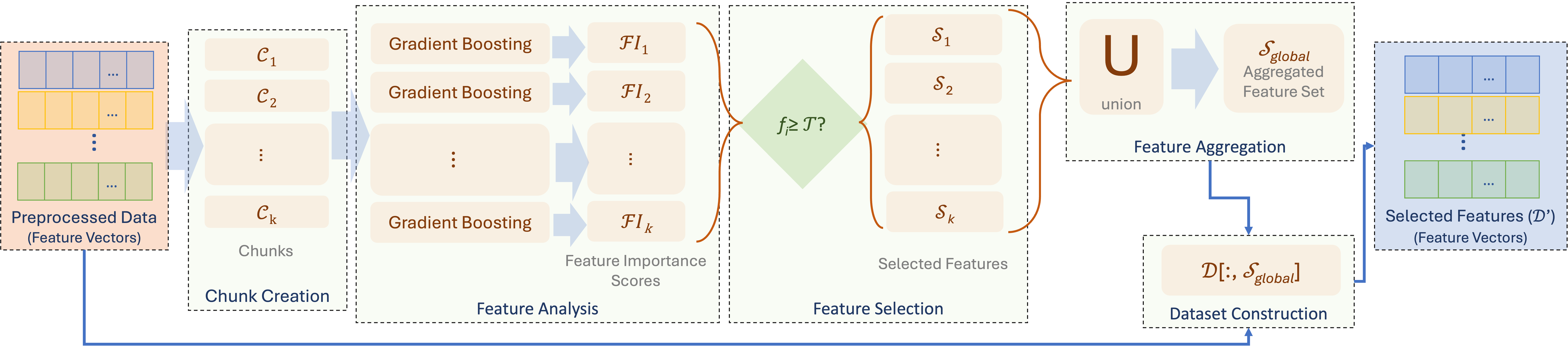
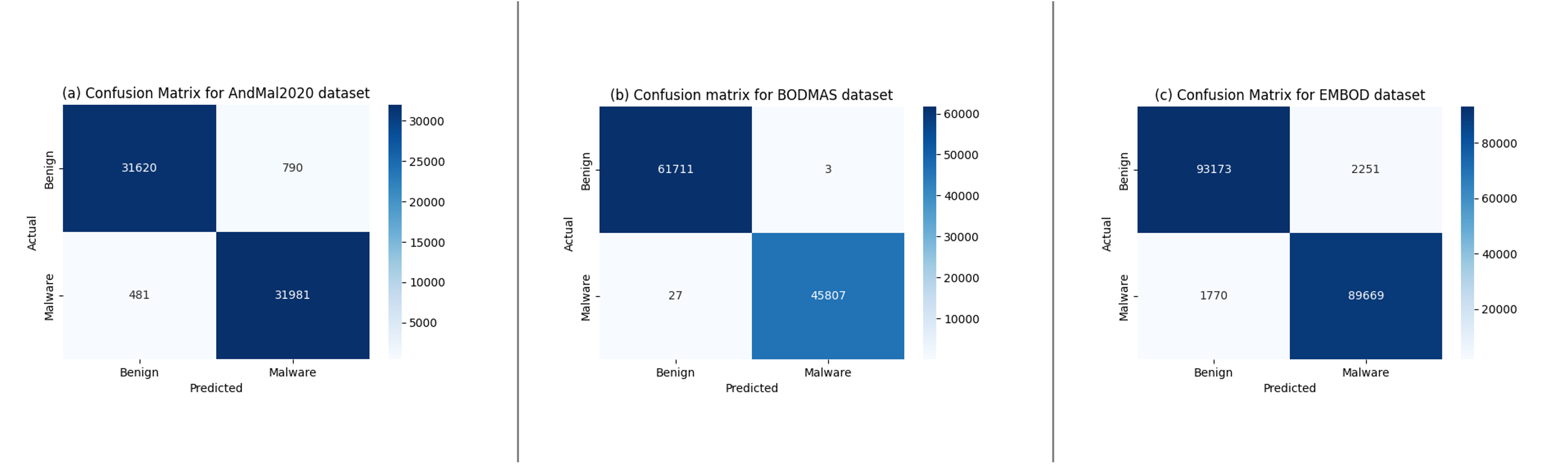
Confronting the substantial challenges of malware detection in cybersecurity necessitates solutions that are both robust and adaptable to the ever-evolving threat environment. The paper introduces Meta Learning Malware Detection (MeLeMaD), a novel framework leveraging the adaptability and generalization capabilities of Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) for malware detection. MeLeMaD incorporates a novel feature selection technique, Chunk-wise Feature Selection based on Gradient Boosting (CFSGB), tailored for handling large-scale, high-dimensional malware datasets, significantly enhancing the detection efficiency. Two benchmark malware datasets (CIC-AndMal2020 and BODMAS) and a custom dataset (EMBOD) were used for rigorously validating the MeLeMaD, achieving a remarkable performance in terms of key evaluation measures, including accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, MCC, and AUC. With accuracies of 98.04\% on CIC-AndMal2020 and 99.97\% on BODMAS, MeLeMaD outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches. The custom dataset, EMBOD, also achieves a commendable accuracy of 97.85\%. The results underscore the MeLeMaD's potential to address the challenges of robustness, adaptability, and large-scale, high-dimensional datasets in malware detection, paving the way for more effective and efficient cybersecurity solutions.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1: New Data Analysis Method** - **Simple Explanation:** The study uses a statistical analysis of survey results to understand the relationship between social media usage and mental health, akin to analyzing the nutritional content of food ingredients.-
Contribution 2: Age Group Differences
- Simple Explanation: Surveys were conducted across different age groups to determine how social media impacts mental health differently for each group, similar to understanding that dietary needs vary with age.
-
Contribution 3: Negative Effects of Excessive Use
- Simple Explanation: The study found that excessive use of social media can exacerbate symptoms of depression and anxiety, much like overusing a smartphone could harm eye health.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)