Zero-Shot Agent Alignment through Automated Reflective Debugging
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: ROAD Reflective Optimization via Automated Debugging for Zero-Shot Agent Alignment- ArXiv ID: 2512.24040
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Natchaya Temyingyong, Daman Jain, Neeraj Kumarsahu, Prabhat Kumar, Rachata Phondi, Wachiravit Modecrua, Krittanon Kaewtawee, Krittin Pachtrachai, Touchapon Kraisingkorn
📝 Abstract
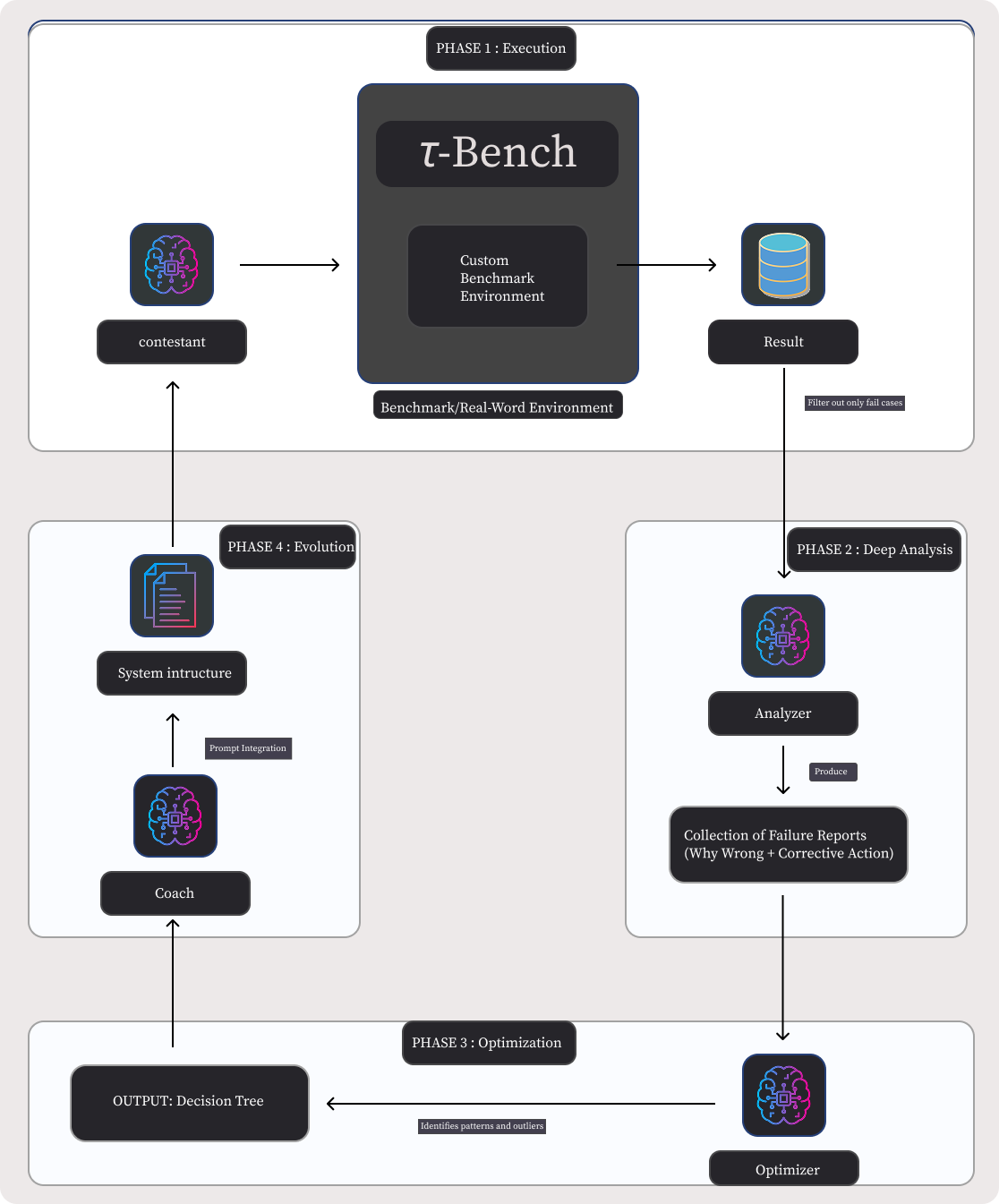
Automatic Prompt Optimization (APO) has emerged as a critical technique for enhancing Large Language Model (LLM) performance, yet current state-of-the-art methods typically rely on large, labeled gold-standard development sets to compute fitness scores for evolutionary or Reinforcement Learning (RL) approaches. In real-world software engineering, however, such curated datasets are rarely available during the initial cold start of agent development, where engineers instead face messy production logs and evolving failure modes. We present ROAD (Reflective Optimization via Automated Debugging), a novel framework that bypasses the need for refined datasets by treating optimization as a dynamic debugging investigation rather than a stochastic search. Unlike traditional mutation strategies, ROAD utilizes a specialized multi-agent architecture, comprising an Analyzer for root-cause analysis, an Optimizer for pattern aggregation, and a Coach for strategy integration, to convert unstructured failure logs into robust, structured Decision Tree Protocols. We evaluated ROAD across both a standardized academic benchmark and a live production Knowledge Management engine. Experimental results demonstrate that ROAD is highly sample-efficient, achieving a 5.6 percent increase in success rate (73.6 percent to 79.2 percent) and a 3.8 percent increase in search accuracy within just three automated iterations. Furthermore, on complex reasoning tasks in the retail domain, ROAD improved agent performance by approximately 19 percent relative to the baseline. These findings suggest that mimicking the human engineering loop of failure analysis and patching offers a viable, data-efficient alternative to resource-intensive RL training for deploying reliable LLM agents.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Deep Neural Networks:** Mimicking the human brain's structure for pattern recognition. 2. **Reinforcement Learning:** An agent learns to make decisions by interacting with its environment, finding optimal action paths through trial and error. 3. **Ensemble Methods:** Combining multiple models to improve predictive performance, similar to a group of experts reaching consensus.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)