Enhancing Ocular Disease Diagnosis with Pathology Context Networks
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Pathology Context Recalibration Network for Ocular Disease Recognition- ArXiv ID: 2512.24066
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Zunjie Xiao, Xiaoqing Zhang, Risa Higashita, Jiang Liu
📝 Abstract
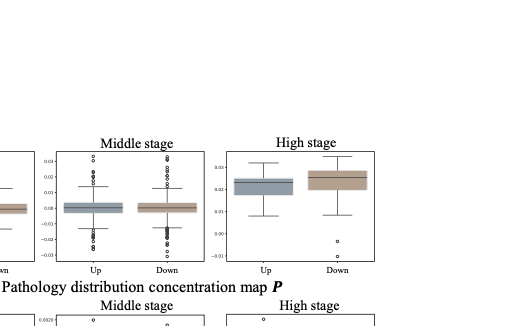
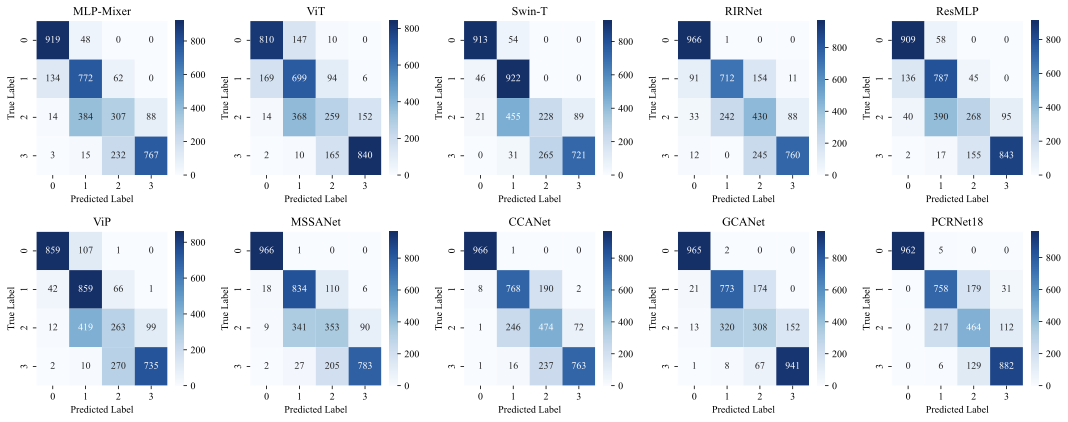
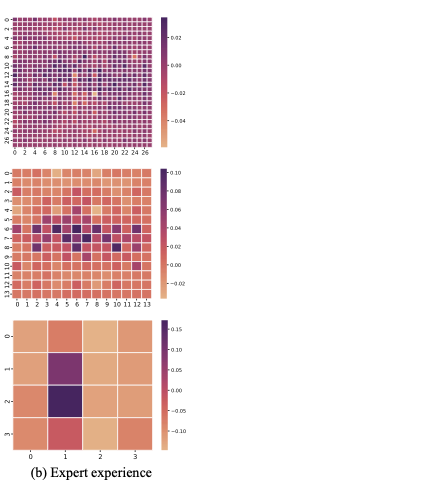
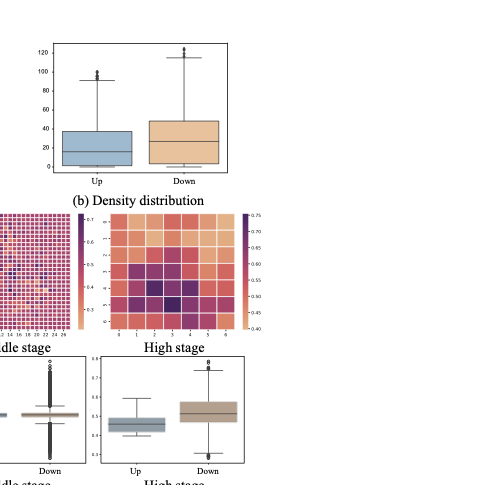
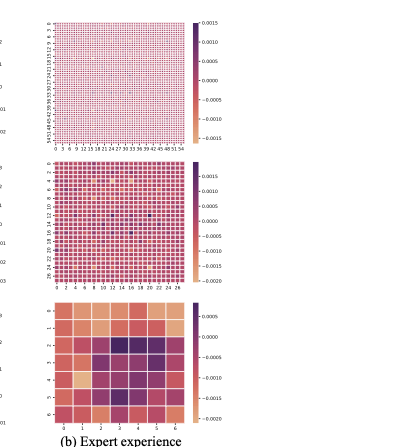
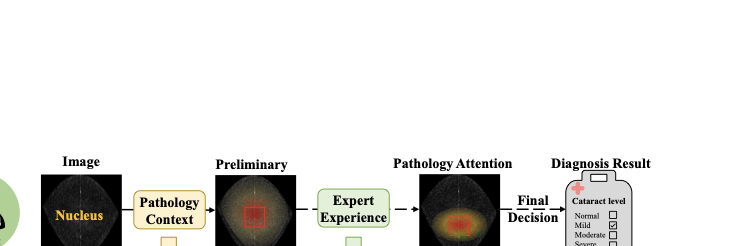
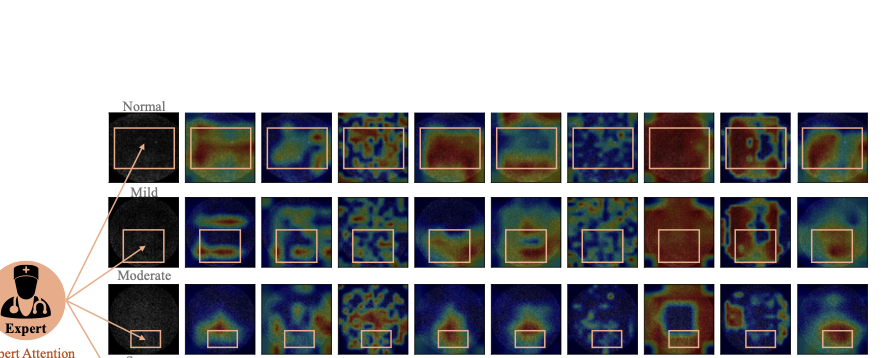
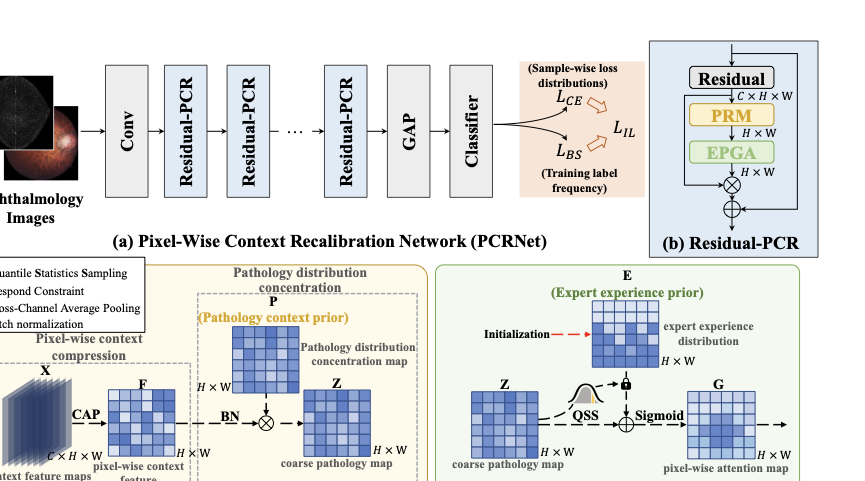
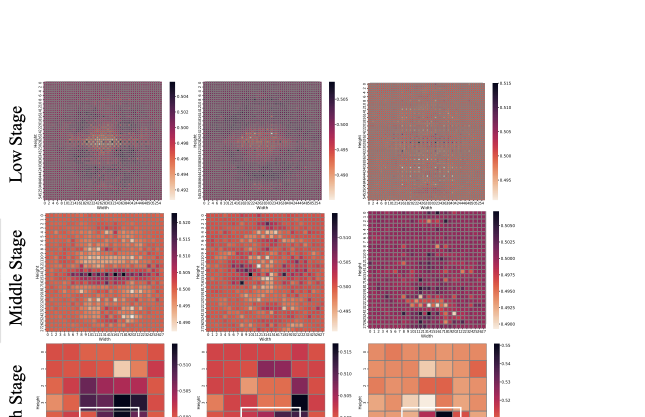
Pathology context and expert experience play significant roles in clinical ocular disease diagnosis. Although deep neural networks (DNNs) have good ocular disease recognition results, they often ignore exploring the clinical pathology context and expert experience priors to improve ocular disease recognition performance and decision-making interpretability. To this end, we first develop a novel Pathology Recalibration Module (PRM) to leverage the potential of pathology context prior via the combination of the well-designed pixel-wise context compression operator and pathology distribution concentration operator; then this paper applies a novel expert prior Guidance Adapter (EPGA) to further highlight significant pixel-wise representation regions by fully mining the expert experience prior. By incorporating PRM and EPGA into the modern DNN, the PCRNet is constructed for automated ocular disease recognition. Additionally, we introduce an Integrated Loss (IL) to boost the ocular disease recognition performance of PCRNet by considering the effects of sample-wise loss distributions and training label frequencies. The extensive experiments on three ocular disease datasets demonstrate the superiority of PCRNet with IL over state-of-the-art attention-based networks and advanced loss methods. Further visualization analysis explains the inherent behavior of PRM and EPGA that affects the decision-making process of DNNs.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Performance Variations Across Datasets** - This research evaluates CNN model performance using various datasets to determine which learning method is most effective for specific types of data. It’s like observing how plants grow in different soils. 2. **Efficiency of Transfer Learning** - Demonstrates that transfer learning is efficient when applying a pre-trained model to new datasets, similar to how knowing one language can aid in learning another. 3. **Flexibility of Custom Models** - Custom models designed for specific problems are optimal for unique datasets or special situations, much like cooking with diverse ingredients.These insights help identify critical factors for choosing learning methods and understand the strengths and weaknesses of each model.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)