Random Multiplexing
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Random Multiplexing- ArXiv ID: 2512.24087
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Lei Liu, Yuhao Chi, Shunqi Huang, Zhaoyang Zhang
📝 Abstract
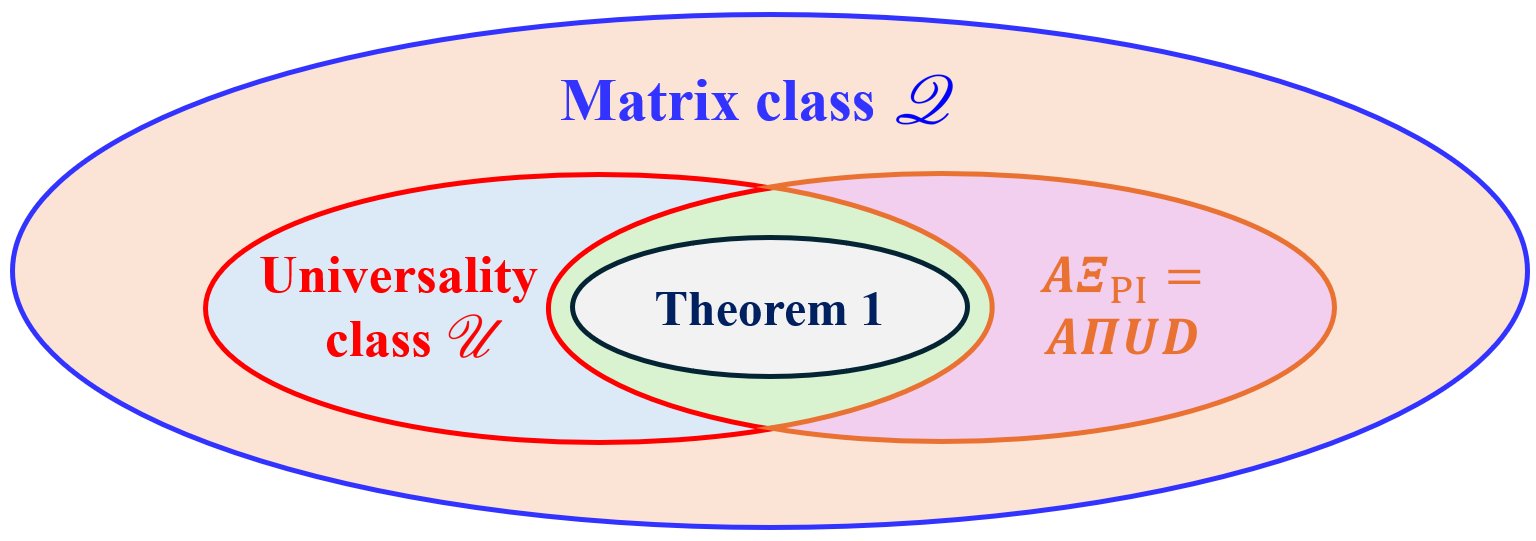
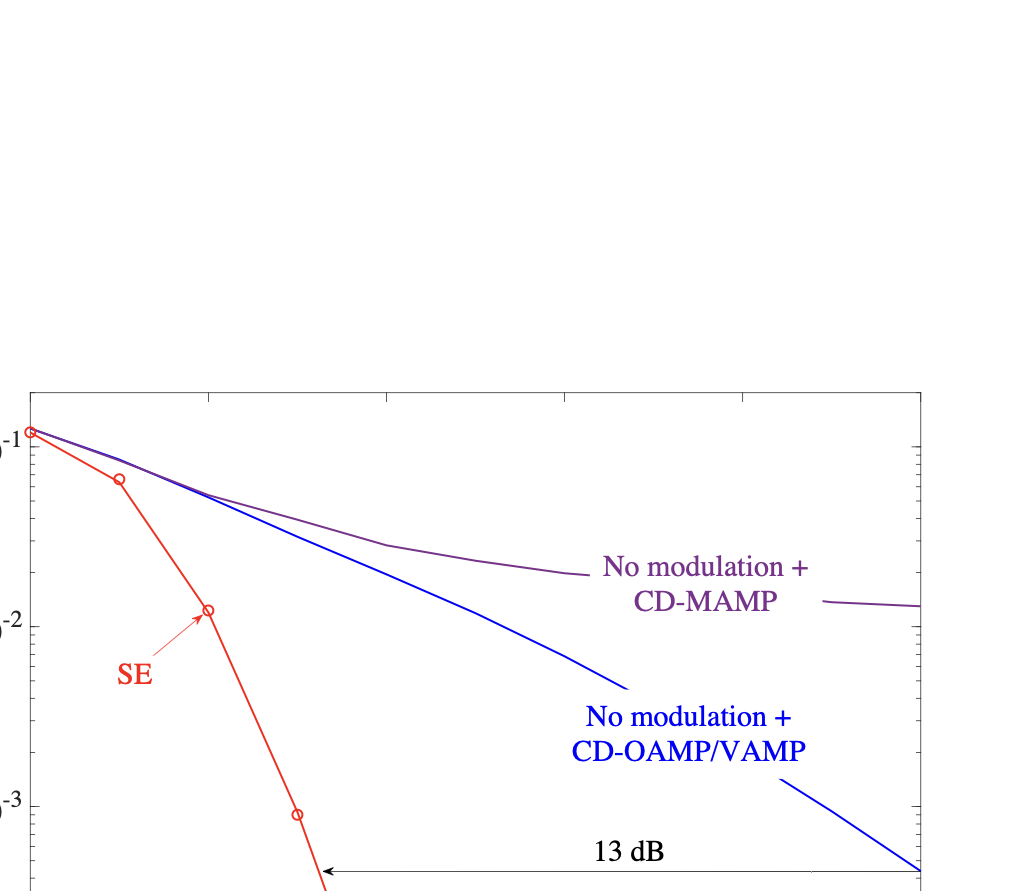
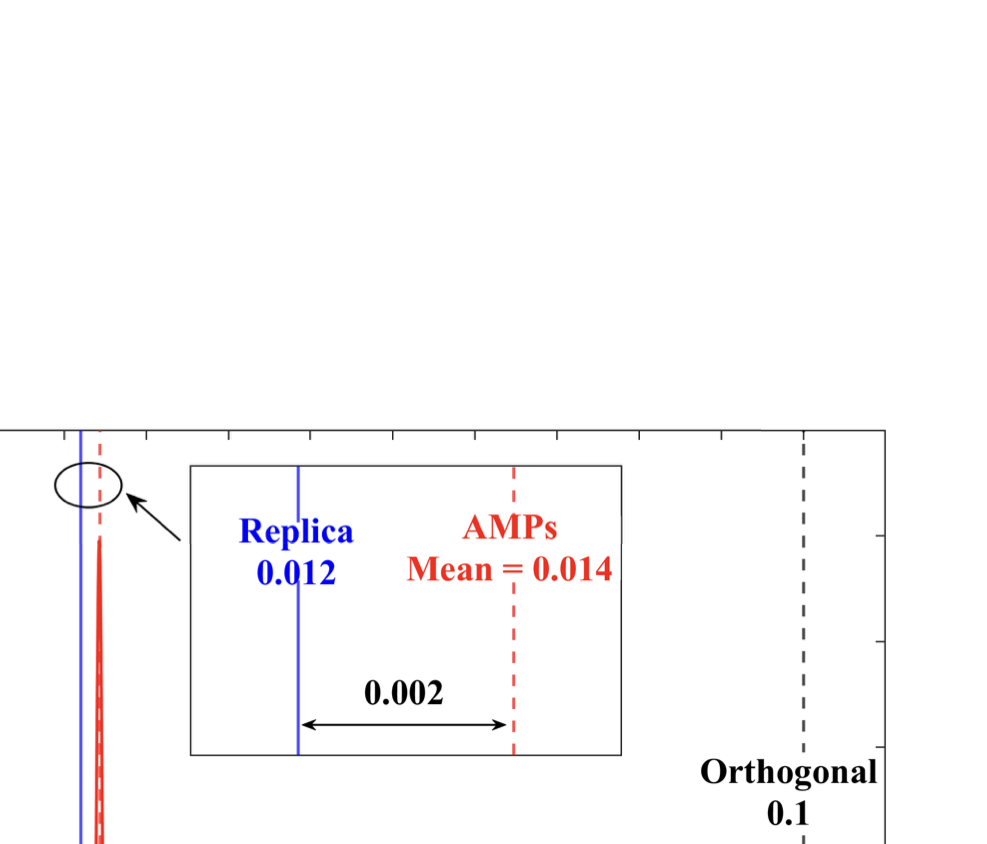
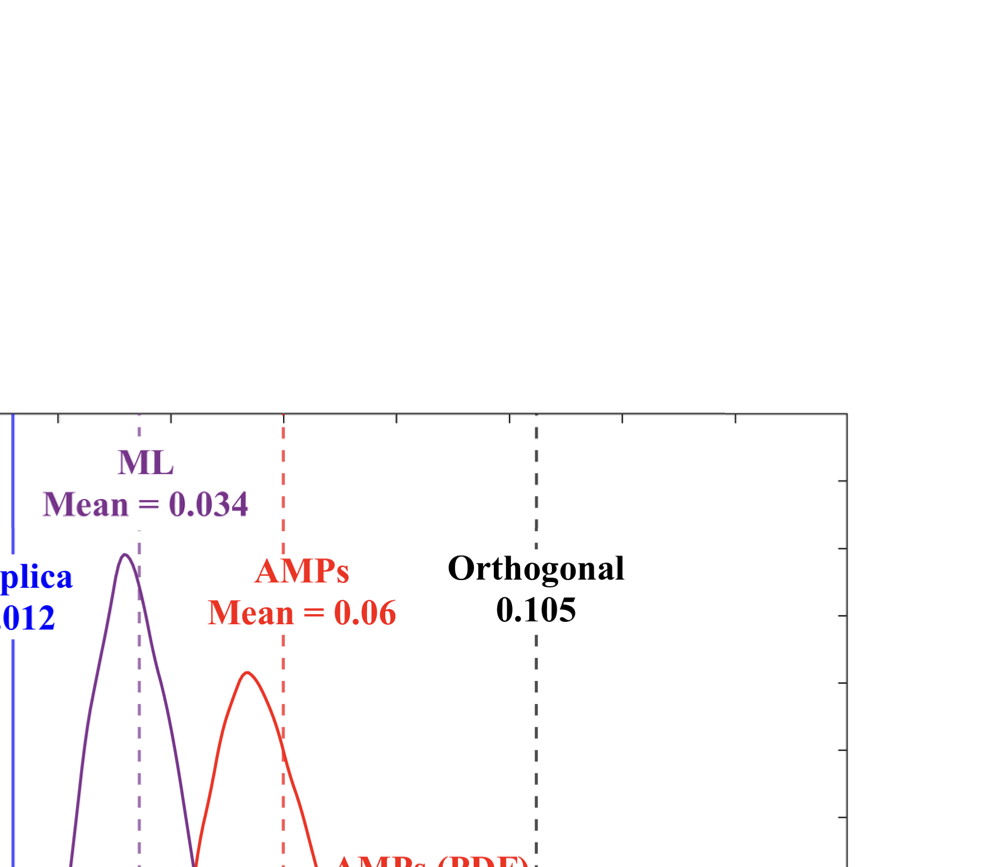
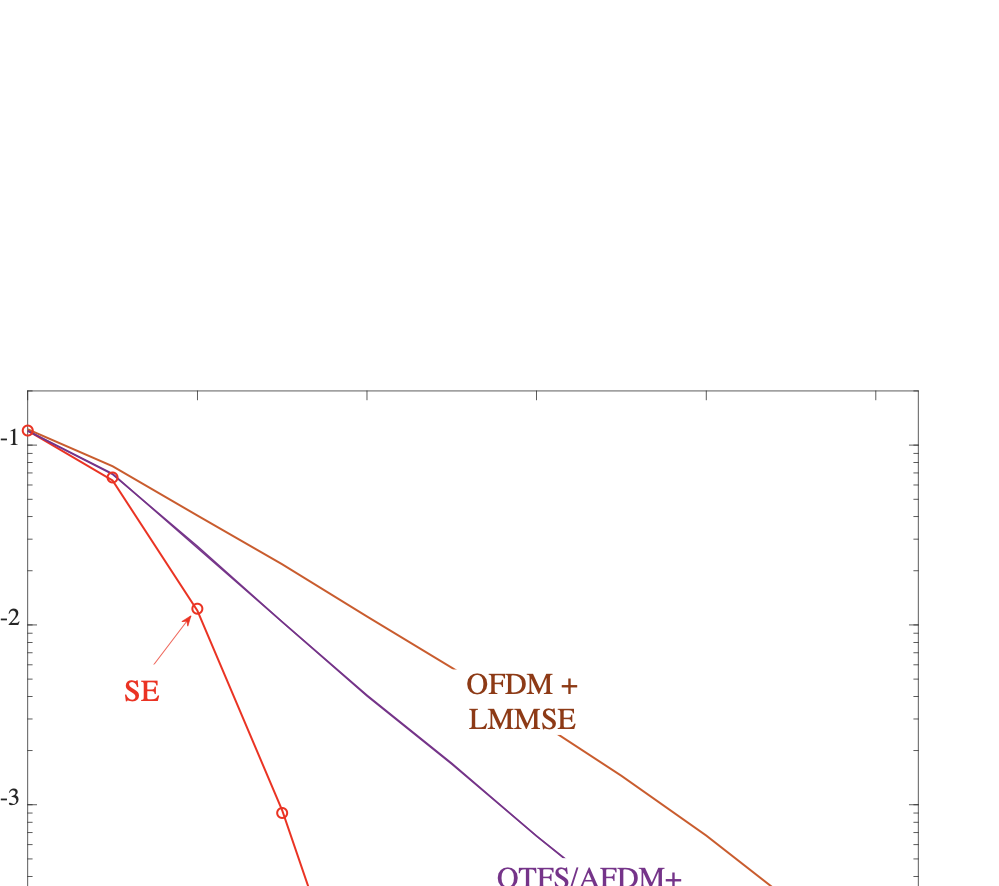
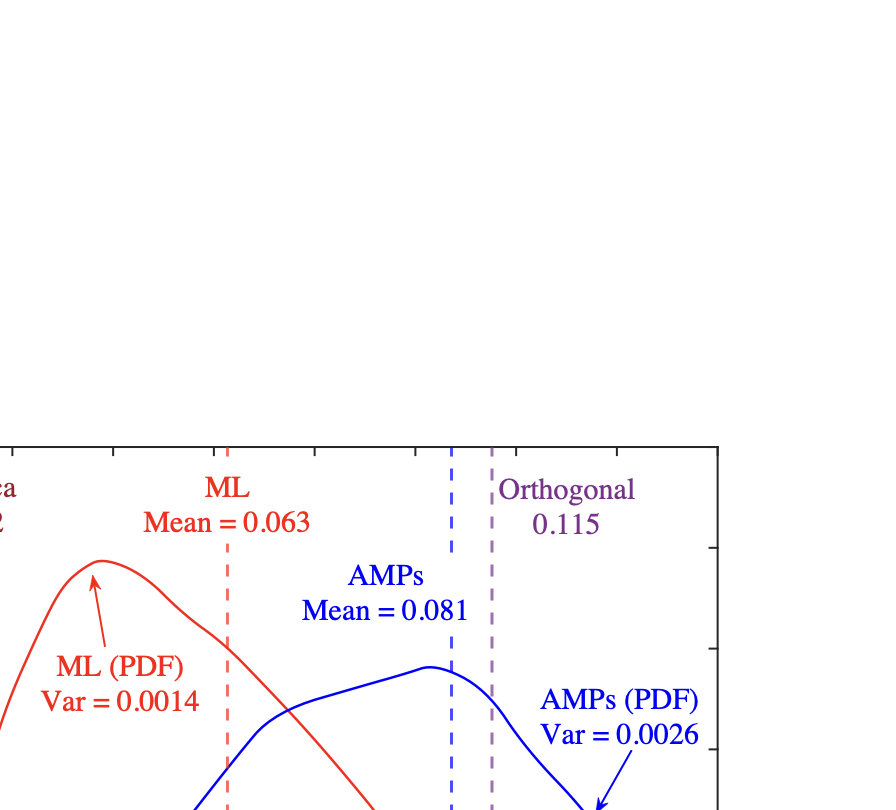
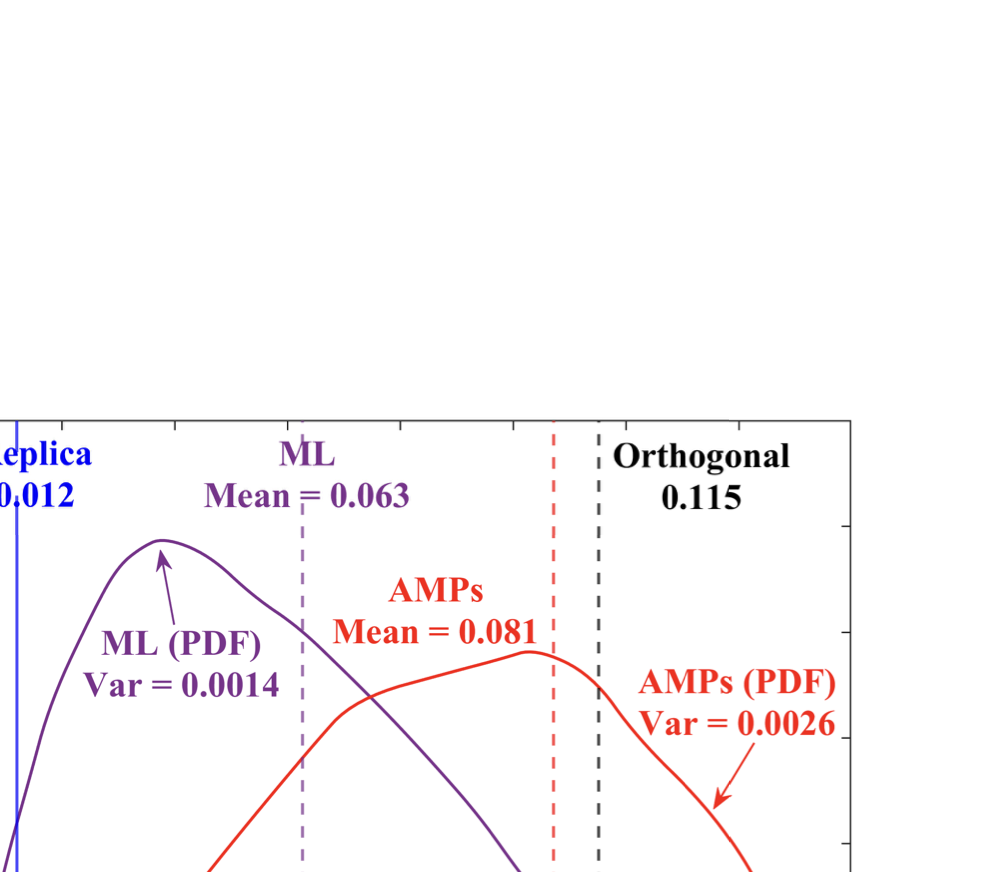
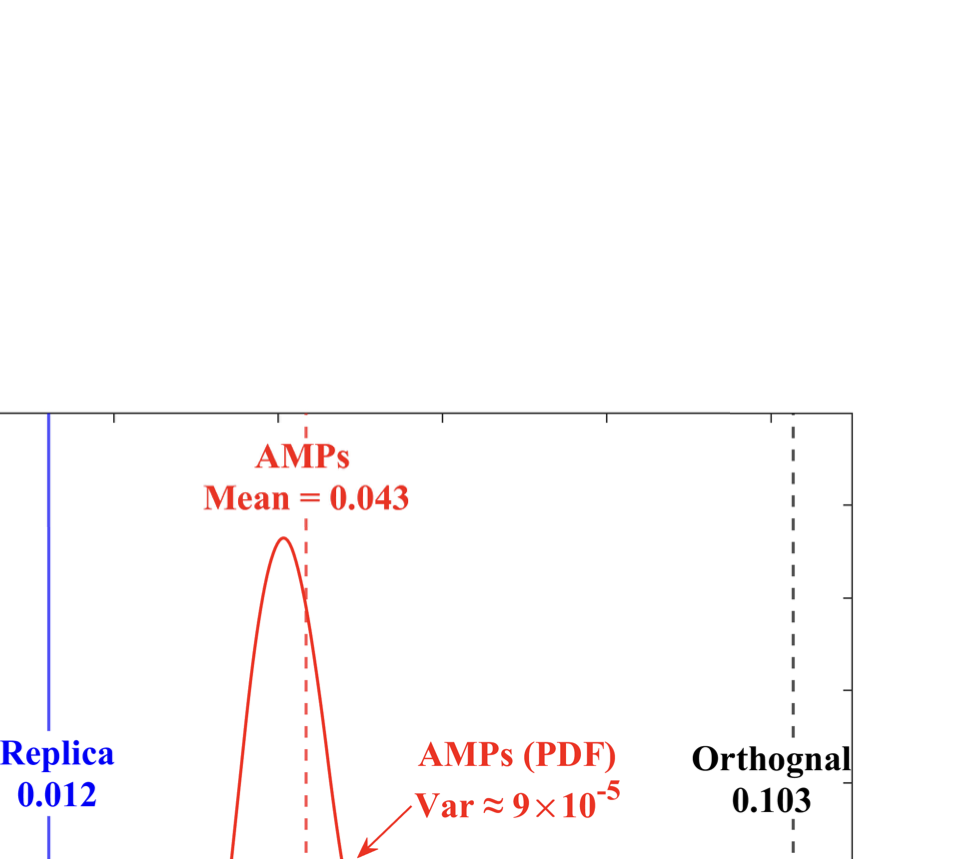
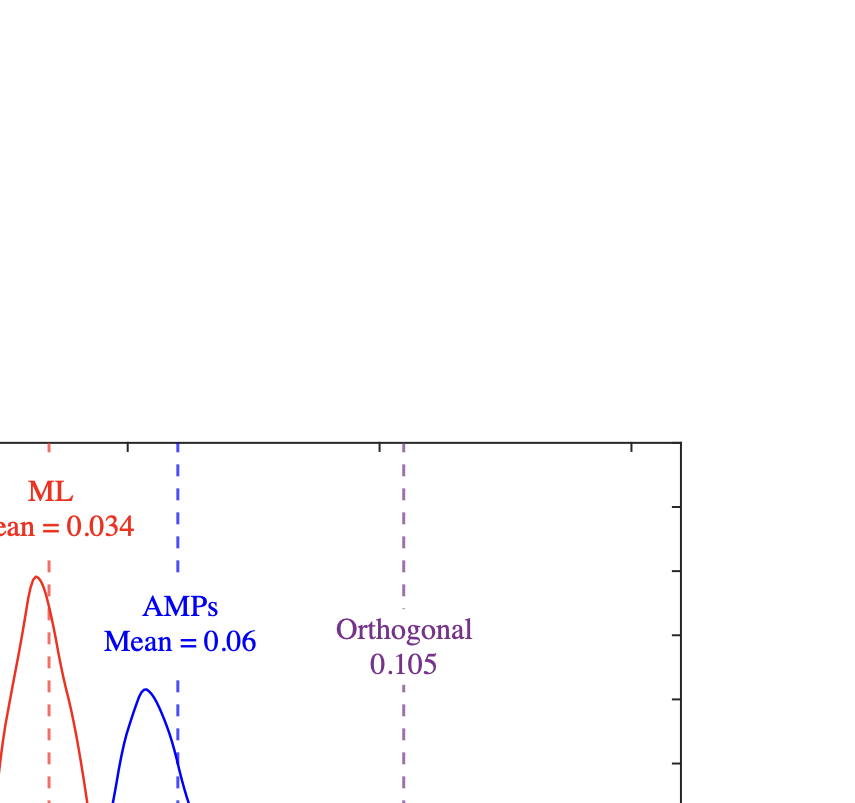
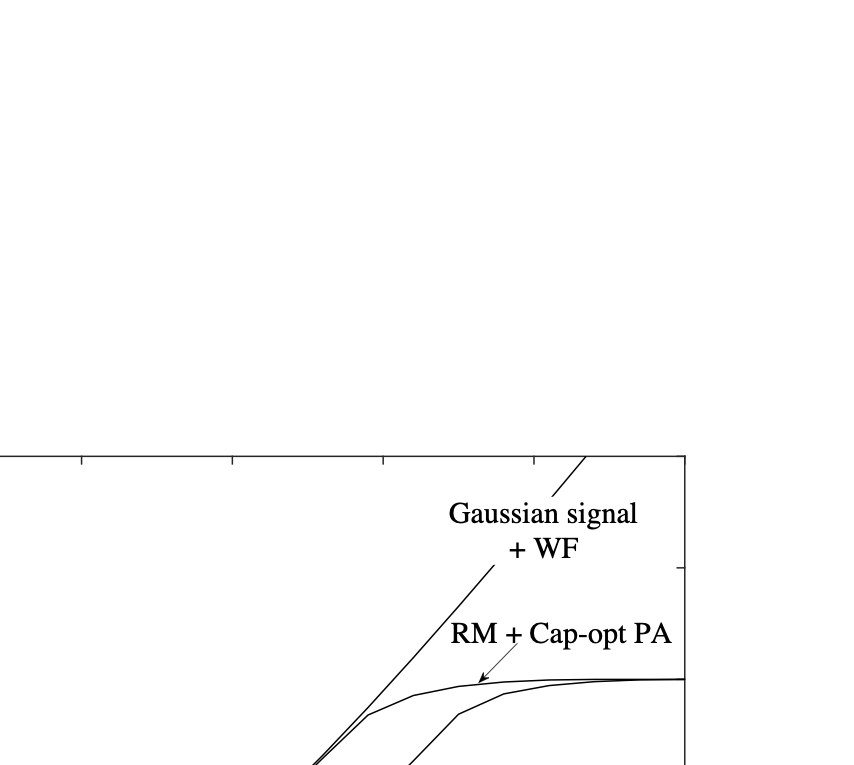
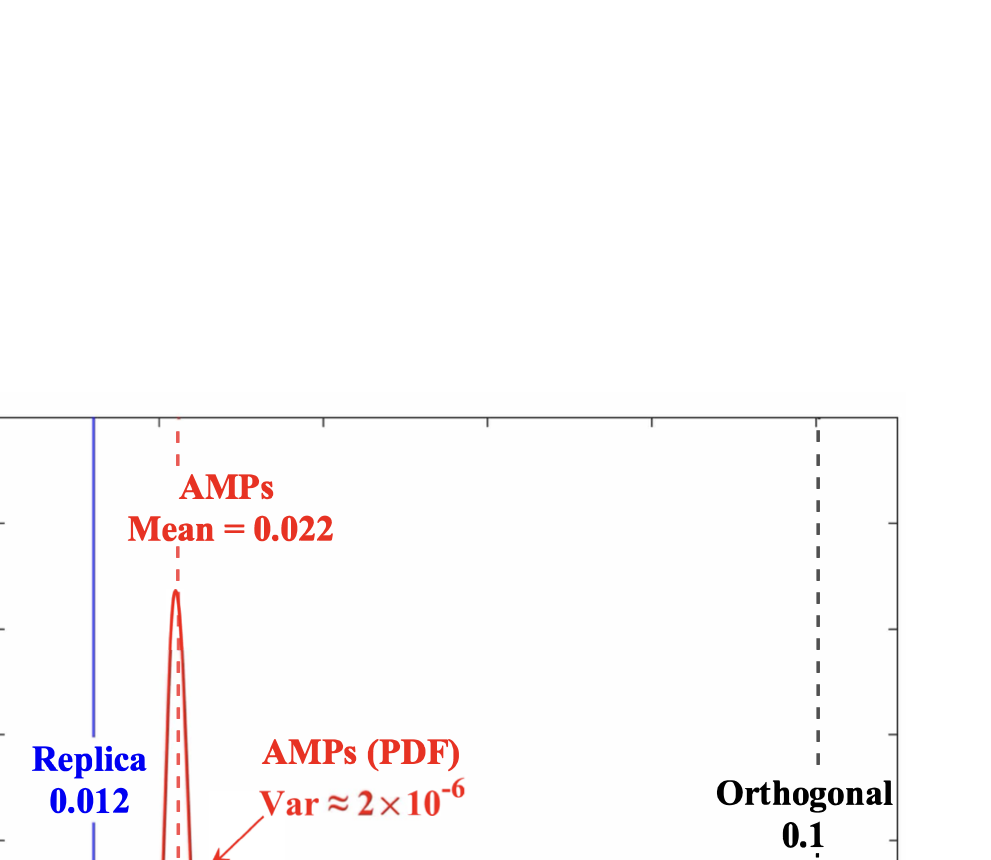
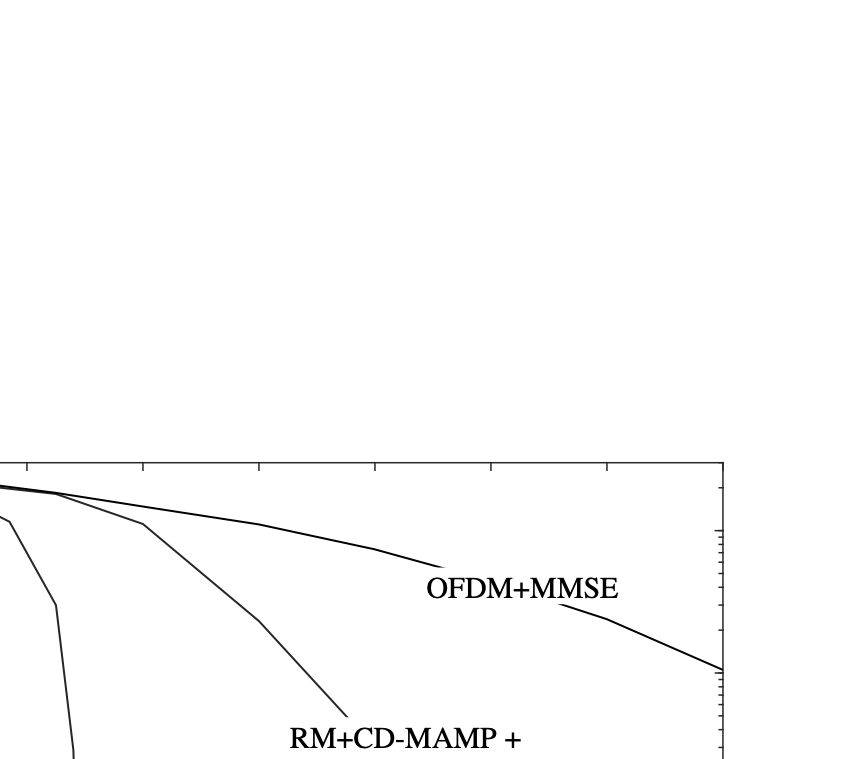
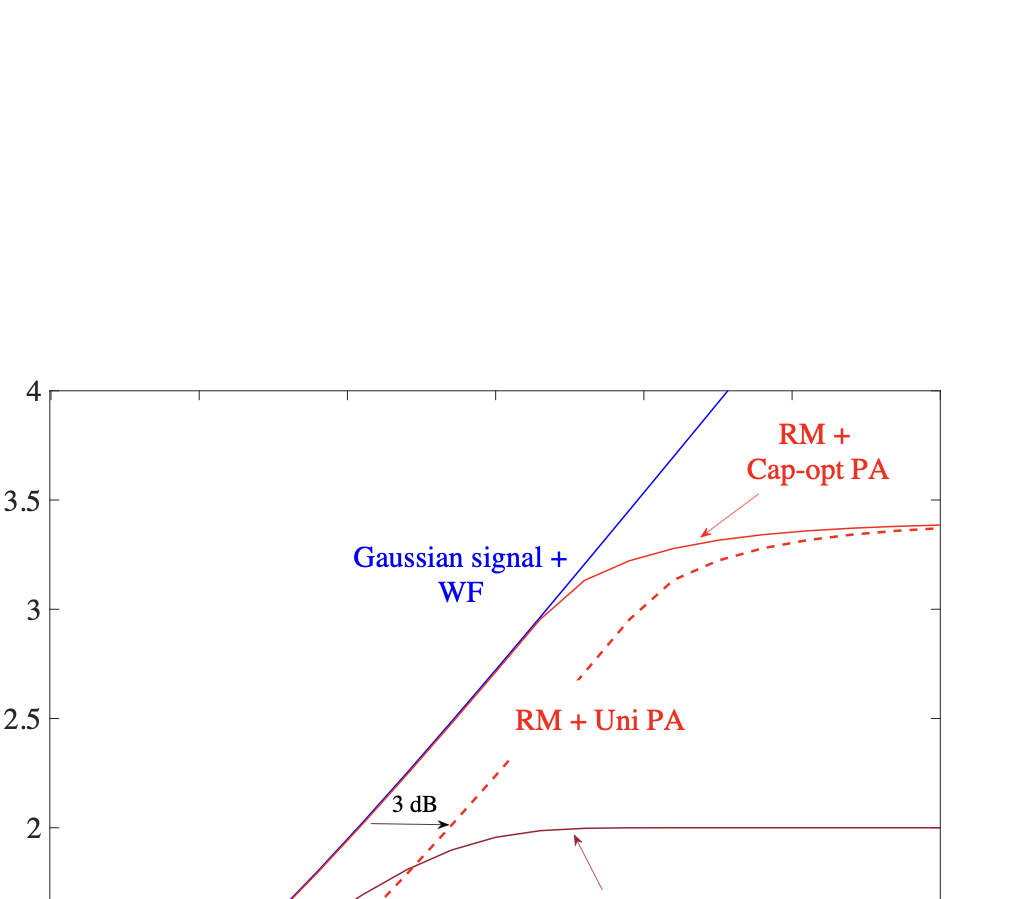
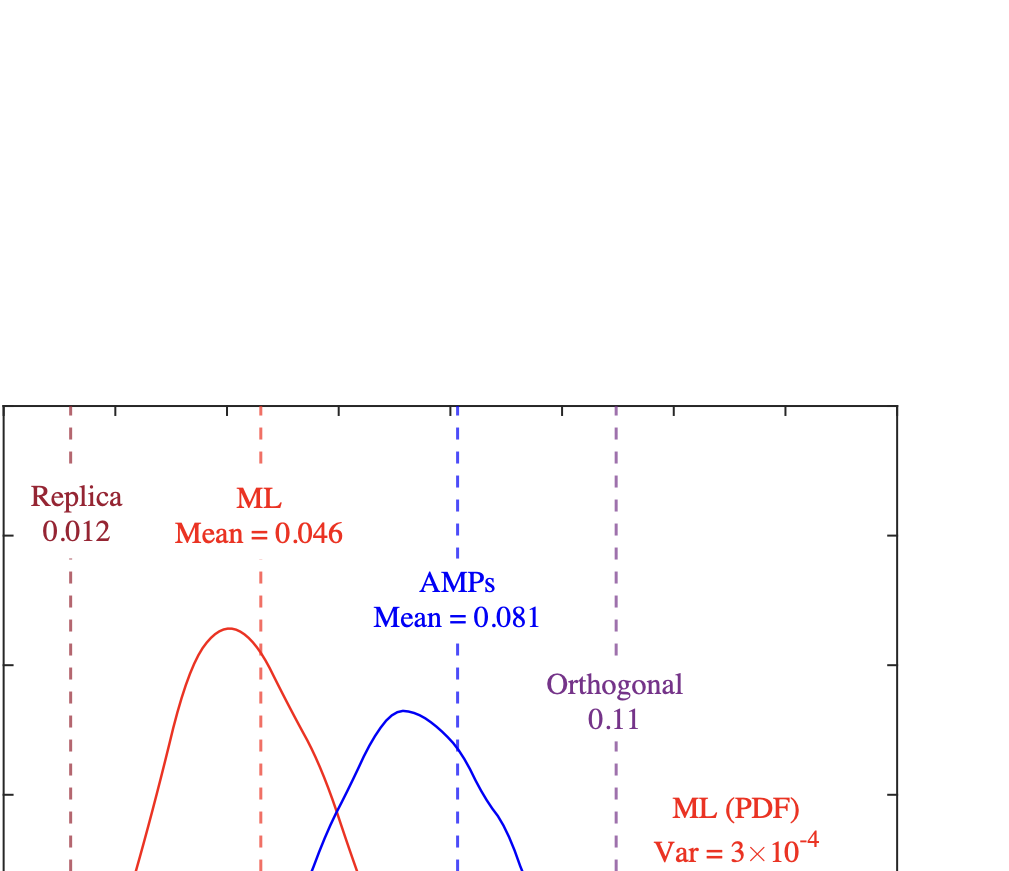
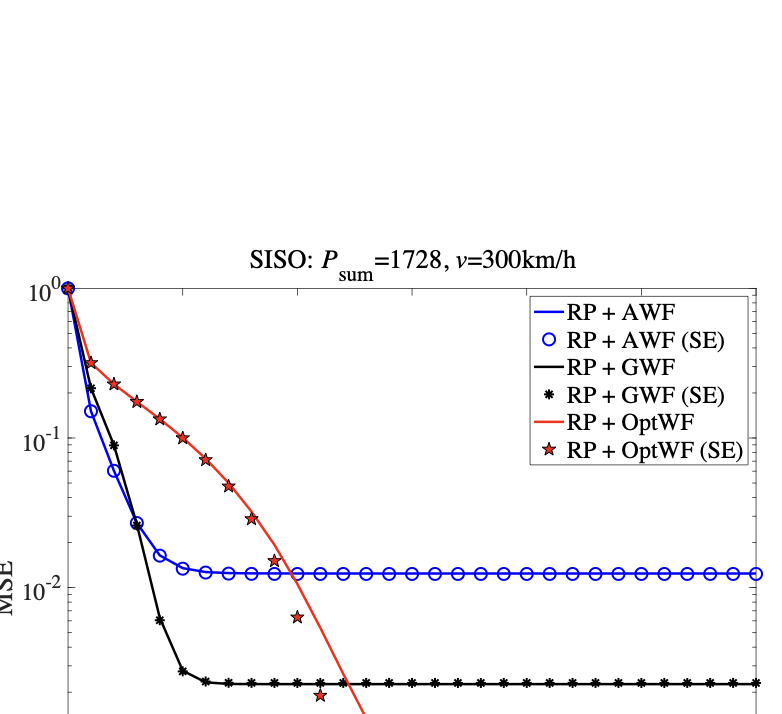
As wireless communication applications evolve from traditional multipath environments to high-mobility scenarios like unmanned aerial vehicles, multiplexing techniques have advanced accordingly. Traditional single-carrier frequency-domain equalization (SC-FDE) and orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) have given way to emerging orthogonal time-frequency space (OTFS) and affine frequency-division multiplexing (AFDM). These approaches exploit specific channel structures to diagonalize or sparsify the effective channel, thereby enabling low-complexity detection. However, their reliance on these structures significantly limits their robustness in dynamic, real-world environments. To address these challenges, this paper studies a random multiplexing technique that is decoupled from the physical channels, enabling its application to arbitrary norm-bounded and spectrally convergent channel matrices. Random multiplexing achieves statistical fading-channel ergodicity for transmitted signals by constructing an equivalent input-isotropic channel matrix in the random transform domain. It guarantees the asymptotic replica MAP bit-error rate (BER) optimality of AMP-type detectors for linear systems with arbitrary norm-bounded, spectrally convergent channel matrices and signaling configurations, under the unique fixed point assumption. A low-complexity cross-domain memory AMP (CD-MAMP) detector is considered, leveraging the sparsity of the time-domain channel and the randomness of the equivalent channel. Optimal power allocations are derived to minimize the replica MAP BER and maximize the replica constrained capacity of random multiplexing systems. The optimal coding principle and replica constrained-capacity optimality of CD-MAMP detector are investigated for random multiplexing systems. Additionally, the versatility of random multiplexing in diverse wireless applications is explored.💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper appears to have been co-authored by researchers in the field of multi-modal communication networks and intelligent information processing. Notably, Lei Liu is affiliated with two institutions, indicating his involvement across multiple research environments. Zhaoyang Zhang and Yuhao Chi share affiliation with the State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks, while Shunqi Huang is part of Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology’s School of Information Science. This suggests that this research was conducted through international collaboration.Additionally, the authors are committed to sharing their work transparently by publicly releasing their source code on GitHub. This practice emphasizes an open culture within academia for knowledge sharing, which can facilitate further studies based on their results by other researchers.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)