Temporal Precision Unlocking Event-Level Video-Text Synchronization
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Factorized Learning for Temporally Grounded Video-Language Models- ArXiv ID: 2512.24097
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Wenzheng Zeng, Difei Gao, Mike Zheng Shou, Hwee Tou Ng
📝 Abstract
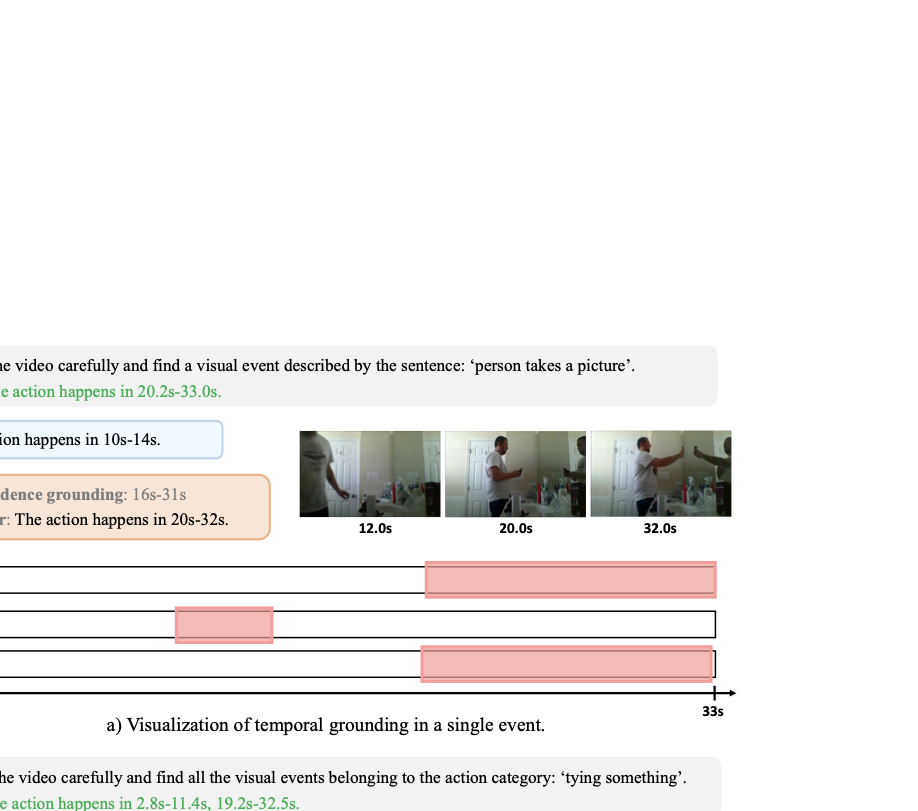
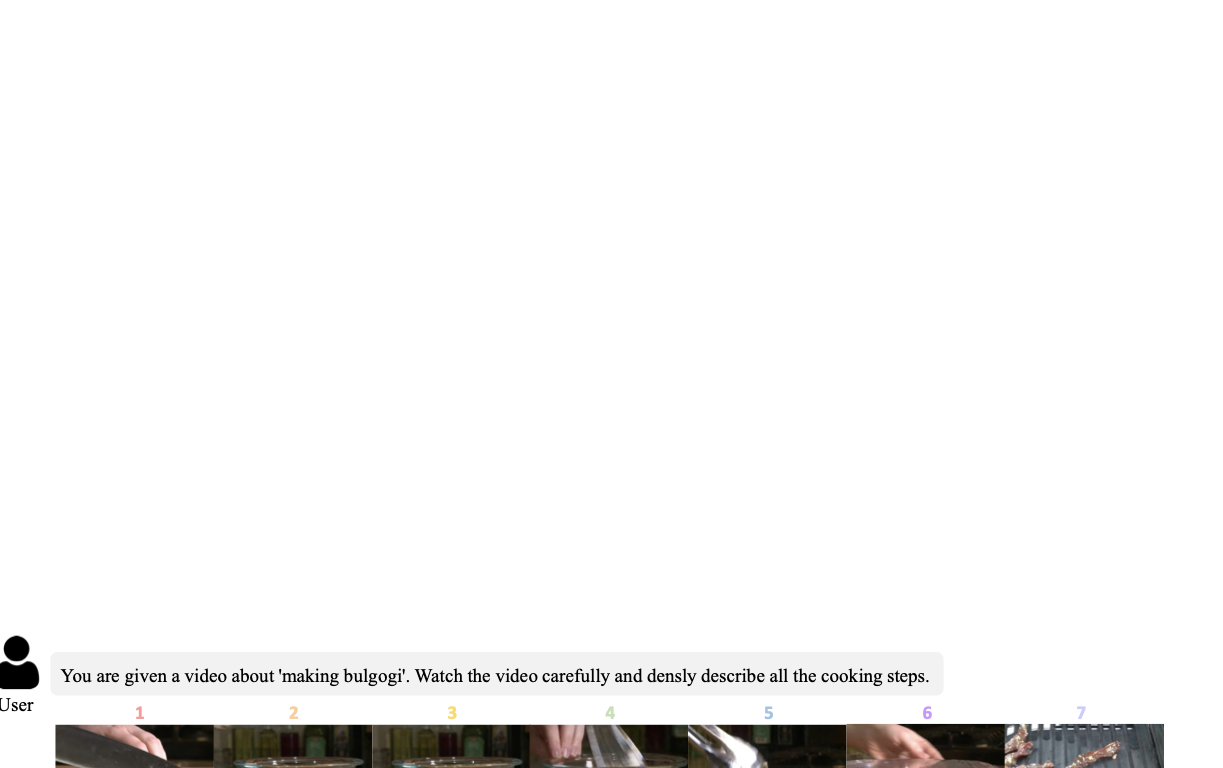
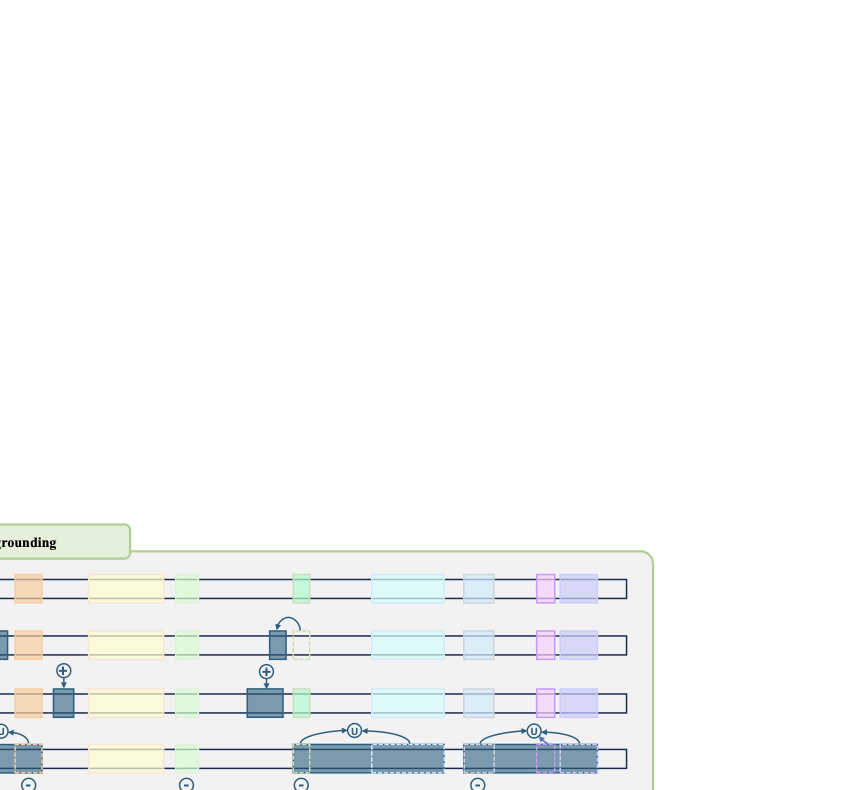
Recent video-language models have shown great potential for video understanding, but still struggle with accurate temporal grounding for event-level perception. We observe that two main factors in video understanding (i.e., temporal grounding and textual response) form a logical hierarchy: accurate temporal evidence grounding lays the foundation for reliable textual response. However, existing works typically handle these two tasks in a coupled manner without a clear logical structure, leading to sub-optimal objectives. We address this from a factorized learning perspective. We first propose D$^2$VLM, a framework that decouples the learning of these two tasks while also emphasizing their inherent dependency. We adopt a "grounding then answering with evidence referencing" paradigm and introduce evidence tokens for evidence grounding, which emphasize event-level visual semantic capture beyond the focus on timestamp representation in existing works. To further facilitate the learning of these two tasks, we introduce a novel factorized preference optimization (FPO) algorithm. Unlike standard preference optimization, FPO explicitly incorporates probabilistic temporal grounding modeling into the optimization objective, enabling preference learning for both temporal grounding and textual response. We also construct a synthetic dataset to address the lack of suitable datasets for factorized preference learning with explicit temporal grounding. Experiments on various tasks demonstrate the clear advantage of our approach. Our source code is available at https://github.com/nusnlp/d2vlm.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Comparison of CNN Training Paradigms**: - Custom Model: Building a house from scratch; precise but costly and time-consuming. - Transfer Learning: Renovating an existing building to suit needs, requiring fewer resources.-
Performance Variability Across Datasets:
- Custom models excel with ample data but falter when data is scarce.
- Transfer learning is more flexible in resource-constrained environments.
-
Advantages of Hybrid Approaches:
- Combining custom and transfer methods to leverage benefits from both.
- Like adding a new room to an existing house, improving while maintaining the structure.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)