Self-Critique Empowers LLM Planning Gains
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Enhancing LLM Planning Capabilities through Intrinsic Self-Critique- ArXiv ID: 2512.24103
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Bernd Bohnet, Pierre-Alexandre Kamienny, Hanie Sedghi, Dilan Gorur, Pranjal Awasthi, Aaron Parisi, Kevin Swersky, Rosanne Liu, Azade Nova, Noah Fiedel
📝 Abstract
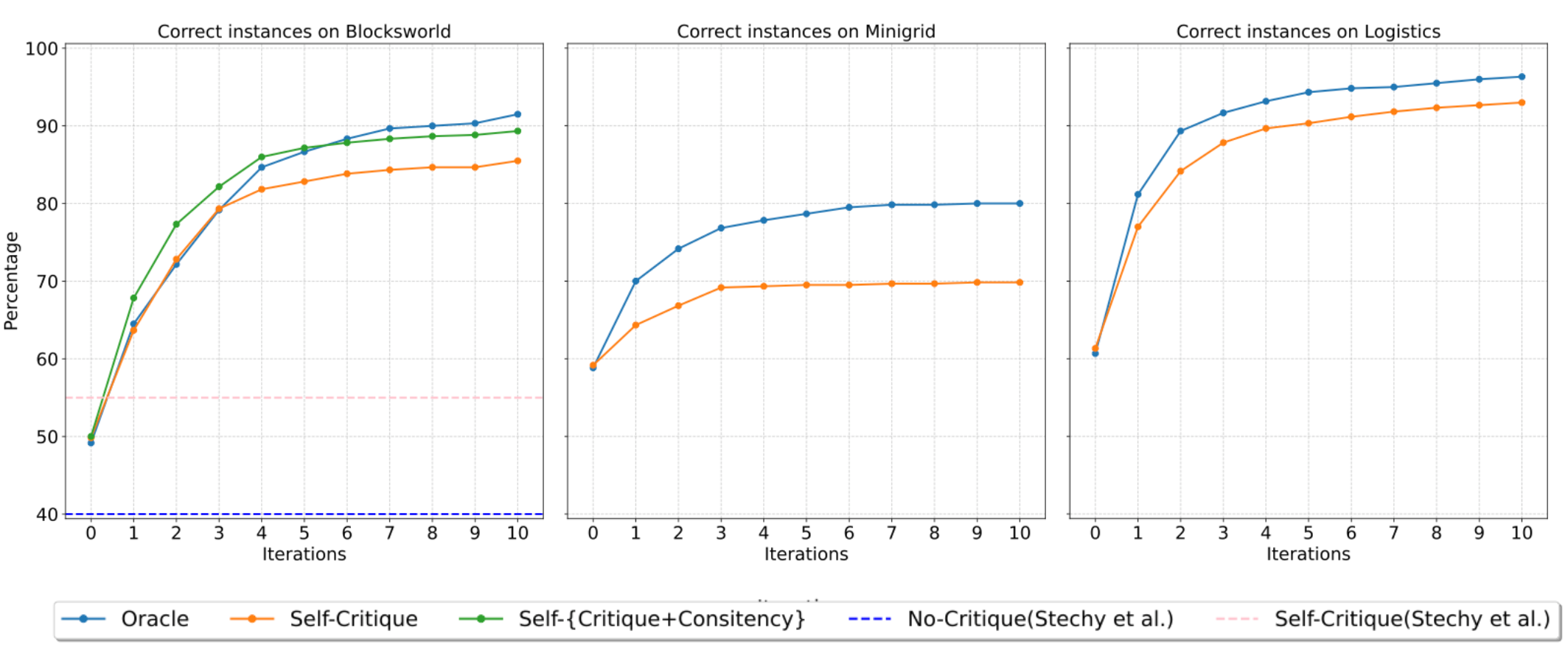
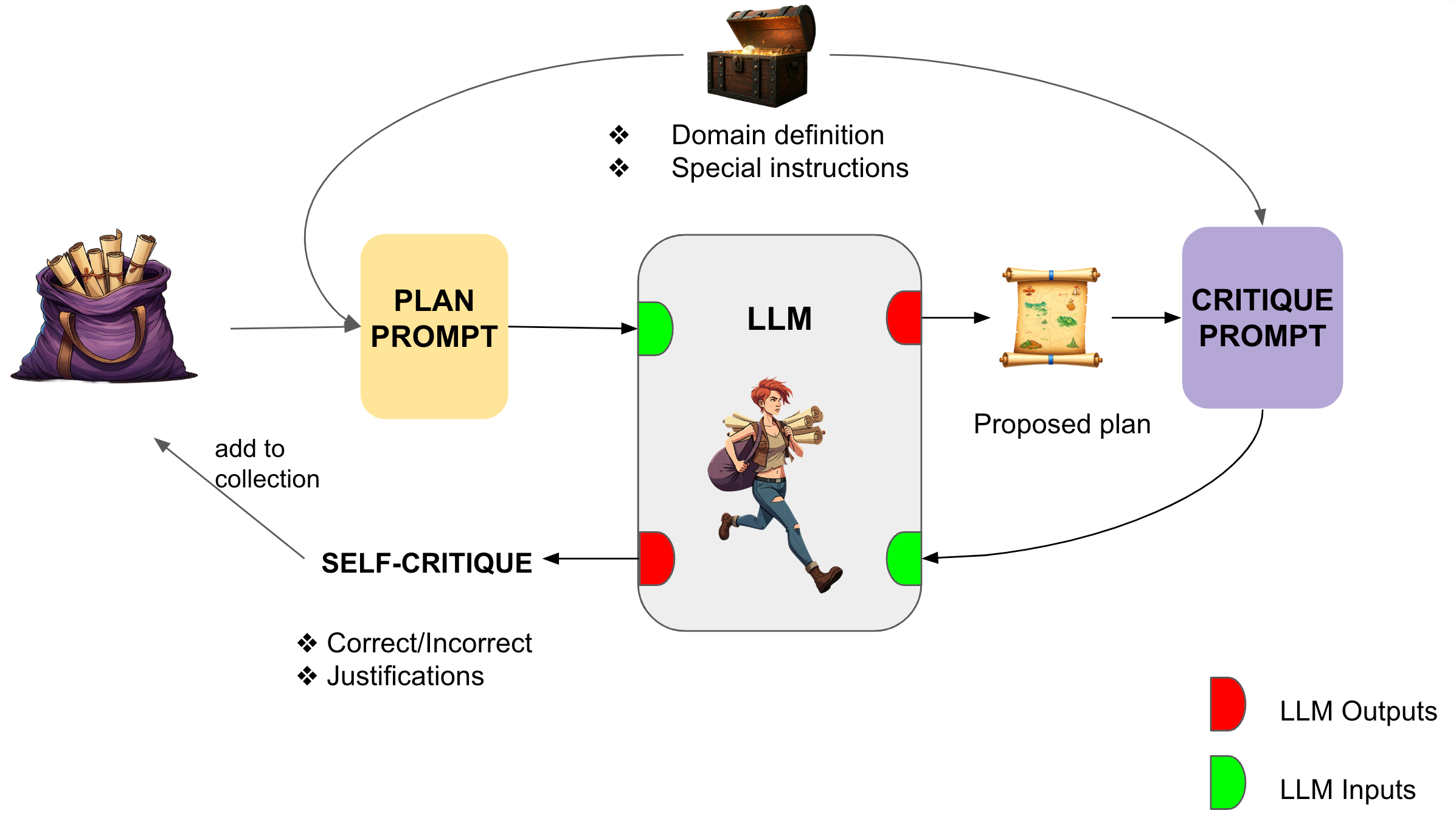
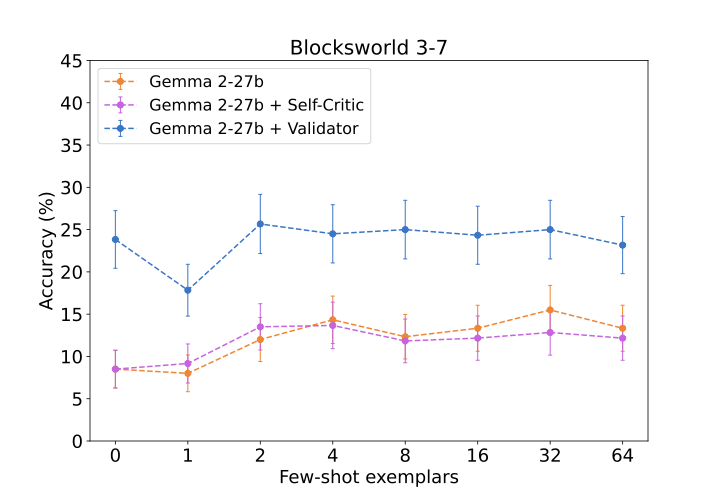
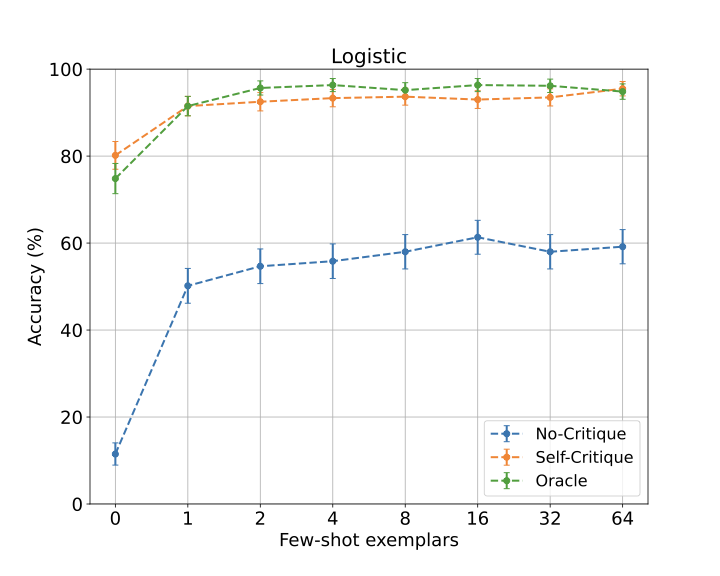
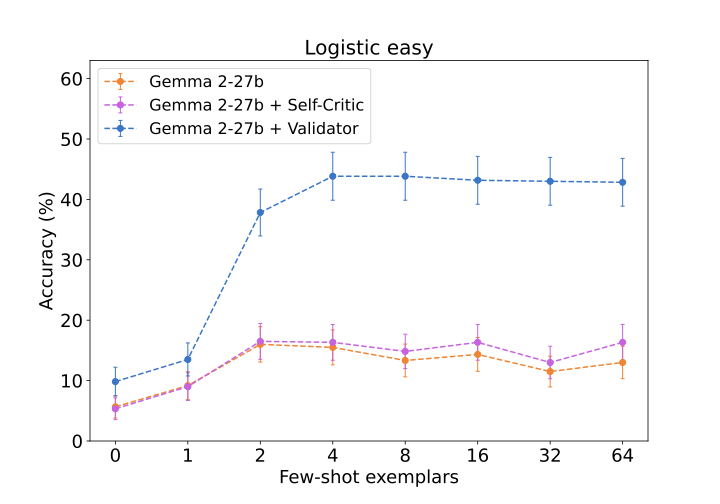
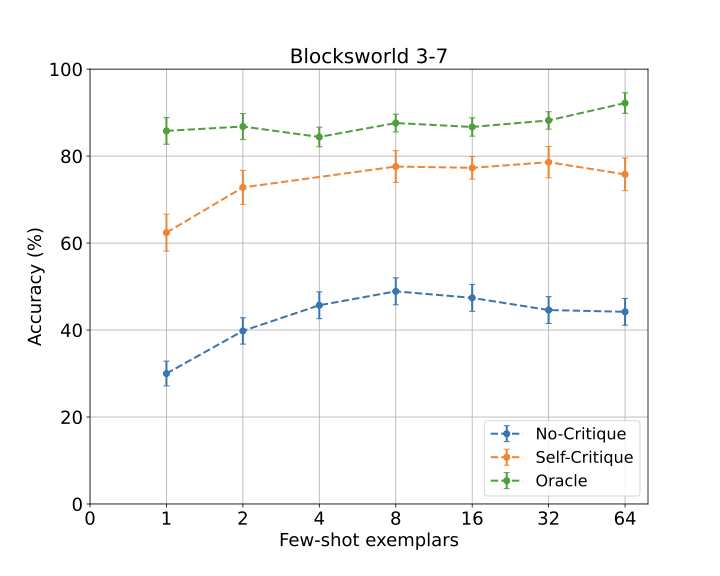
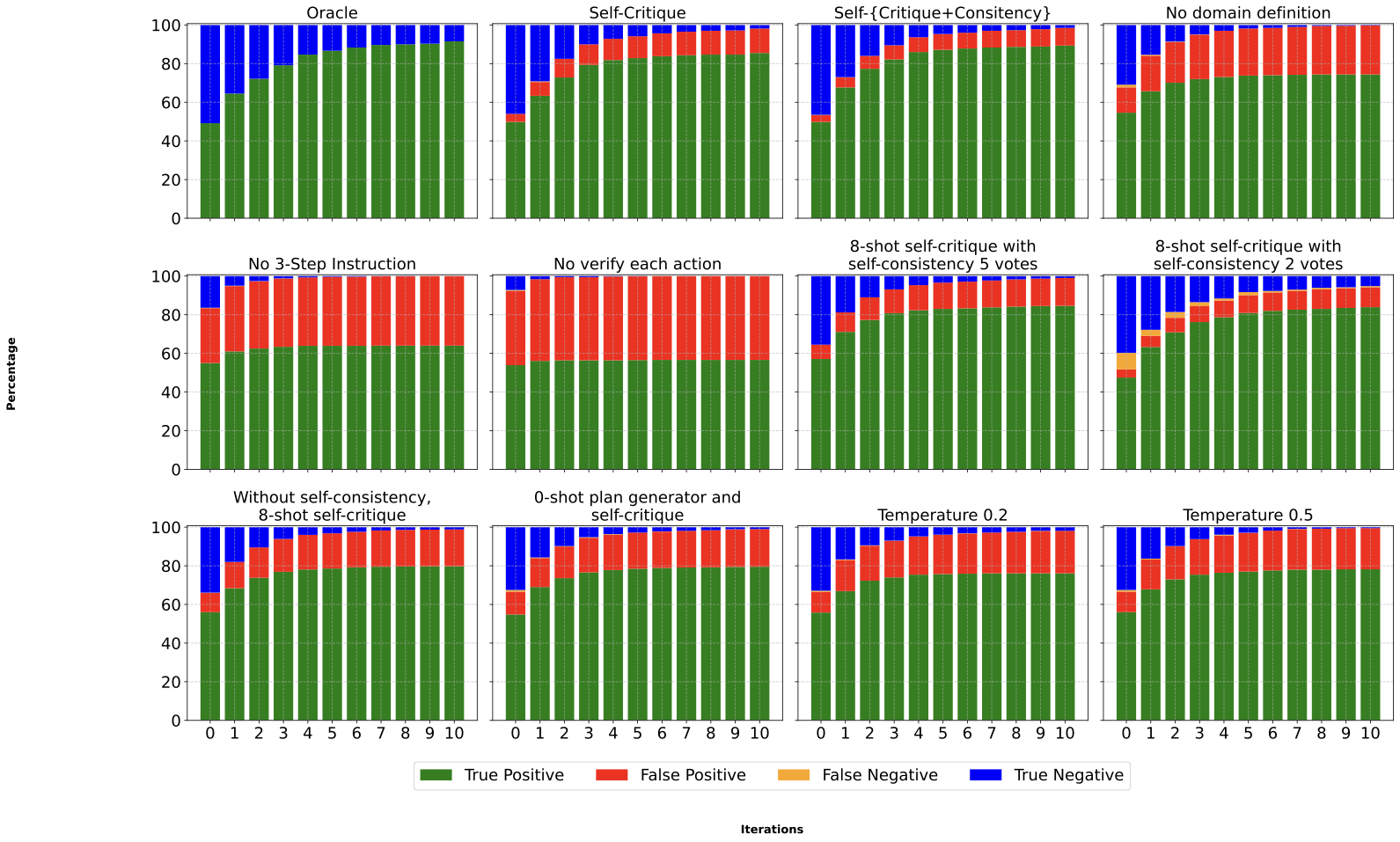
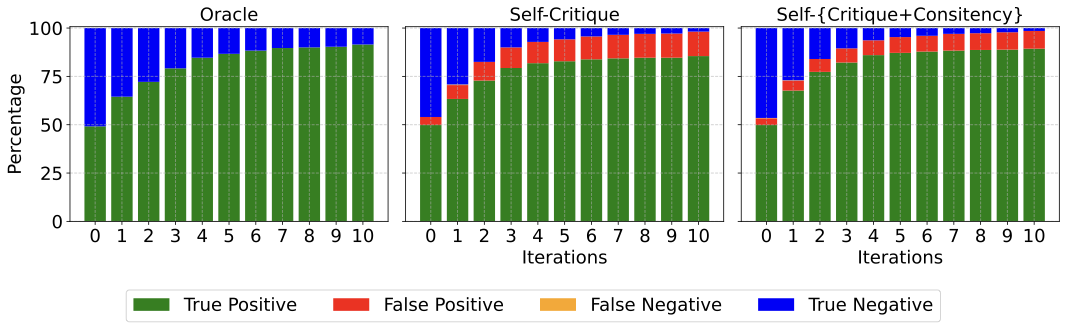
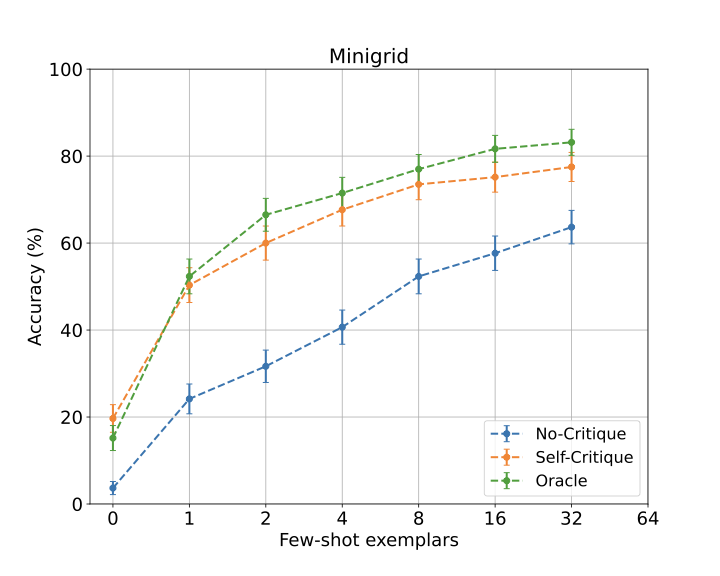
We demonstrate an approach for LLMs to critique their \emph{own} answers with the goal of enhancing their performance that leads to significant improvements over established planning benchmarks. Despite the findings of earlier research that has cast doubt on the effectiveness of LLMs leveraging self critique methods, we show significant performance gains on planning datasets in the Blocksworld domain through intrinsic self-critique, without external source such as a verifier. We also demonstrate similar improvements on Logistics and Mini-grid datasets, exceeding strong baseline accuracies. We employ a few-shot learning technique and progressively extend it to a many-shot approach as our base method and demonstrate that it is possible to gain substantial improvement on top of this already competitive approach by employing an iterative process for correction and refinement. We illustrate how self-critique can significantly boost planning performance. Our empirical results present new state-of-the-art on the class of models considered, namely LLM model checkpoints from October 2024. Our primary focus lies on the method itself, demonstrating intrinsic self-improvement capabilities that are applicable regardless of the specific model version, and we believe that applying our method to more complex search techniques and more capable models will lead to even better performance.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Performance Variance Across Learning Methods:** Machine learning models behave differently based on the learning methods used. Custom models are like building a house from scratch, while transfer learning is akin to adding new rooms onto an existing structure. 2. **Advantages of Transfer Learning:** Leveraging pre-trained models saves significant time and resources. It’s similar to using prefabricated furniture; you can make adjustments as needed without starting over. 3. **Utilizing Pre-Trained Models:** Pre-trained models show high performance in image recognition tasks, akin to solving new problems by leveraging expert knowledge.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)