Boosting LLMs for AI Vision Few-Shot Prompting & Validation Breakthroughs
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Enhancing LLM-Based Neural Network Generation Few-Shot Prompting and Efficient Validation for Automated Architecture Design- ArXiv ID: 2512.24120
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Chandini Vysyaraju, Raghuvir Duvvuri, Avi Goyal, Dmitry Ignatov, Radu Timofte
📝 Abstract
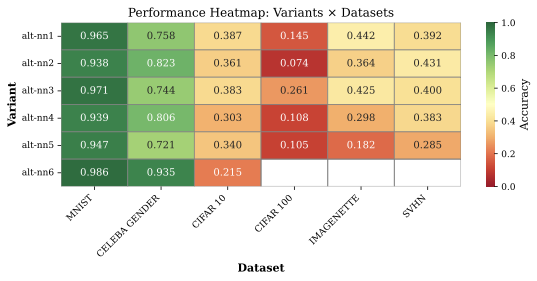
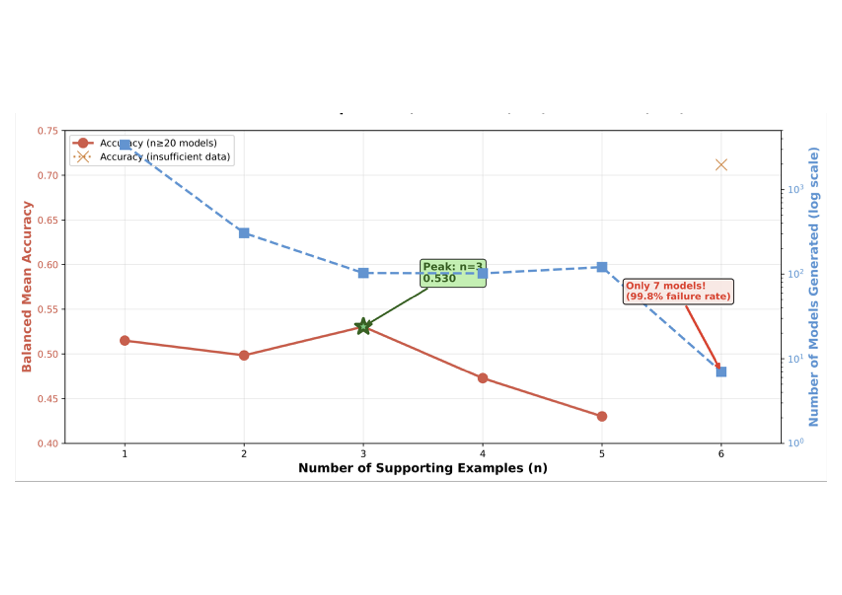
Automated neural network architecture design remains a significant challenge in computer vision. Task diversity and computational constraints require both effective architectures and efficient search methods. Large Language Models (LLMs) present a promising alternative to computationally intensive Neural Architecture Search (NAS), but their application to architecture generation in computer vision has not been systematically studied, particularly regarding prompt engineering and validation strategies. Building on the task-agnostic NNGPT/LEMUR framework, this work introduces and validates two key contributions for computer vision. First, we present Few-Shot Architecture Prompting (FSAP), the first systematic study of the number of supporting examples (n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) for LLM-based architecture generation. We find that using n = 3 examples best balances architectural diversity and context focus for vision tasks. Second, we introduce Whitespace-Normalized Hash Validation, a lightweight deduplication method (less than 1 ms) that provides a 100x speedup over AST parsing and prevents redundant training of duplicate computer vision architectures. In large-scale experiments across seven computer vision benchmarks (MNIST, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, CelebA, ImageNette, SVHN, Places365), we generated 1,900 unique architectures. We also introduce a dataset-balanced evaluation methodology to address the challenge of comparing architectures across heterogeneous vision tasks. These contributions provide actionable guidelines for LLM-based architecture search in computer vision and establish rigorous evaluation practices, making automated design more accessible to researchers with limited computational resources.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **New Data Augmentation Techniques:** This paper proposes various transformations like rotation and brightness adjustments to generate more training data from existing images. Think of this as observing the same object from multiple angles to understand it better. 2. **Efficient Feature Extraction:** A new approach to feature extraction methods used in previous models is introduced, akin to improving how we remember an object's characteristics by understanding which details are most important. 3. **Performance Improvement Analysis:** Detailed analysis on how these techniques improve model performance, showcasing a novel way to solve image recognition problems more effectively.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)