PointRAFT Estimating Potato Tuber Weight from Incomplete 3D Data
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: PointRAFT 3D deep learning for high-throughput prediction of potato tuber weight from partial point clouds- ArXiv ID: 2512.24193
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Pieter M. Blok, Haozhou Wang, Hyun Kwon Suh, Peicheng Wang, James Burridge, Wei Guo
📝 Abstract
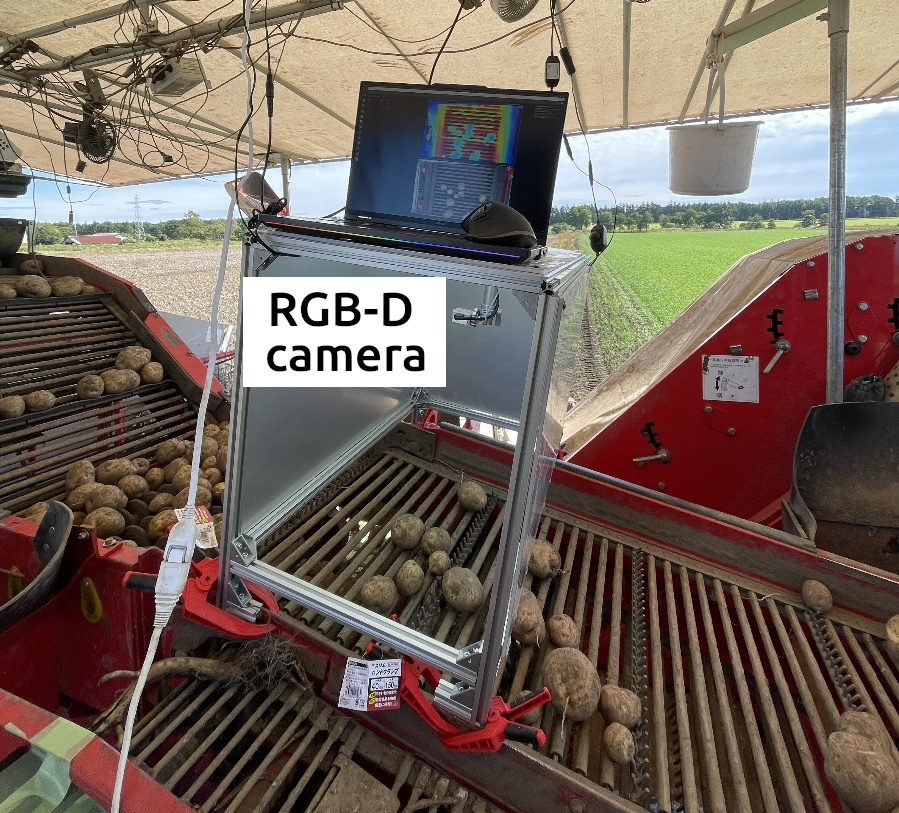
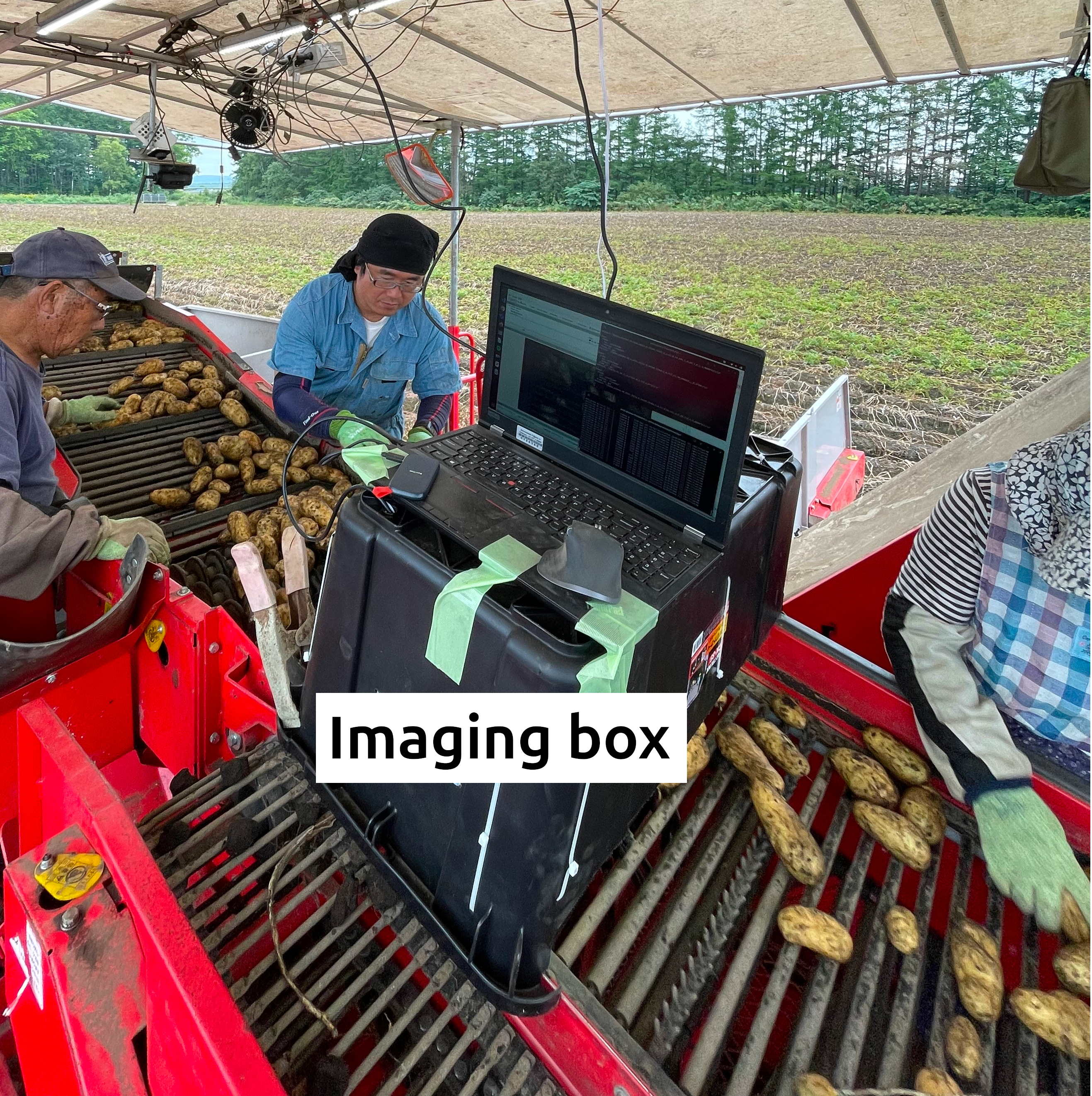
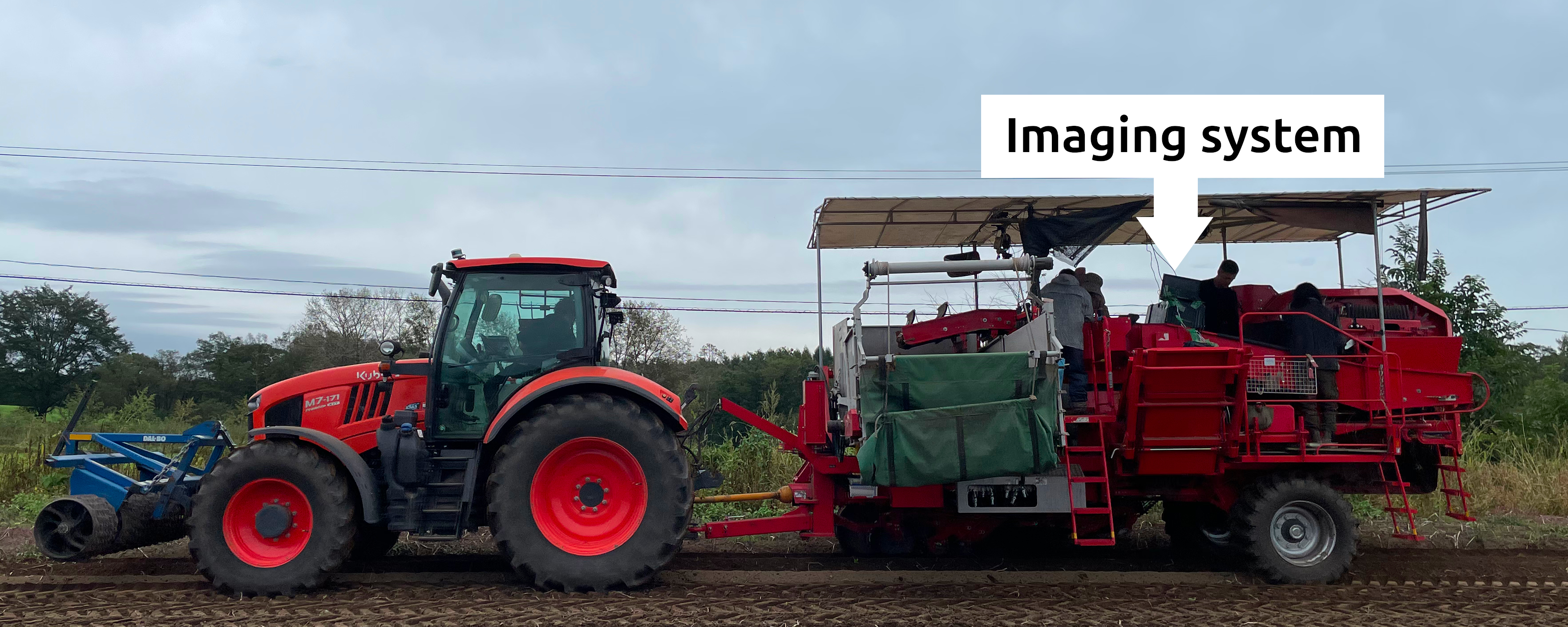
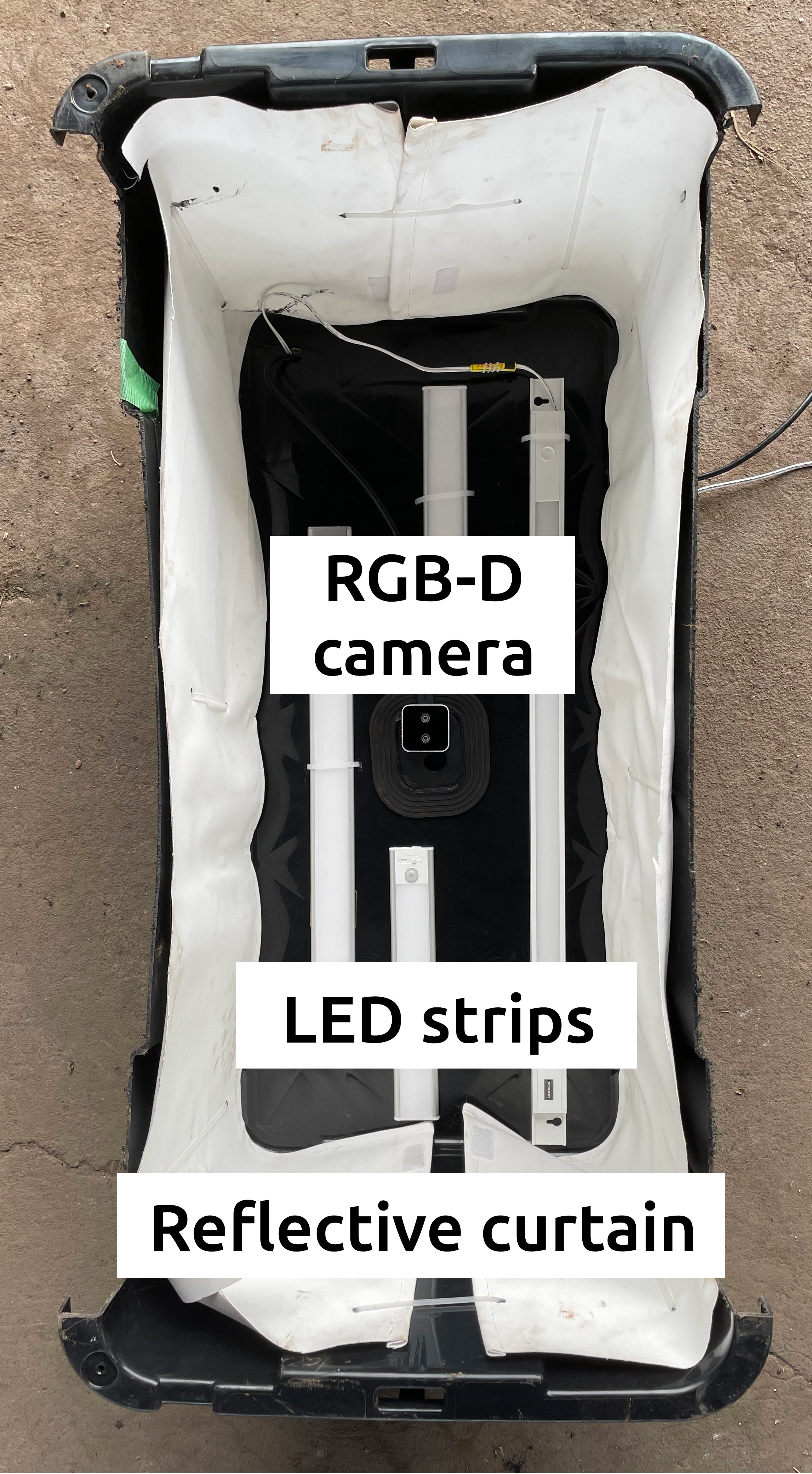
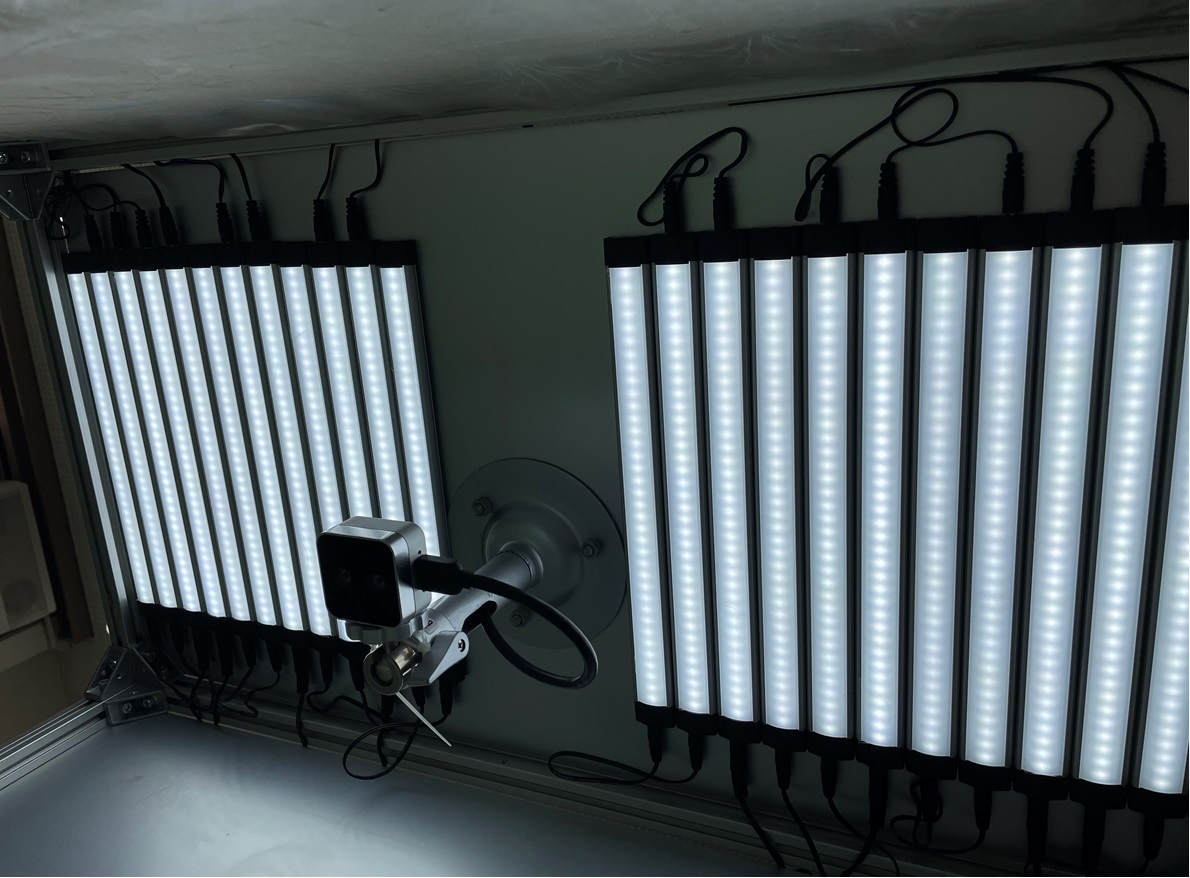
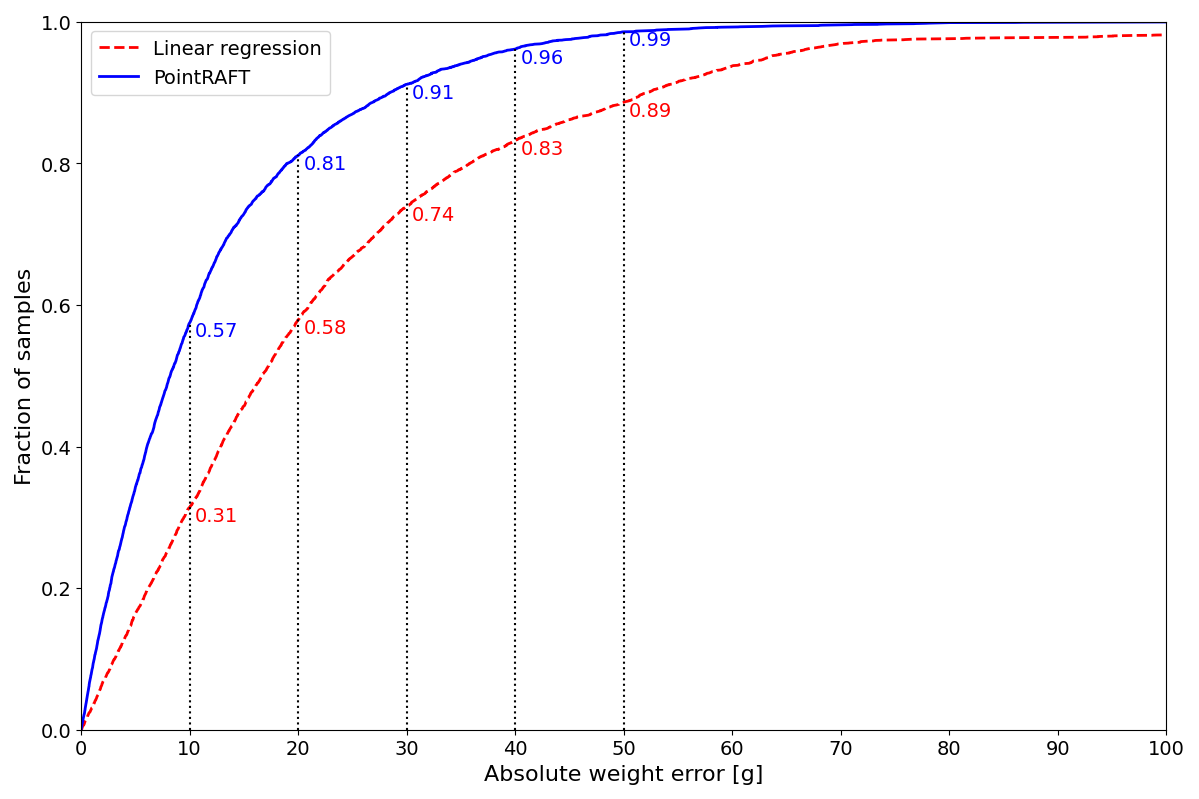
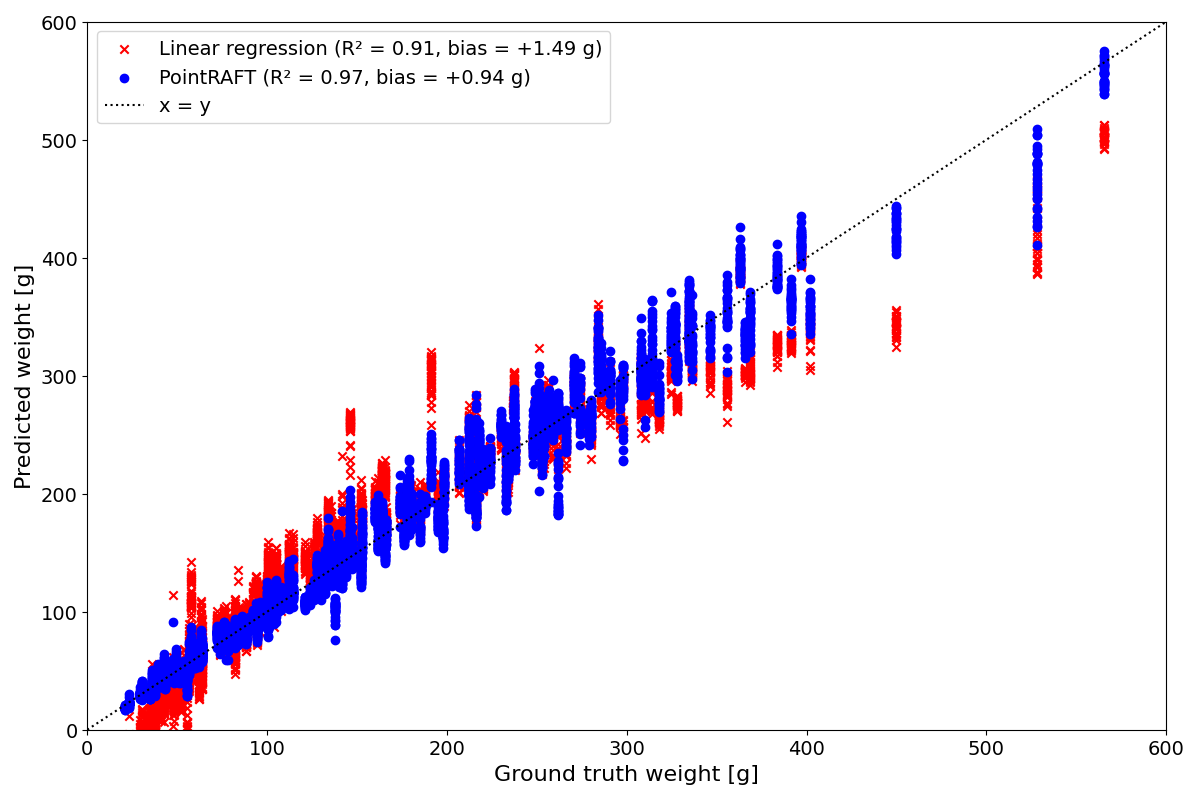
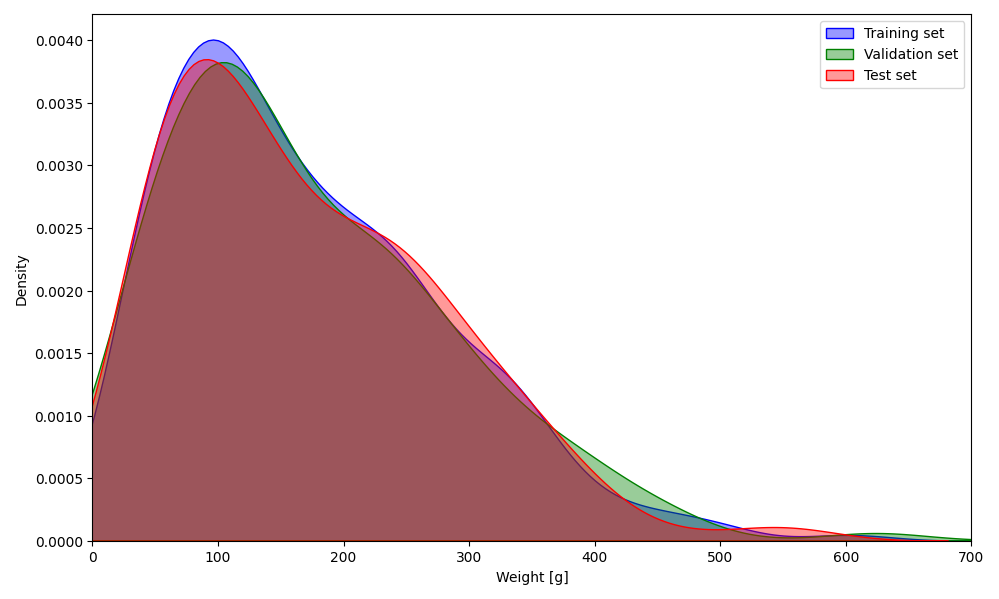
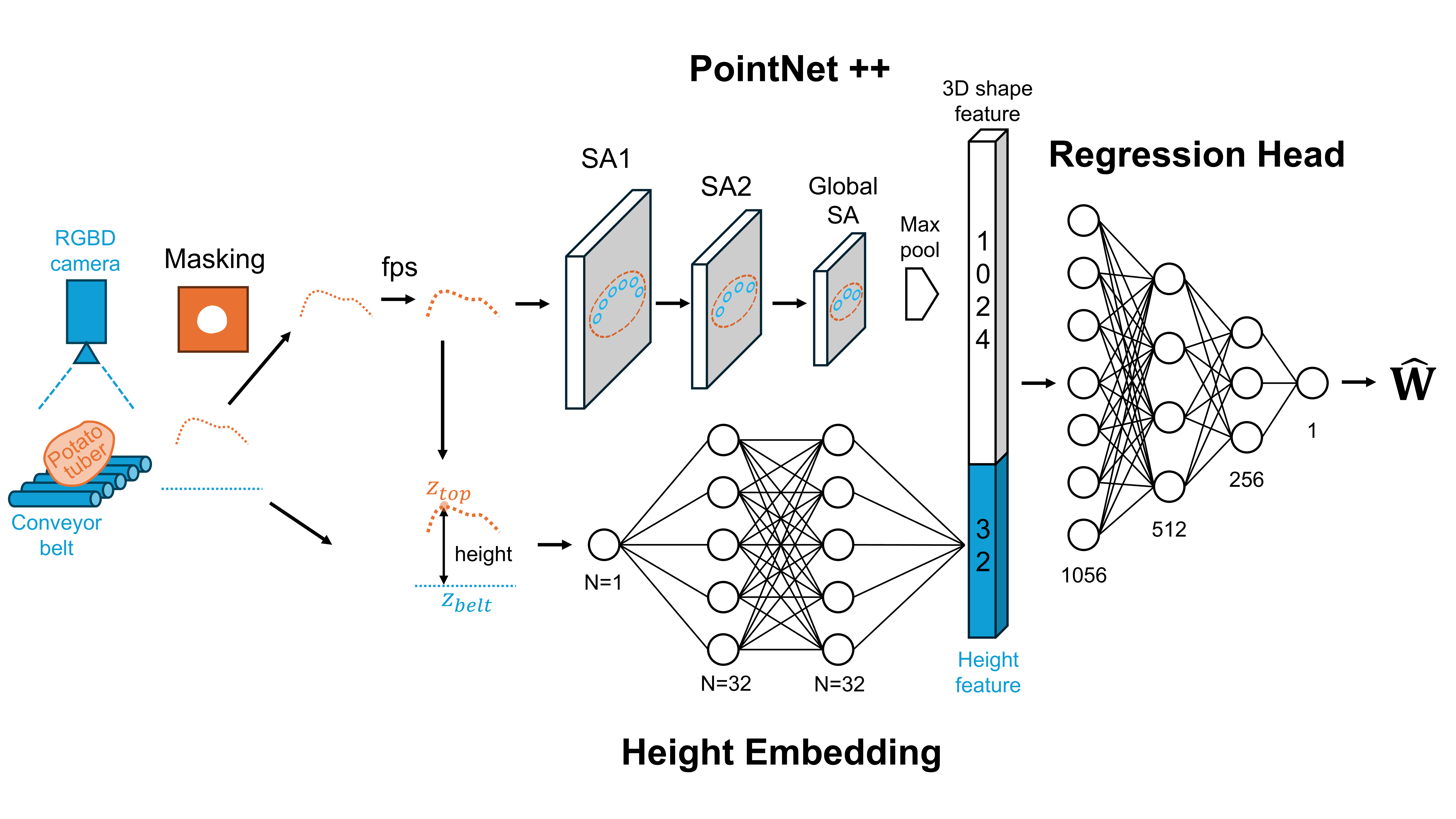
Potato yield is a key indicator for optimizing cultivation practices in agriculture. Potato yield can be estimated on harvesters using RGB-D cameras, which capture three-dimensional (3D) information of individual tubers moving along the conveyor belt. However, point clouds reconstructed from RGB-D images are incomplete due to self-occlusion, leading to systematic underestimation of tuber weight. To address this, we introduce PointRAFT, a high-throughput point cloud regression network that directly predicts continuous 3D shape properties, such as tuber weight, from partial point clouds. Rather than reconstructing full 3D geometry, PointRAFT infers target values directly from raw 3D data. Its key architectural novelty is an object height embedding that incorporates tuber height as an additional geometric cue, improving weight prediction under practical harvesting conditions. PointRAFT was trained and evaluated on 26,688 partial point clouds collected from 859 potato tubers across four cultivars and three growing seasons on an operational harvester in Japan. On a test set of 5,254 point clouds from 172 tubers, PointRAFT achieved a mean absolute error of 12.0 g and a root mean squared error of 17.2 g, substantially outperforming a linear regression baseline and a standard PointNet++ regression network. With an average inference time of 6.3 ms per point cloud, PointRAFT supports processing rates of up to 150 tubers per second, meeting the high-throughput requirements of commercial potato harvesters. Beyond potato weight estimation, PointRAFT provides a versatile regression network applicable to a wide range of 3D phenotyping and robotic perception tasks. The code, network weights, and a subset of the dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/pieterblok/pointraft.git.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1:** How machine learning understands stock markets is like a cat observing birds. 2. **Contribution 2:** Comparing the performance of three models is akin to choosing ingredients accurately when cooking. 3. **Contribution 3:** The most complex part involves how each model processes data, similar to logical thinking required in solving complex math problems.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)