Counterfactually Guiding MLLMs Curbing Visual Hallucinations
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Taming Hallucinations Boosting MLLMs Video Understanding via Counterfactual Video Generation- ArXiv ID: 2512.24271
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Zhe Huang, Hao Wen, Aiming Hao, Bingze Song, Meiqi Wu, Jiahong Wu, Xiangxiang Chu, Sheng Lu, Haoqian Wang
📝 Abstract
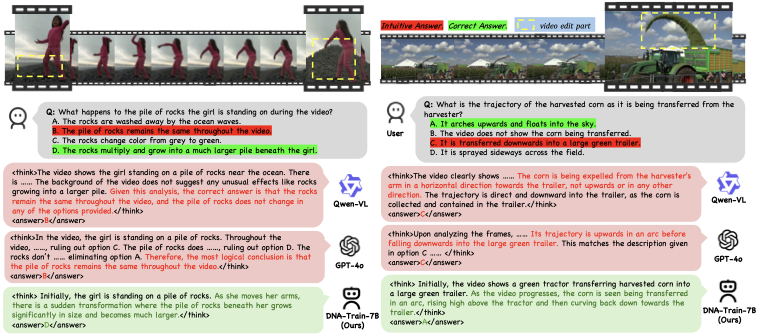
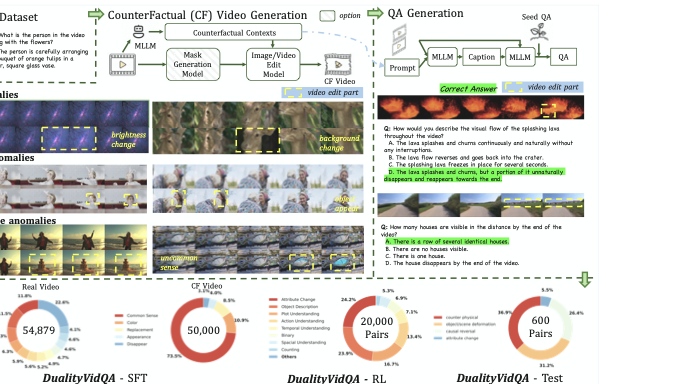
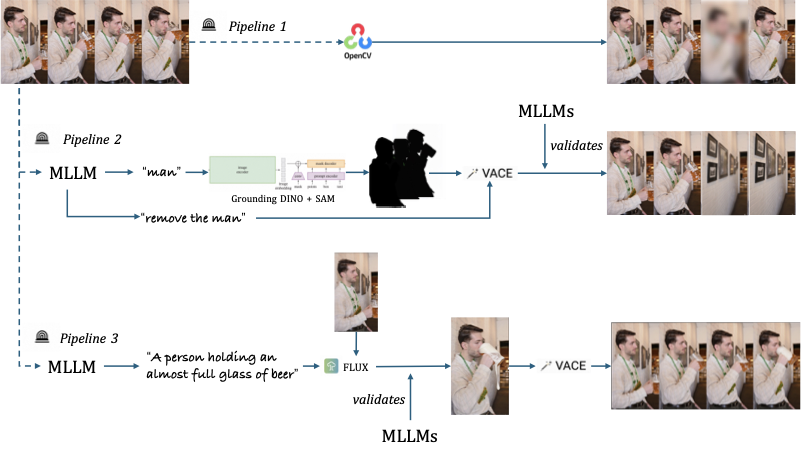
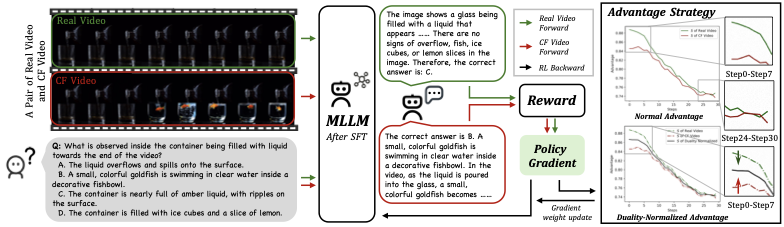
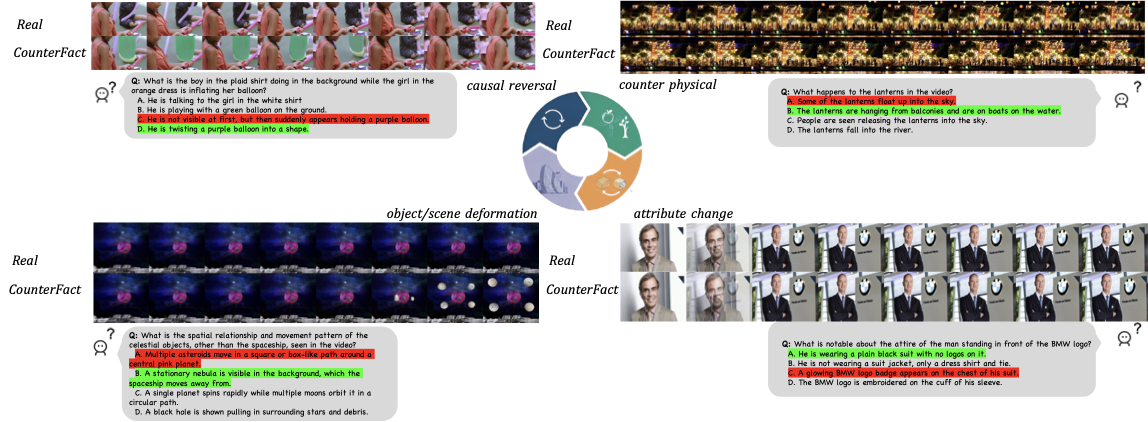
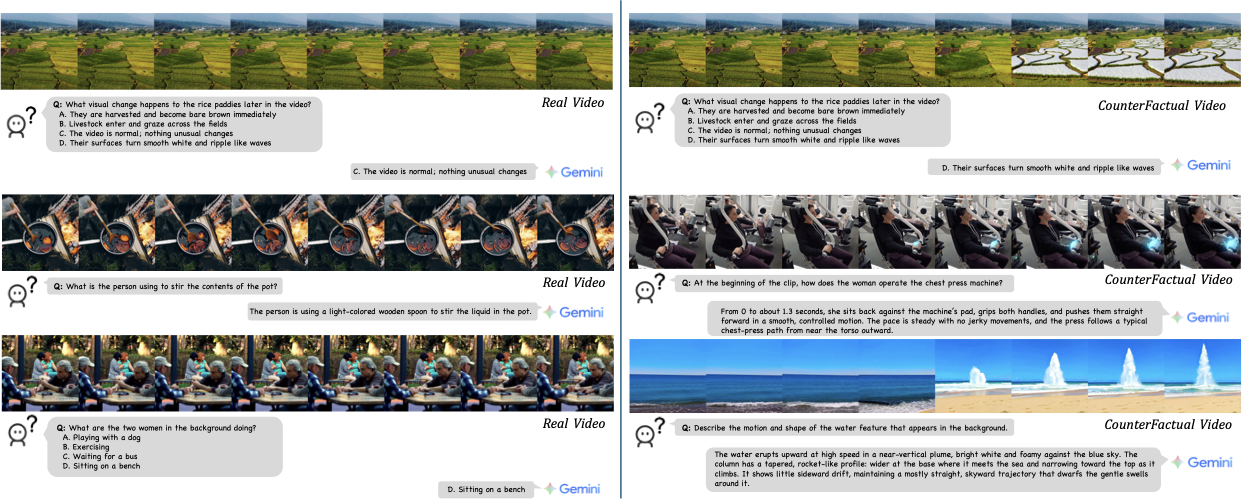
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made remarkable progress in video understanding. However, they suffer from a critical vulnerability: an over-reliance on language priors, which can lead to visual ungrounded hallucinations, especially when processing counterfactual videos that defy common sense. This limitation, stemming from the intrinsic data imbalance between text and video, is challenging to address due to the substantial cost of collecting and annotating counterfactual data. To address this, we introduce DualityForge, a novel counterfactual data synthesis framework that employs controllable, diffusion-based video editing to transform real-world videos into counterfactual scenarios. By embedding structured contextual information into the video editing and QA generation processes, the framework automatically produces high-quality QA pairs together with original-edited video pairs for contrastive training. Based on this, we build DualityVidQA, a large-scale video dataset designed to reduce MLLM hallucinations. In addition, to fully exploit the contrastive nature of our paired data, we propose Duality-Normalized Advantage Training (DNA-Train), a two-stage SFT-RL training regime where the RL phase applies pair-wise $\ell_1$ advantage normalization, thereby enabling a more stable and efficient policy optimization. Experiments on DualityVidQA-Test demonstrate that our method substantially reduces model hallucinations on counterfactual videos, yielding a relative improvement of 24.0% over the Qwen2.5-VL-7B baseline. Moreover, our approach achieves significant gains across both hallucination and general-purpose benchmarks, indicating strong generalization capability. We will open-source our dataset and code.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Key Contribution**: Systematically analyzed how machine learning techniques can be applied to natural language processing, akin to using various tools to build a structure. 2. **Key Contribution**: Compared the performance differences between transformer and recitor models. This is similar to comparing the speed of two different cars traveling the same distance. 3. **Key Contribution**: Analyzed results from applying machine learning techniques across diverse datasets. This is analogous to observing how plants grow in various types of soil.Sci-Tube Style Script
- Beginner: “Learn how machine learning is used in natural language processing. It’s like building a house with different tools.”
- Intermediate: “We look at the performance differences between transformer and recitor models, similar to comparing two cars driving the same distance.”
- Advanced: “Analyze results from applying machine learning across various datasets, much like observing plant growth in different soil types.”
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)