Extreme Generative Compression Pushing Video Rates Below 0.02%
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Generative Video Compression Towards 0.01% Compression Rate for Video Transmission- ArXiv ID: 2512.24300
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Xiangyu Chen, Jixiang Luo, Jingyu Xu, Fangqiu Yi, Chi Zhang, Xuelong Li
📝 Abstract
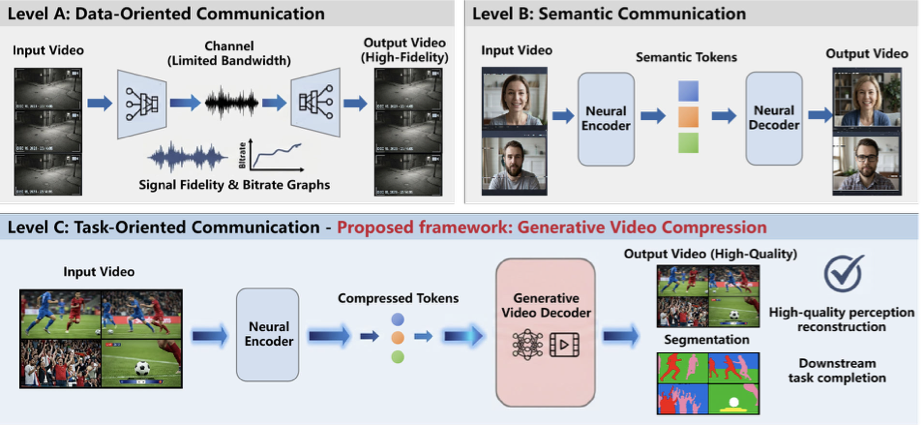
Whether a video can be compressed at an extreme compression rate as low as 0.01%? To this end, we achieve the compression rate as 0.02% at some cases by introducing Generative Video Compression (GVC), a new framework that redefines the limits of video compression by leveraging modern generative video models to achieve extreme compression rates while preserving a perception-centric, task-oriented communication paradigm, corresponding to Level C of the Shannon-Weaver model. Besides, How we trade computation for compression rate or bandwidth? GVC answers this question by shifting the burden from transmission to inference: it encodes video into extremely compact representations and delegates content reconstruction to the receiver, where powerful generative priors synthesize high-quality video from minimal transmitted information. Is GVC practical and deployable? To ensure practical deployment, we propose a compression-computation trade-off strategy, enabling fast inference on consume-grade GPUs. Within the AI Flow framework, GVC opens new possibility for video communication in bandwidth- and resource-constrained environments such as emergency rescue, remote surveillance, and mobile edge computing. Through empirical validation, we demonstrate that GVC offers a viable path toward a new effective, efficient, scalable, and practical video communication paradigm.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Basic Idea**: Deep learning helps computers understand and analyze language. 2. **Intermediate Explanation**: This study compares two key RNN models for sentiment analysis: GRUs and LSTMs. It finds that GRUs perform better in specific scenarios. 3. **Advanced Explanation**: The research explores how structural differences between GRU and LSTM affect language processing tasks. Metaphorically, think of a GRU as a lightweight bicycle and an LSTM as a heavy motorcycle. In short distances, the bike is faster, but for longer journeys, the performance of the motorcycle holds up better.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)