Summarizing the Unseen Less-Resourced Language Techniques
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Comparing Approaches to Automatic Summarization in Less-Resourced Languages- ArXiv ID: 2512.24410
- Date: 2025-12-30
- Authors: Chester Palen-Michel, Constantine Lignos
📝 Abstract
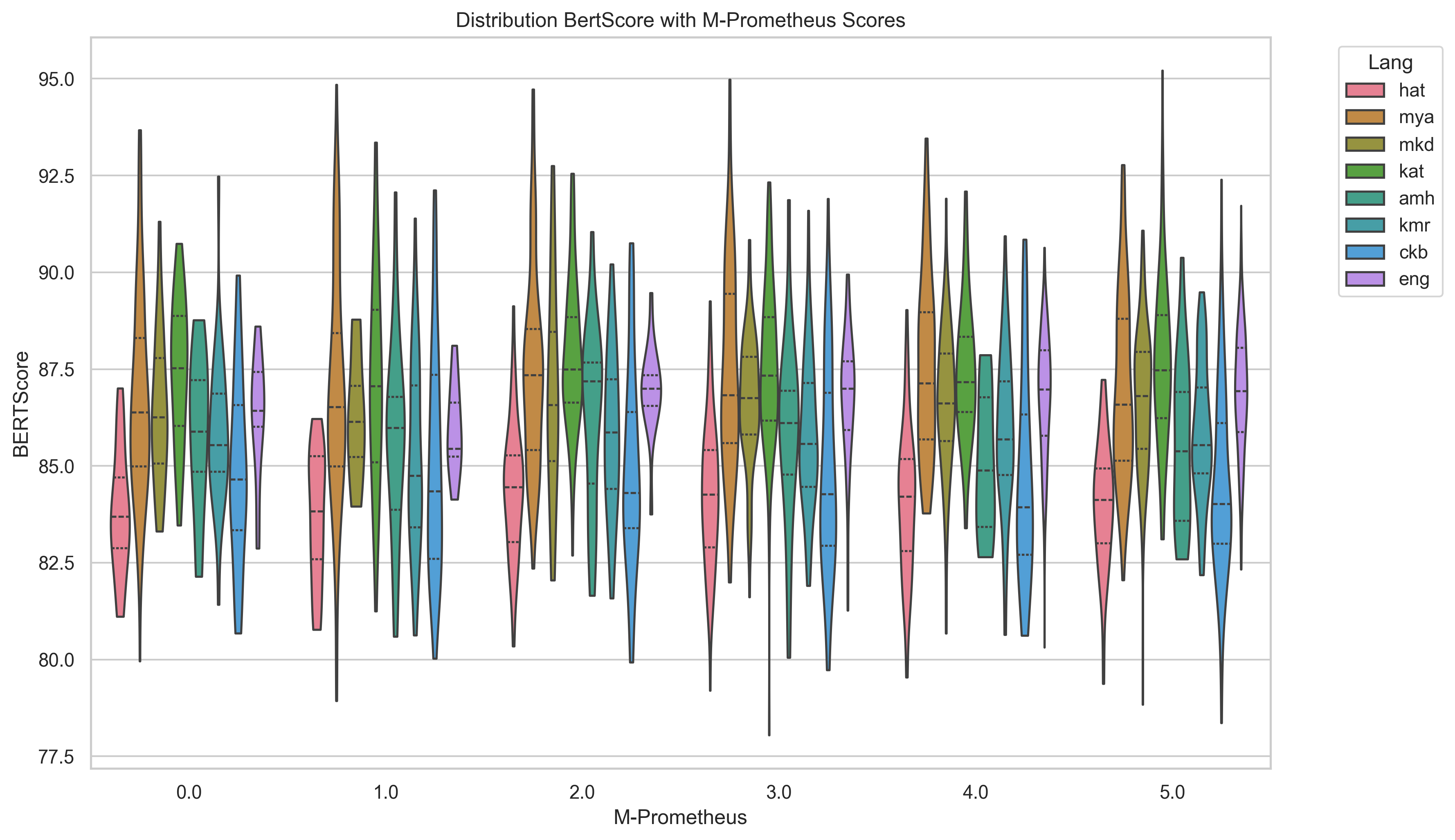
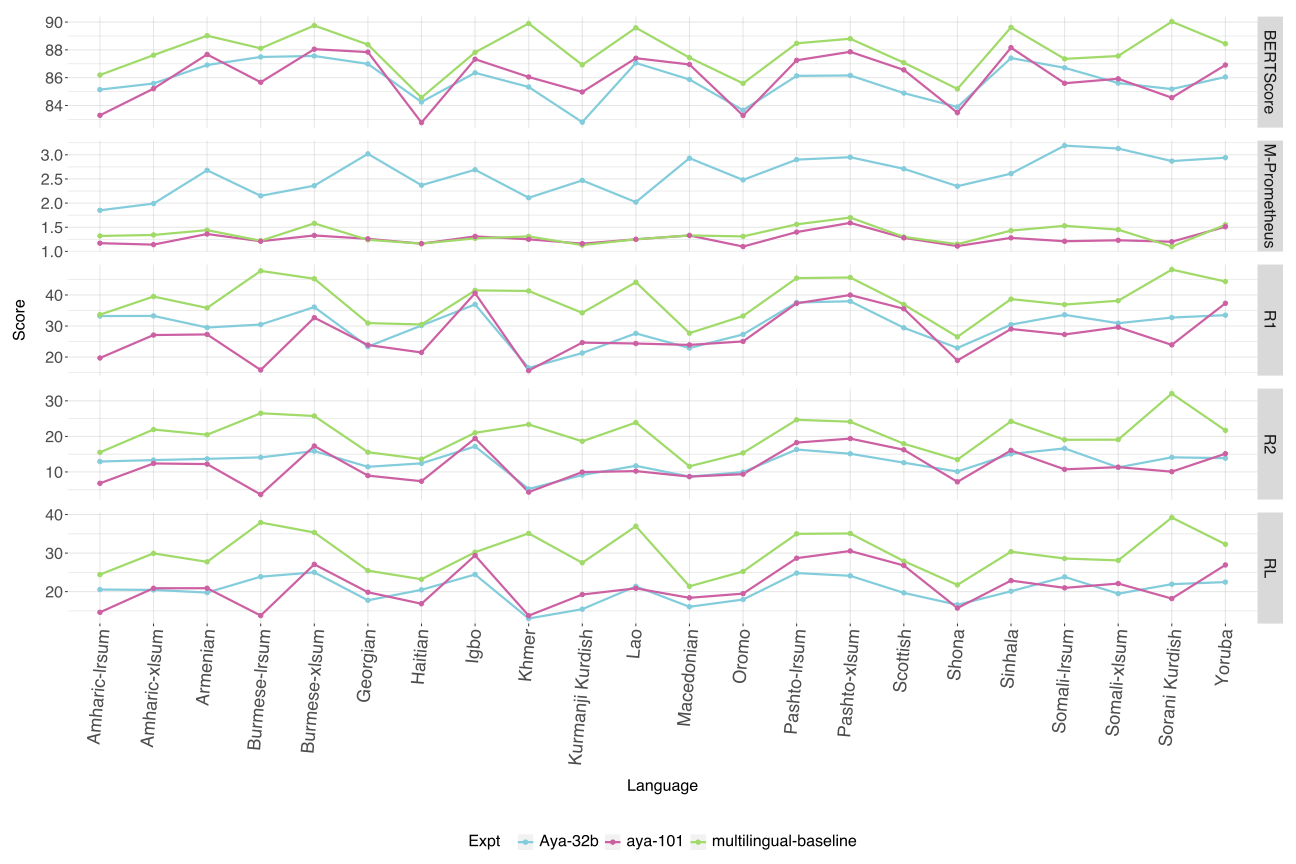
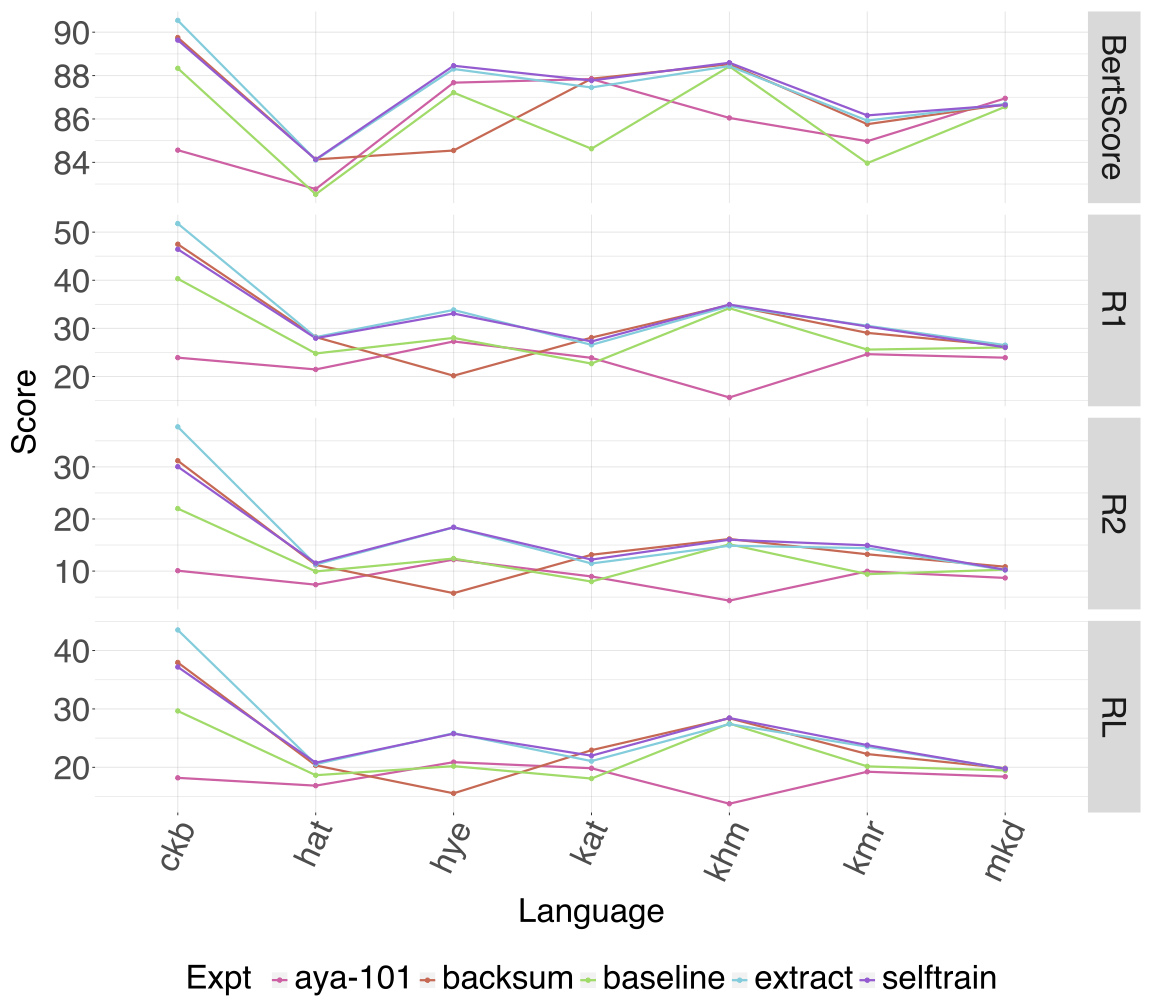
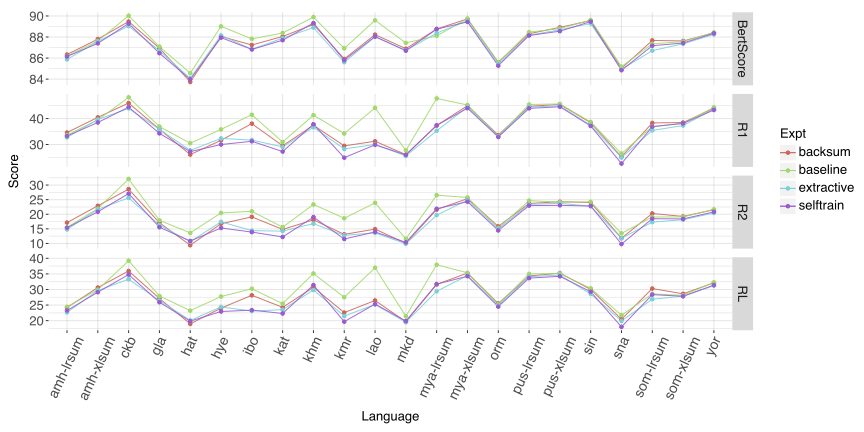
Automatic text summarization has achieved high performance in high-resourced languages like English, but comparatively less attention has been given to summarization in less-resourced languages. This work compares a variety of different approaches to summarization from zero-shot prompting of LLMs large and small to fine-tuning smaller models like mT5 with and without three data augmentation approaches and multilingual transfer. We also explore an LLM translation pipeline approach, translating from the source language to English, summarizing and translating back. Evaluating with five different metrics, we find that there is variation across LLMs in their performance across similar parameter sizes, that our multilingual fine-tuned mT5 baseline outperforms most other approaches including zero-shot LLM performance for most metrics, and that LLM as judge may be less reliable on less-resourced languages.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **New Algorithm**: The paper introduces a new algorithm that is much more accurate than previous natural language processing methods. This can be likened to moving from having one bread recipe to using optimized recipes for different types of bread. 2. **Efficient Learning Method**: The new technique makes data processing and model training more efficient, akin to developing an engine that uses less fuel while driving further. 3. **Real-World Applications**: The paper demonstrates how these new methodologies are applied in solving real-world problems, such as building more effective customer service chatbots.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)