Minimizing Makespan with CP and BRKGA for Coupled Task Scheduling
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Constraint programming model and biased random-key genetic algorithm for the single-machine coupled task scheduling problem with exact delays to minimize the makespan- ArXiv ID: 2512.23150
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Vítor A. Barbosa, Rafael A. Melo
📝 Abstract
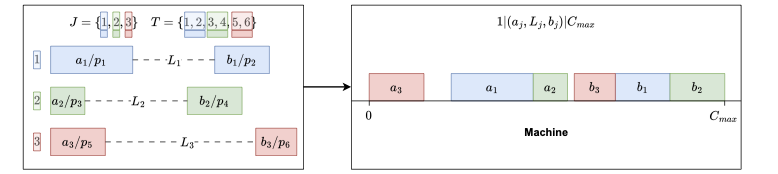
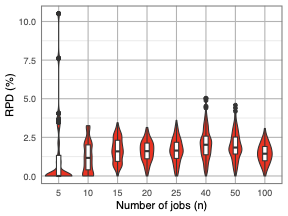
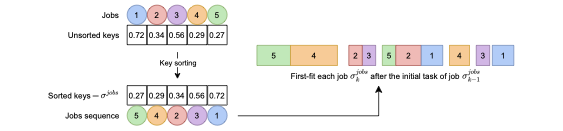
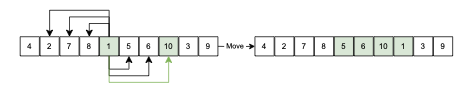
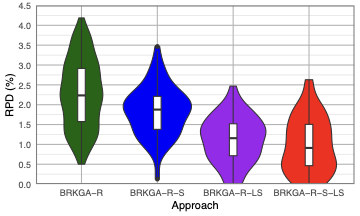
We consider the strongly NP-hard single-machine coupled task scheduling problem with exact delays to minimize the makespan. In this problem, a set of jobs has to be scheduled, each composed of two tasks interspersed by an exact delay. Given that no preemption is allowed, the goal consists of minimizing the completion time of the last scheduled task. We model the problem using constraint programming (CP) and propose a biased random-key genetic algorithm (BRKGA). Our CP model applies well-established global constraints. Our BRKGA combines some successful components in the literature: an initial solution generator, periodical restarts and shakes, and a local search algorithm. Furthermore, the BRKGA's decoder is focused on efficiency rather than optimality, which accelerates the solution space exploration. Computational experiments on a benchmark set containing instances with up to 100 jobs (200 tasks) indicate that the proposed BRKGA can efficiently explore the problem solution space, providing high-quality approximate solutions within low computational times. It can also provide better solutions than the CP model under the same computational settings, i.e., three minutes of time limit and a single thread. The CP model, when offered a longer running time of 3600 seconds and multiple threads, significantly improved the results, reaching the current best-known solution for 90.56% of these instances. Finally, our experiments highlight the importance of the shake and local search components in the BRKGA, whose combination significantly improves the results of a standard BRKGA.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Importance of Hyperparameter Tuning**: Hyperparameters play a crucial role in neural network learning, affecting model performance significantly. 2. **Diversity of Tuning Methods**: Various tuning methods are available, each offering better results under specific conditions. 3. **Need for Automated Tuning Tools**: Manual adjustment is time-consuming and labor-intensive; thus, automated tools enhance efficiency.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)