ForCM Mapping Forest Cover with Deep Learning & OBIA
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: ForCM Forest Cover Mapping from Multispectral Sentinel-2 Image by Integrating Deep Learning with Object-Based Image Analysis- ArXiv ID: 2512.23196
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Maisha Haque, Israt Jahan Ayshi, Sadaf M. Anis, Nahian Tasnim, Mithila Moontaha, Md. Sabbir Ahmed, Muhammad Iqbal Hossain, Mohammad Zavid Parvez, Subrata Chakraborty, Biswajeet Pradhan, Biswajit Banik
📝 Abstract
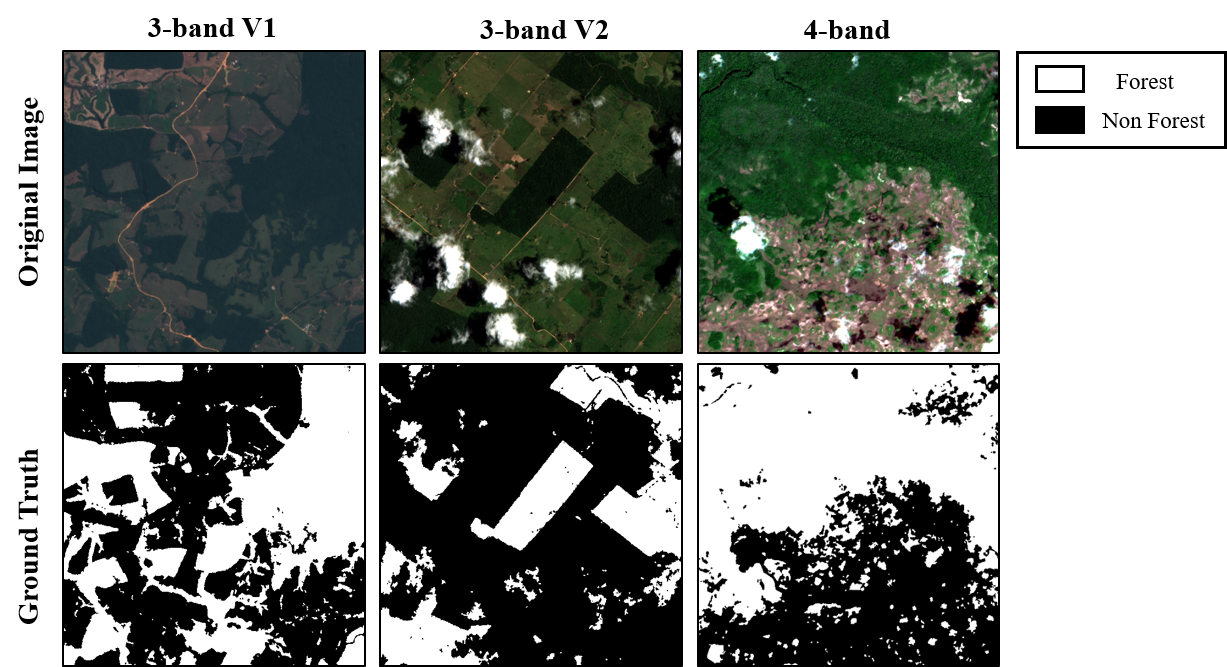
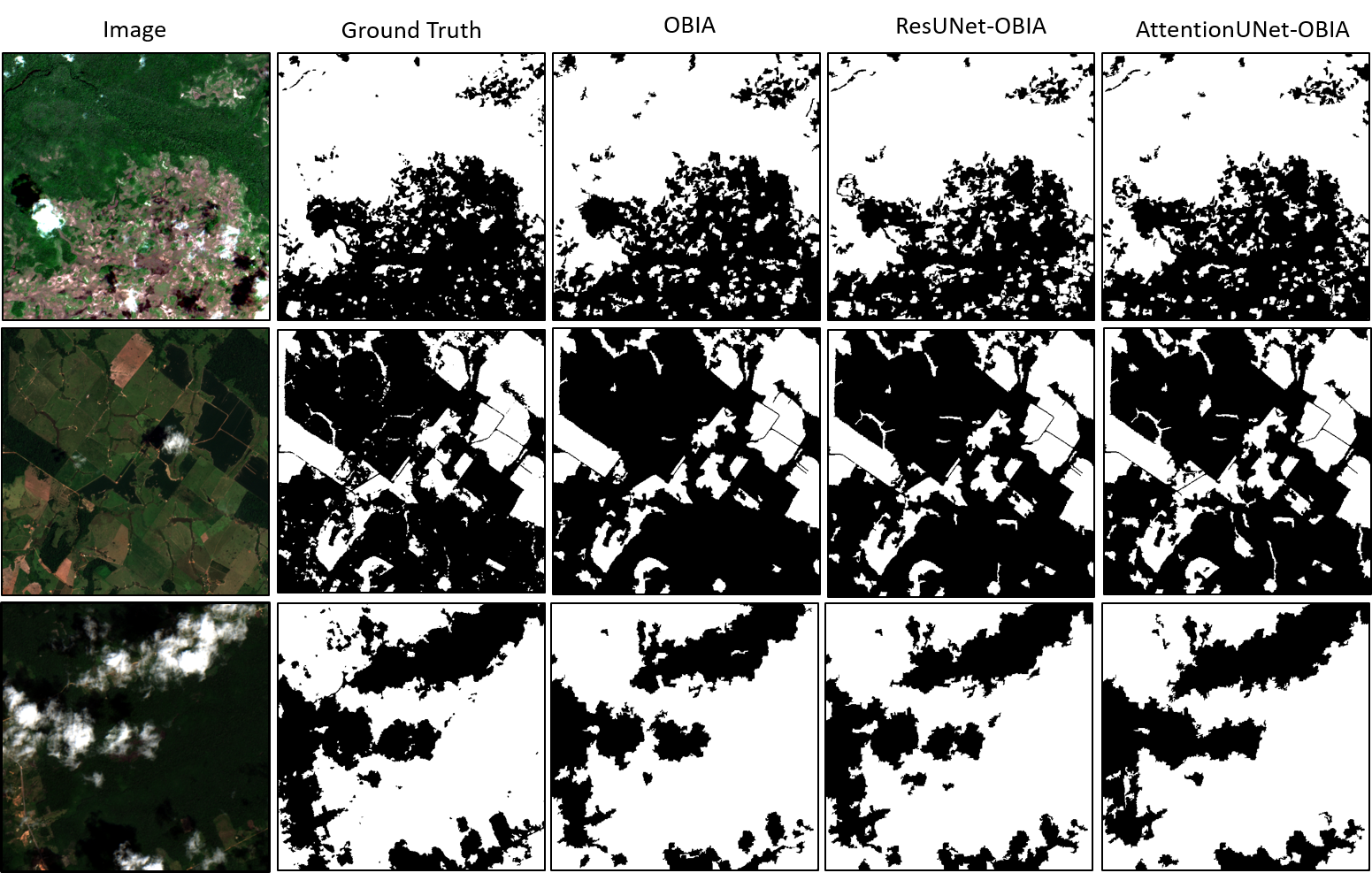
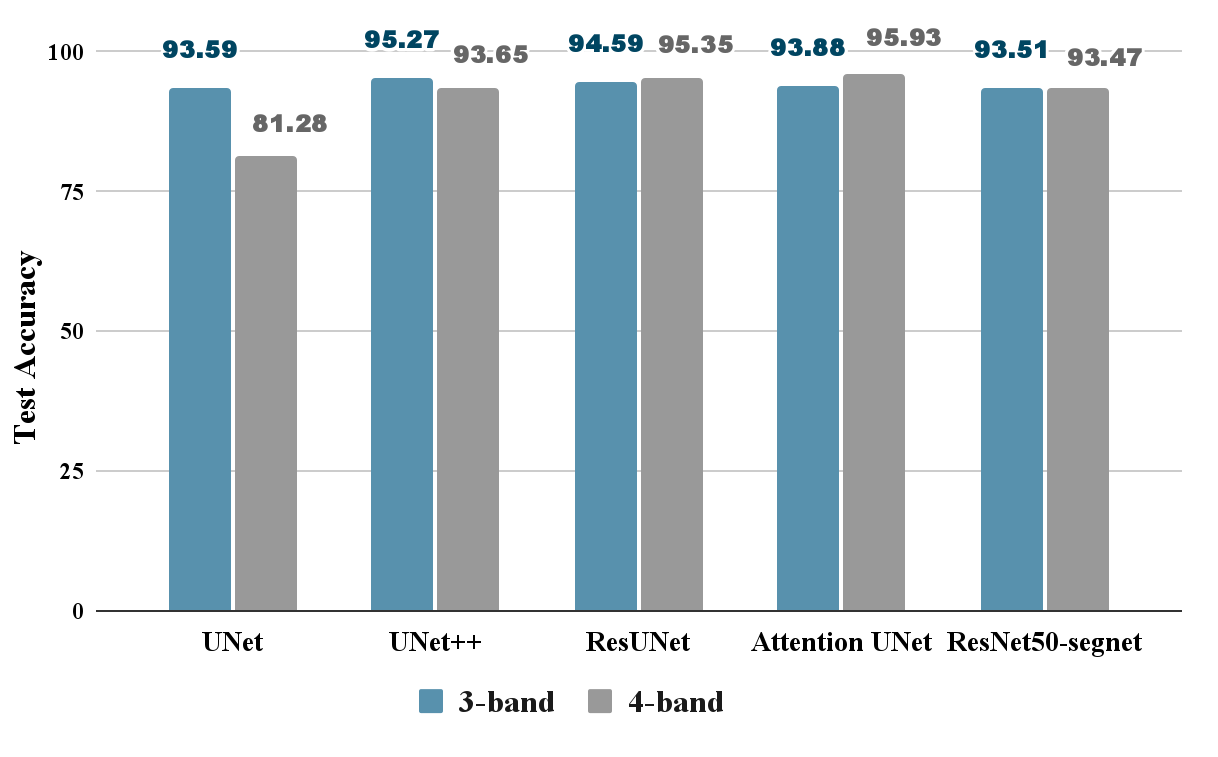
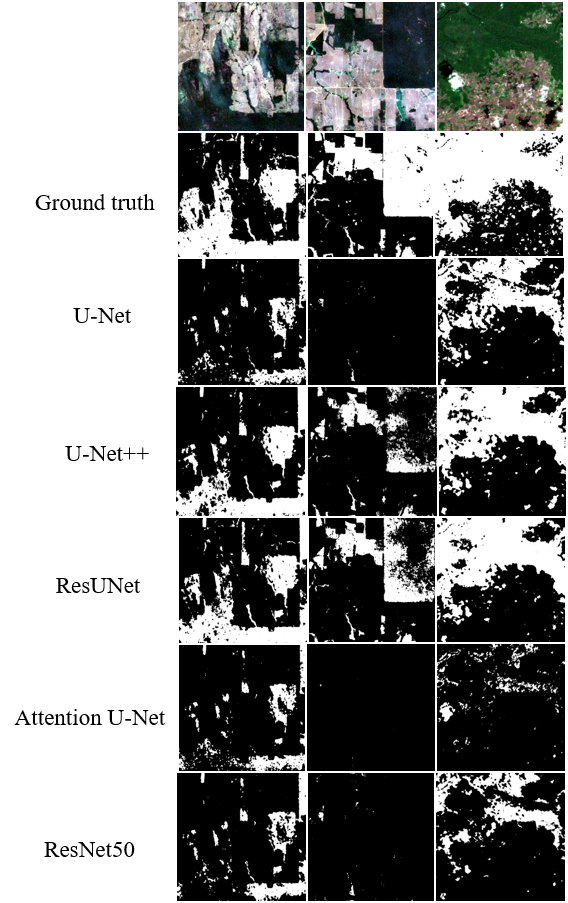
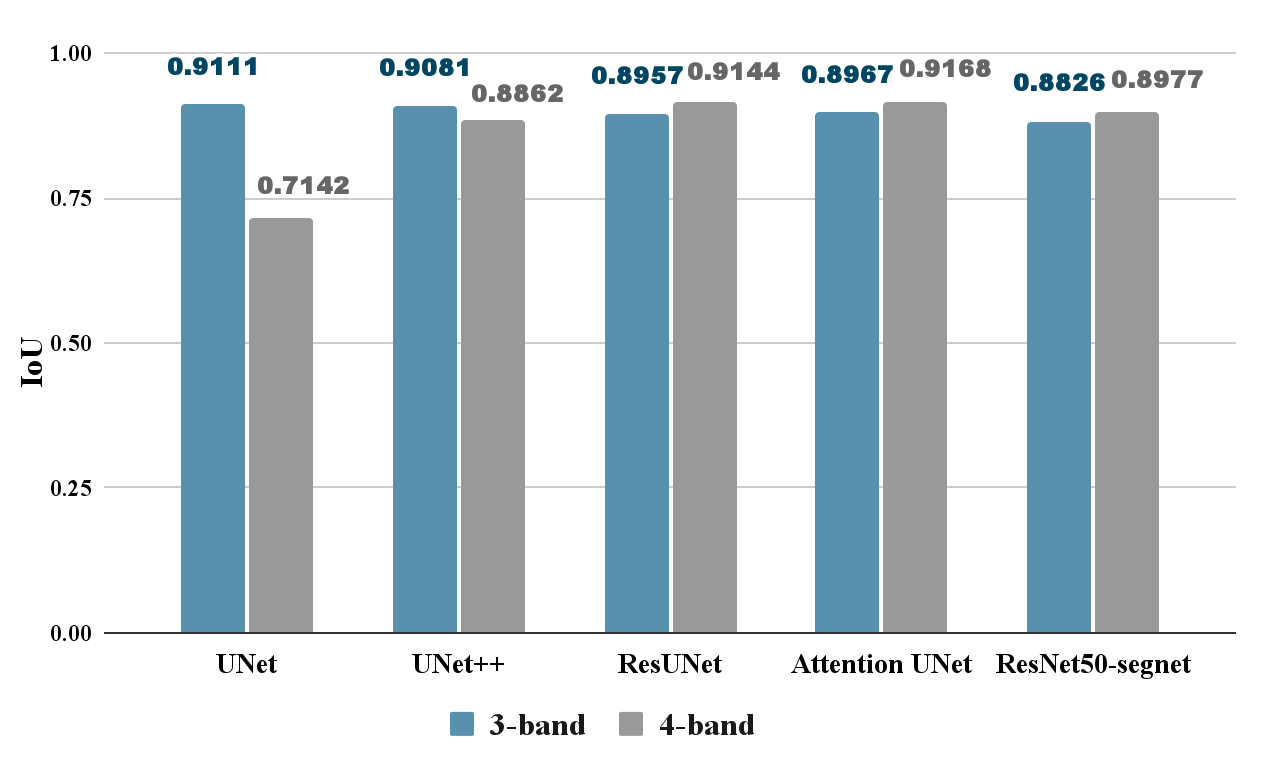
This research proposes "ForCM", a novel approach to forest cover mapping that combines Object-Based Image Analysis (OBIA) with Deep Learning (DL) using multispectral Sentinel-2 imagery. The study explores several DL models, including UNet, UNet++, ResUNet, AttentionUNet, and ResNet50-Segnet, applied to high-resolution Sentinel-2 Level 2A satellite images of the Amazon Rainforest. The datasets comprise three collections: two sets of three-band imagery and one set of four-band imagery. After evaluation, the most effective DL models are individually integrated with the OBIA technique to enhance mapping accuracy. The originality of this work lies in evaluating different deep learning models combined with OBIA and comparing them with traditional OBIA methods. The results show that the proposed ForCM method improves forest cover mapping, achieving overall accuracies of 94.54 percent with ResUNet-OBIA and 95.64 percent with AttentionUNet-OBIA, compared to 92.91 percent using traditional OBIA. This research also demonstrates the potential of free and user-friendly tools such as QGIS for accurate mapping within their limitations, supporting global environmental monitoring and conservation efforts.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Algorithm Performance Evaluation Across Datasets:** This study systematically compares various machine learning algorithms across different datasets to understand which ones are most effective under varying conditions.-
Importance of Algorithm Selection: The research highlights the critical nature of choosing the right algorithm based on dataset characteristics and specific problem requirements.
-
Performance Based on Dataset Size and Complexity: Decision trees work well for small datasets, while random forests excel with large datasets that have many features. SVMs are effective in high-dimensional data scenarios, and neural networks perform best on complex patterns within large-scale datasets.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)