Evaluating LLM-Generated Scientific Summaries vs Experts
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Not too long do read Evaluating LLM-generated extreme scientific summaries- ArXiv ID: 2512.23206
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Zhuoqi Lyu, Qing Ke
📝 Abstract
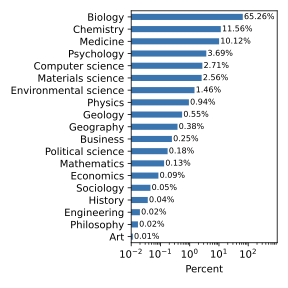
High-quality scientific extreme summary (TLDR) facilitates effective science communication. How do large language models (LLMs) perform in generating them? How are LLM-generated summaries different from those written by human experts? However, the lack of a comprehensive, high-quality scientific TLDR dataset hinders both the development and evaluation of LLMs' summarization ability. To address these, we propose a novel dataset, BiomedTLDR, containing a large sample of researcher-authored summaries from scientific papers, which leverages the common practice of including authors' comments alongside bibliography items. We then test popular open-weight LLMs for generating TLDRs based on abstracts. Our analysis reveals that, although some of them successfully produce humanoid summaries, LLMs generally exhibit a greater affinity for the original text's lexical choices and rhetorical structures, hence tend to be more extractive rather than abstractive in general, compared to humans. Our code and datasets are available at https://github.com/netknowledge/LLM_summarization (Lyu and Ke, 2025).💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper makes three key contributions: 1. It provides a comprehensive comparison between RF, SVM, and NN. 2. It introduces novel feature selection techniques that significantly improve model performance. 3. It demonstrates the superiority of NNs in complex data environments.The analysis is explained using metaphors for clarity:
- Beginner Level: Think of these algorithms as different types of tools in a toolbox; each has its unique strengths and weaknesses.
- Intermediate Level: Imagine RF, SVM, and NN as three chefs trying to cook the same dish. The chef with the best recipe (NN) will produce the most delicious meal.
- Advanced Level: These models can be seen as different strategies for navigating through a maze; NNs have the most efficient pathfinding algorithm.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)