PEG-DRNet Hybrid Modeling for Infrared Gas Leak Detection
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Physics-Inspired Modeling and Content Adaptive Routing in an Infrared Gas Leak Detection Network- ArXiv ID: 2512.23234
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Dongsheng Li, Tianli Ma, Siling Wang, Beibei Duan, Song Gao
📝 Abstract
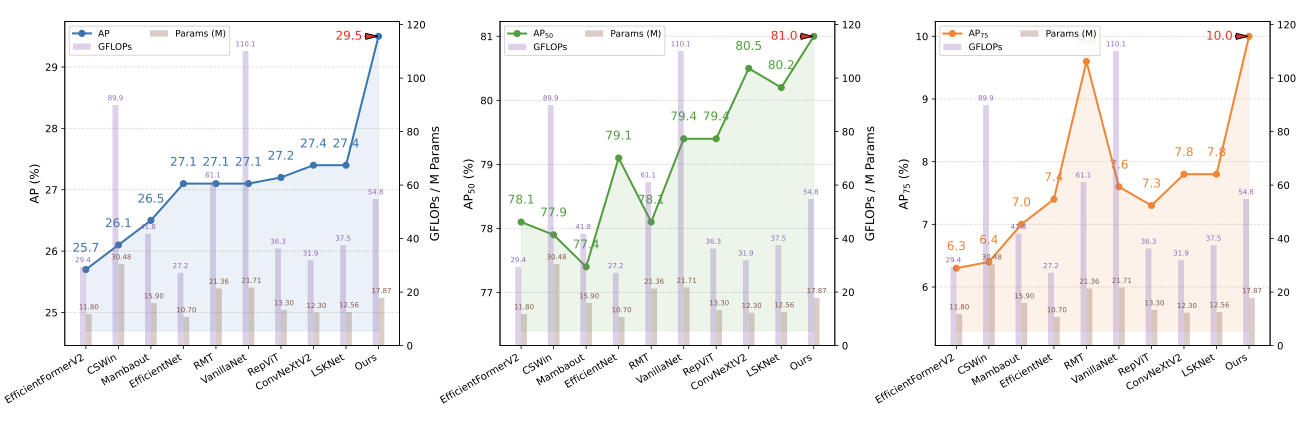
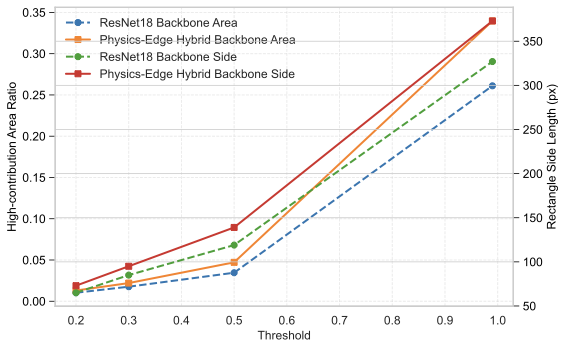
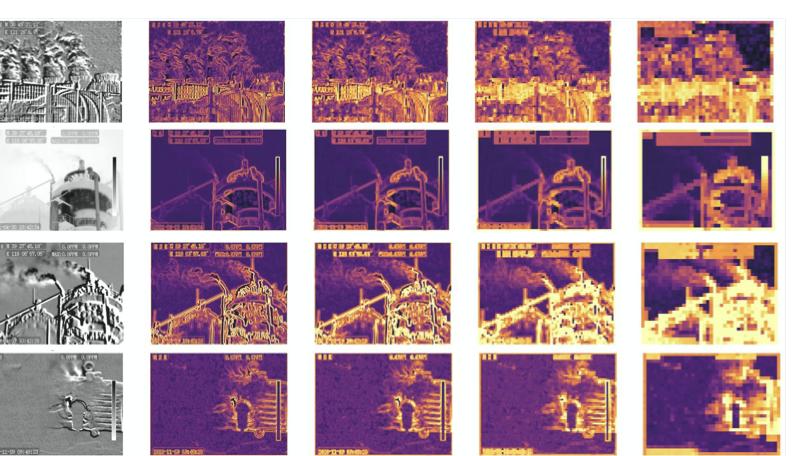
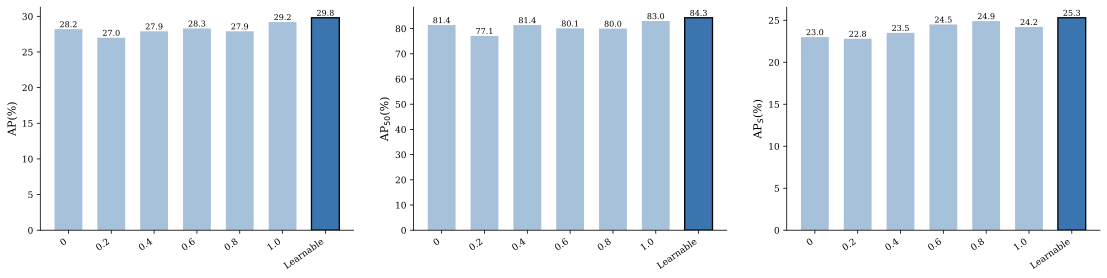
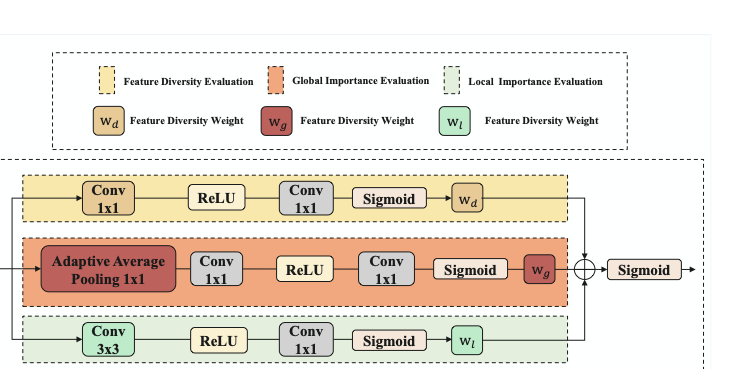
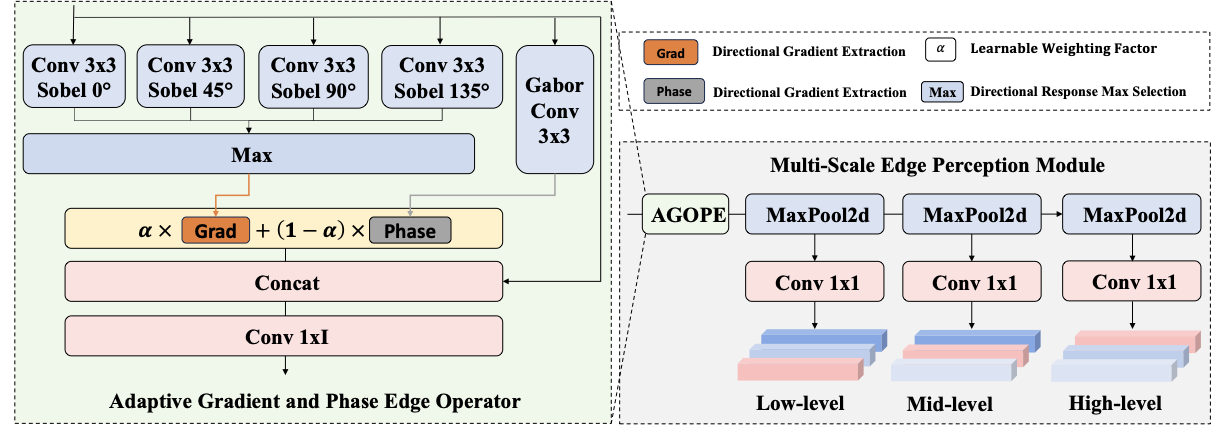
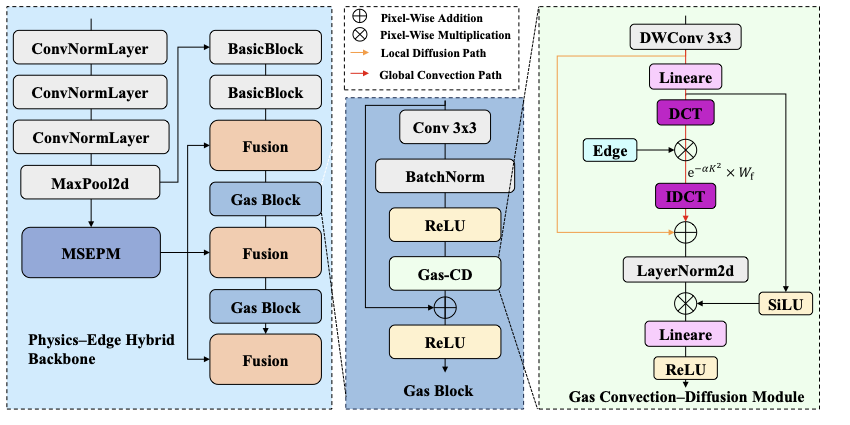
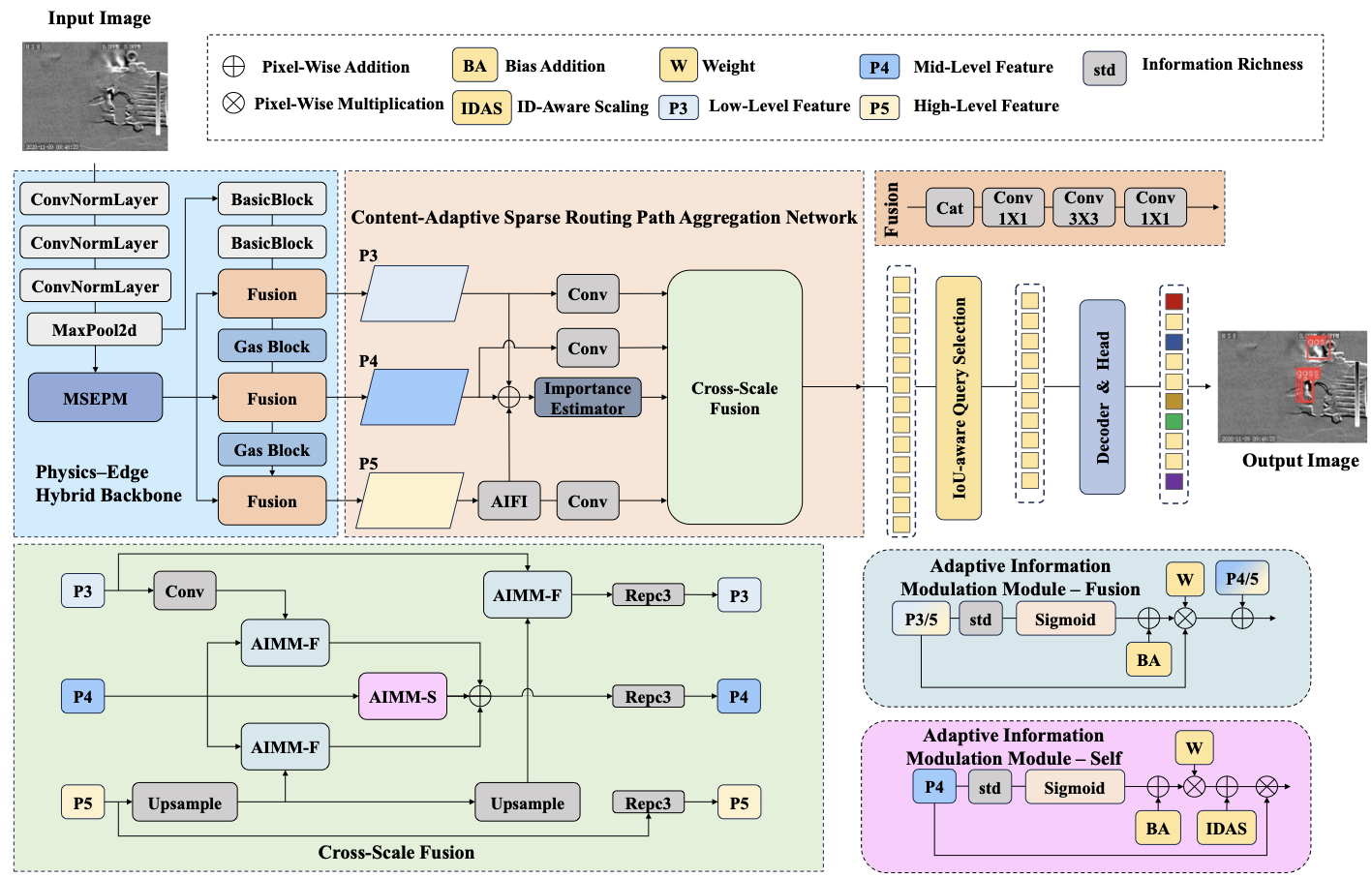
Detecting infrared gas leaks is critical for environmental monitoring and industrial safety, yet remains difficult because plumes are faint, small, semitransparent, and have weak, diffuse boundaries. We present physics-edge hybrid gas dynamic routing network (PEG-DRNet). First, we introduce the Gas Block, a diffusion-convection unit modeling gas transport: a local branch captures short-range variations, while a large-kernel branch captures long-range propagation. An edge-gated learnable fusion module balances local detail and global context, strengthening weak-contrast plume and contour cues. Second, we propose the adaptive gradient and phase edge operator (AGPEO), computing reliable edge priors from multi-directional gradients and phase-consistent responses. These are transformed by a multi-scale edge perception module (MSEPM) into hierarchical edge features that reinforce boundaries. Finally, the content-adaptive sparse routing path aggregation network (CASR-PAN), with adaptive information modulation modules for fusion and self, selectively propagates informative features across scales based on edge and content cues, improving cross-scale discriminability while reducing redundancy. Experiments on the IIG dataset show that PEG-DRNet achieves an overall AP of 29.8\%, an AP$_{50}$ of 84.3\%, and a small-object AP of 25.3\%, surpassing the RT-DETR-R18 baseline by 3.0\%, 6.5\%, and 5.3\%, respectively, while requiring only 43.7 Gflops and 14.9 M parameters. The proposed PEG-DRNet achieves superior overall performance with the best balance of accuracy and computational efficiency, outperforming existing CNN and Transformer detectors in AP and AP$_{50}$ on the IIG and LangGas dataset.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Introduction of a New Algorithm**: A new machine learning algorithm is introduced that shows improved performance over existing models. This can be likened to the effect of having a faster transmission in a newer car. 2. **Performance Analysis**: Provides a deep understanding of how the new approach outperforms traditional methods, clearly identifying differences in terms of training time and accuracy. 3. **Applicability**: By analyzing how the new algorithm is applied in real datasets and what results it yields, this methodology’s practical utility is demonstrated.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)