KernelEvolve Automating DLRM Kernels for AI Heterogeneity
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: KernelEvolve Scaling Agentic Kernel Coding for Heterogeneous AI Accelerators at Meta- ArXiv ID: 2512.23236
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Gang Liao, Hongsen Qin, Ying Wang, Alicia Golden, Michael Kuchnik, Yavuz Yetim, Jia Jiunn Ang, Chunli Fu, Yihan He, Samuel Hsia, Zewei Jiang, Dianshi Li, Uladzimir Pashkevich, Varna Puvvada, Feng Shi, Matt Steiner, Ruichao Xiao, Nathan Yan, Xiayu Yu, Zhou Fang, Roman Levenstein, Kunming Ho, Haishan Zhu, Alec Hammond, Richard Li, Ajit Mathews, Kaustubh Gondkar, Abdul Zainul-Abedin, Ketan Singh, Hongtao Yu, Wenyuan Chi, Barney Huang, Sean Zhang, Noah Weller, Zach Marine, Wyatt Cook, Carole-Jean Wu, Gaoxiang Liu
📝 Abstract
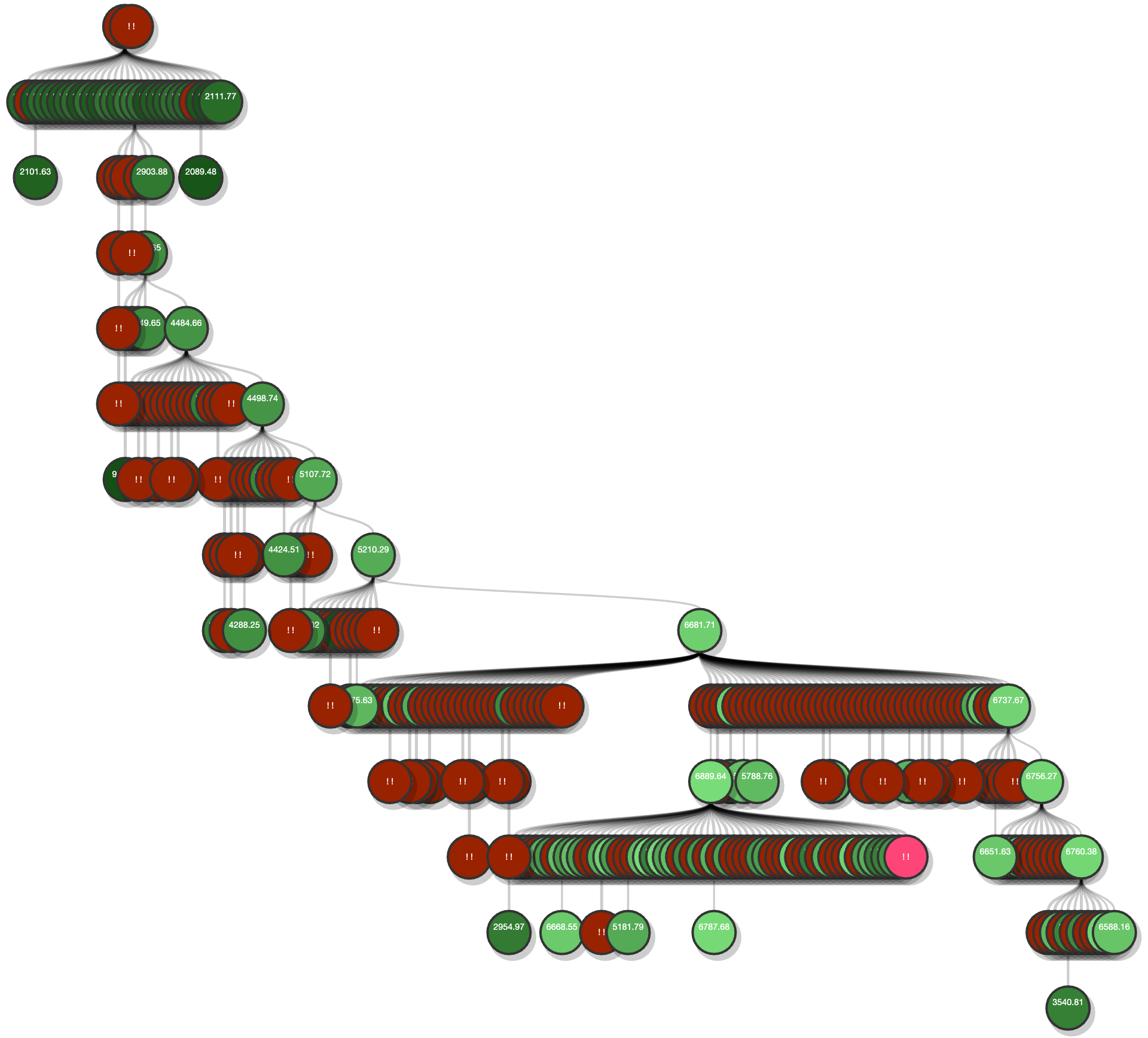
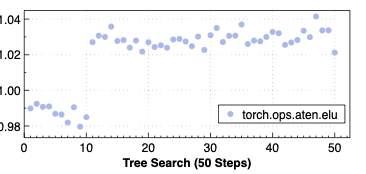
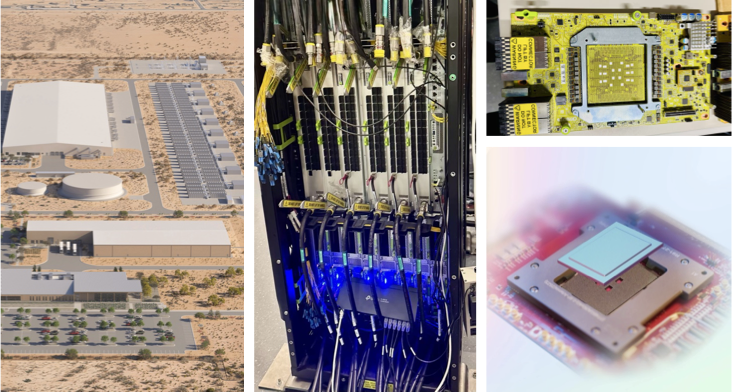
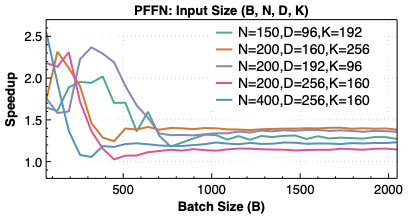
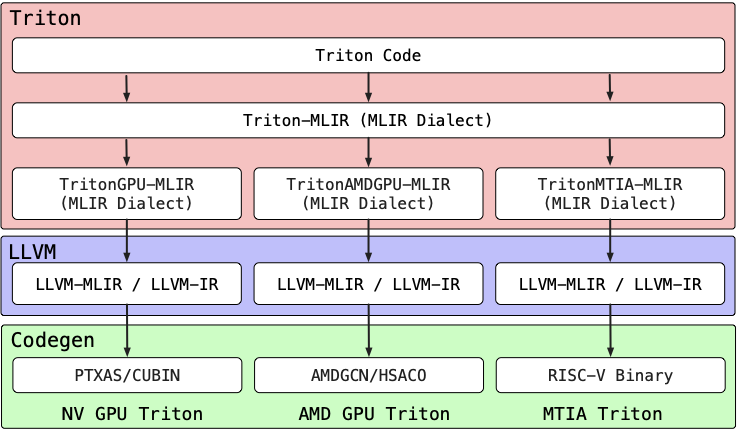
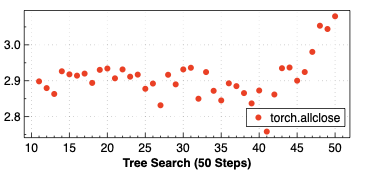
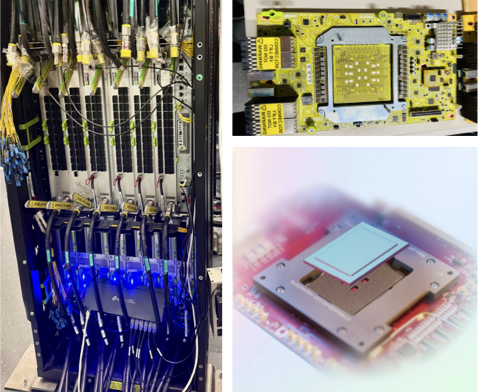
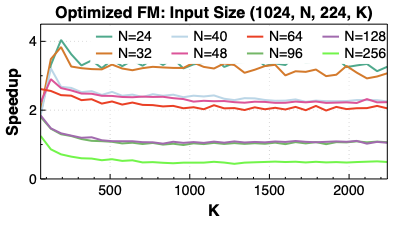
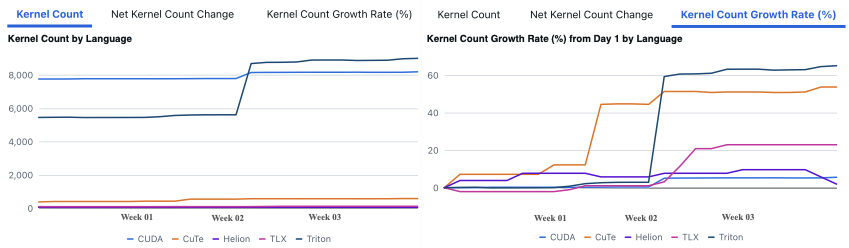
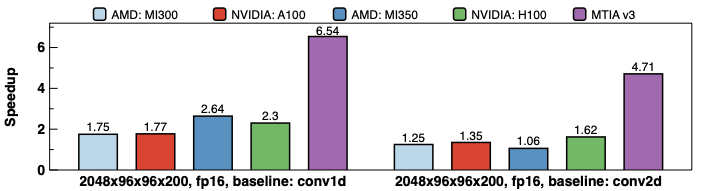
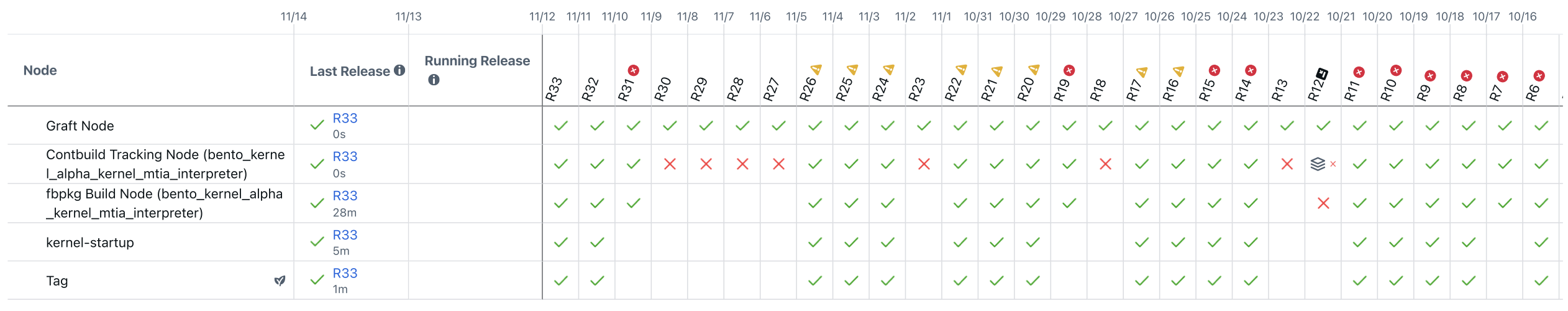
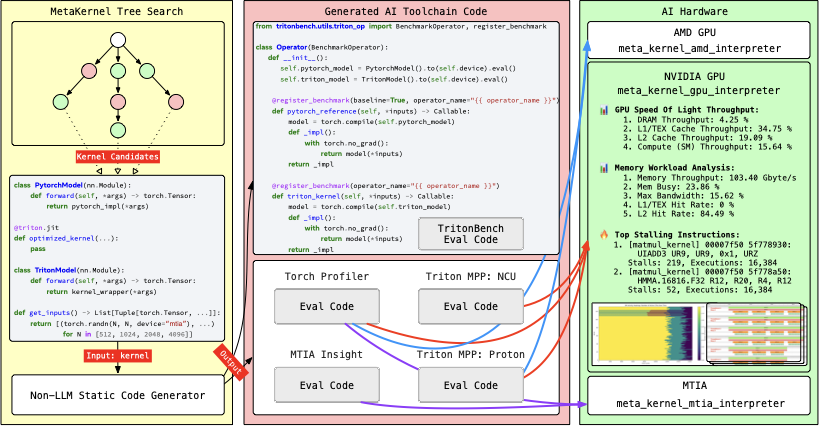
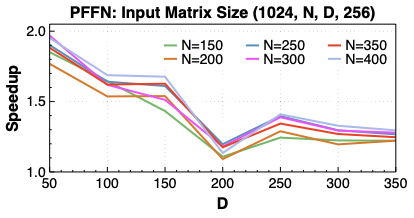
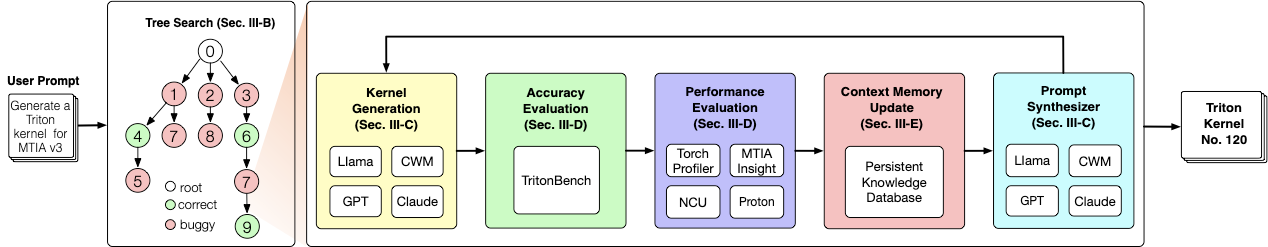
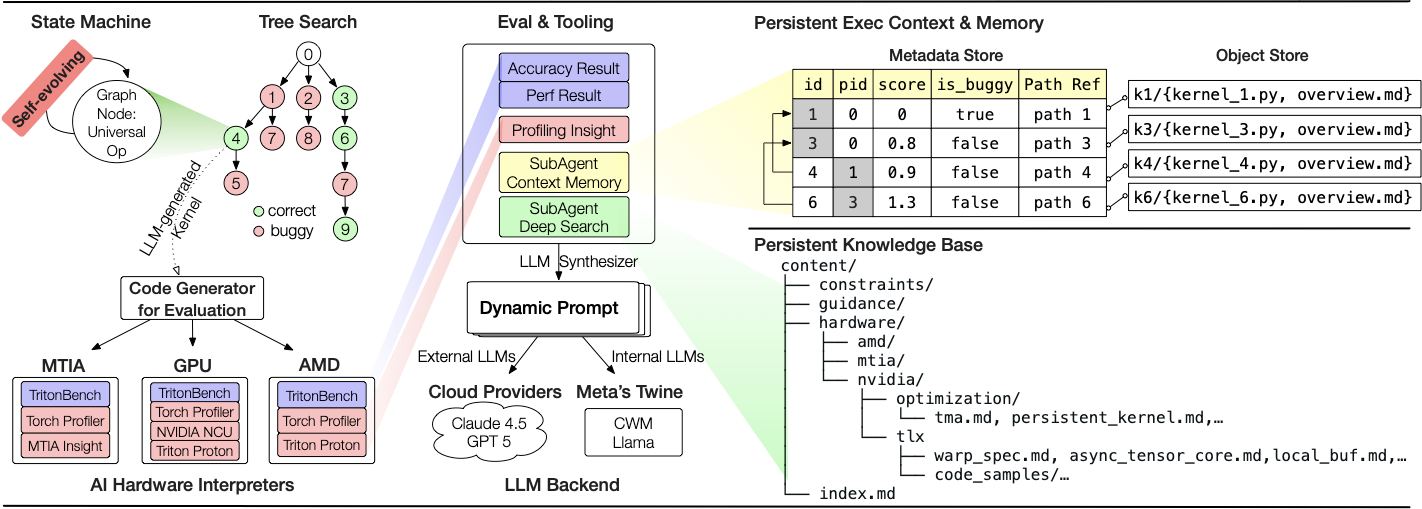
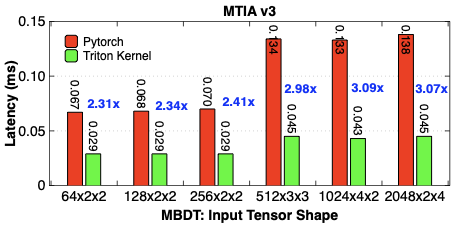
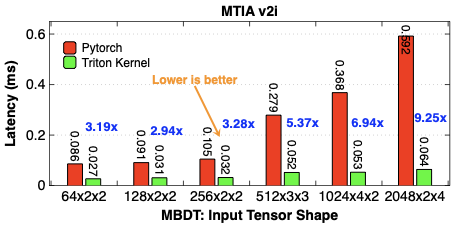
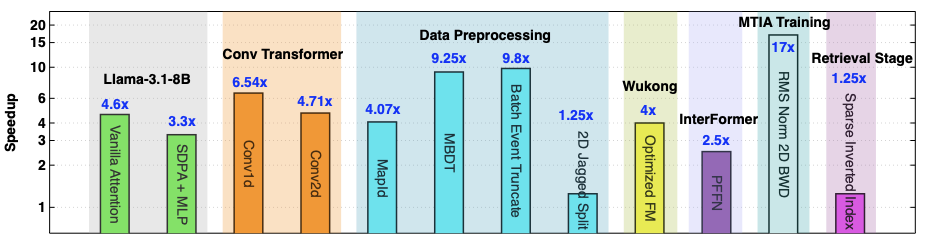
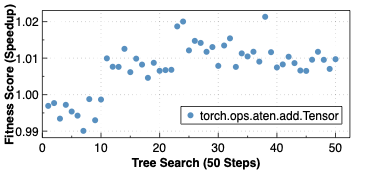
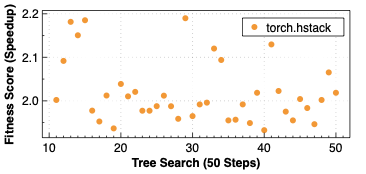
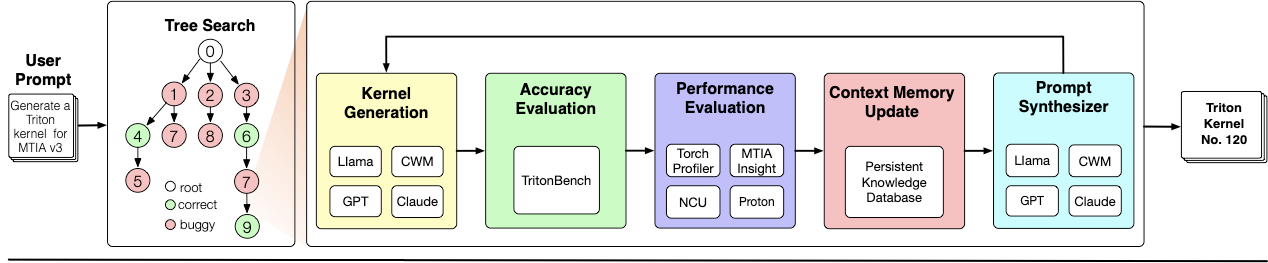
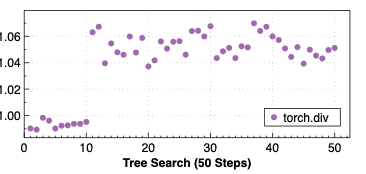
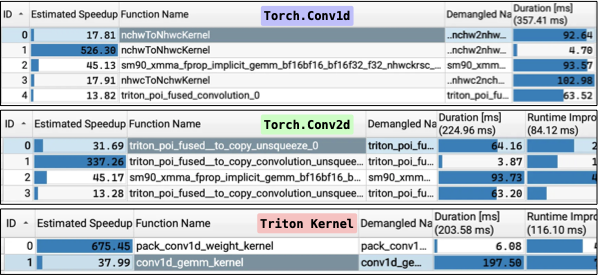
Making deep learning recommendation model (DLRM) training and inference fast and efficient is important. However, this presents three key system challenges - model architecture diversity, kernel primitive diversity, and hardware generation and architecture heterogeneity. This paper presents KernelEvolve-an agentic kernel coding framework-to tackle heterogeneity at-scale for DLRM. KernelEvolve is designed to take kernel specifications as input and automate the process of kernel generation and optimization for recommendation model across heterogeneous hardware architectures. KernelEvolve does so by operating at multiple programming abstractions, from Triton and CuTe DSL to low-level hardware agnostic languages, spanning the full hardware-software optimization stack. The kernel optimization process is described as graph-based search with selection policy, universal operator, fitness function, and termination rule, dynamically adapts to runtime execution context through retrieval-augmented prompt synthesis. We designed, implemented, and deployed KernelEvolve to optimize a wide variety of production recommendation models across generations of NVIDIA and AMD GPUs, as well as Meta's AI accelerators. We validate KernelEvolve on the publicly-available KernelBench suite, achieving 100% pass rate on all 250 problems across three difficulty levels, and 160 PyTorch ATen operators across three heterogeneous hardware platforms, demonstrating 100% correctness. KernelEvolve reduces development time from weeks to hours and achieves substantial performance improvements over PyTorch baselines across diverse production use cases and for heterogeneous AI systems at-scale. Beyond performance efficiency improvements, KernelEvolve significantly mitigates the programmability barrier for new AI hardware by enabling automated kernel generation for in-house developed AI hardware.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Effectiveness of Various Regularization Techniques**: This research analyzes how different regularization methods like dropout and L1/L2 affect deep neural network performance. 2. **Understanding Differences Across Datasets**: By comparing these techniques across various datasets, the study aims to identify which method is most effective for specific problems. 3. **Improving Model Generalization**: One of the primary goals is to enhance a model's ability to perform well on unseen data.(Simple Explanation with Metaphors: Regularization techniques help prevent overfitting in neural networks. Dropout can be likened to excluding some test questions, randomly deactivating neurons to reduce complexity. L1/L2 regularization is like preventing students from studying too much by regulating weights to improve generalization.)
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)