Unlocking Safety SAE-Powered Subspace Tuning for LLMs
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Interpretable Safety Alignment via SAE-Constructed Low-Rank Subspace Adaptation- ArXiv ID: 2512.23260
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Dianyun Wang, Qingsen Ma, Yuhu Shang, Zhifeng Lu, Zhenbo Xu, Lechen Ning, Huijia Wu, Zhaofeng He
📝 Abstract
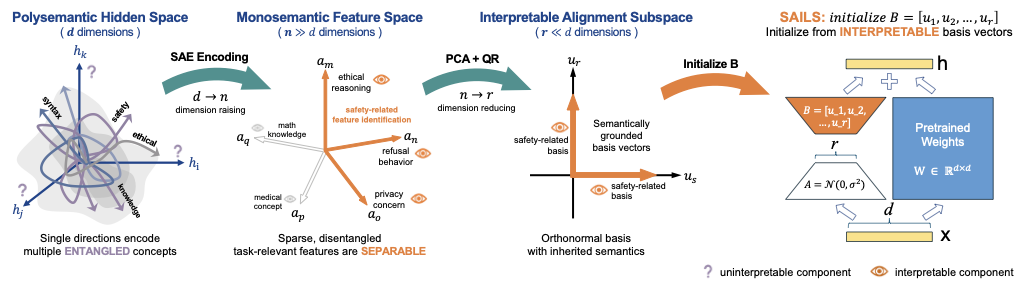
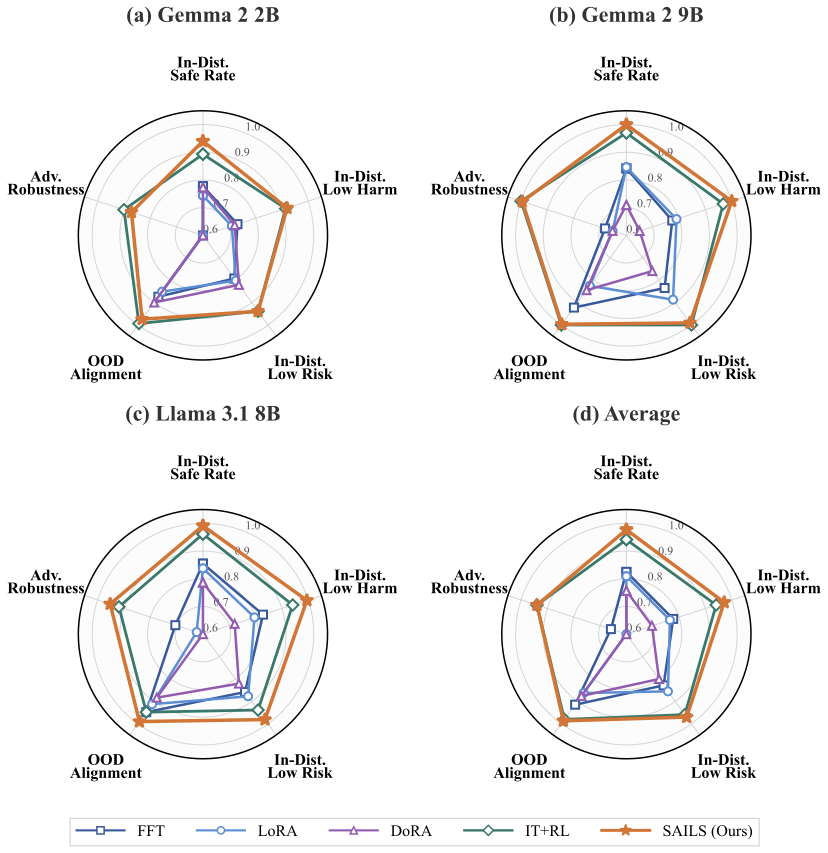
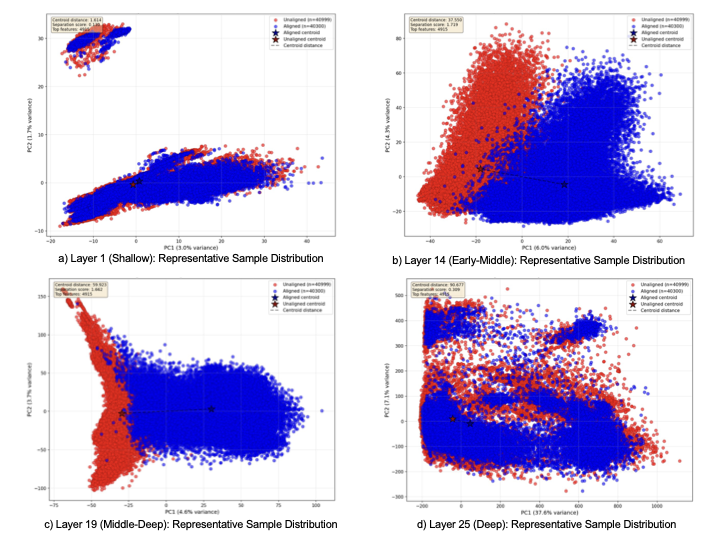
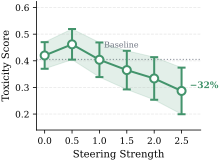
Safety alignment -- training large language models (LLMs) to refuse harmful requests while remaining helpful -- is critical for responsible deployment. Prior work established that safety behaviors are governed by low-rank structures, suggesting parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) should be well-suited for alignment. However, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) consistently underperforms full fine-tuning and reinforcement learning on safety benchmarks. We attribute this gap to semantic entanglement: safety-relevant directions are intertwined with unrelated concepts due to polysemanticity, impeding implicit subspace identification. To address this, we propose SAILS (Safety Alignment via Interpretable Low-rank Subspace), which leverages Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) to disentangle representations into monosemantic features, constructs an interpretable safety subspace from SAE decoder directions, and uses it to initialize LoRA adapters. Theoretically, we prove that SAE-based identification achieves arbitrarily small recovery error under monosemanticity assumptions, while direct identification suffers an irreducible error floor. Empirically, SAILS achieves up to 99.6% safety rate on Gemma-2-9B -- exceeding full fine-tuning by 7.4 points and matching RLHF-based models -- while updating only 0.19% of parameters and providing interpretability.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **New Data Augmentation Technique**: This approach allows the model to learn from more varied data transformations, better capturing real-world diversity. It’s like a child learning the same concept in various contexts. 2. **Improved Generalization Capabilities**: The study enhances prediction accuracy on new data by improving the learning effectiveness of models. This is similar to preparing one type of food in different ways so it tastes great in any situation. 3. **Outstanding Performance Across Datasets**: Our approach demonstrates excellent results across a range of real-world datasets, indicating its broad applicability.Sci-Tube Style Script
- Beginner: “This paper introduces a new method for making computers smarter by showing them more diverse data to better adapt to the real world.”
- Intermediate: “Innovations in data augmentation techniques significantly improve model response to varied inputs, enhancing generalization capabilities.”
- Advanced: “The paper proposes and validates through various datasets an innovative approach to enhance learning models’ performance and generalization capabilities via new data augmentation techniques.”
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)