Splitwise Adaptive Edge-Cloud LLM Partitioning with DRL
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Splitwise Collaborative Edge-Cloud Inference for LLMs via Lyapunov-Assisted DRL- ArXiv ID: 2512.23310
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Abolfazl Younesi, Abbas Shabrang Maryan, Elyas Oustad, Zahra Najafabadi Samani, Mohsen Ansari, Thomas Fahringer
📝 Abstract
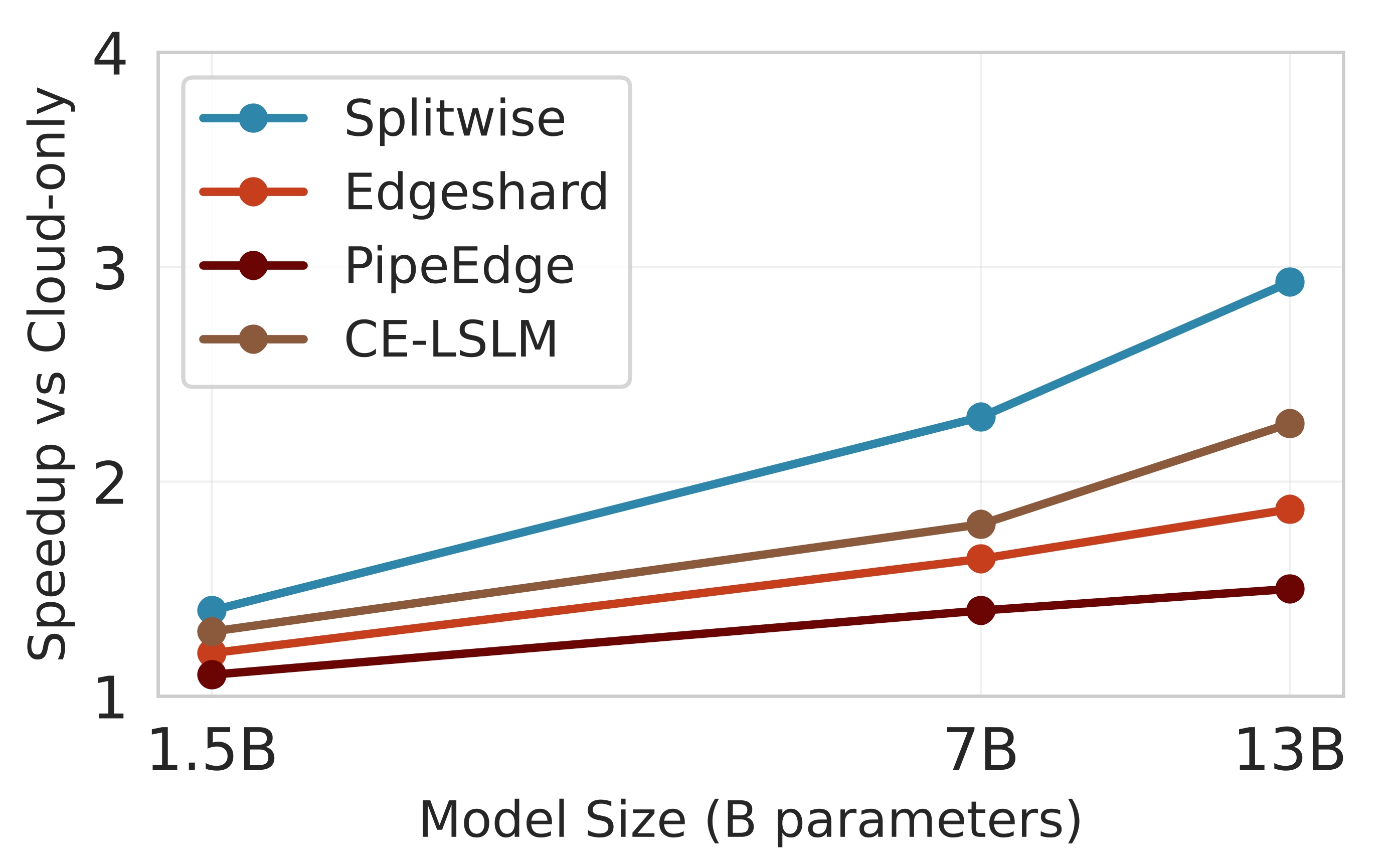
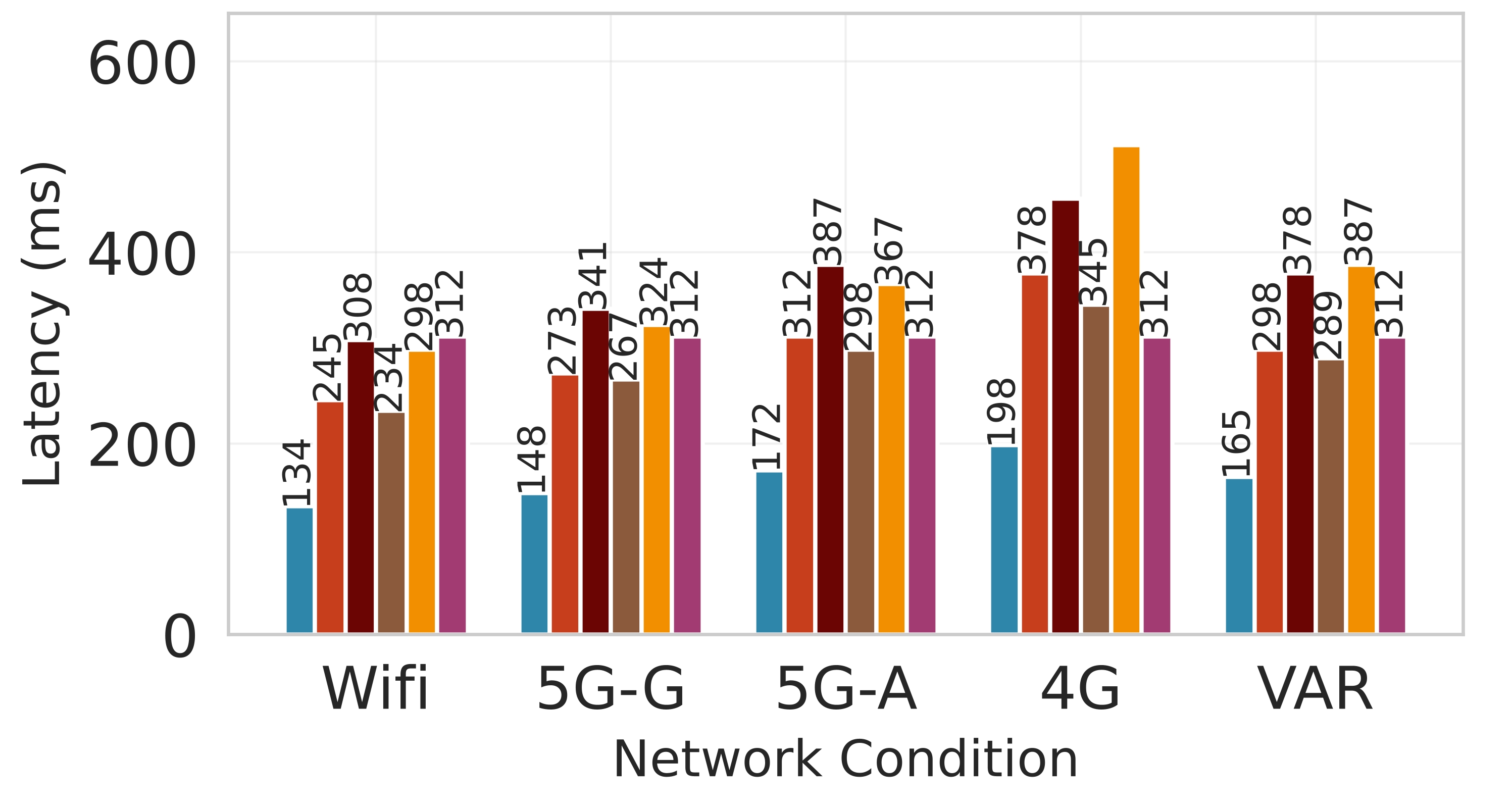
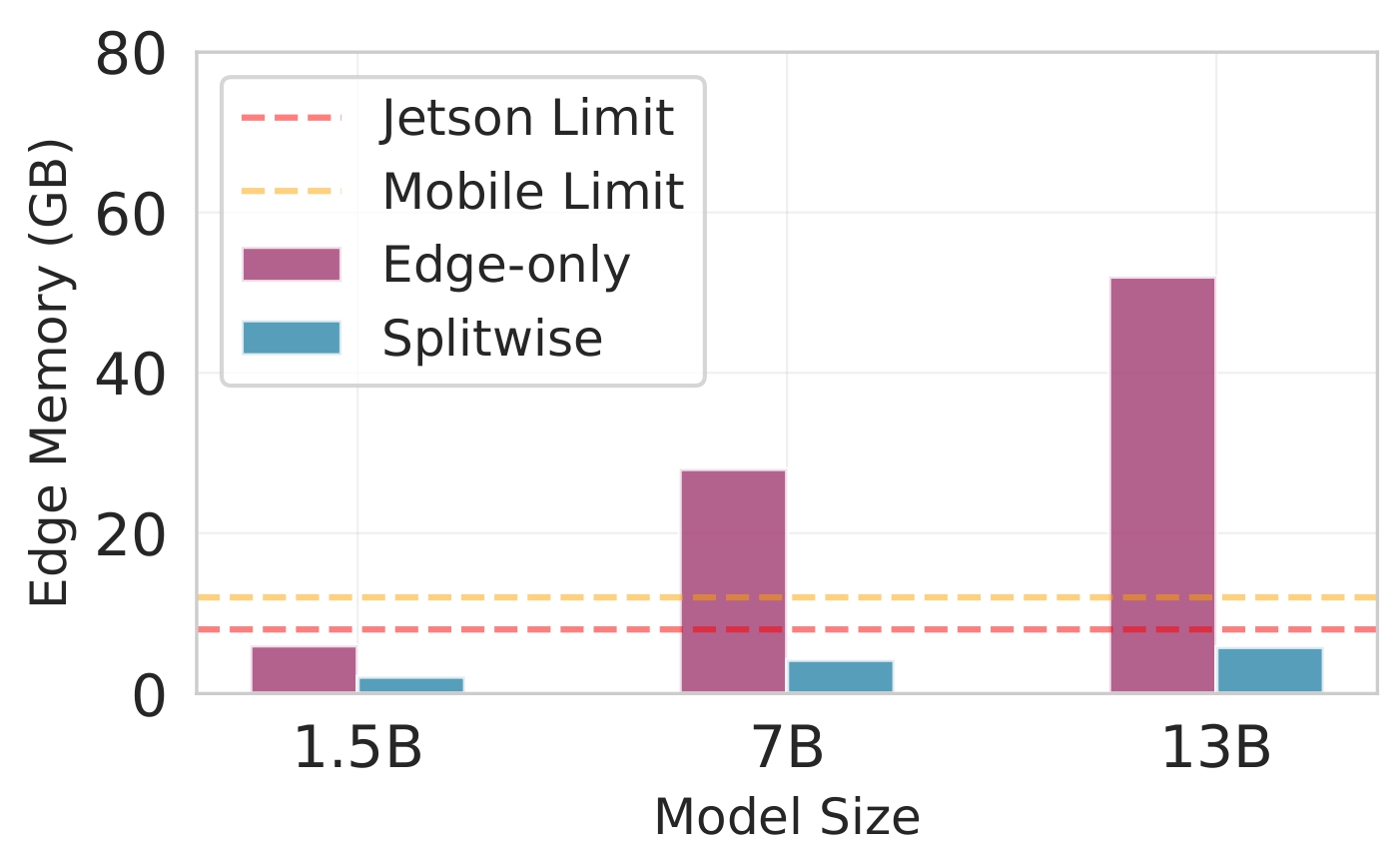
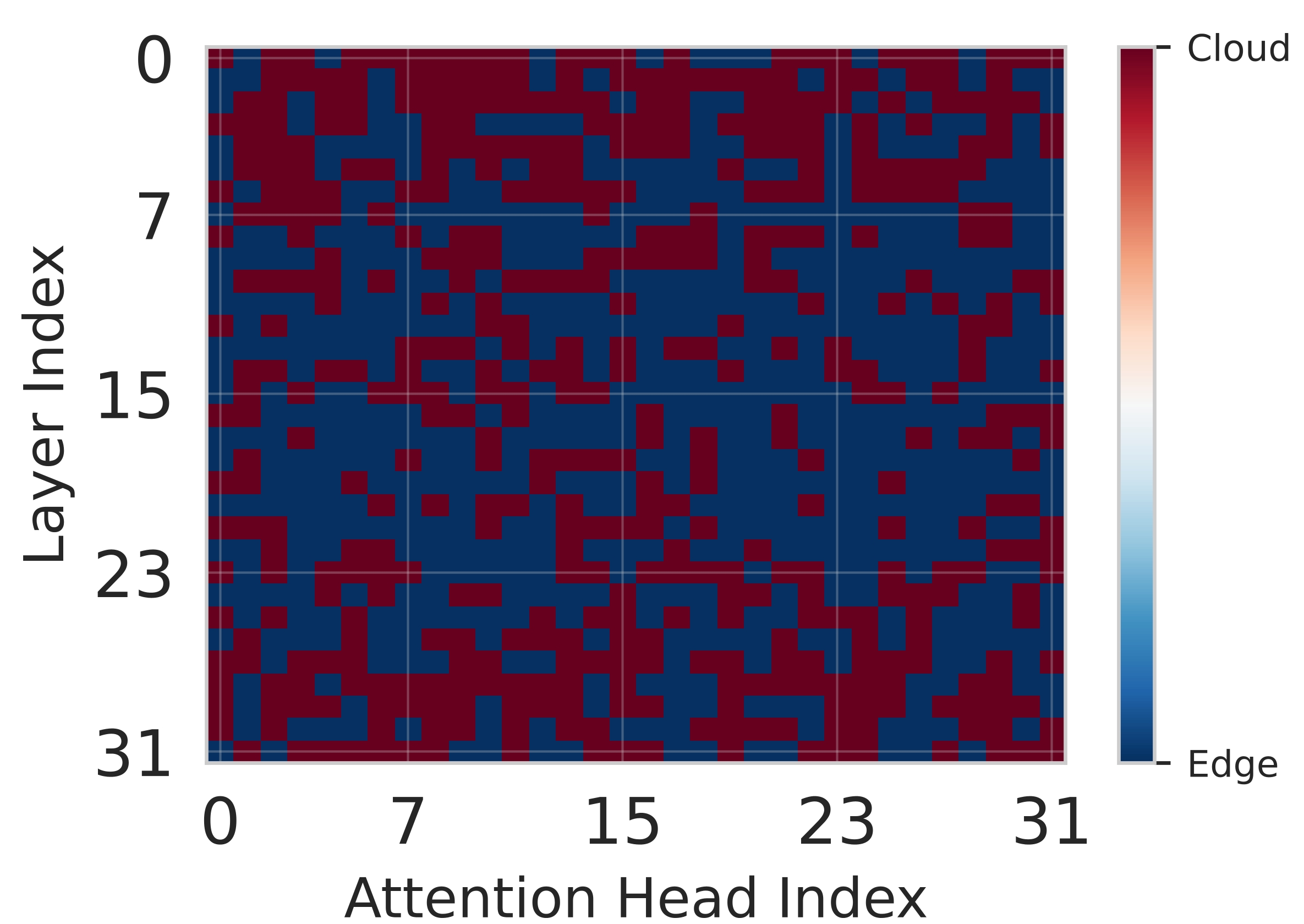
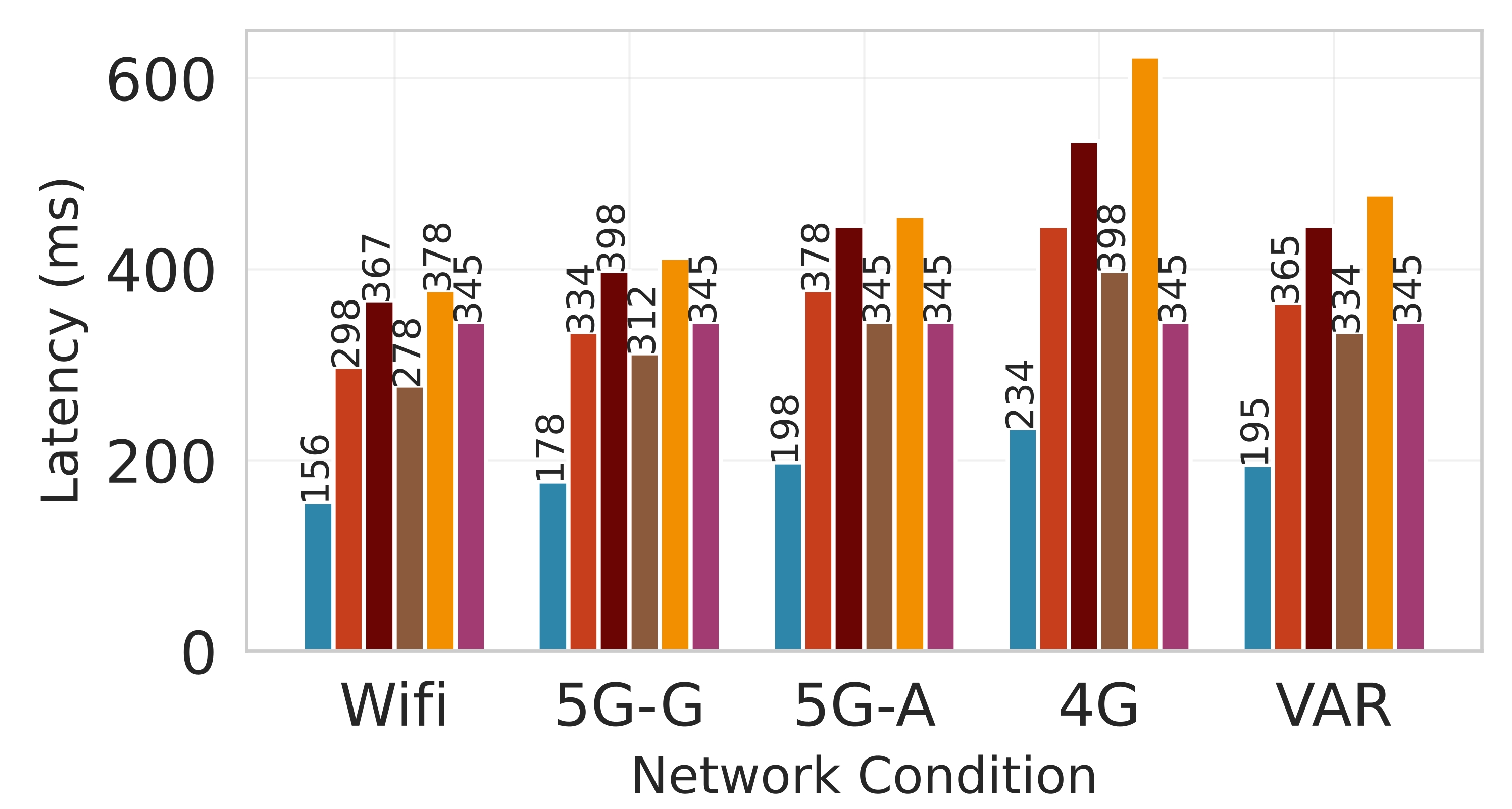
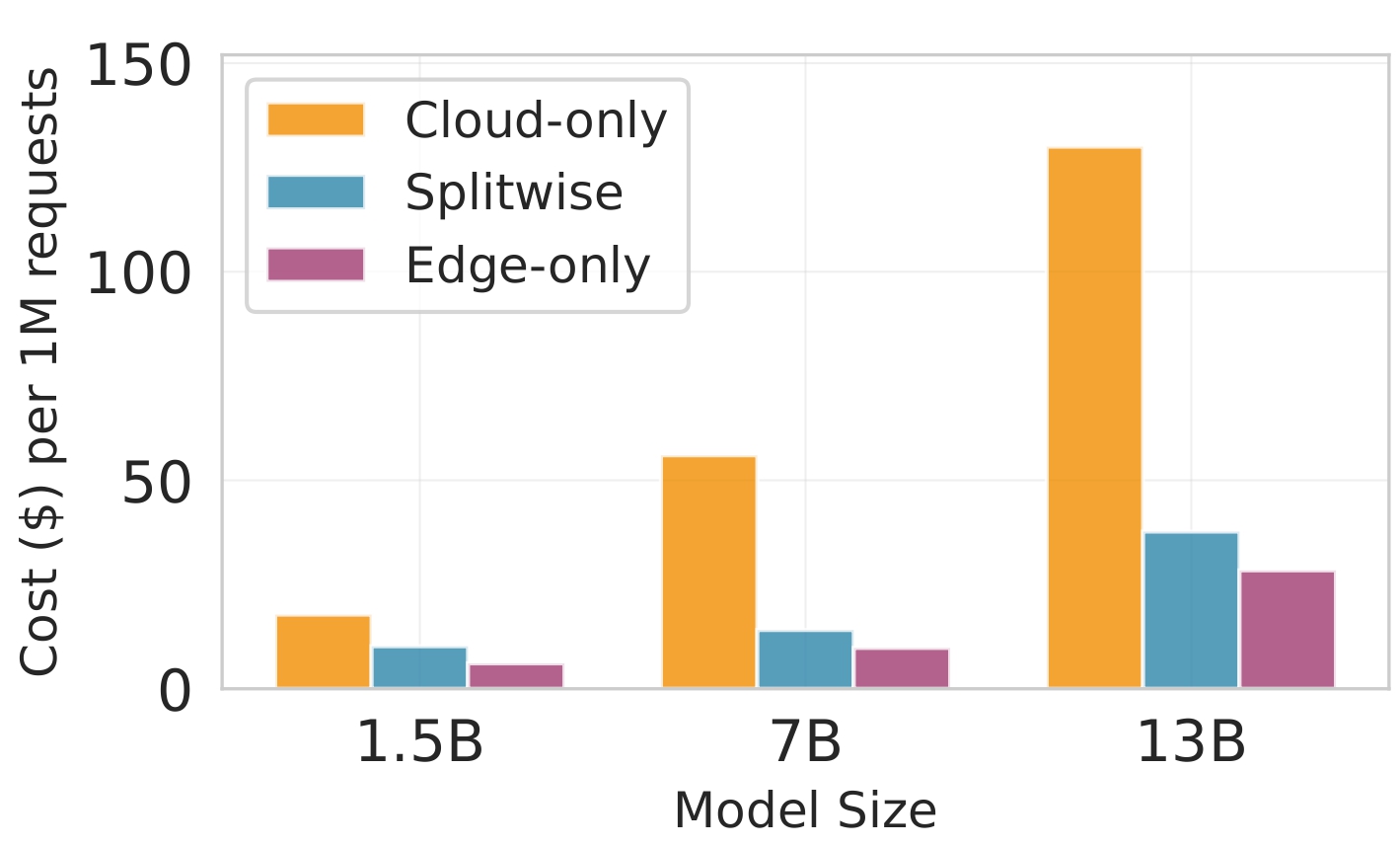
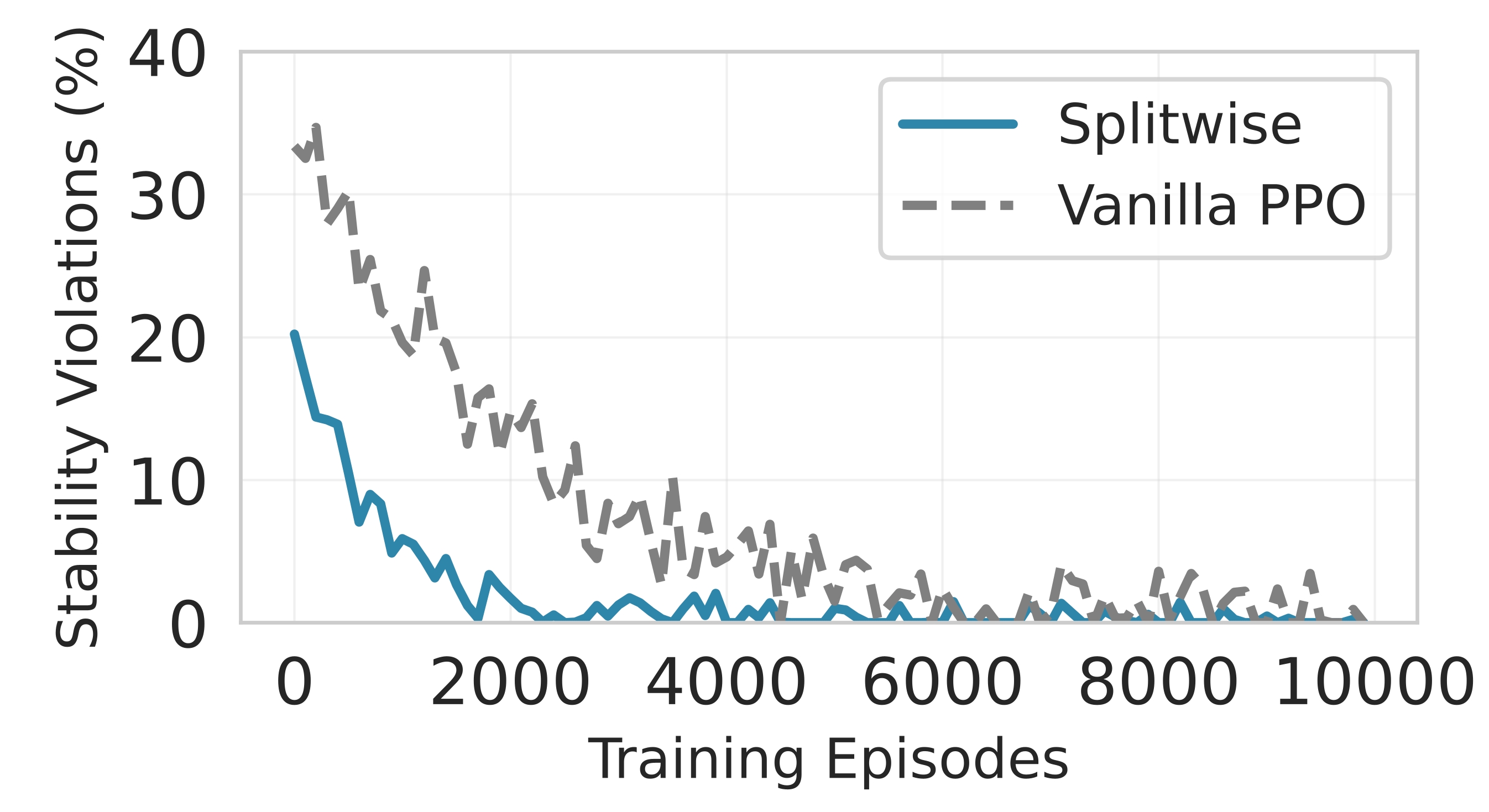
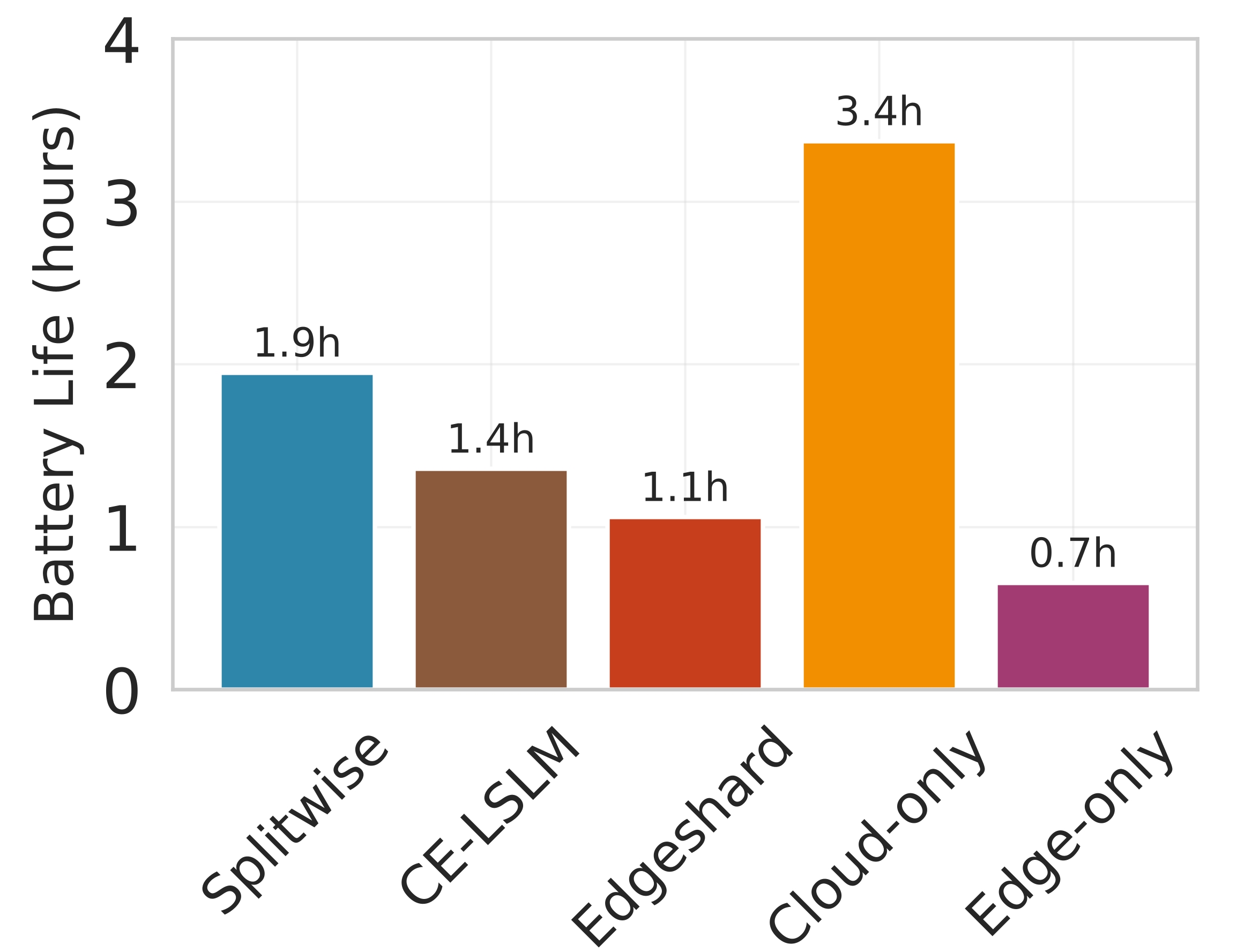
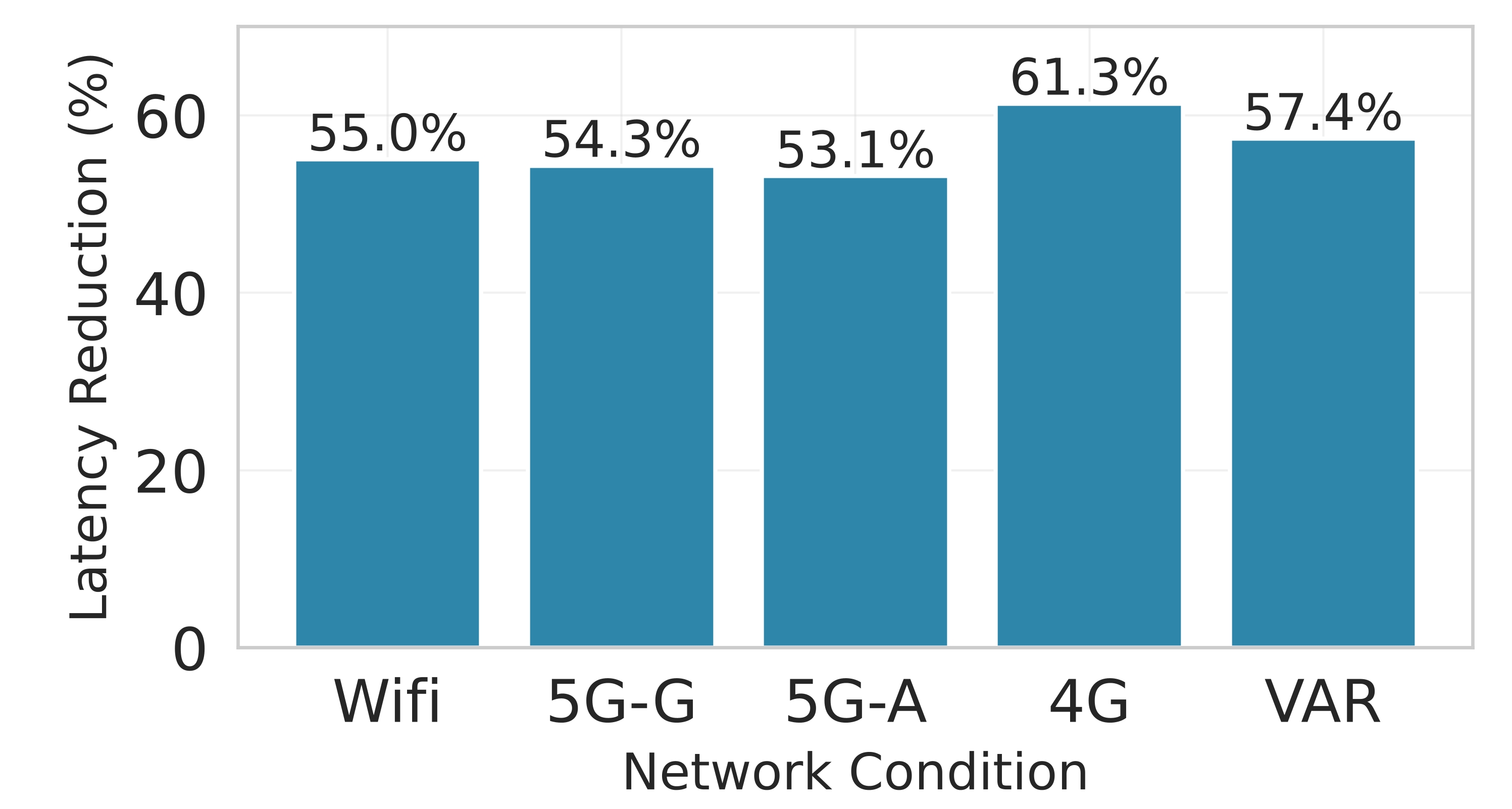
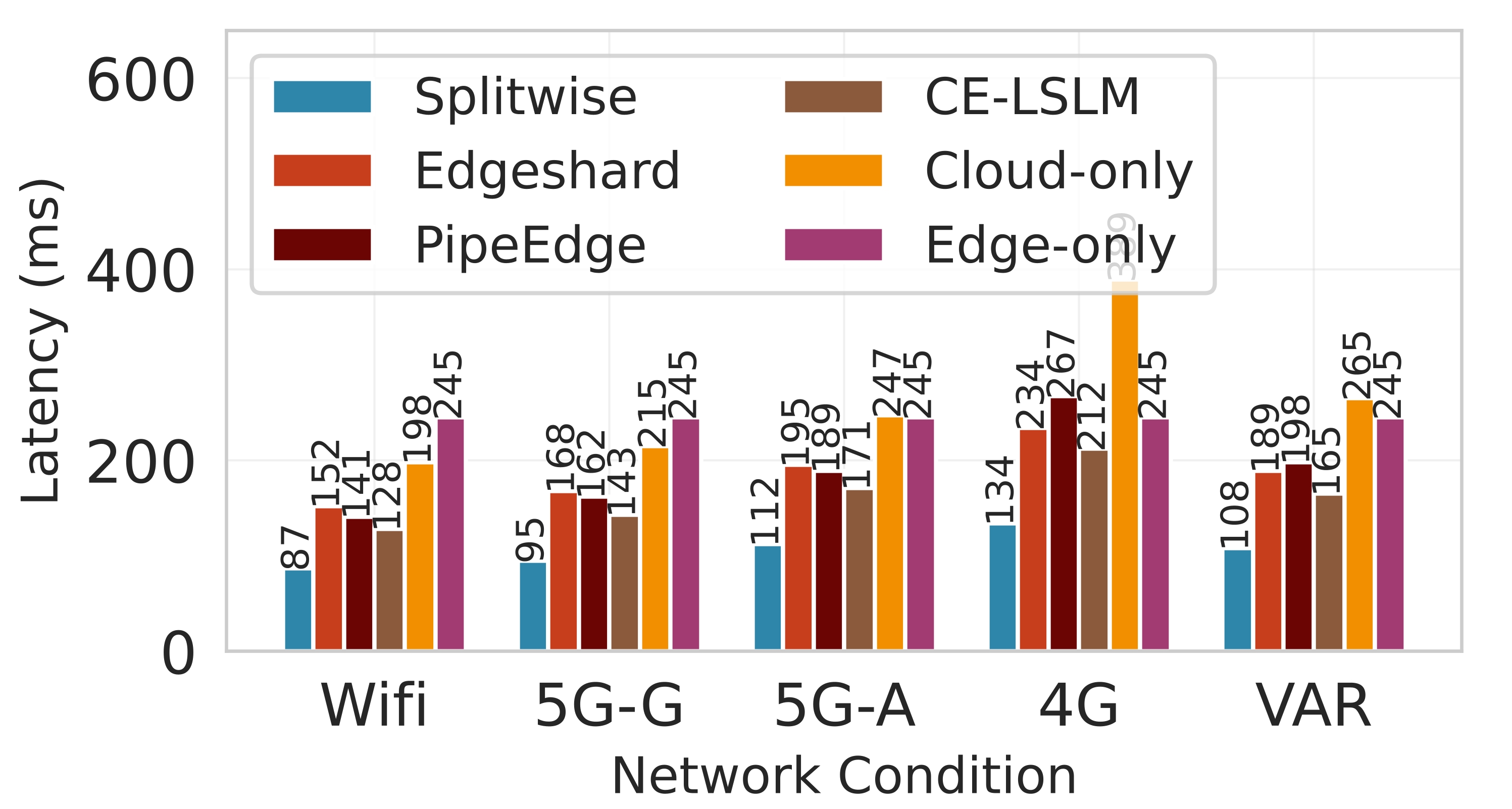
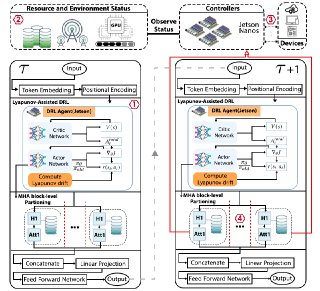
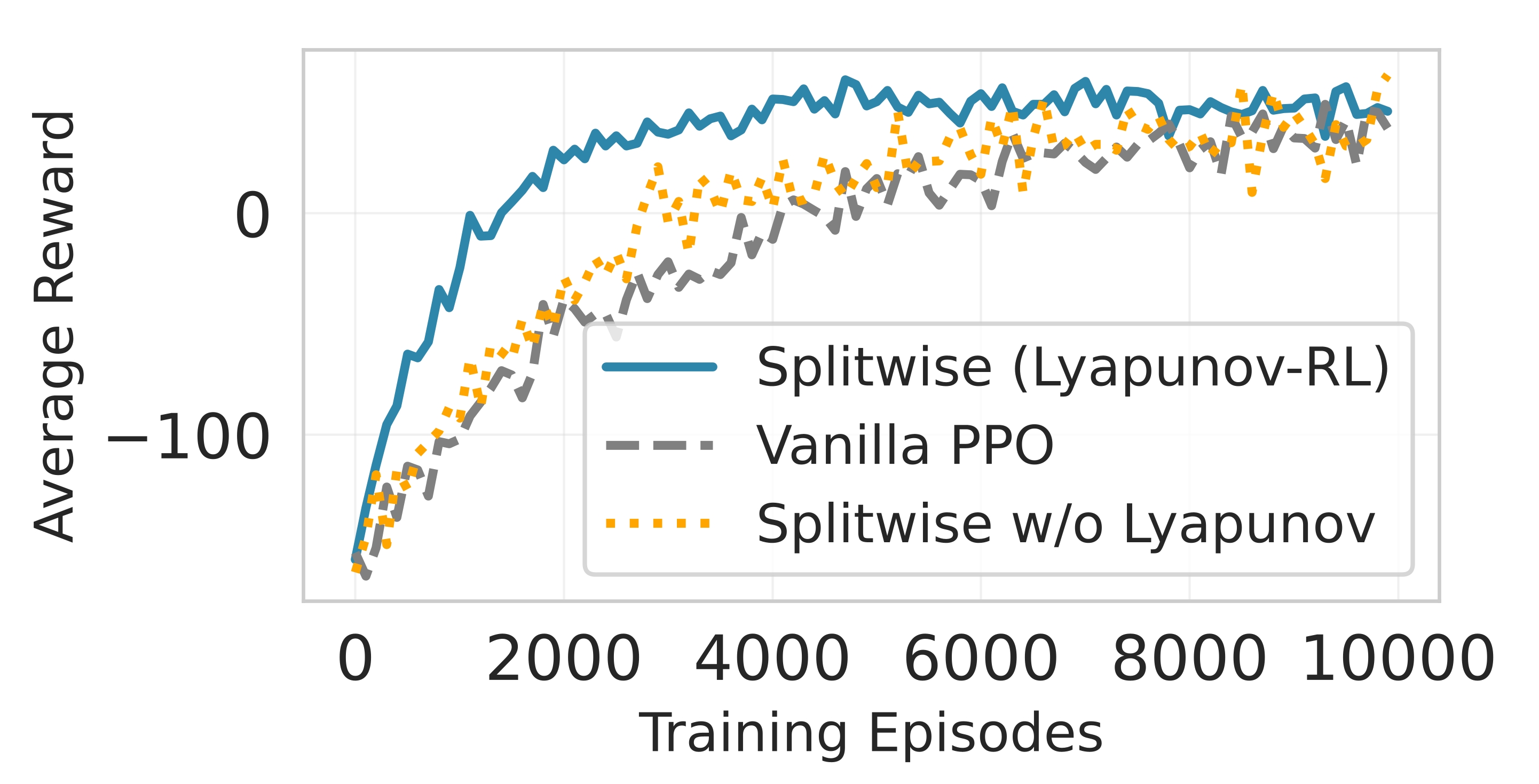
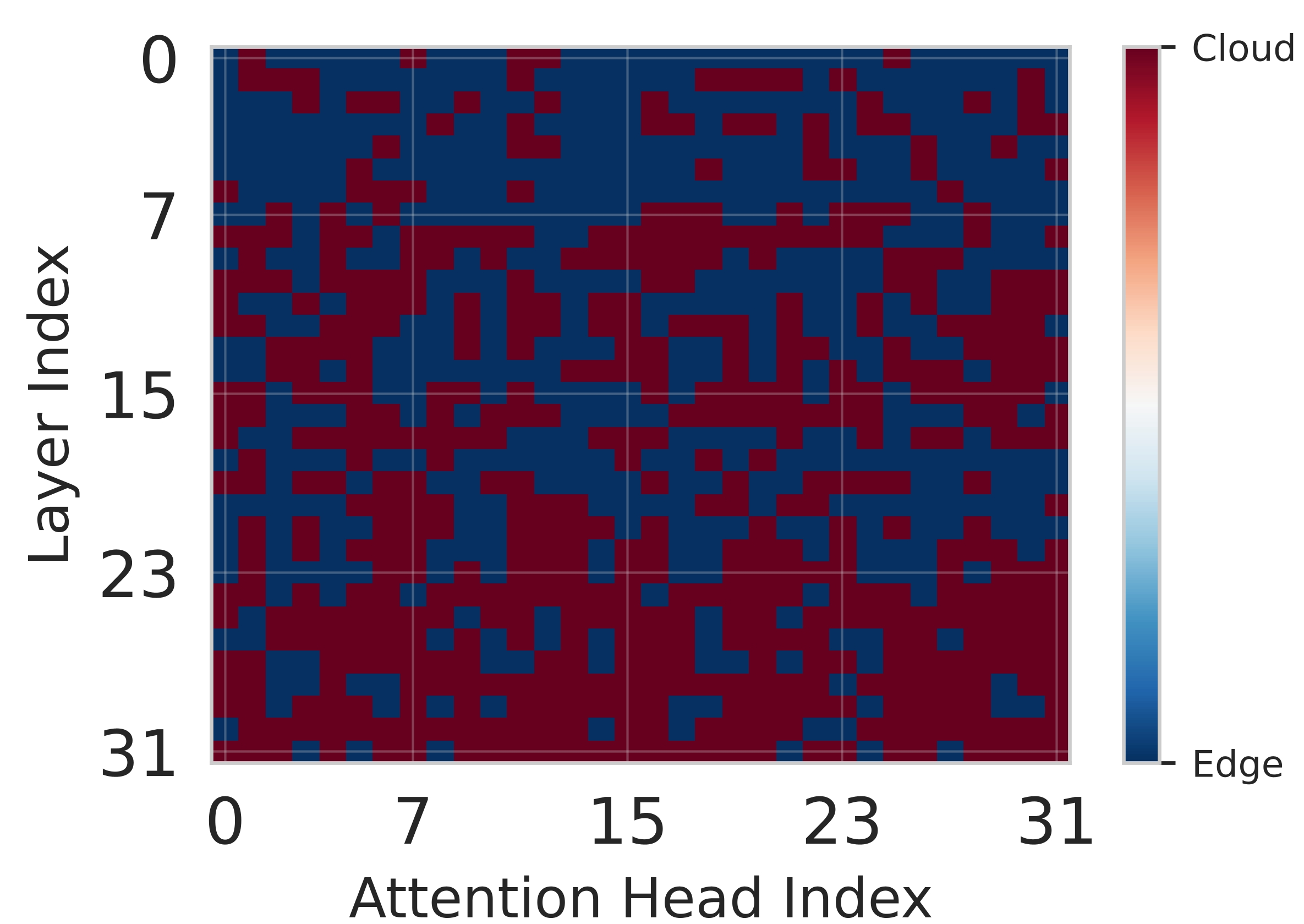
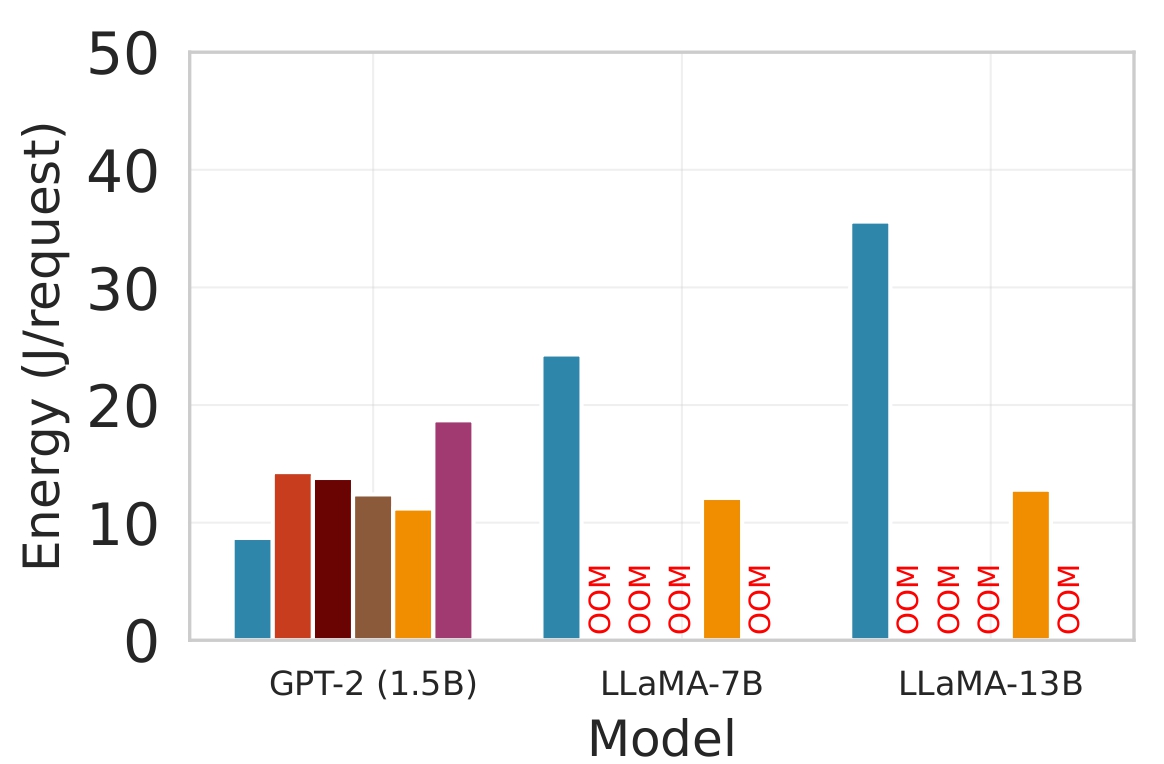
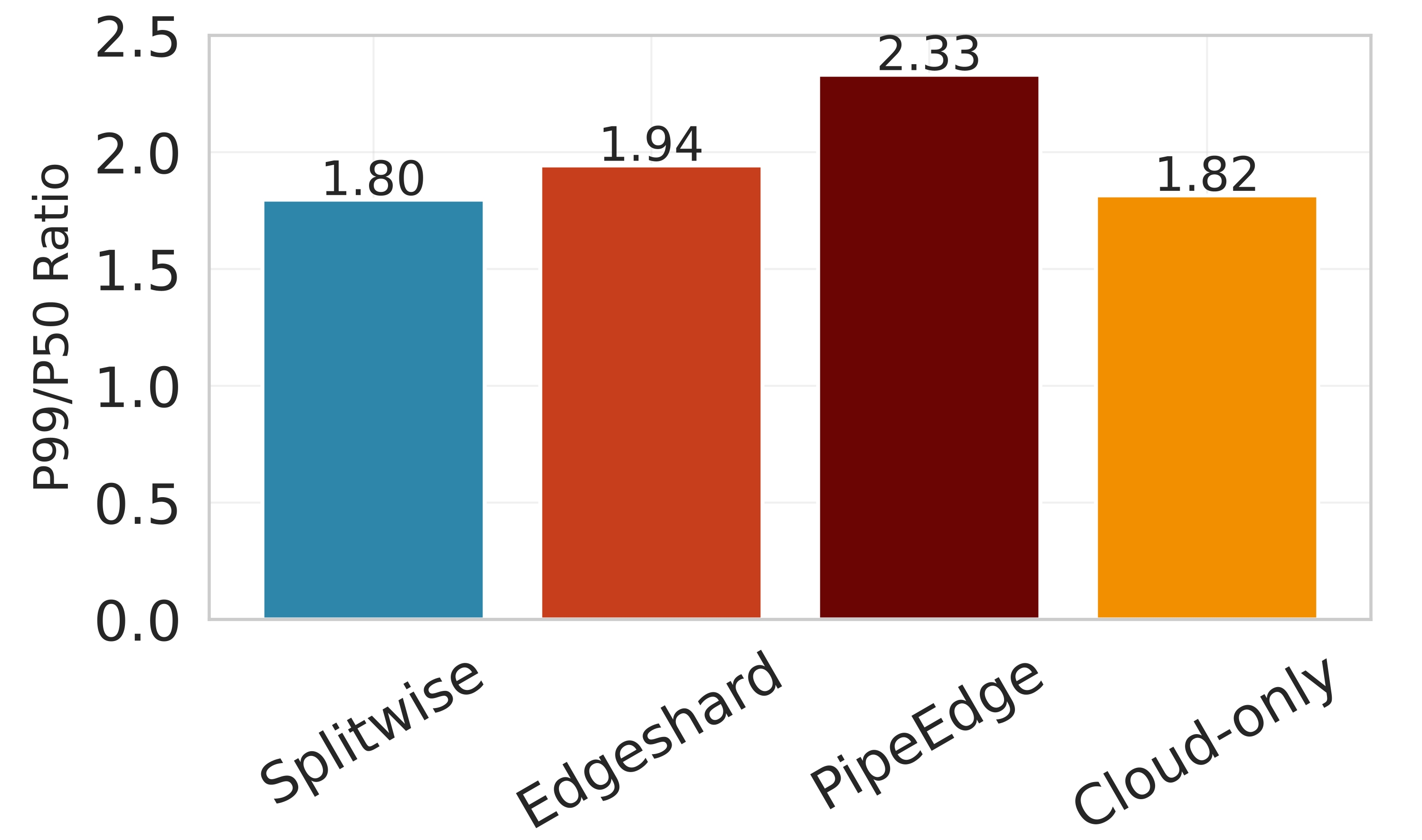
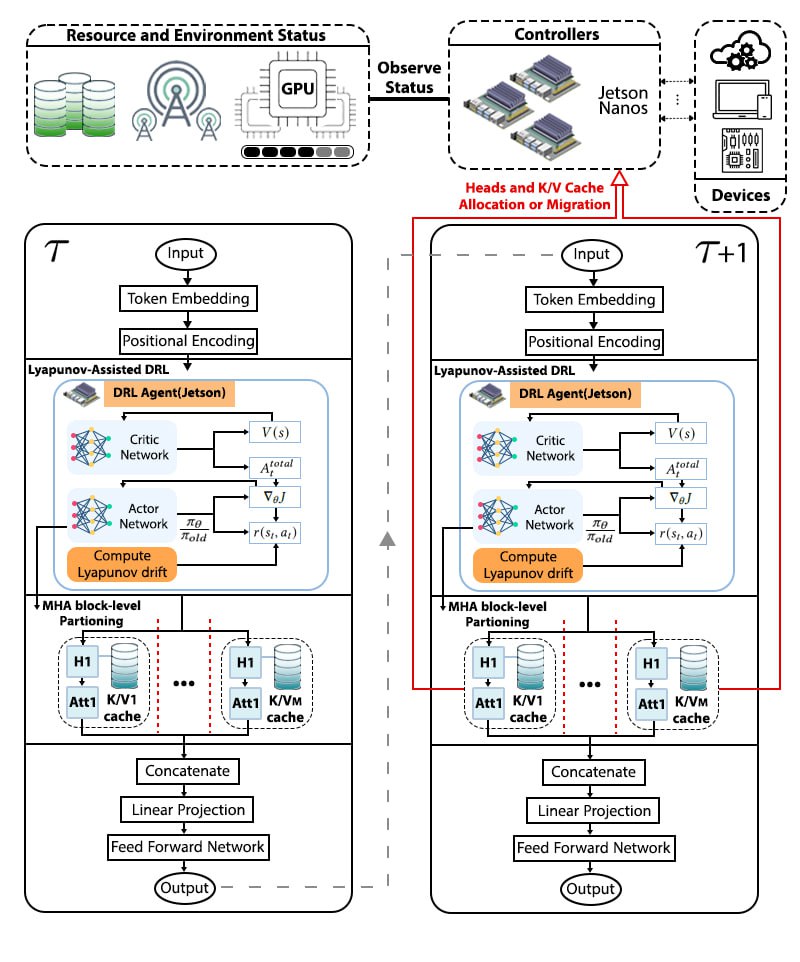
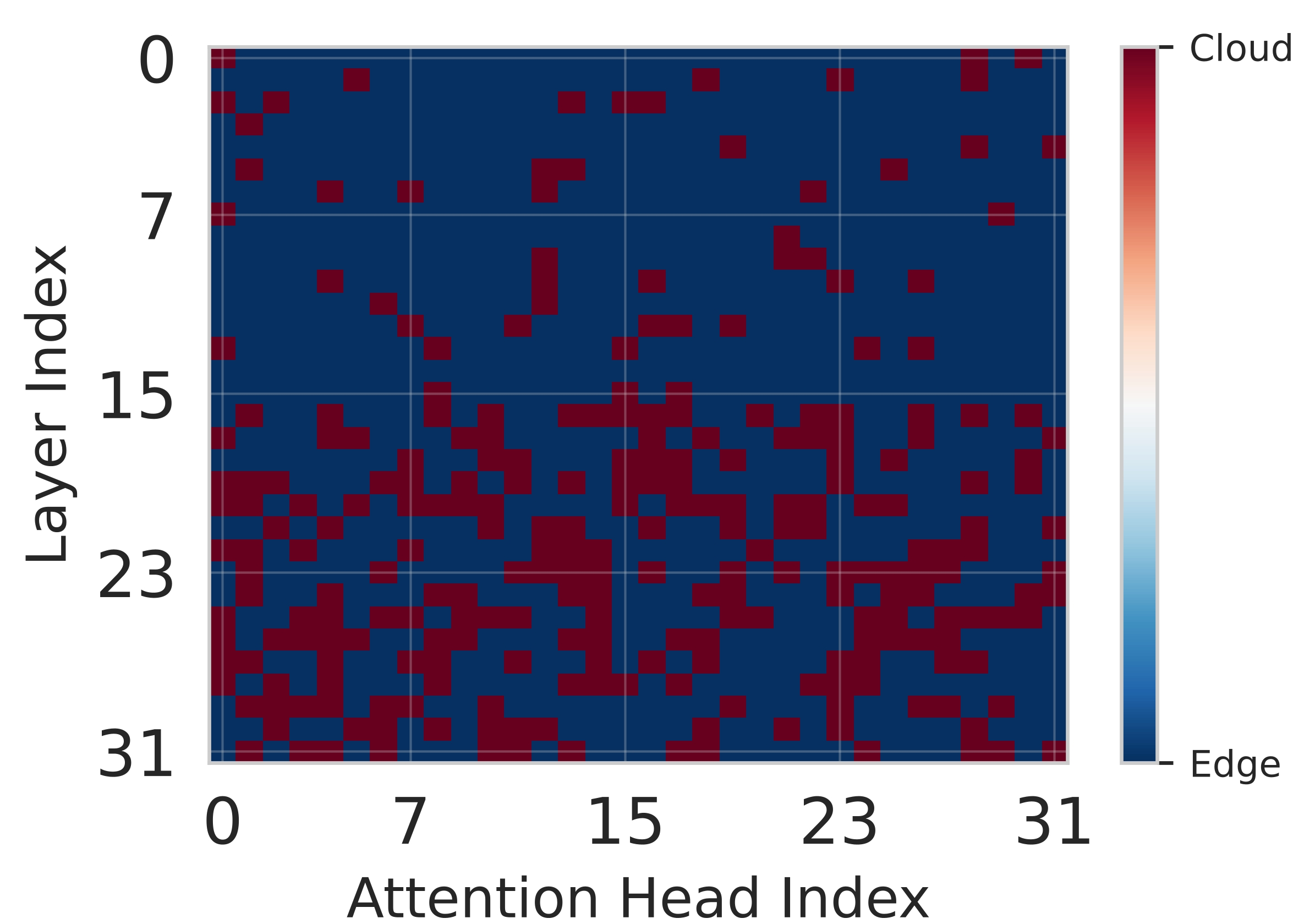
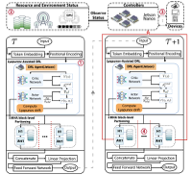
Deploying large language models (LLMs) on edge devices is challenging due to their limited memory and power resources. Cloud-only inference reduces device burden but introduces high latency and cost. Static edge-cloud partitions optimize a single metric and struggle when bandwidth fluctuates. We propose Splitwise, a novel Lyapunov-assisted deep reinforcement learning (DRL) framework for fine-grained, adaptive partitioning of LLMs across edge and cloud environments. Splitwise decomposes transformer layers into attention heads and feed-forward sub-blocks, exposing more partition choices than layer-wise schemes. A hierarchical DRL policy, guided by Lyapunov optimization, jointly minimizes latency, energy consumption, and accuracy degradation while guaranteeing queue stability under stochastic workloads and variable network bandwidth. Splitwise also guarantees robustness via partition checkpoints with exponential backoff recovery in case of communication failures. Experiments on Jetson Orin NX, Galaxy S23, and Raspberry Pi 5 with GPT-2 (1.5B), LLaMA-7B, and LLaMA-13B show that Splitwise reduces end-to-end latency by 1.4x-2.8x and cuts energy consumption by up to 41% compared with existing partitioners. It lowers the 95th-percentile latency by 53-61% relative to cloud-only execution, while maintaining accuracy and modest memory requirements.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Performance Evaluation on Diverse Datasets** This research demonstrates how well neural network models work across various image datasets, helping us understand the outcomes when these learning methodologies are applied to real-world problems.-
Systematic Comparison of Learning Methodologies
The study systematically analyzes and compares three different neural network training methods, akin to test-driving several types of cars to determine which is the most efficient. -
Improving Generalization Ability
This research also examines how well the neural network models adapt to new data, much like understanding how students acquire knowledge that allows them to solve diverse problems and how a model performs in novel situations.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)