CubeBench Testing Spatial Skills Under Partial Views
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: CubeBench Diagnosing Interactive, Long-Horizon Spatial Reasoning Under Partial Observations- ArXiv ID: 2512.23328
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Huan-ang Gao, Zikang Zhang, Tianwei Luo, Kaisen Yang, Xinzhe Juan, Jiahao Qiu, Tianxing Chen, Bingxiang He, Hao Zhao, Hao Zhou, Shilong Liu, Mengdi Wang
📝 Abstract
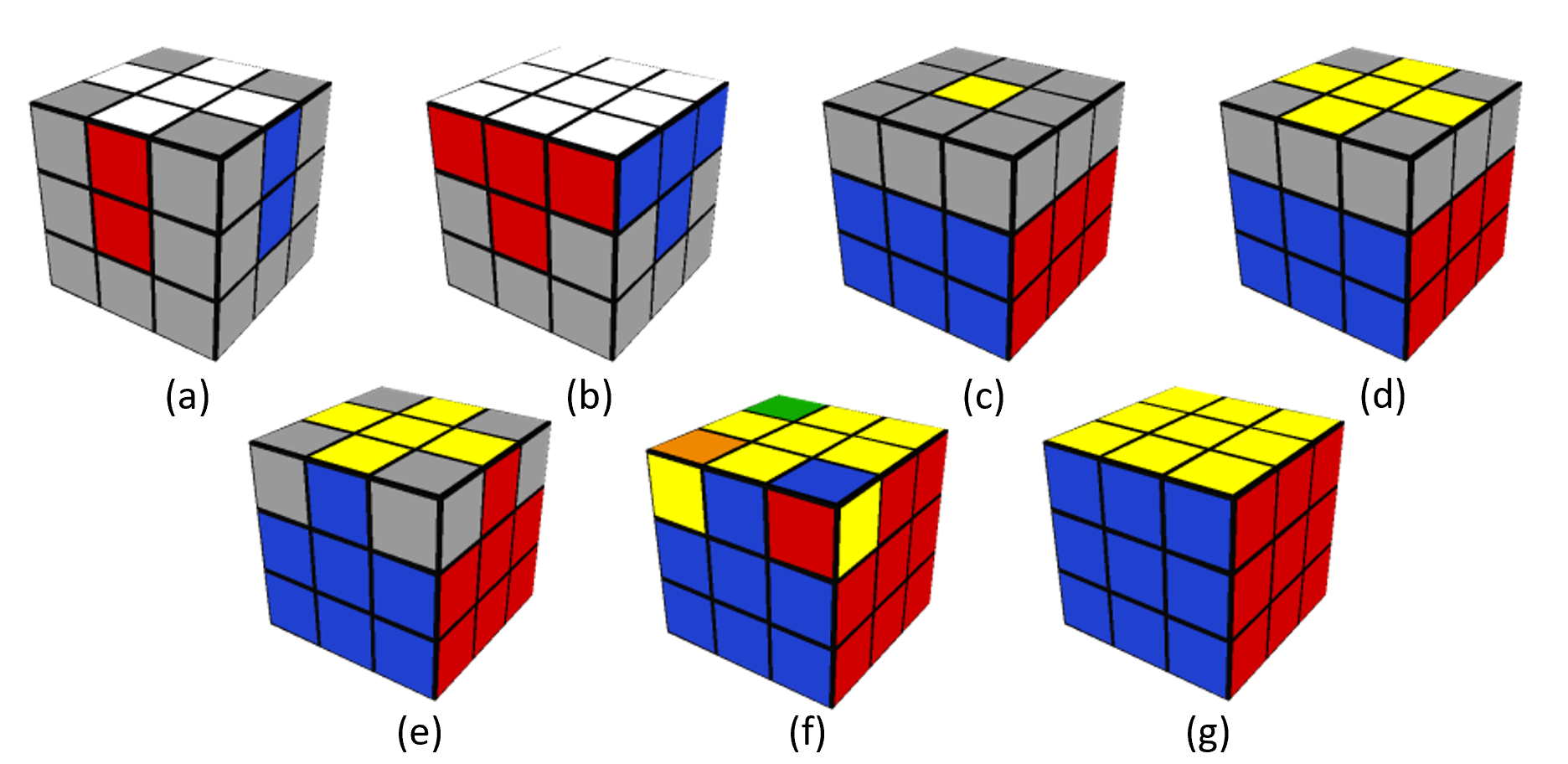
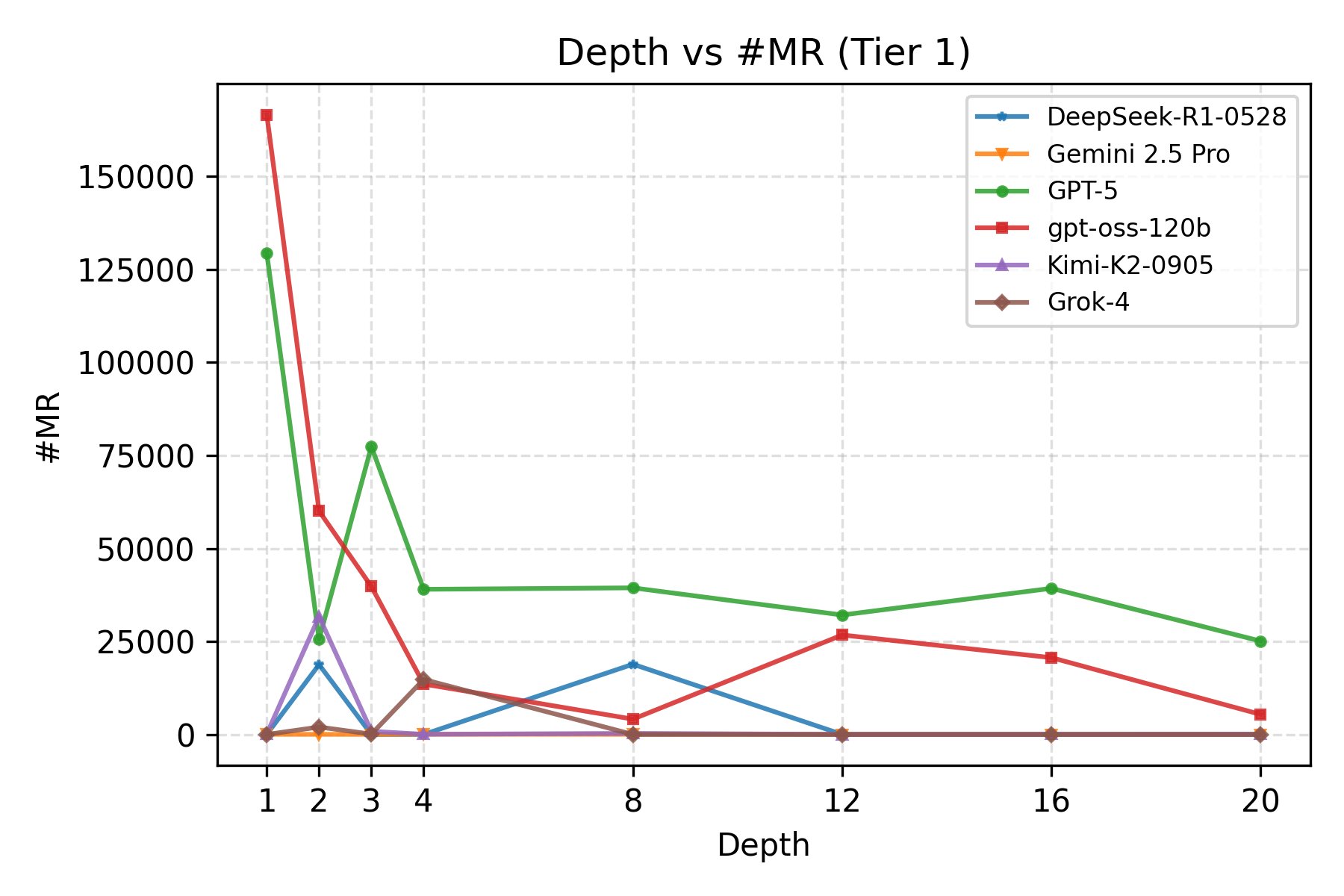
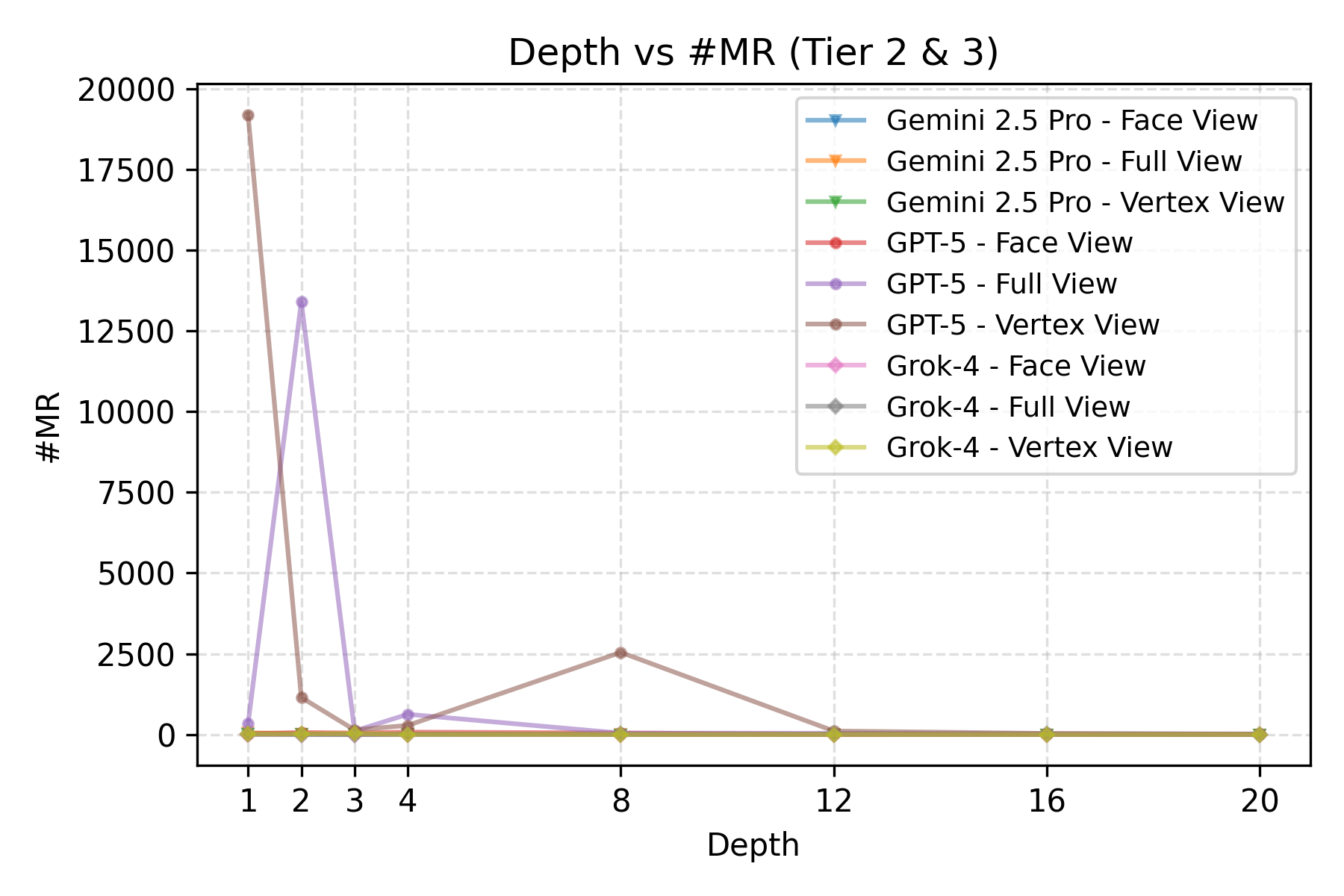
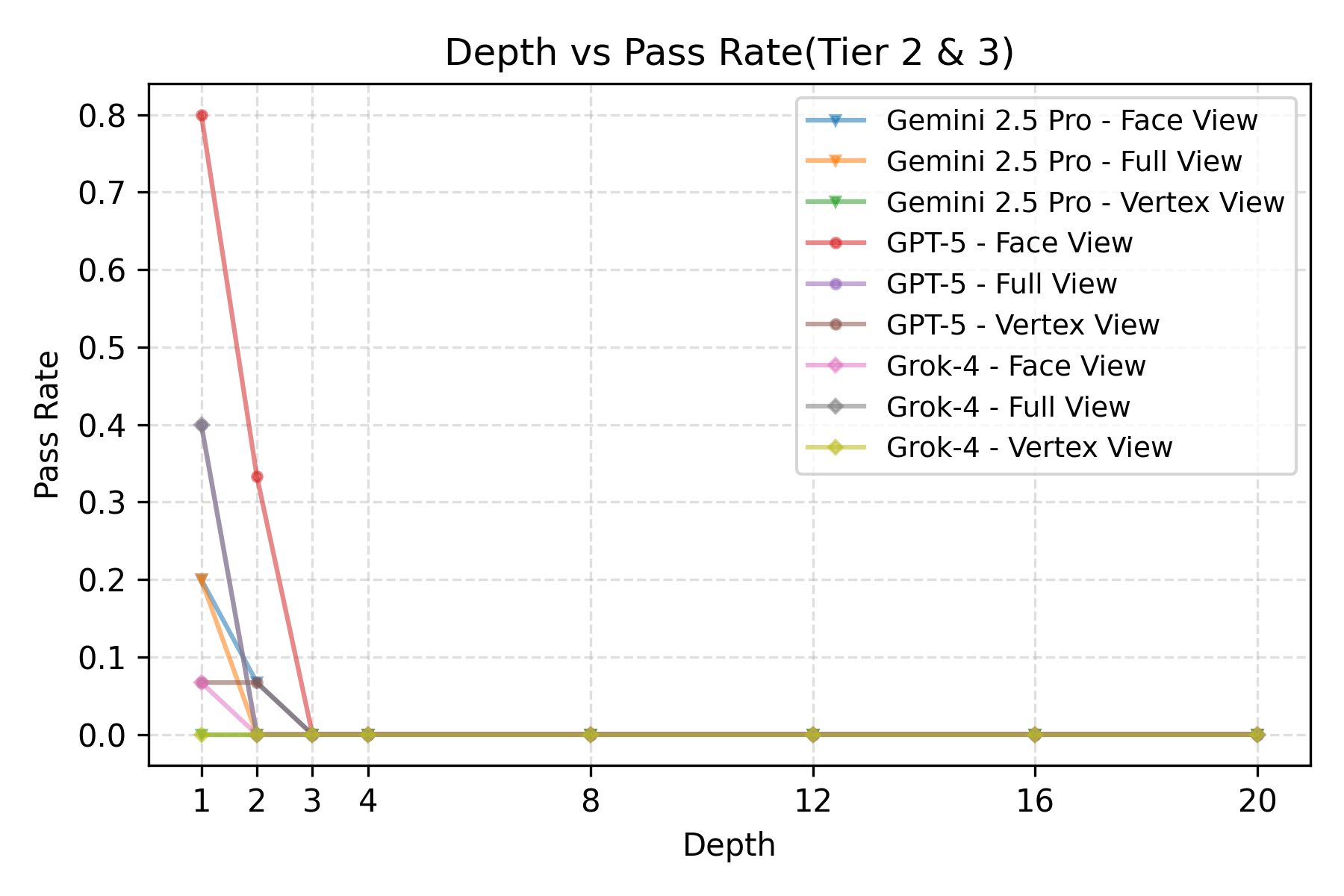
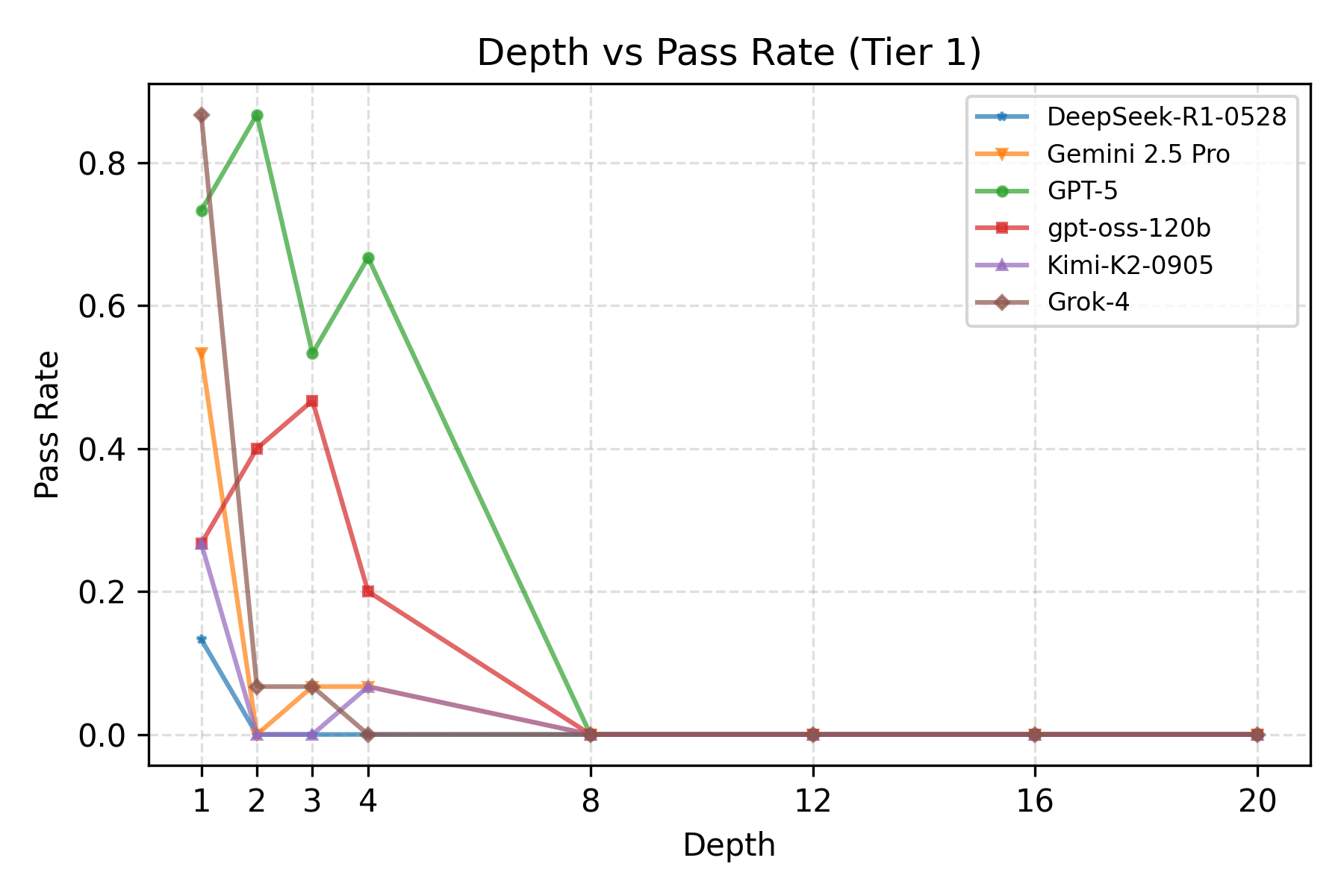
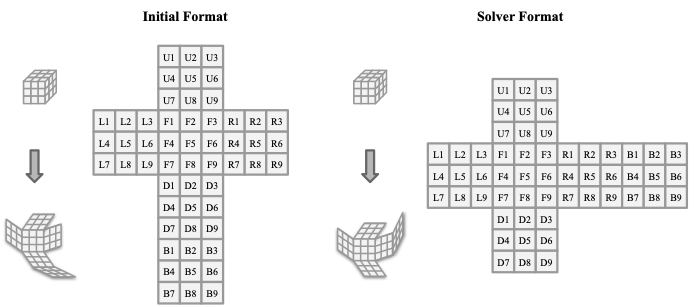
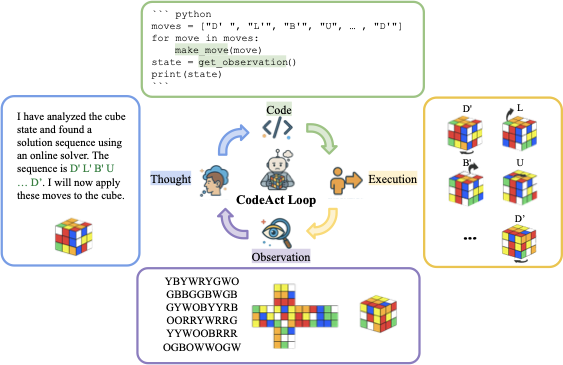
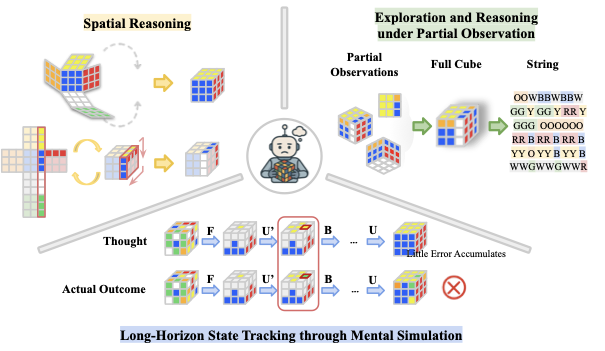
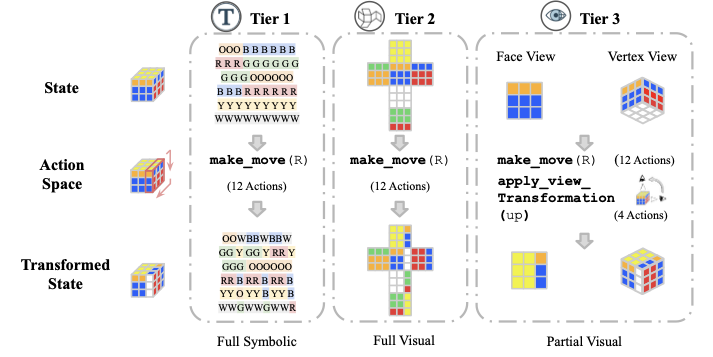
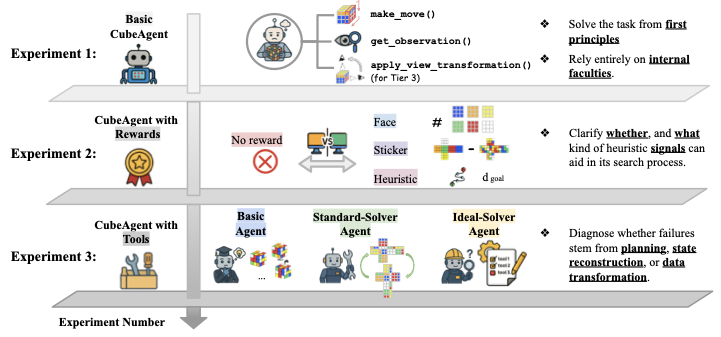
Large Language Model (LLM) agents, while proficient in the digital realm, face a significant gap in physical-world deployment due to the challenge of forming and maintaining a robust spatial mental model. We identify three core cognitive challenges hindering this transition: spatial reasoning, long-horizon state tracking via mental simulation, and active exploration under partial observation. To isolate and evaluate these faculties, we introduce CubeBench, a novel generative benchmark centered on the Rubik's Cube. CubeBench uses a three-tiered diagnostic framework that progressively assesses agent capabilities, from foundational state tracking with full symbolic information to active exploration with only partial visual data. Our experiments on leading LLMs reveal critical limitations, including a uniform 0.00% pass rate on all long-horizon tasks, exposing a fundamental failure in long-term planning. We also propose a diagnostic framework to isolate these cognitive bottlenecks by providing external solver tools. By analyzing the failure modes, we provide key insights to guide the development of more physically-grounded intelligent agents.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **New Transfer Learning Technique**: This study introduces an additional fine-tuning step to improve image classification models' performance, akin to deep-diagnostics in car repair beyond basic checks. 2. **Performance Improvement Across Datasets**: The proposed method shows excellent results across various image datasets, much like how a versatile recipe can adapt to different ingredients and tastes. 3. **Scientific Approach**: Based on experimental results, this research evaluates effectiveness and generalizability, similar to how scientists test new drugs under varied conditions.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)