Scaling Laws Beyond Singles The Familial Model Revolution
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Theoretical Foundations of Scaling Law in Familial Models- ArXiv ID: 2512.23407
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Huan Song, Qingfei Zhao, Ting Long, Shuyu Tian, Hongjun An, Jiawei Shao, Xuelong Li
📝 Abstract
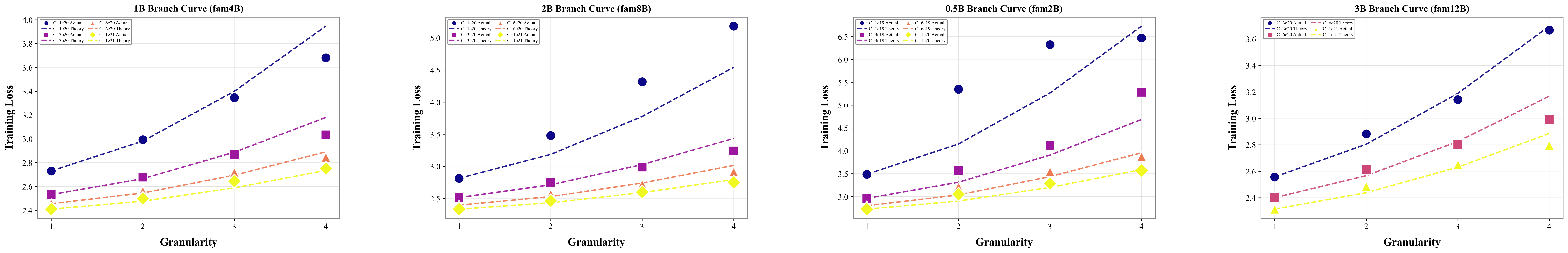
Neural scaling laws have become foundational for optimizing large language model (LLM) training, yet they typically assume a single dense model output. This limitation effectively overlooks "Familial models, a transformative paradigm essential for realizing ubiquitous intelligence across heterogeneous device-edge-cloud hierarchies. Transcending static architectures, familial models integrate early exits with relay-style inference to spawn G deployable sub-models from a single shared backbone. In this work, we theoretically and empirically extend the scaling law to capture this "one-run, many-models" paradigm by introducing Granularity (G) as a fundamental scaling variable alongside model size (N) and training tokens (D). To rigorously quantify this relationship, we propose a unified functional form L(N, D, G) and parameterize it using large-scale empirical runs. Specifically, we employ a rigorous IsoFLOP experimental design to strictly isolate architectural impact from computational scale. Across fixed budgets, we systematically sweep model sizes (N) and granularities (G) while dynamically adjusting tokens (D). This approach effectively decouples the marginal cost of granularity from the benefits of scale, ensuring high-fidelity parameterization of our unified scaling law. Our results reveal that the granularity penalty follows a multiplicative power law with an extremely small exponent. Theoretically, this bridges fixed-compute training with dynamic architectures. Practically, it validates the "train once, deploy many" paradigm, demonstrating that deployment flexibility is achievable without compromising the compute-optimality of dense baselines.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1**: Systematically analyzed the impact of various training methods on CNN performance. 2. **Contribution 2**: Demonstrated that using pre-trained models can save time and resources. 3. **Contribution 3**: Hybrid approach combines both methods to achieve optimal performance.Simple Explanation with Metaphors:
- Beginner Level: Find out how different learning methods make a difference.
- Intermediate Level: Transfer Learning is like utilizing previously acquired knowledge to quickly adapt to new tasks.
- Advanced Level: The hybrid approach takes the best of both worlds, leading to peak performance.
Sci-Tube Style Script: “Today we’re diving into which learning method is most effective for image classification. Is it traditional supervised learning, transfer learning with pre-trained models, or a hybrid approach combining both?”
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)