Combatting Reward Hacking through Information-Theoretic Bias Reduction
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Eliminating Inductive Bias in Reward Models with Information-Theoretic Guidance- ArXiv ID: 2512.23461
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Zhuo Li, Pengyu Cheng, Zhechao Yu, Feifei Tong, Anningzhe Gao, Tsung-Hui Chang, Xiang Wan, Erchao Zhao, Xiaoxi Jiang, Guanjun Jiang
📝 Abstract
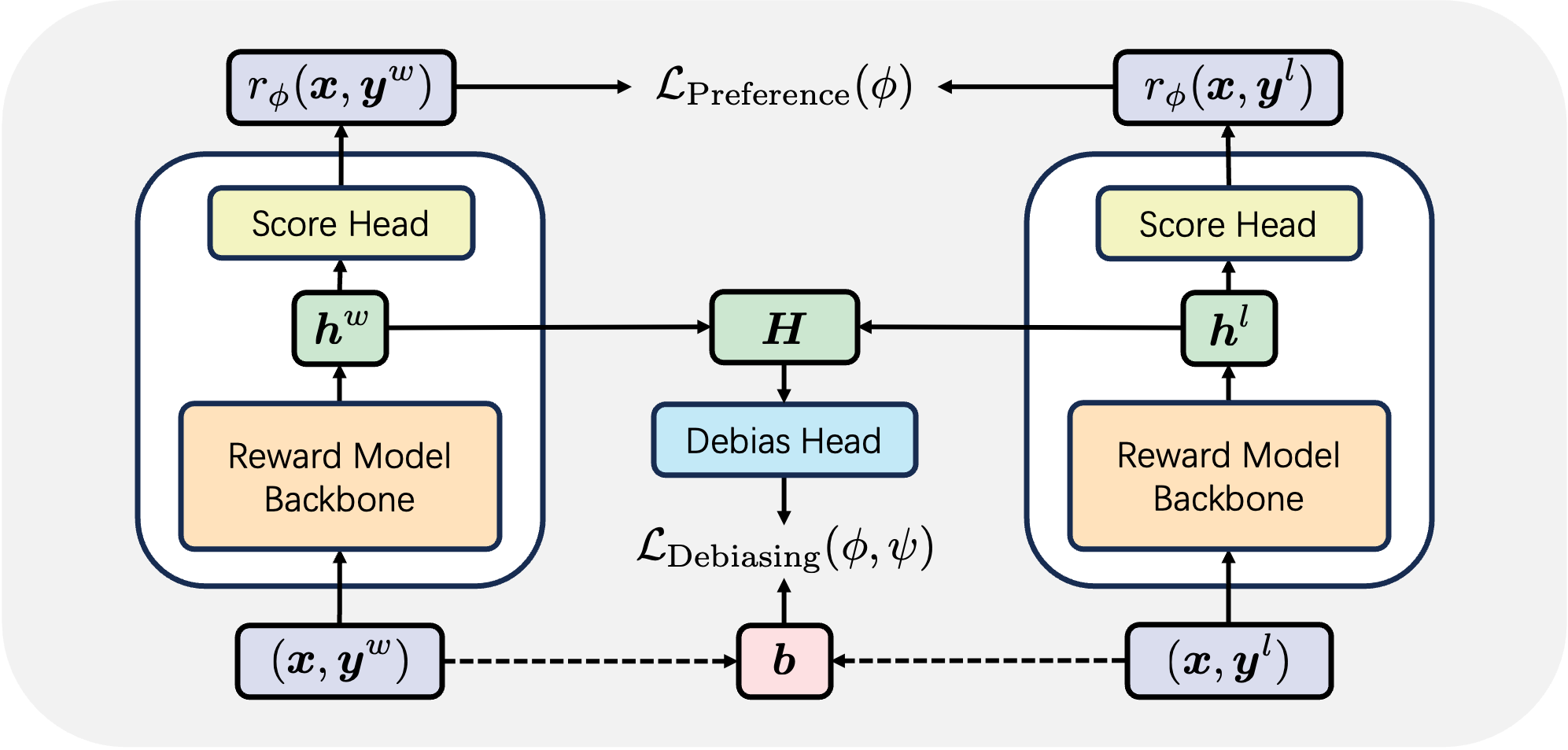
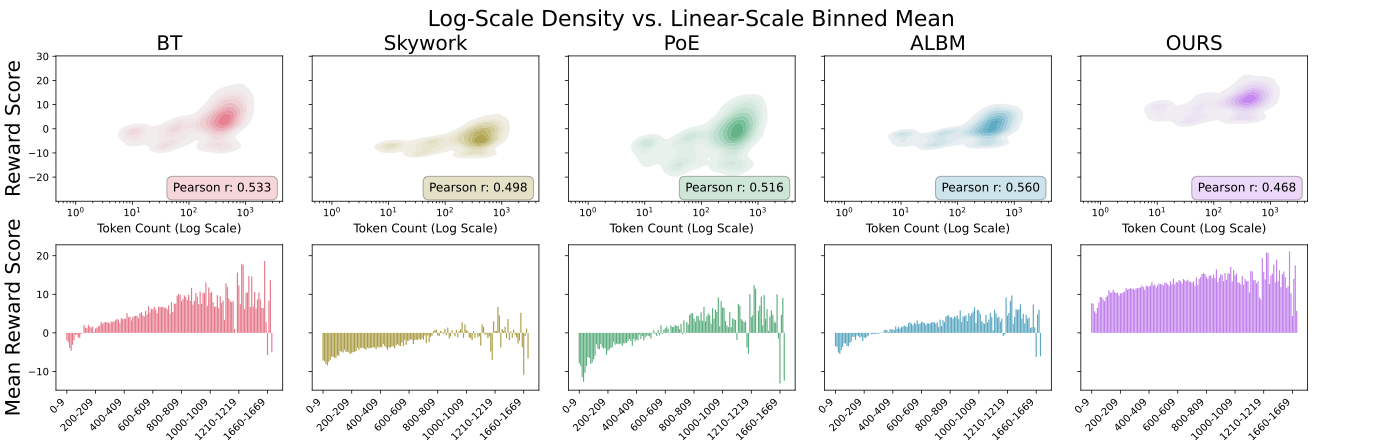
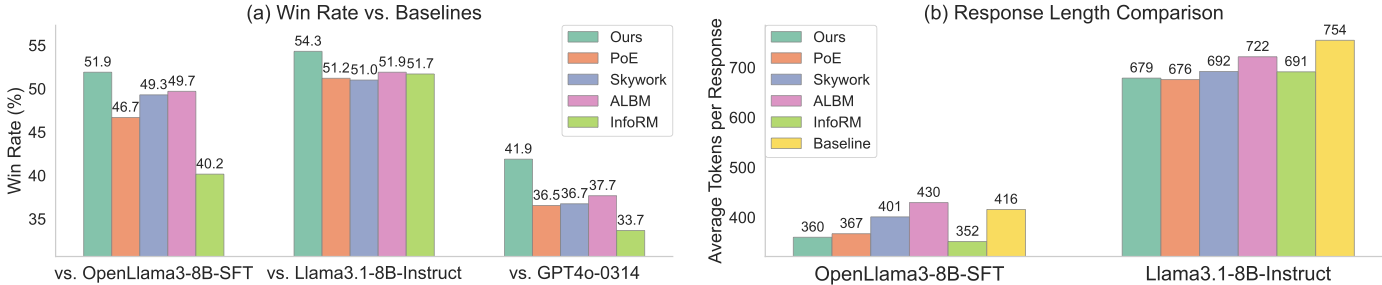
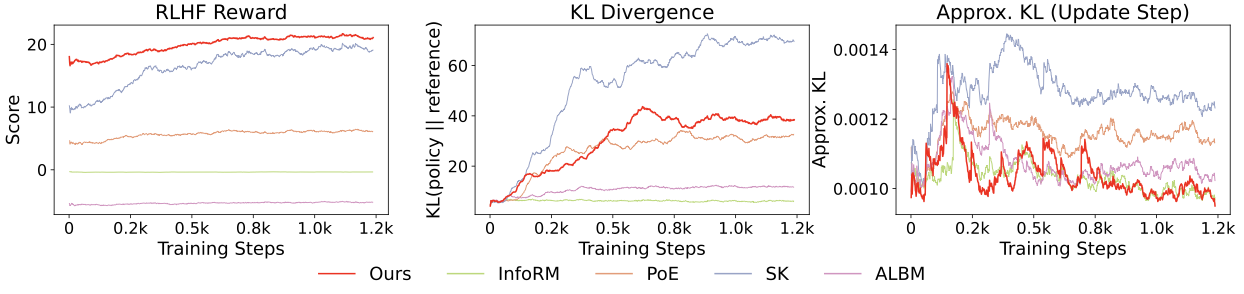
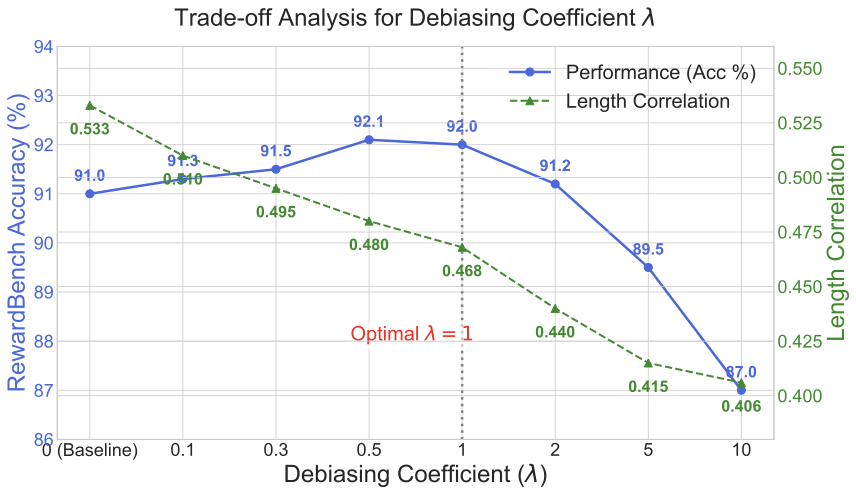
Reward models (RMs) are essential in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to align large language models (LLMs) with human values. However, RM training data is commonly recognized as low-quality, containing inductive biases that can easily lead to overfitting and reward hacking. For example, more detailed and comprehensive responses are usually human-preferred but with more words, leading response length to become one of the inevitable inductive biases. A limited number of prior RM debiasing approaches either target a single specific type of bias or model the problem with only simple linear correlations, \textit{e.g.}, Pearson coefficients. To mitigate more complex and diverse inductive biases in reward modeling, we introduce a novel information-theoretic debiasing method called \textbf{D}ebiasing via \textbf{I}nformation optimization for \textbf{R}M (DIR). Inspired by the information bottleneck (IB), we maximize the mutual information (MI) between RM scores and human preference pairs, while minimizing the MI between RM outputs and biased attributes of preference inputs. With theoretical justification from information theory, DIR can handle more sophisticated types of biases with non-linear correlations, broadly extending the real-world application scenarios for RM debiasing methods. In experiments, we verify the effectiveness of DIR with three types of inductive biases: \textit{response length}, \textit{sycophancy}, and \textit{format}. We discover that DIR not only effectively mitigates target inductive biases but also enhances RLHF performance across diverse benchmarks, yielding better generalization abilities. The code and training recipes are available at https://github.com/Qwen-Applications/DIR.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Impact of Climate Change Analysis**: Understanding how climate change is transforming ecosystems can be likened to observing a mountain landscape from atop a large rock, witnessing its gradual transformation. 2. **Tracking Changes in Biodiversity**: The study discovered the decrease and migration of certain species. This is akin to smaller fish moving to warmer waters within a river, forming new ecosystems as they go. 3. **Importance of International Cooperation**: For effective conservation strategies, countries need to work together. This means sharing information and collaborating on solutions, similar to many people piecing together one large puzzle.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)