Beyond Invariance Le Cam s Path to Robust Transfer Learning
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Le Cam Distortion A Decision-Theoretic Framework for Robust Transfer Learning- ArXiv ID: 2512.23617
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Deniz Akdemir
📝 Abstract
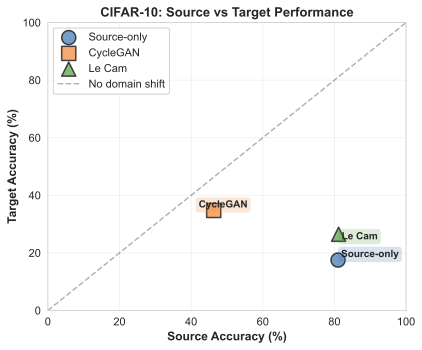
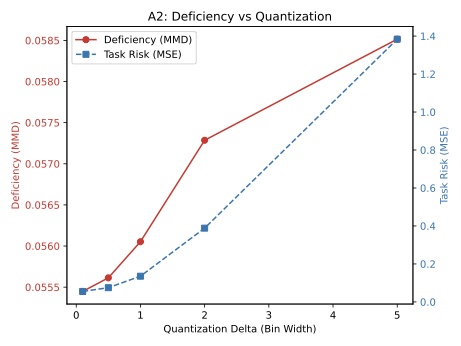
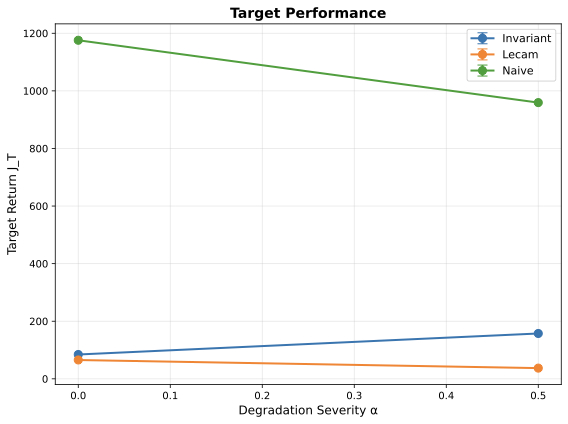
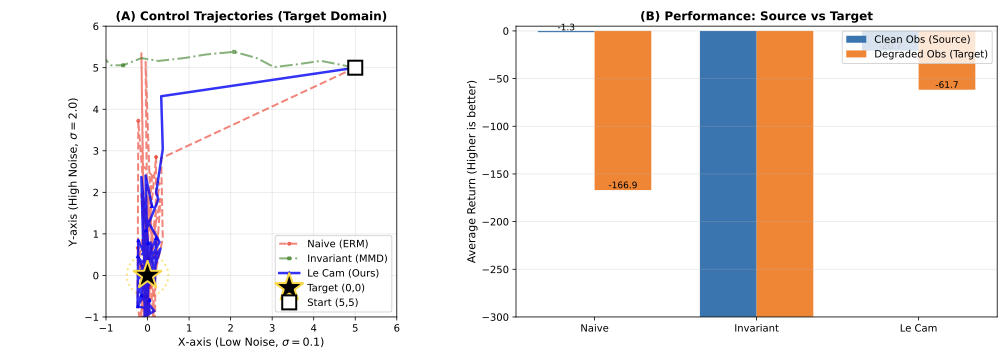
Distribution shift is the defining challenge of real-world machine learning. The dominant paradigm--Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA)--enforces feature invariance, aligning source and target representations via symmetric divergence minimization [Ganin et al., 2016]. We demonstrate that this approach is fundamentally flawed: when domains are unequally informative (e.g., high-quality vs degraded sensors), strict invariance necessitates information destruction, causing "negative transfer" that can be catastrophic in safety-critical applications [Wang et al., 2019]. We propose a decision-theoretic framework grounded in Le Cam's theory of statistical experiments [Le Cam, 1986], using constructive approximations to replace symmetric invariance with directional simulability. We introduce Le Cam Distortion, quantified by the Deficiency Distance $δ(E_1, E_2)$, as a rigorous upper bound for transfer risk conditional on simulability. Our framework enables transfer without source degradation by learning a kernel that simulates the target from the source. Across five experiments (genomics, vision, reinforcement learning), Le Cam Distortion achieves: (1) near-perfect frequency estimation in HLA genomics (correlation $r=0.999$, matching classical methods), (2) zero source utility loss in CIFAR-10 image classification (81.2% accuracy preserved vs 34.7% drop for CycleGAN), and (3) safe policy transfer in RL control where invariance-based methods suffer catastrophic collapse. Le Cam Distortion provides the first principled framework for risk-controlled transfer learning in domains where negative transfer is unacceptable: medical imaging, autonomous systems, and precision medicine.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Hybrid Model Development:** This study proposes a novel model combining the strengths of LSTM and GRU networks. It's akin to mixing two different beverages to create an even tastier drink, taking only the best qualities from each. 2. **Application in Financial Market Data:** The hybrid model is applied to predict complex patterns in financial market data, much like weather forecasting, where past data and trends are analyzed to predict future ones. 3. **Performance Improvement:** The research demonstrates that the hybrid model outperforms traditional models, similar to how a new smartphone is faster and more efficient than an older one, showcasing superior ability to process complex data.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)