Navigating the Web World Model A Middle Ground Approach
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Web World Models- ArXiv ID: 2512.23676
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Jichen Feng, Yifan Zhang, Chenggong Zhang, Yifu Lu, Shilong Liu, Mengdi Wang
📝 Abstract
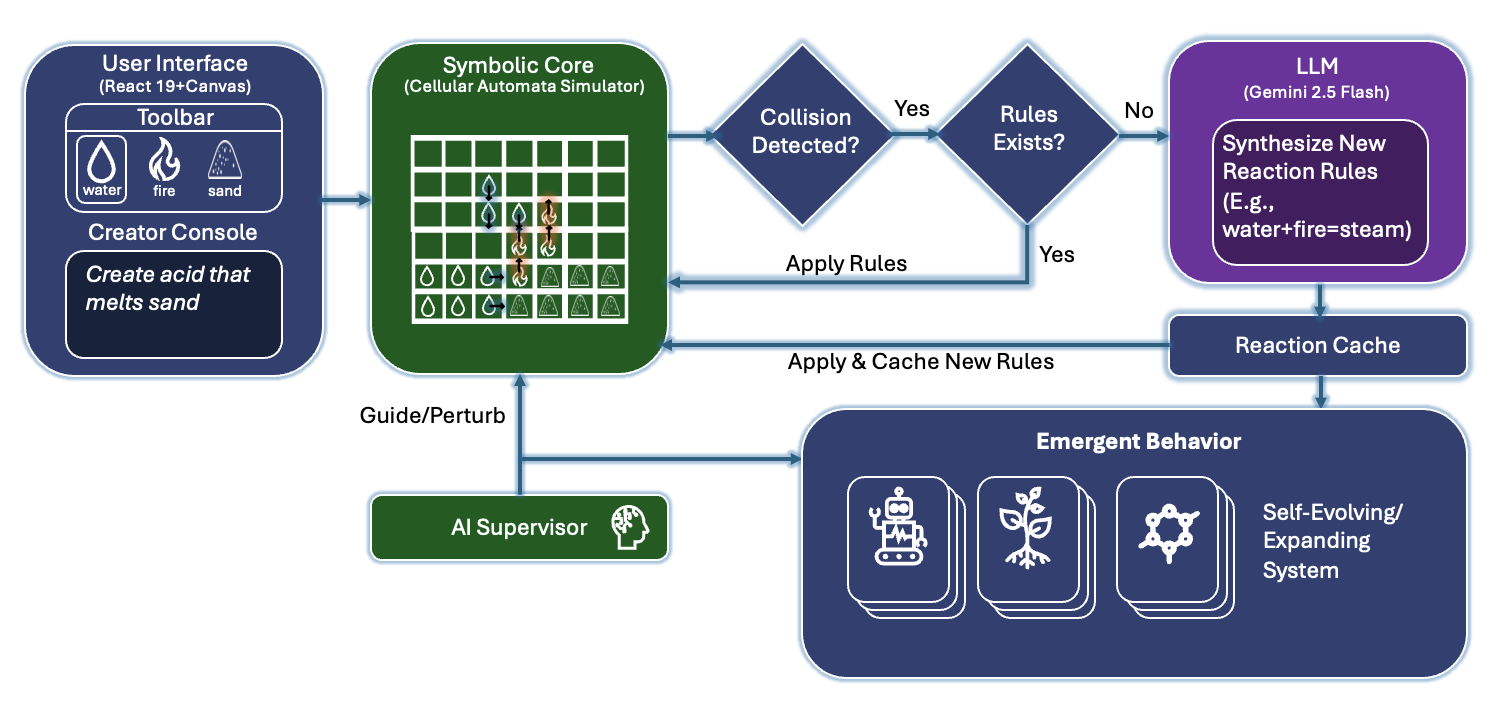
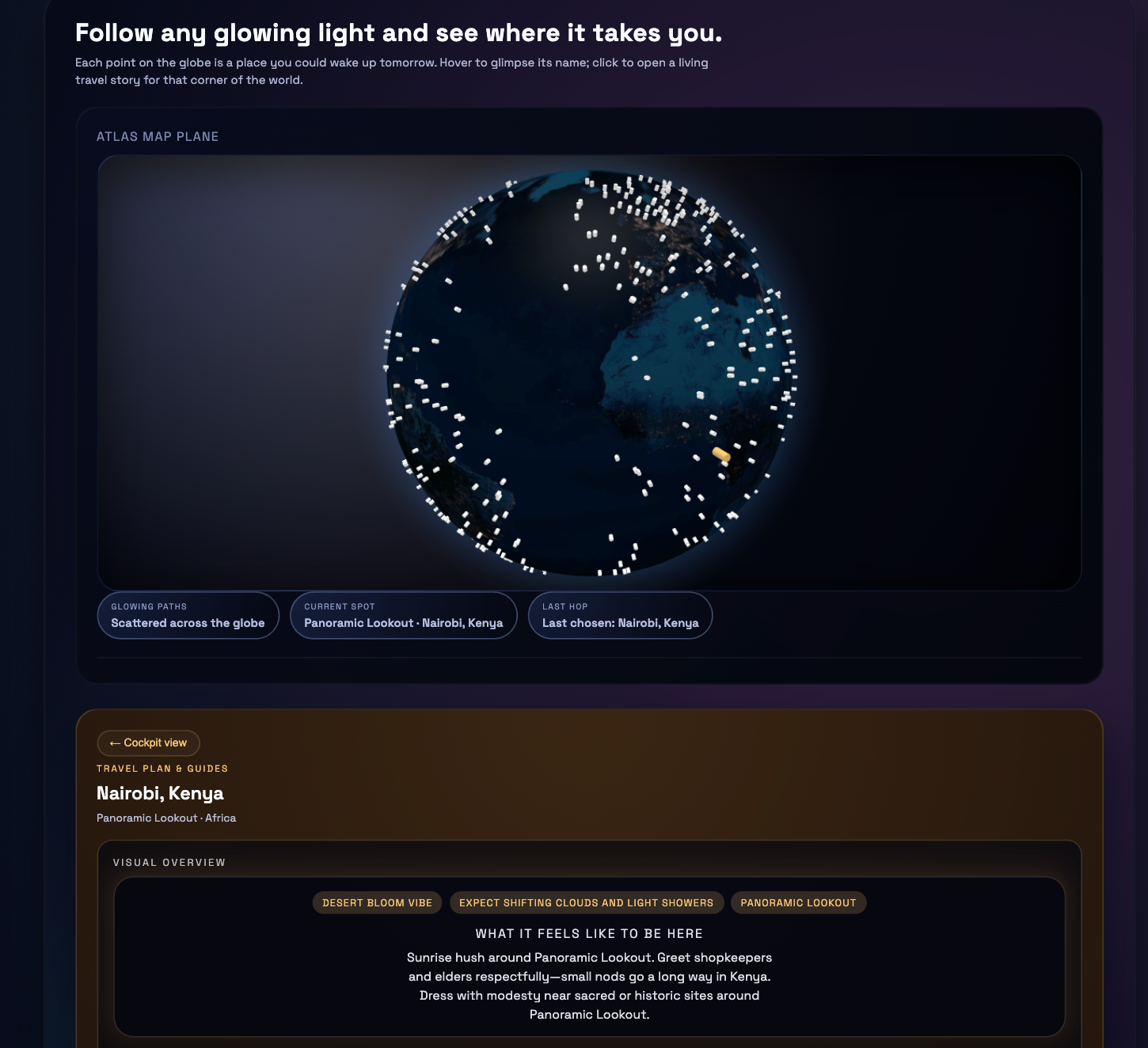
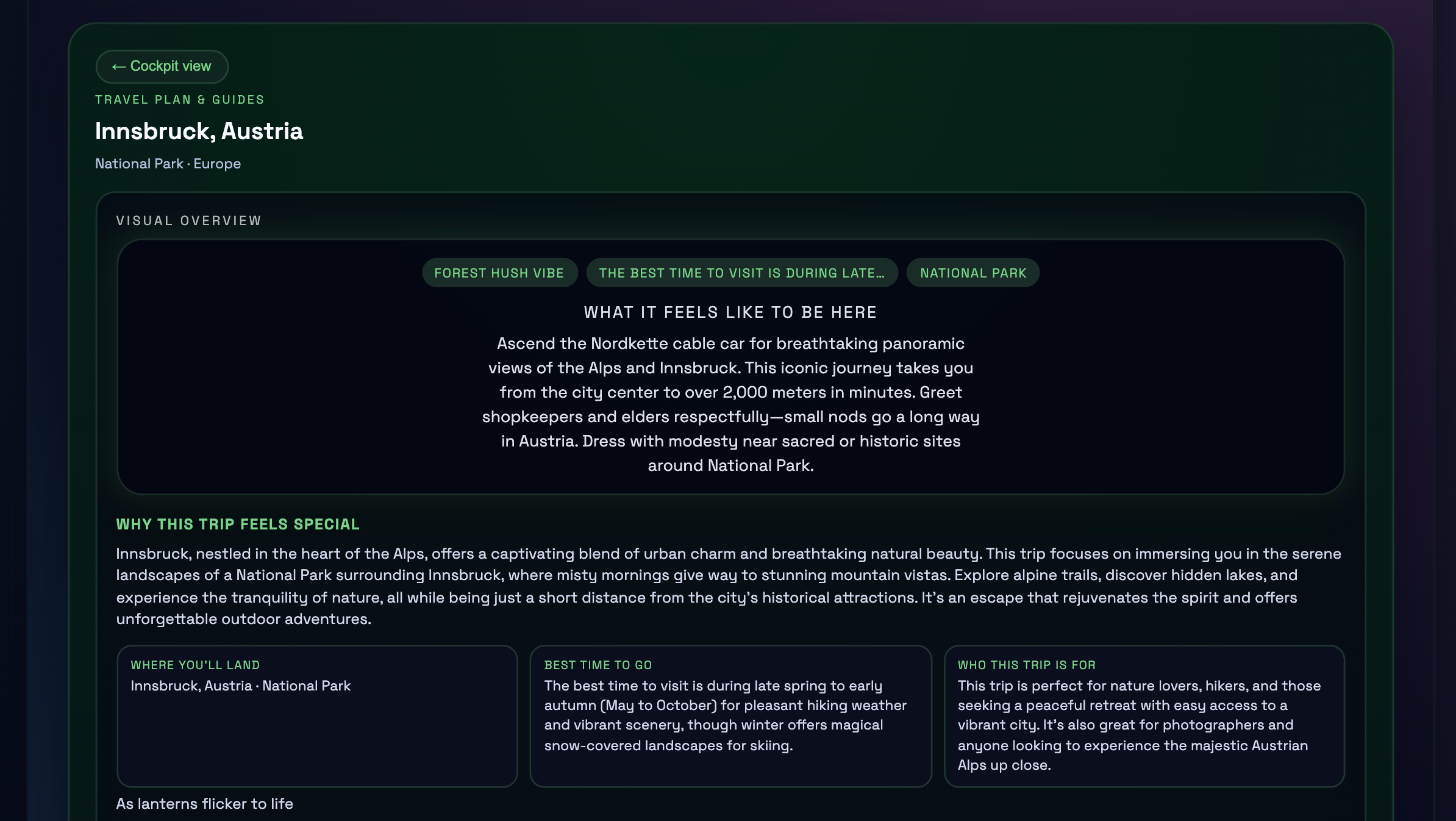
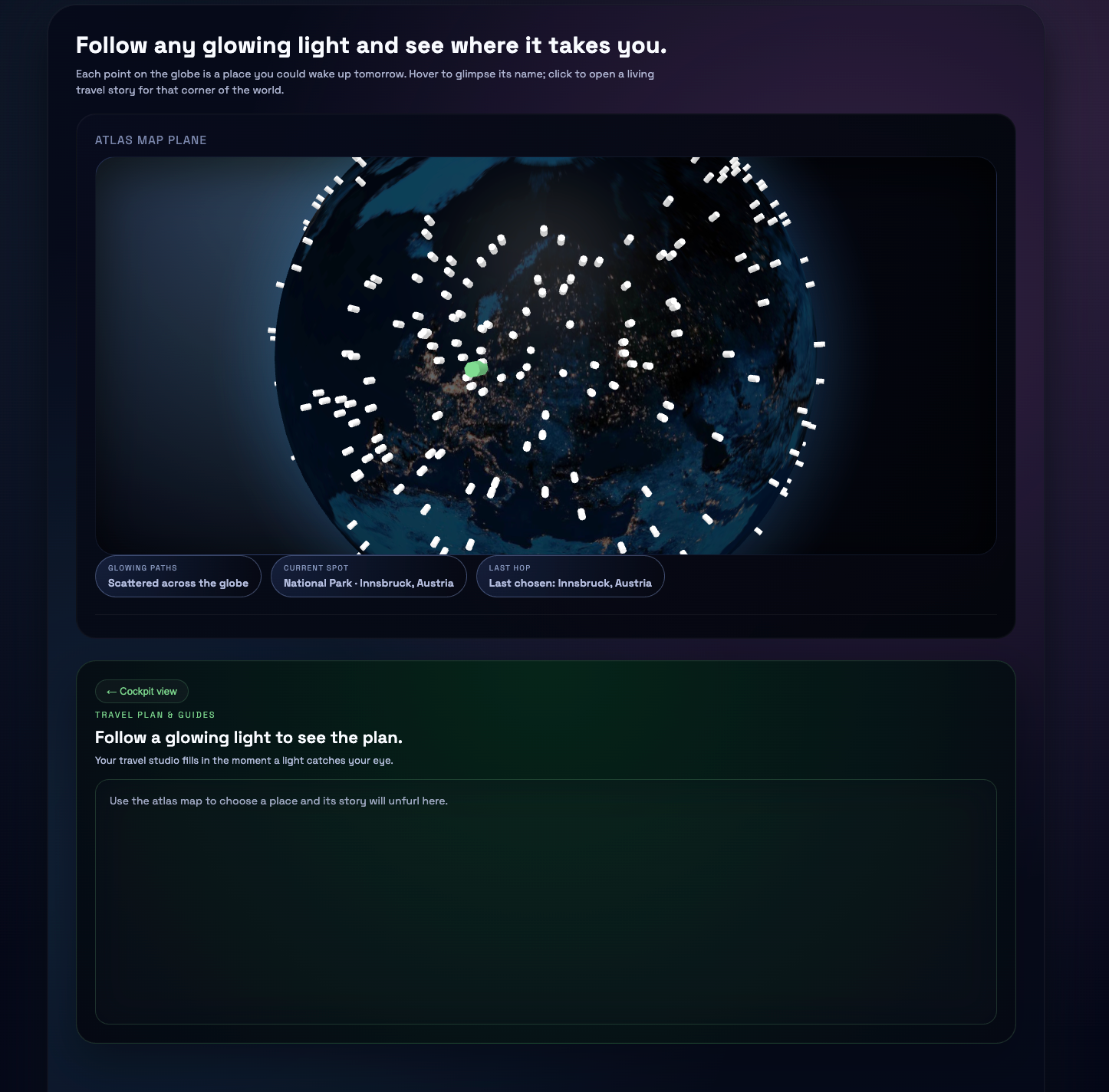
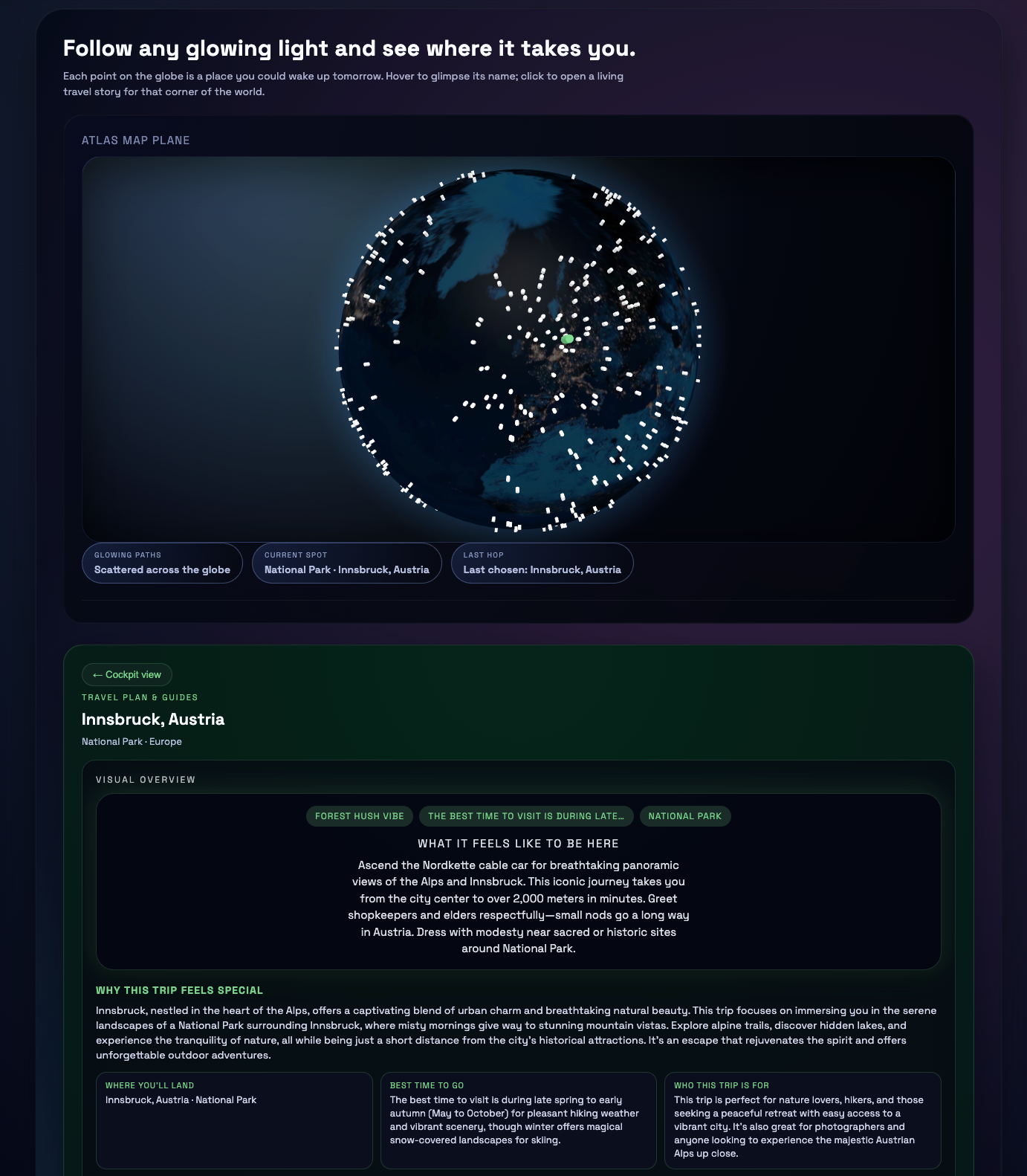
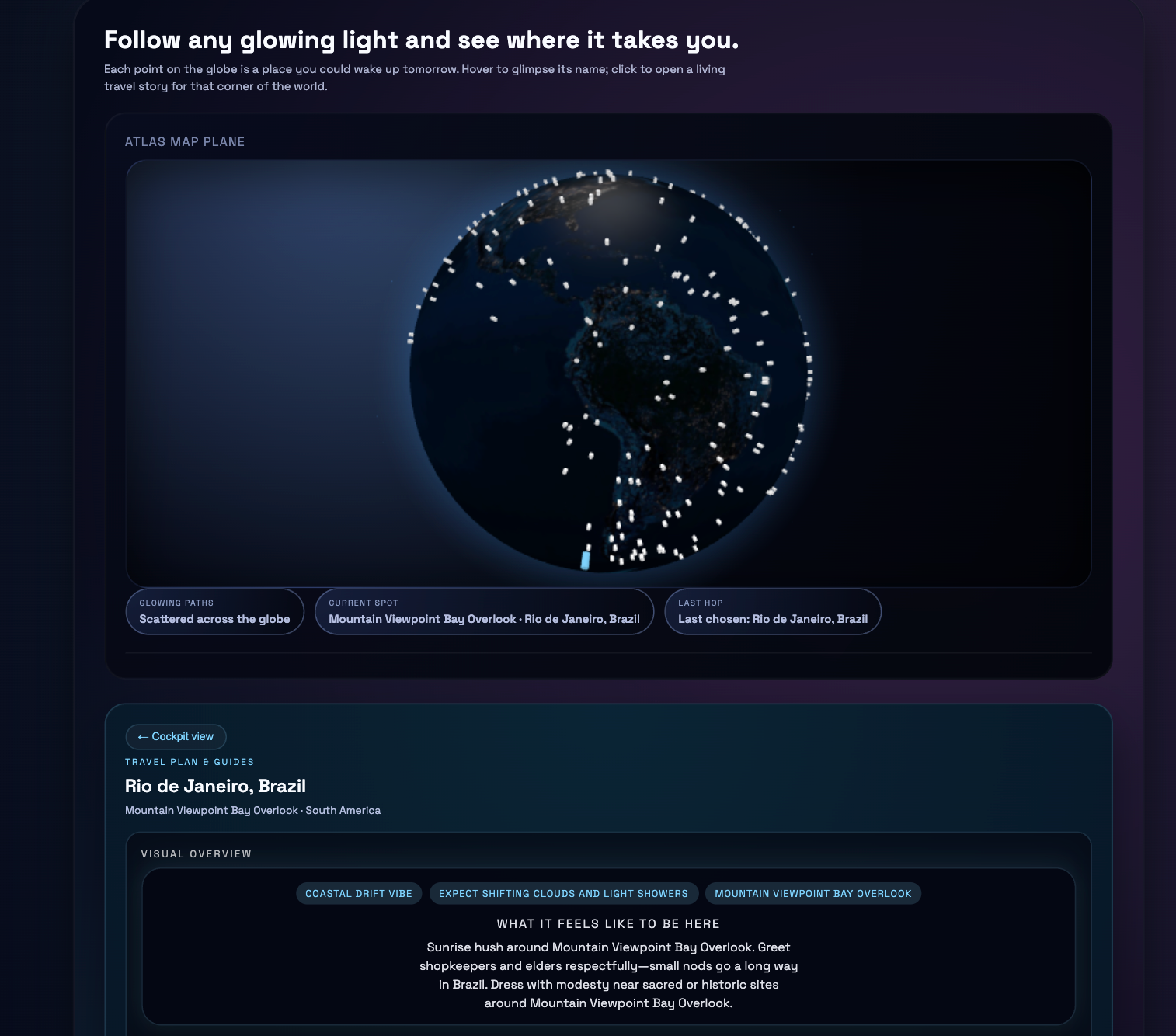
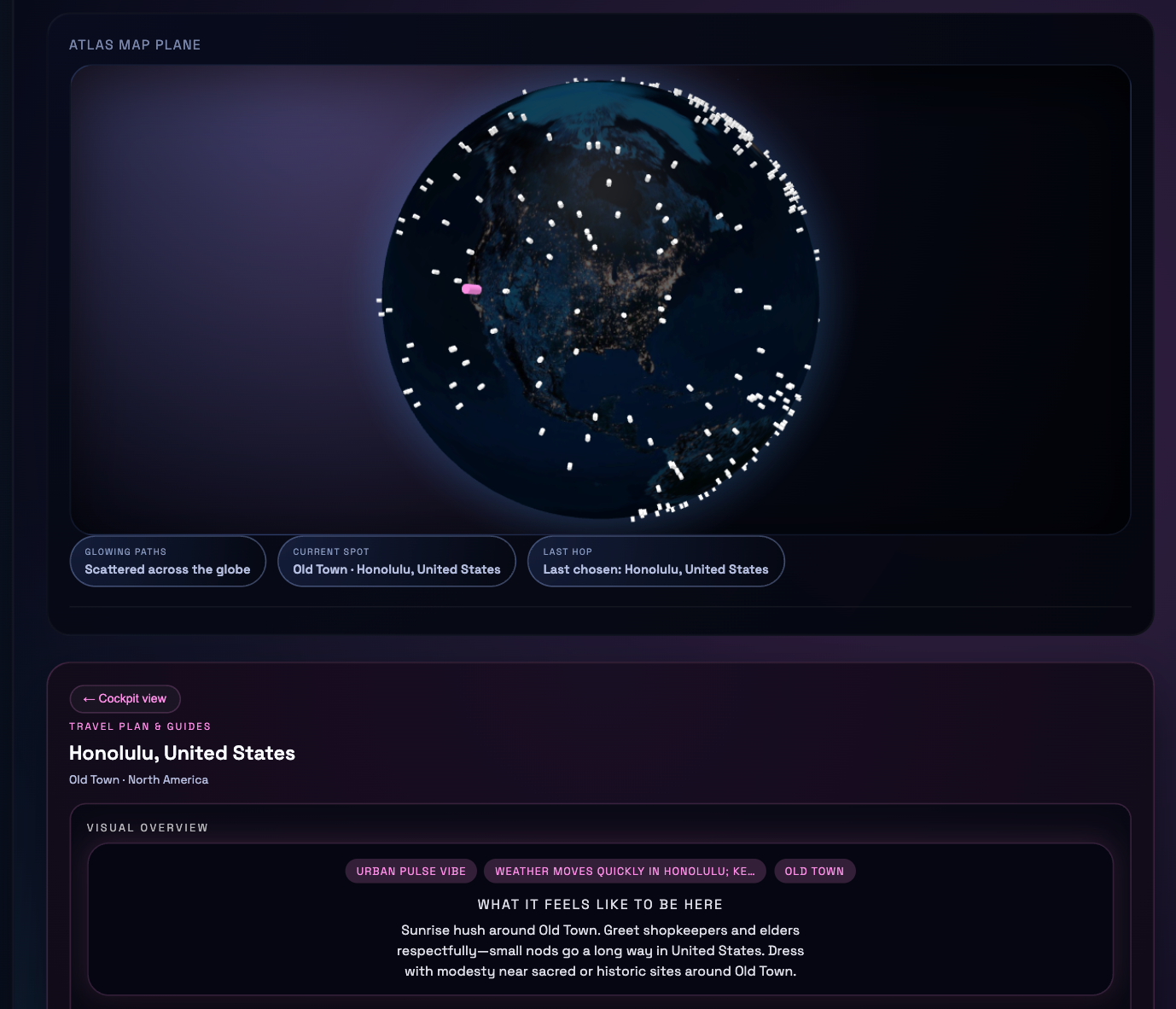
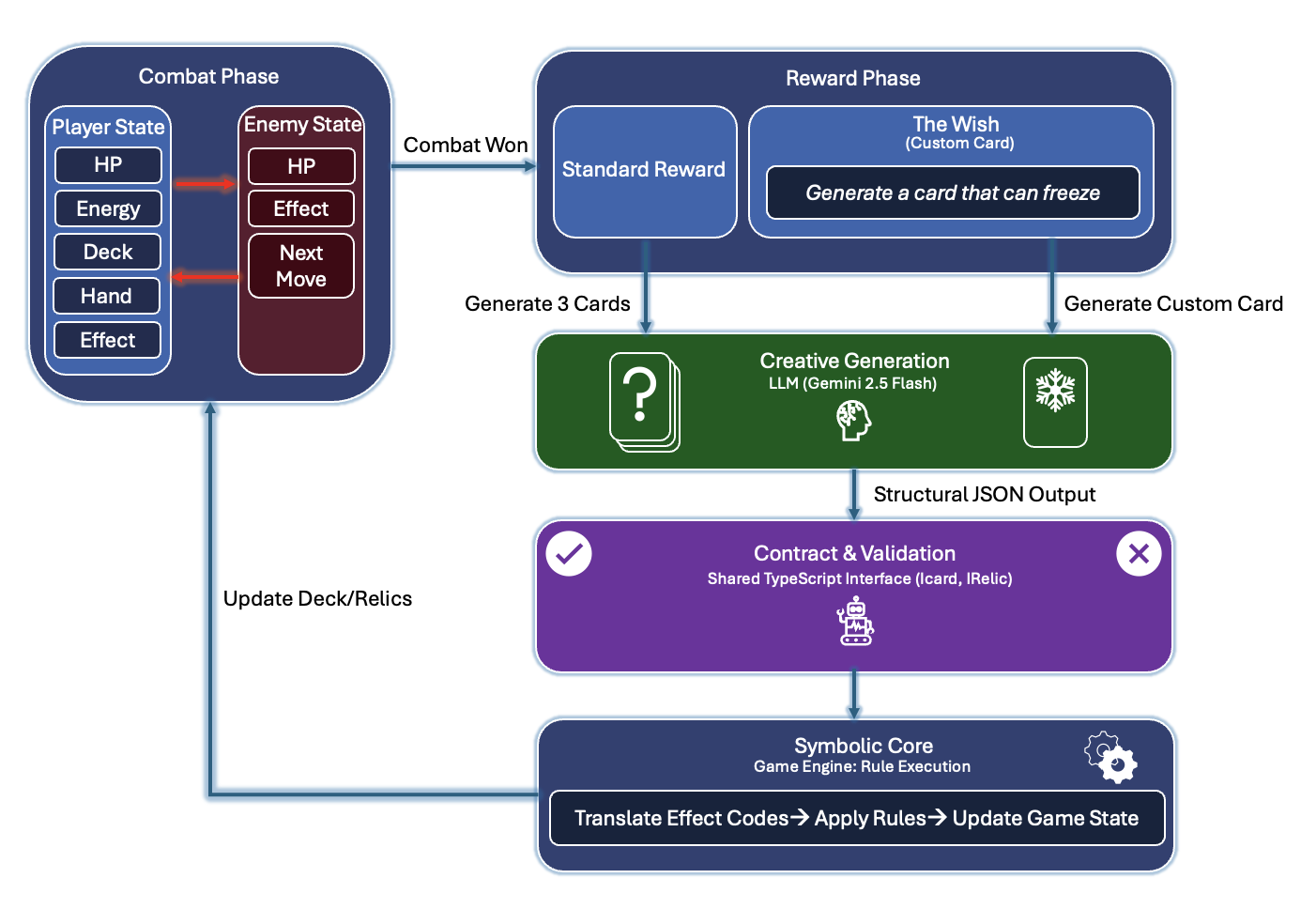
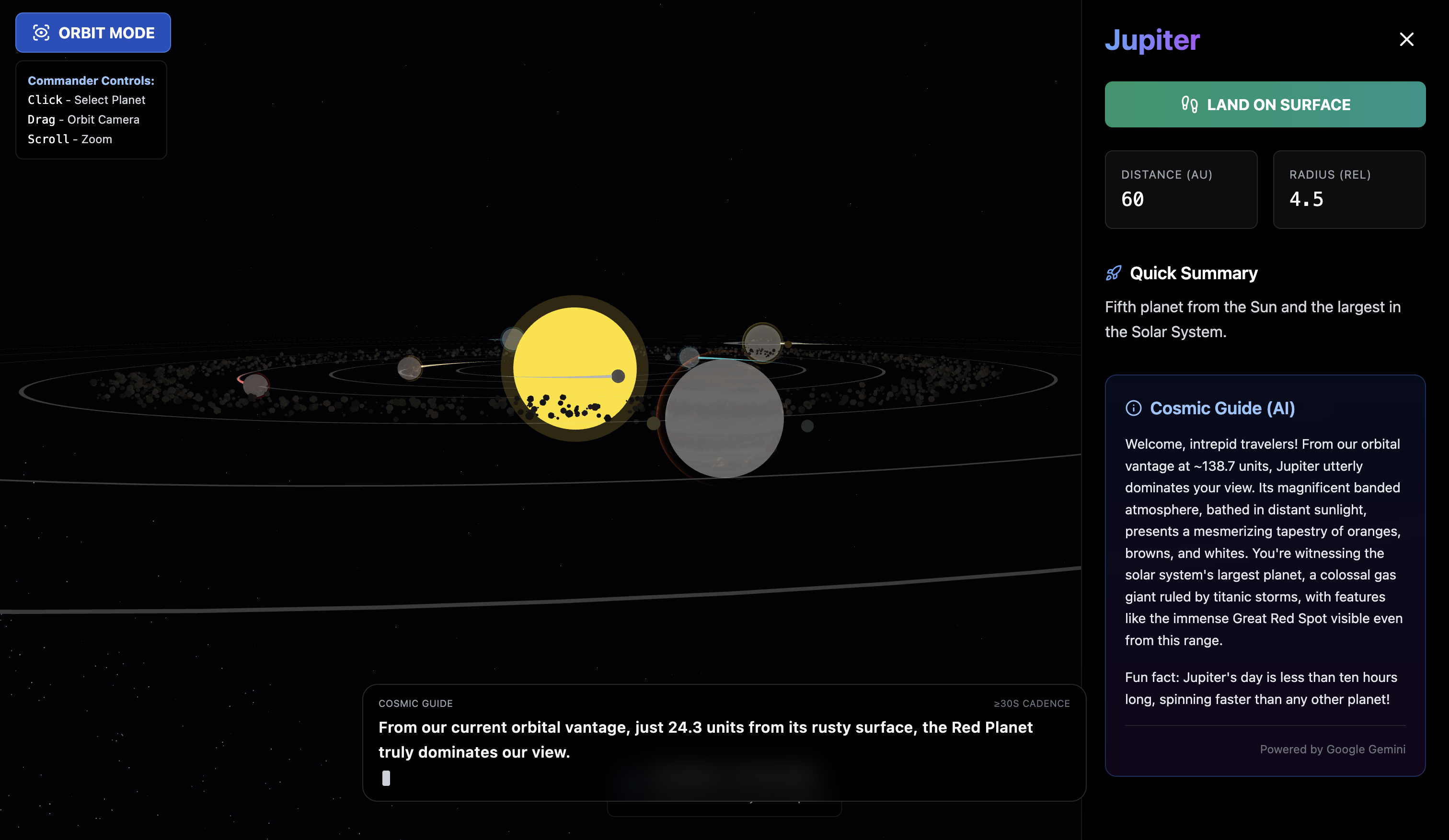
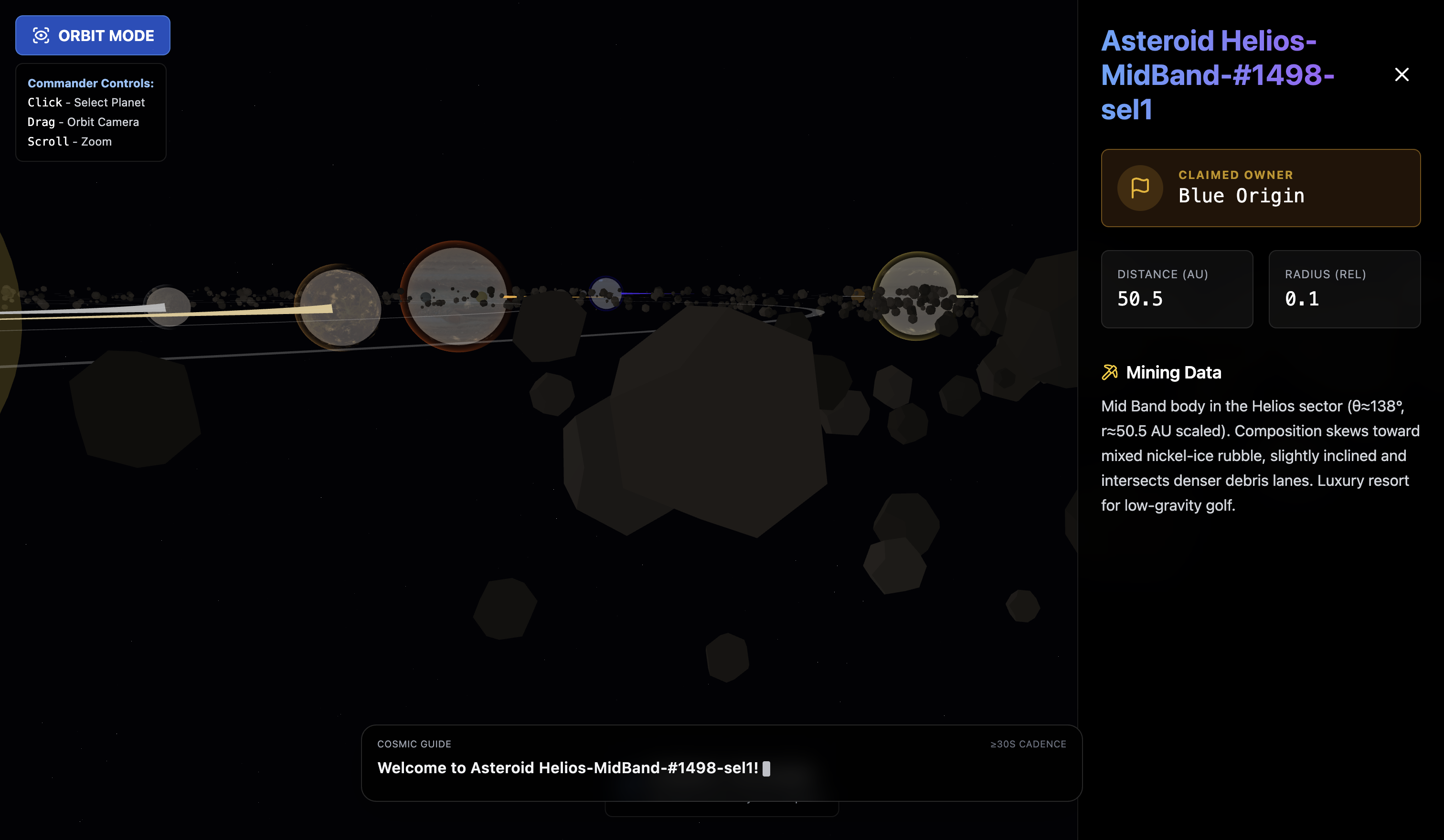
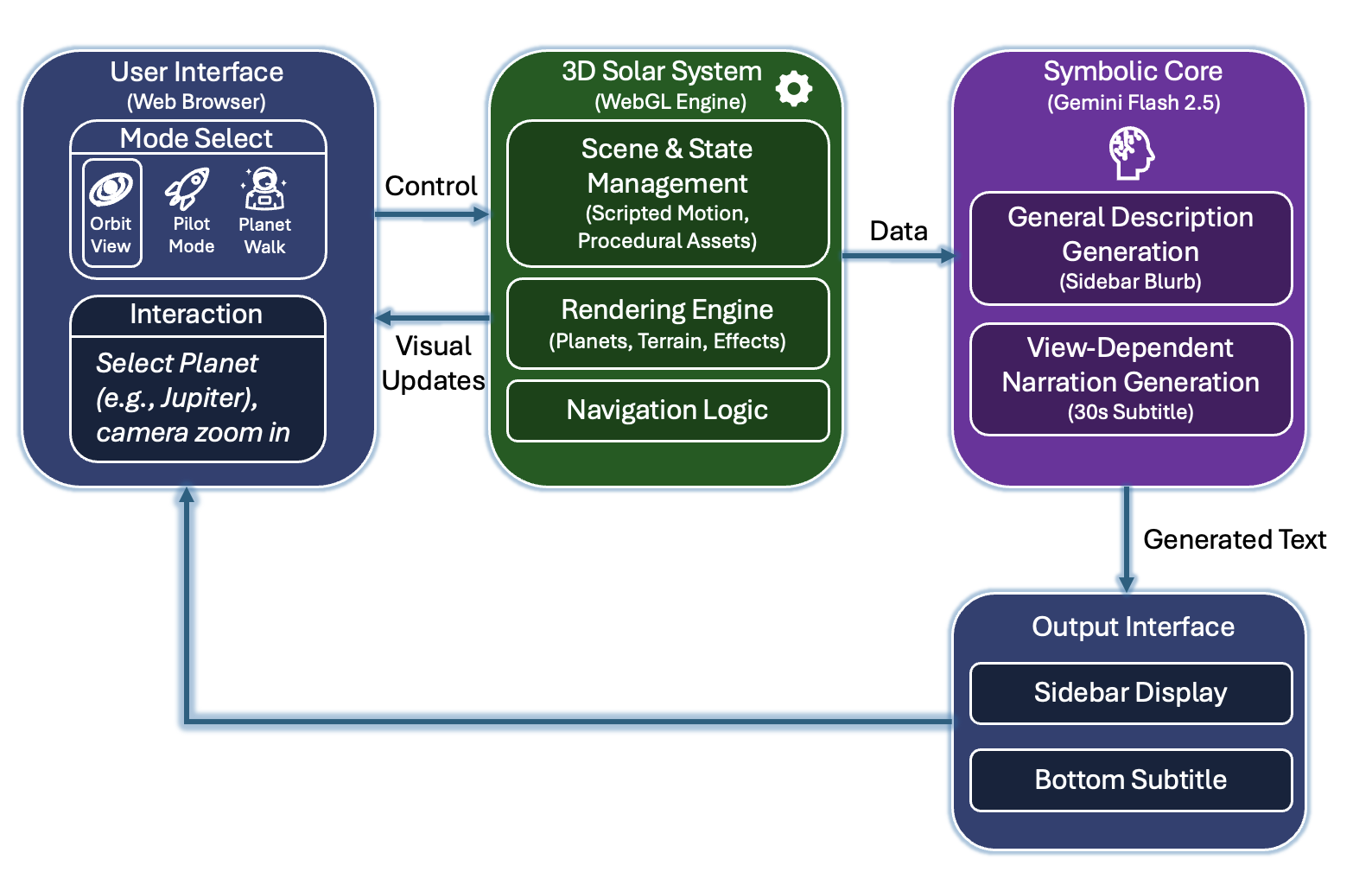
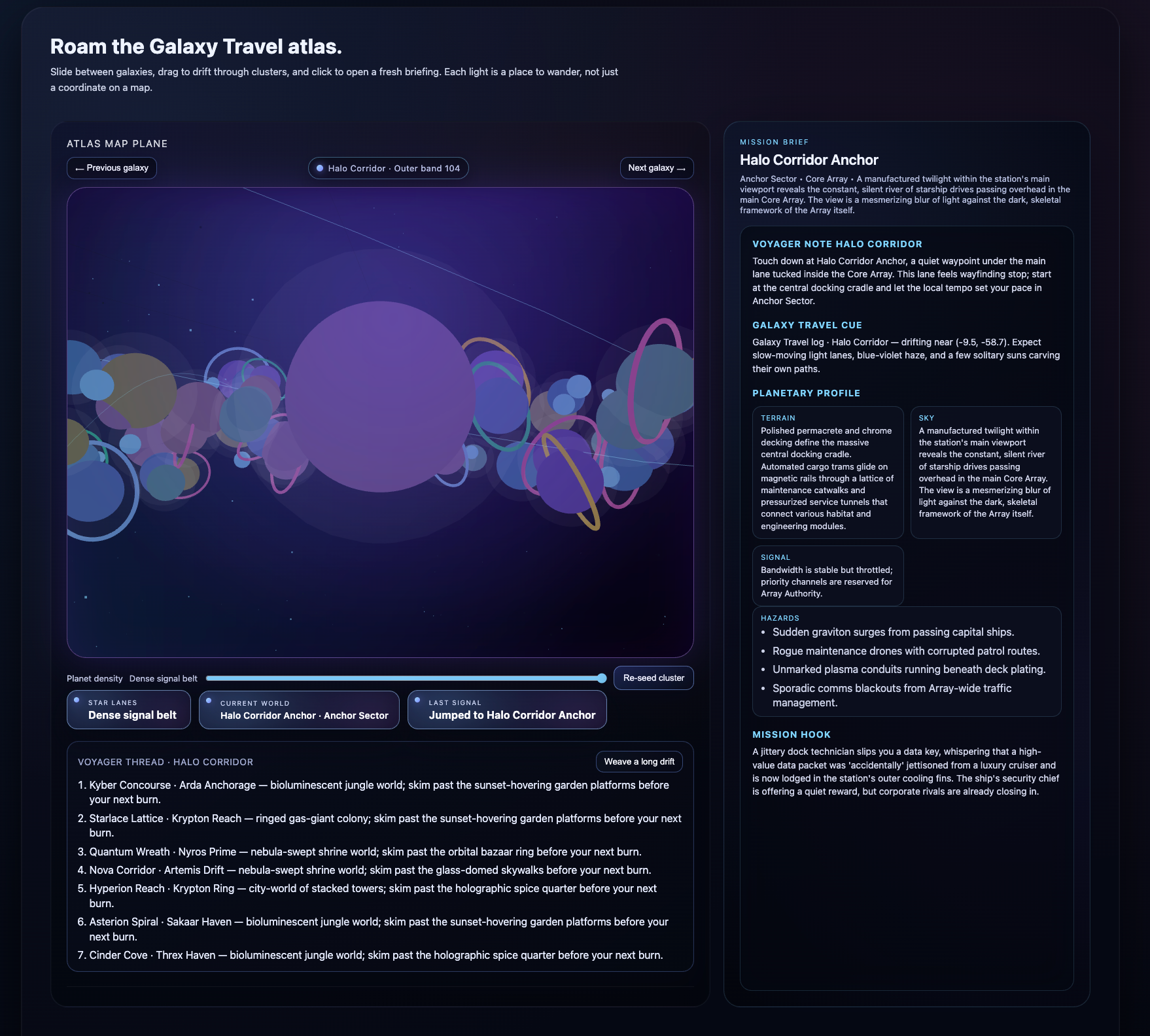
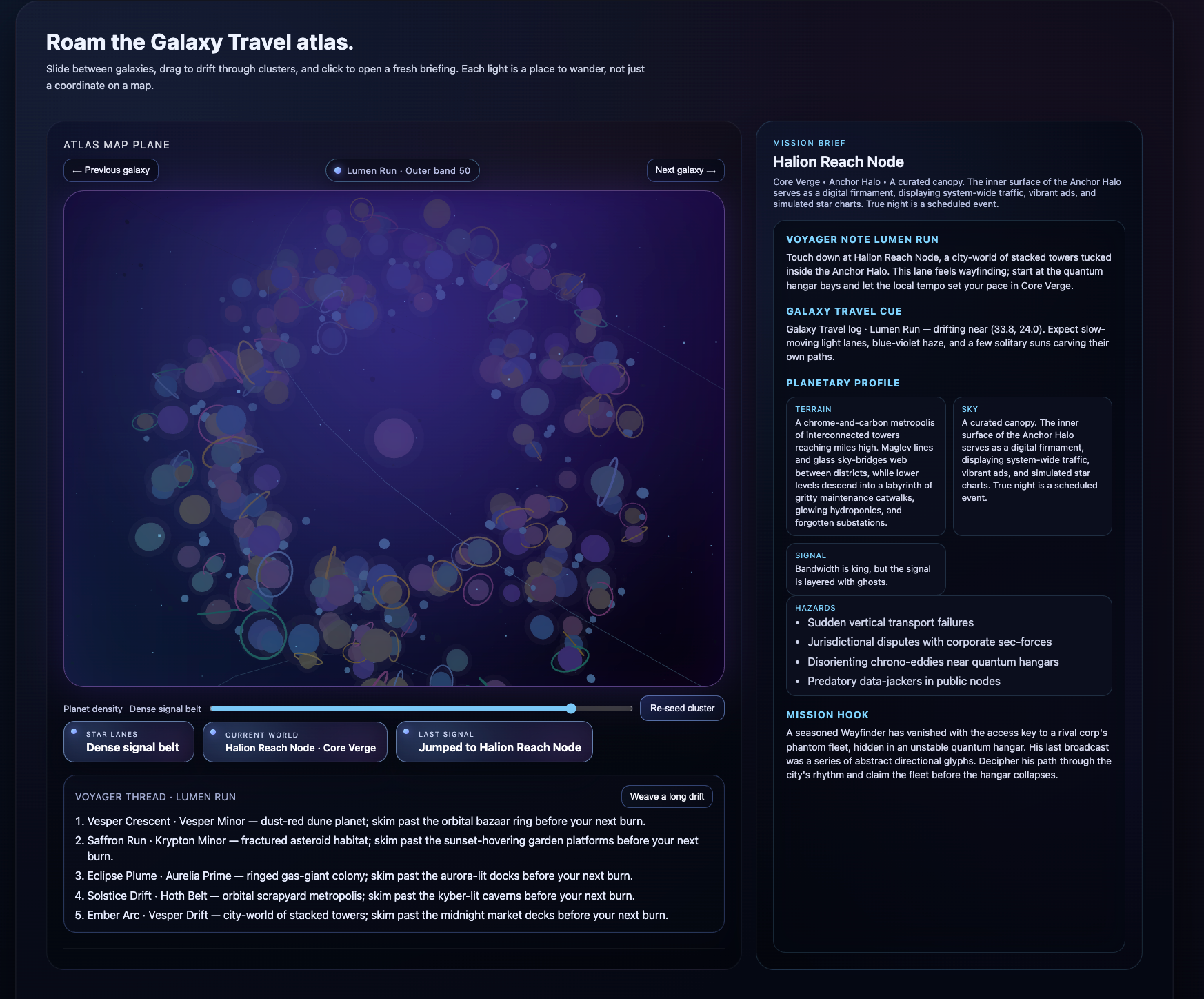
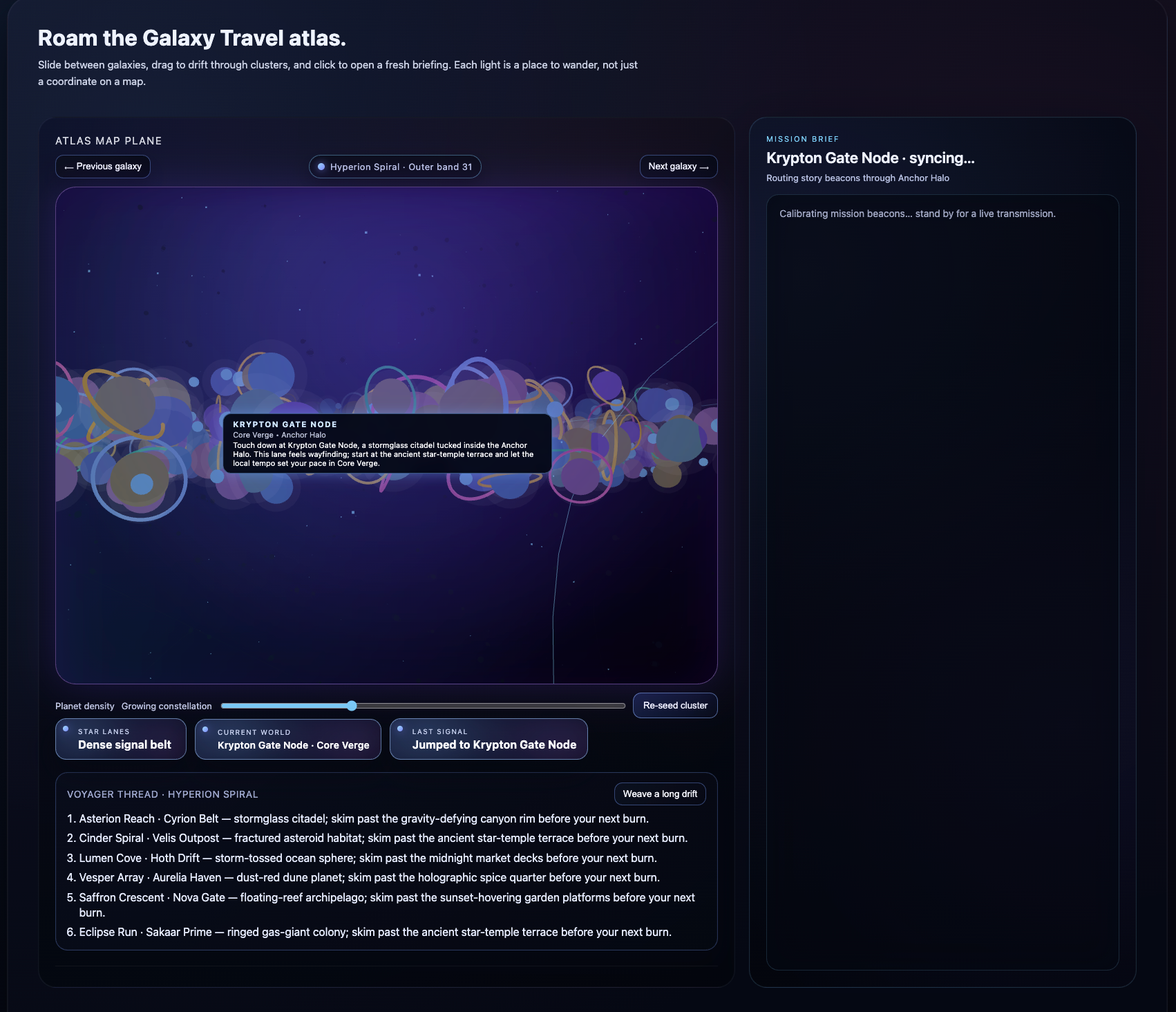
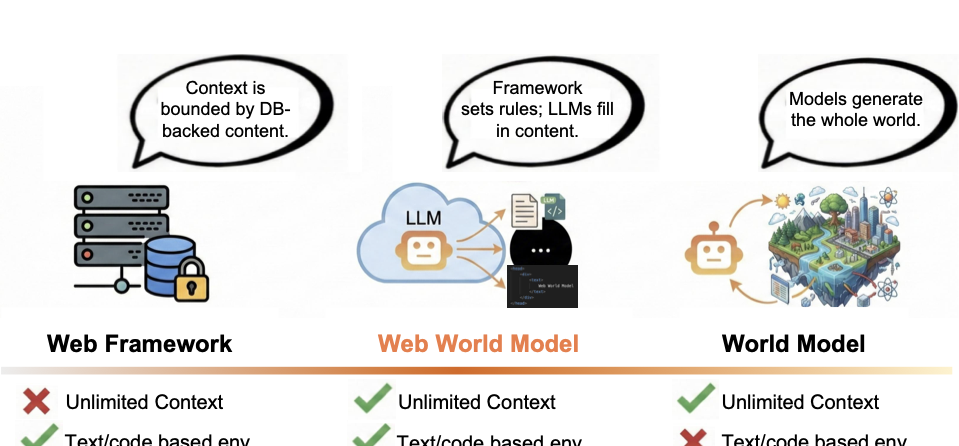
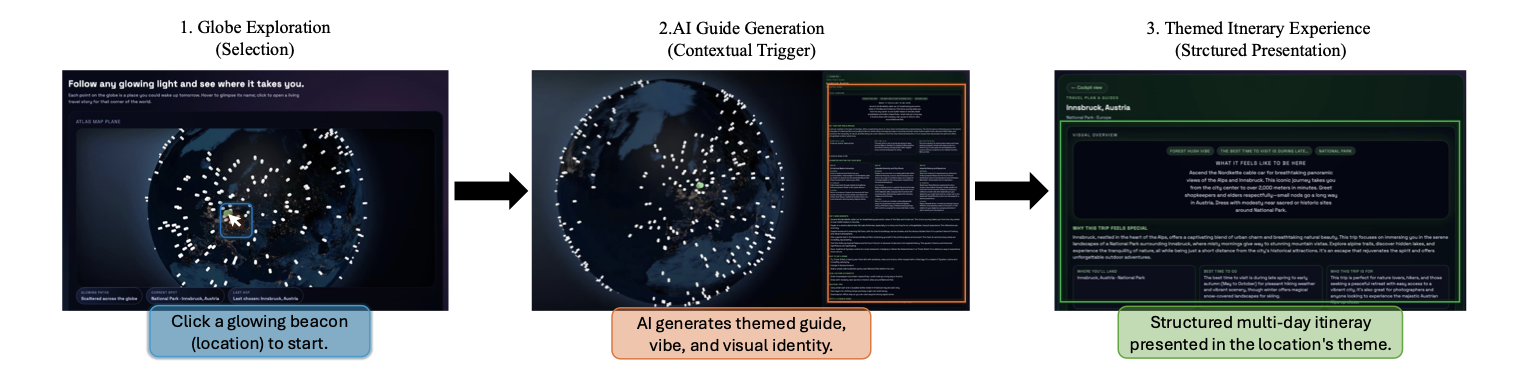
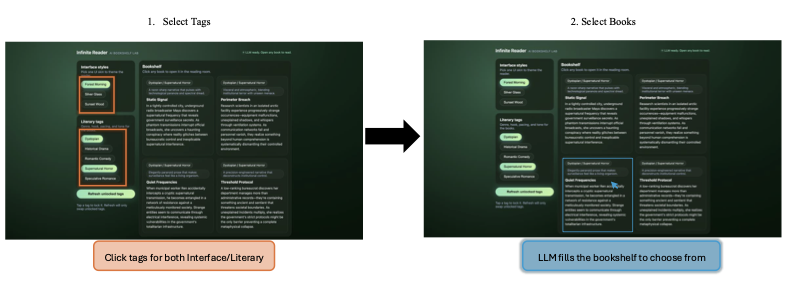
Language agents increasingly require persistent worlds in which they can act, remember, and learn. Existing approaches sit at two extremes: conventional web frameworks provide reliable but fixed contexts backed by databases, while fully generative world models aim for unlimited environments at the expense of controllability and practical engineering. In this work, we introduce the Web World Model (WWM), a middle ground where world state and ``physics'' are implemented in ordinary web code to ensure logical consistency, while large language models generate context, narratives, and high-level decisions on top of this structured latent state. We build a suite of WWMs on a realistic web stack, including an infinite travel atlas grounded in real geography, fictional galaxy explorers, web-scale encyclopedic and narrative worlds, and simulation- and game-like environments. Across these systems, we identify practical design principles for WWMs: separating code-defined rules from model-driven imagination, representing latent state as typed web interfaces, and utilizing deterministic generation to achieve unlimited but structured exploration. Our results suggest that web stacks themselves can serve as a scalable substrate for world models, enabling controllable yet open-ended environments. Project Page: https://github.com/Princeton-AI2-Lab/Web-World-Models.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Introduction of New Transformer Architecture**: This research improves the efficiency of deep learning models by adding a new architecture to existing transformer frameworks. It's akin to enhancing a car engine for faster and more efficient driving. 2. **Enhanced Performance in Sentiment Analysis**: The proposed model significantly improved accuracy, especially for sentiment analysis tasks. Think of it as an app that better understands user preferences and makes more accurate recommendations. 3. **Potential of Deep Learning Models**: This work demonstrates the potential of deep learning models to improve NLP applications, setting a foundation for further research in this field.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)