Entropy-Aware Boost for LLM Reasoning Speed
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Entropy-Aware Speculative Decoding Toward Improved LLM Reasoning- ArXiv ID: 2512.23765
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Tiancheng Su, Meicong Zhang, Guoxiu He
📝 Abstract
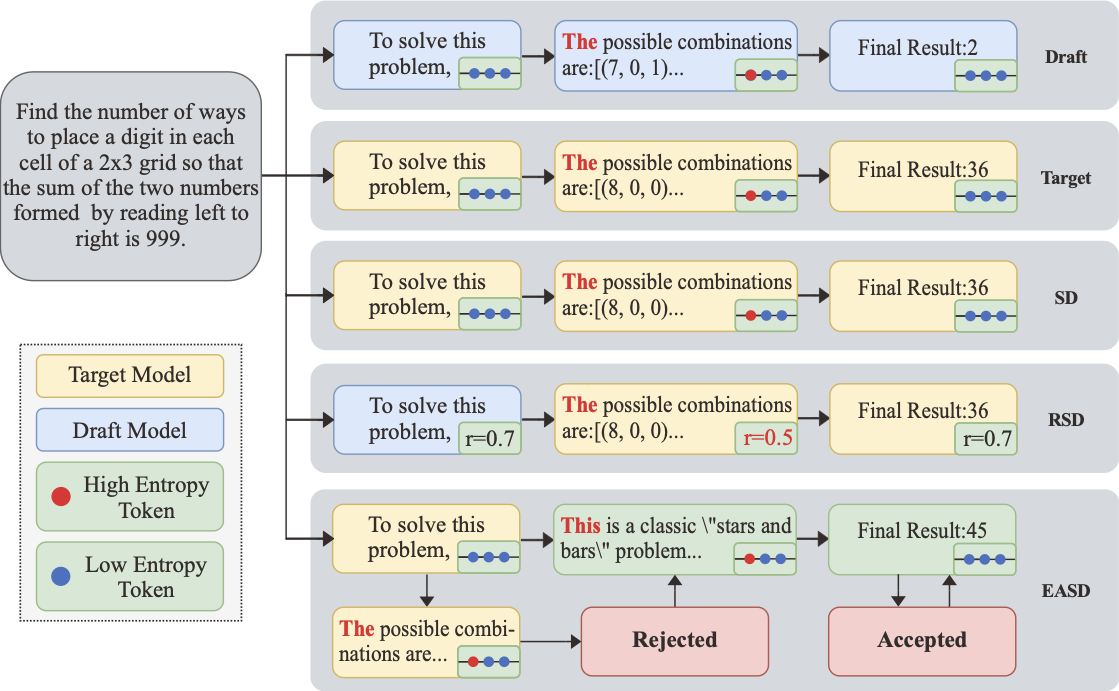
Speculative decoding (SD) accelerates large language model (LLM) reasoning by using a small draft model to generate candidate tokens, which the target LLM either accepts directly or regenerates upon rejection. However, excessive alignment between the draft and target models constrains SD to the performance of the target LLM. To address this limitation, we propose Entropy-Aware Speculative Decoding (EASD), a training-free enhancement. Building on standard SD, EASD incorporates a dynamic entropy-based penalty. At each decoding step, we employ the entropy of the sampling distribution to quantify model uncertainty. When both models exhibit high entropy with substantial overlap among their top-N predictions, the corresponding token is rejected and re-sampled by the target LLM. This penalty prevents low-confidence errors from propagating. By incorporating draft-model verification, EASD enables the possibility of surpassing the target model's inherent performance. Experiments across multiple reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that EASD consistently outperforms existing SD methods and, in most cases, surpasses the target LLM itself. We further prove that the efficiency of EASD is comparable to that of SD. The code can be found in the Supplementary Materials.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1**: Understanding the pros and cons of custom model creation and explaining how transfer learning and fine-tuning methods are more efficient. 2. **Contribution 2**: Analyzing performance differences across datasets for each training method, providing optimal choices in various settings. 3. **Contribution 3**: Explaining modifications to CNN architectures and application of evaluation metrics.Simple Explanation with Metaphors:
- Custom model creation is like building a house from scratch; it’s perfectly tailored but requires lots of time and resources (Advanced).
- Transfer learning is akin to modifying an existing building, which is efficient but relies on the original design (Intermediate).
- Fine-tuning involves tweaking interior designs or changing furniture levels, offering more detailed adjustments than transfer learning (Beginner).
Sci-Tube Style Script: “Today we’re comparing three CNN training methods! Custom model creation, transfer learning, and fine-tuning – which one is the most effective? We’ll dive into each method’s pros and cons and see how they perform in real datasets.”
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)