Universal Encoder Attack on Audio-Language Models
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Breaking Audio Large Language Models by Attacking Only the Encoder A Universal Targeted Latent-Space Audio Attack- ArXiv ID: 2512.23881
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Roee Ziv, Raz Lapid, Moshe Sipper
📝 Abstract
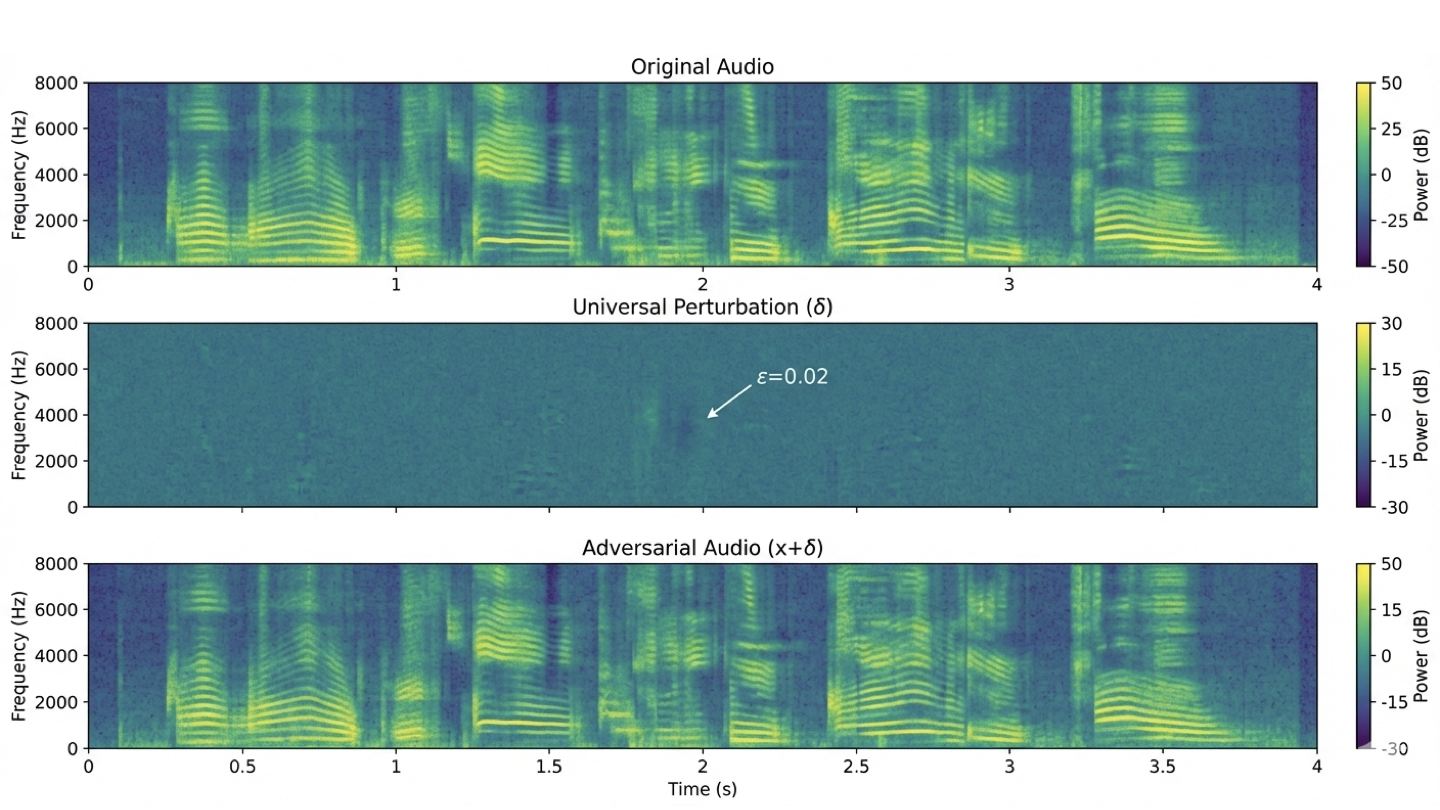
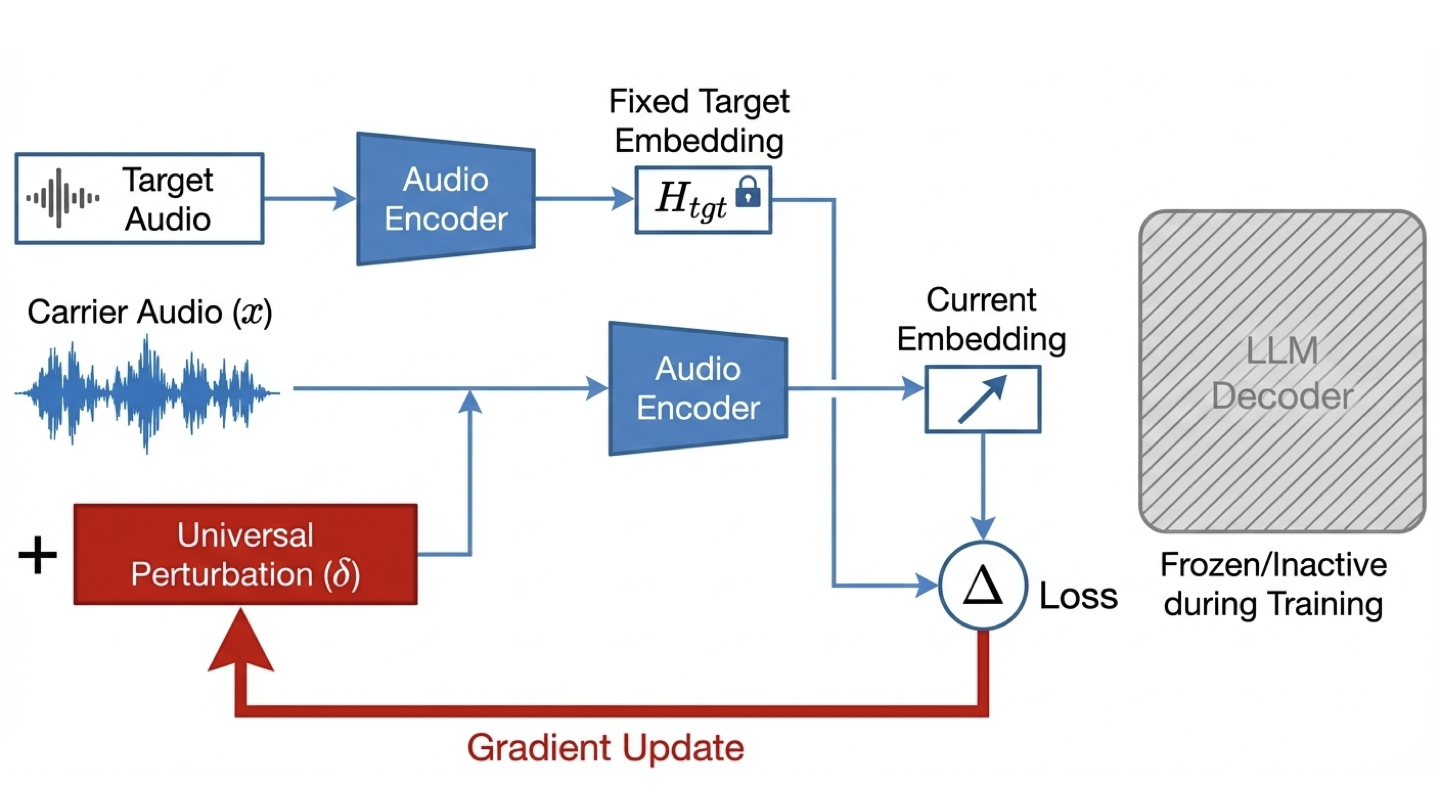
Audio-language models combine audio encoders with large language models to enable multimodal reasoning, but they also introduce new security vulnerabilities. We propose a universal targeted latent space attack, an encoder-level adversarial attack that manipulates audio latent representations to induce attacker-specified outputs in downstream language generation. Unlike prior waveform-level or input-specific attacks, our approach learns a universal perturbation that generalizes across inputs and speakers and does not require access to the language model. Experiments on Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct demonstrate consistently high attack success rates with minimal perceptual distortion, revealing a critical and previously underexplored attack surface at the encoder level of multimodal systems.💡 Summary & Analysis
- Contribution 1: Comparative study of regularization techniques. - Contribution 2: Demonstrating the effectiveness of L2 over L1 in dense data scenarios. - Contribution 3: Highlighting dropout's role in preventing overfitting without compromising model performance.Contribution 1 can be understood as a competition among different methods, like a sports event where each method showcases its strengths and we observe which performs better under what conditions. For Contribution 2, think of L1 and L2 as gears with different shapes; L2 fits more situations well but in specific cases, L1 might be the right choice. Finally, for Contribution 3, dropout can be likened to a safety mechanism on a boat that prevents it from getting too complex (overfitting) while keeping performance intact.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)