Transformer Surrogates Predict Plasma Edge Dynamics Efficiently
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Autoregressive long-horizon prediction of plasma edge dynamics- ArXiv ID: 2512.23884
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Hunor Csala, Sebastian De Pascuale, Paul Laiu, Jeremy Lore, Jae-Sun Park, Pei Zhang
📝 Abstract
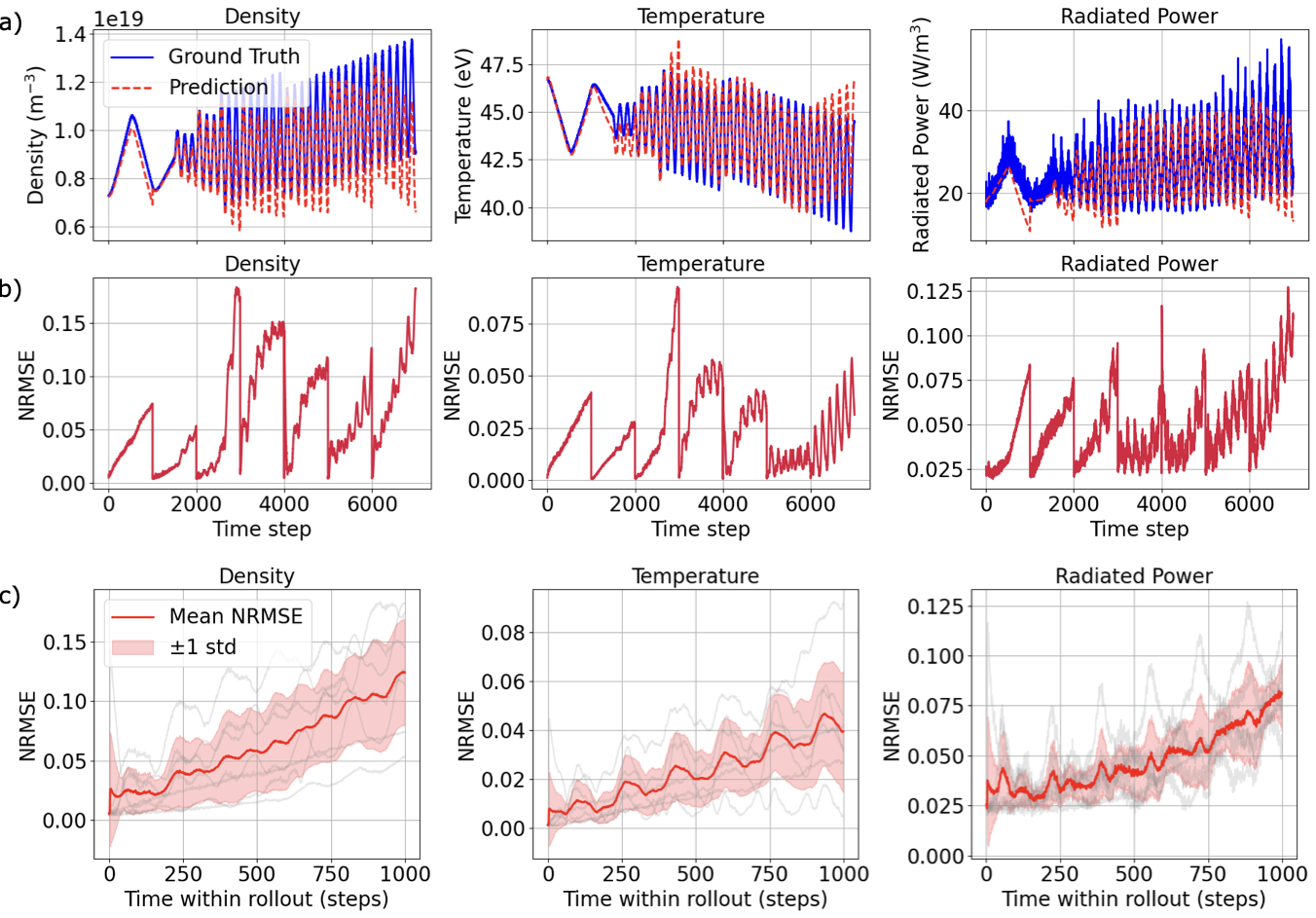
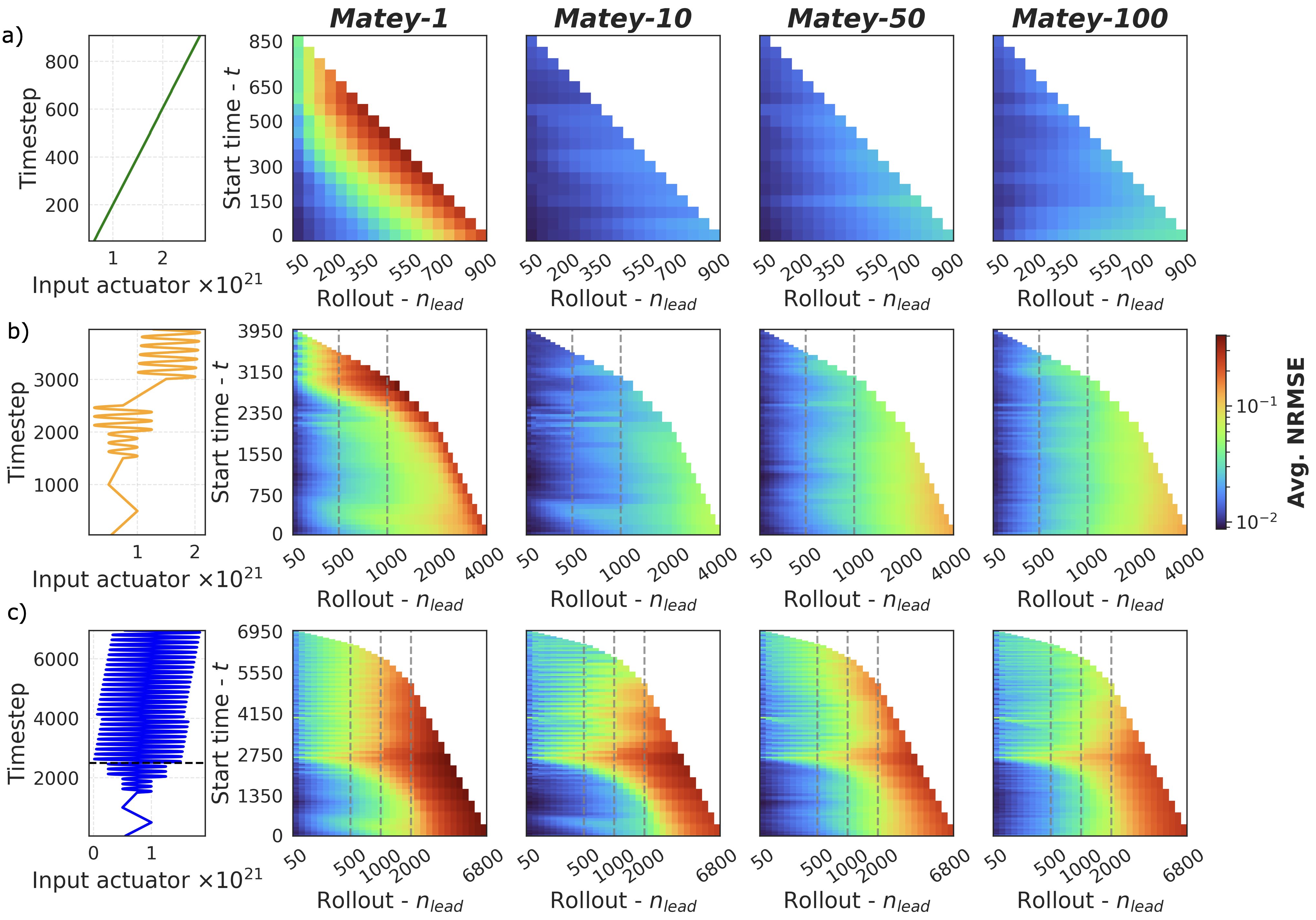
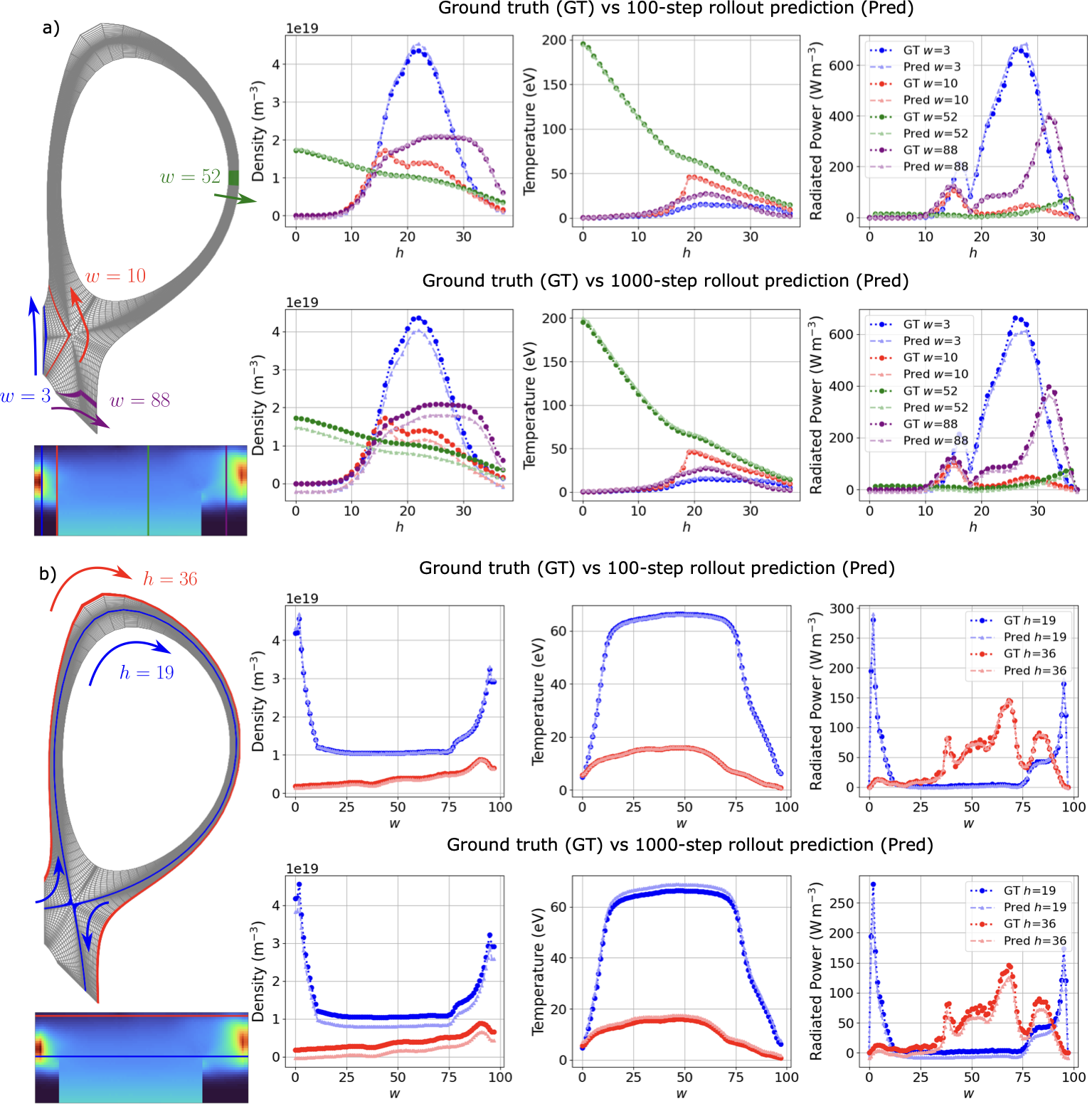
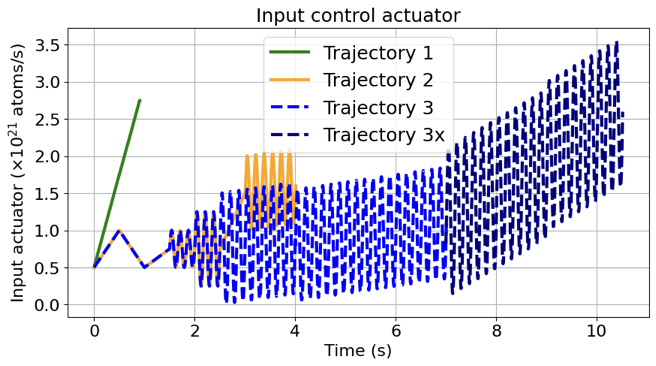
Accurate modeling of scrape-off layer (SOL) and divertor-edge dynamics is vital for designing plasma-facing components in fusion devices. High-fidelity edge fluid/neutral codes such as SOLPS-ITER capture SOL physics with high accuracy, but their computational cost limits broad parameter scans and long transient studies. We present transformer-based, autoregressive surrogates for efficient prediction of 2D, time-dependent plasma edge state fields. Trained on SOLPS-ITER spatiotemporal data, the surrogates forecast electron temperature, electron density, and radiated power over extended horizons. We evaluate model variants trained with increasing autoregressive horizons (1-100 steps) on short- and long-horizon prediction tasks. Longer-horizon training systematically improves rollout stability and mitigates error accumulation, enabling stable predictions over hundreds to thousands of steps and reproducing key dynamical features such as the motion of high-radiation regions. Measured end-to-end wall-clock times show the surrogate is orders of magnitude faster than SOLPS-ITER, enabling rapid parameter exploration. Prediction accuracy degrades when the surrogate enters physical regimes not represented in the training dataset, motivating future work on data enrichment and physics-informed constraints. Overall, this approach provides a fast, accurate surrogate for computationally intensive plasma edge simulations, supporting rapid scenario exploration, control-oriented studies, and progress toward real-time applications in fusion devices.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1**: Systematically understood the impact of deep learning on NLP tasks, akin to understanding how advanced cooking methods affect food taste and texture. 2. **Contribution 2**: Analyzed neural network performance across different datasets, similar to knowing which ingredients and cooking techniques best suit specific dishes. 3. **Contribution 3**: Provided insights into future research directions, much like obtaining information needed for developing new food menus.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)