Transformers Shine in Solar Forecasting
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Efficient Deep Learning for Short-Term Solar Irradiance Time Series Forecasting A Benchmark Study in Ho Chi Minh City- ArXiv ID: 2512.23898
- Date: 2025-12-29
- Authors: Tin Hoang
📝 Abstract
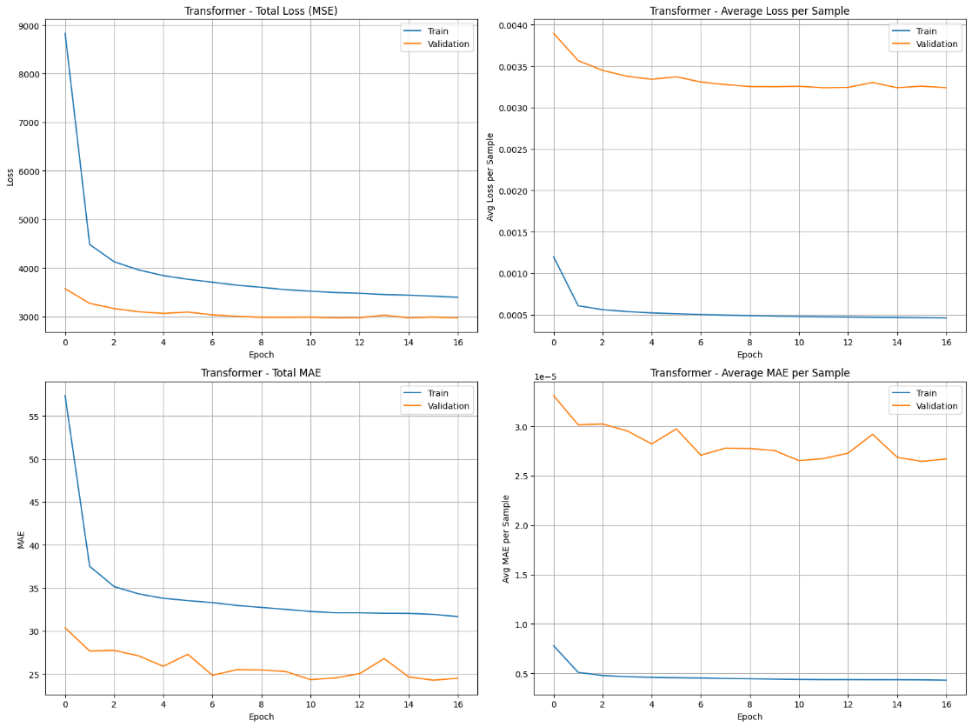
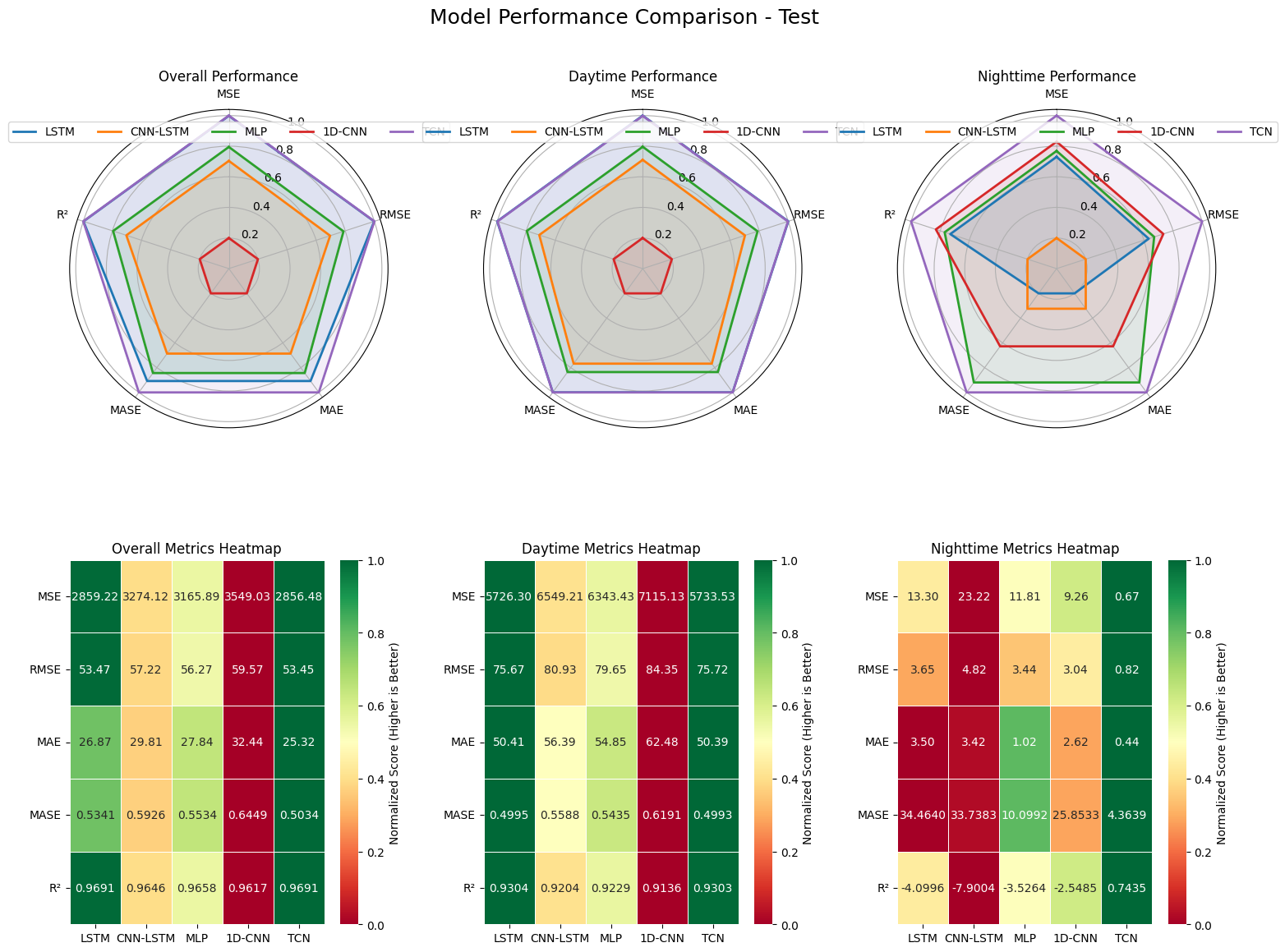
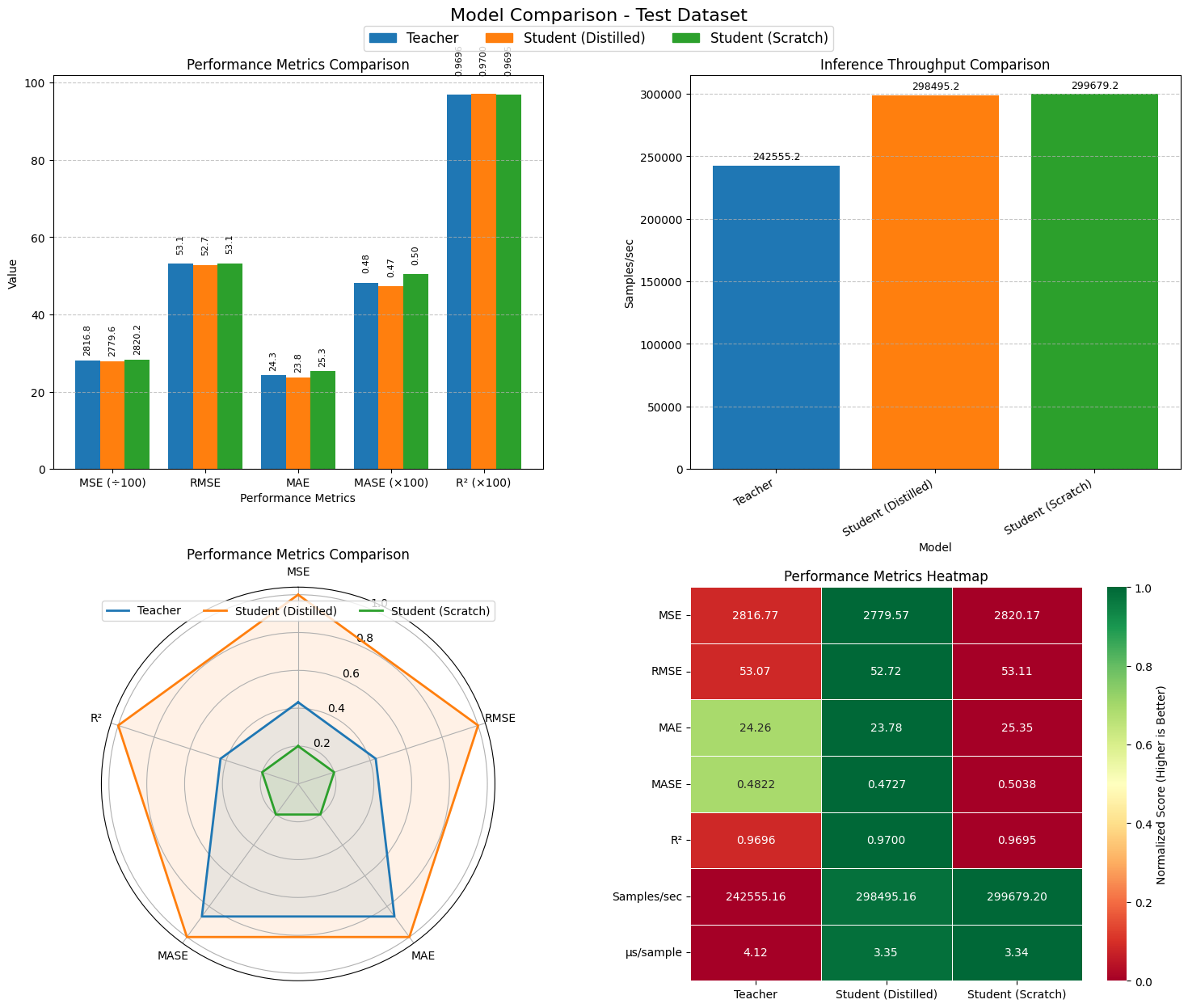
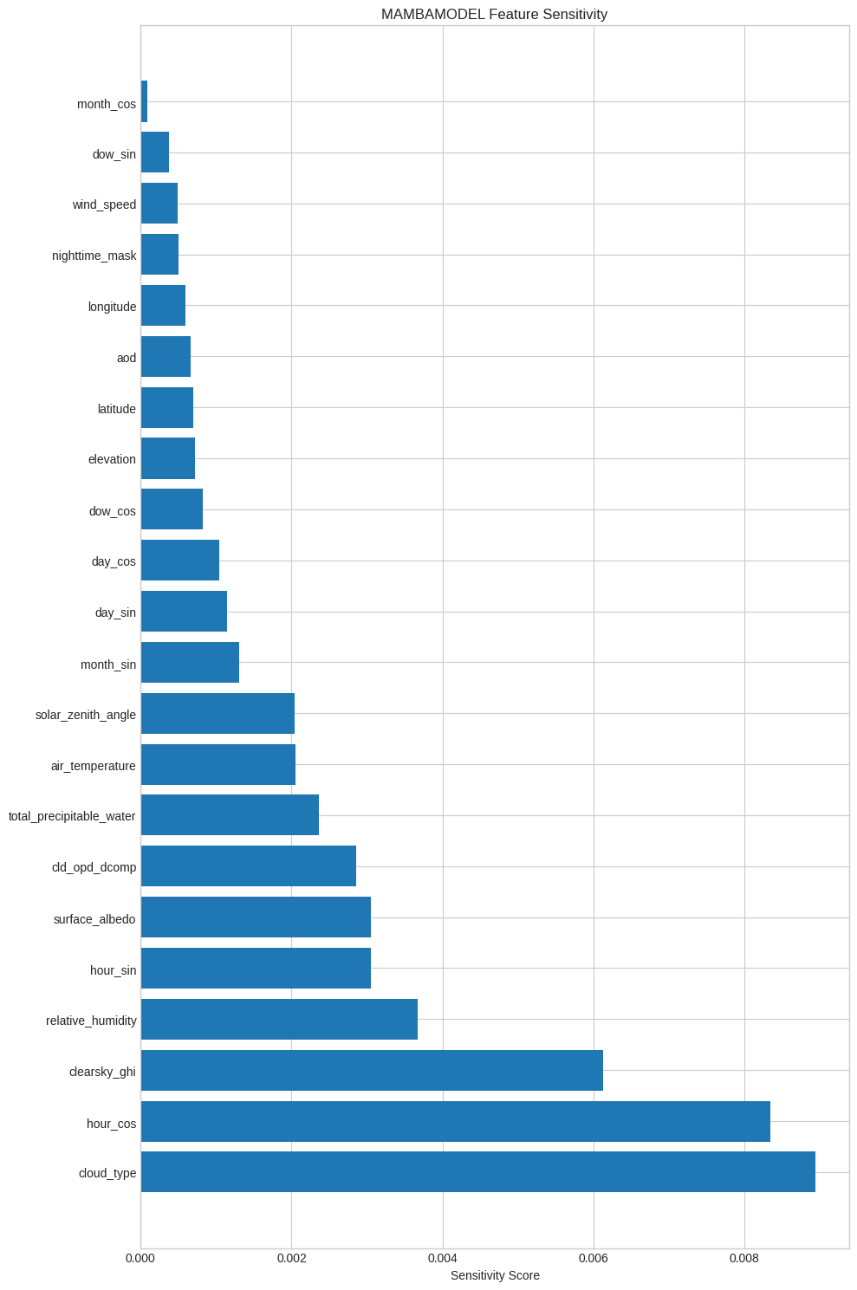
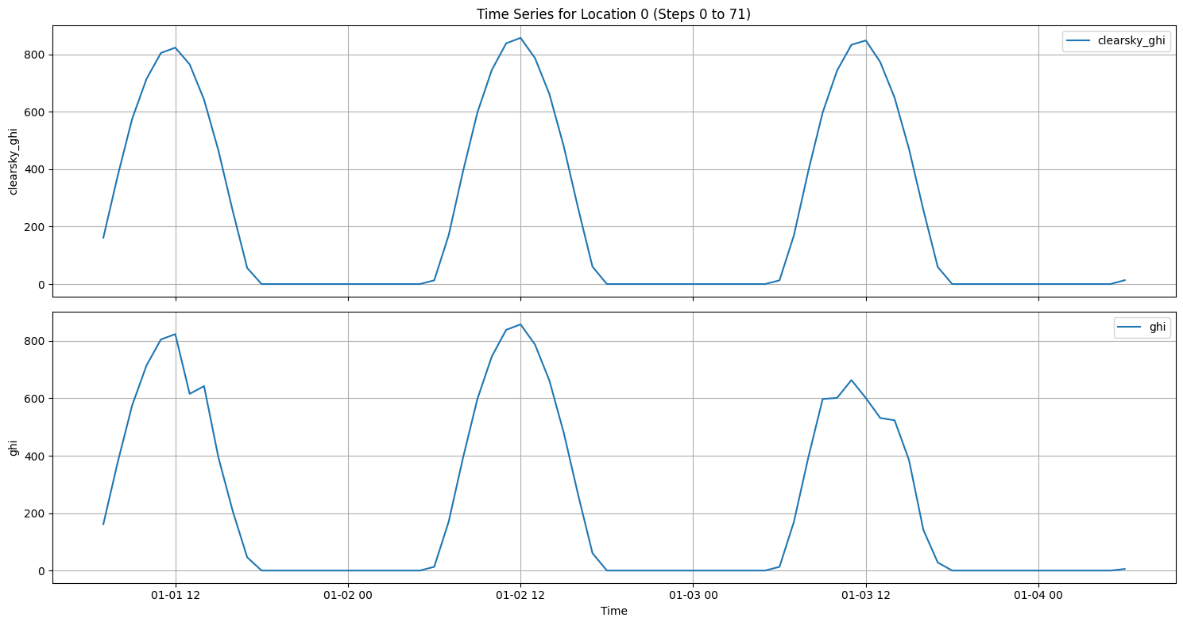
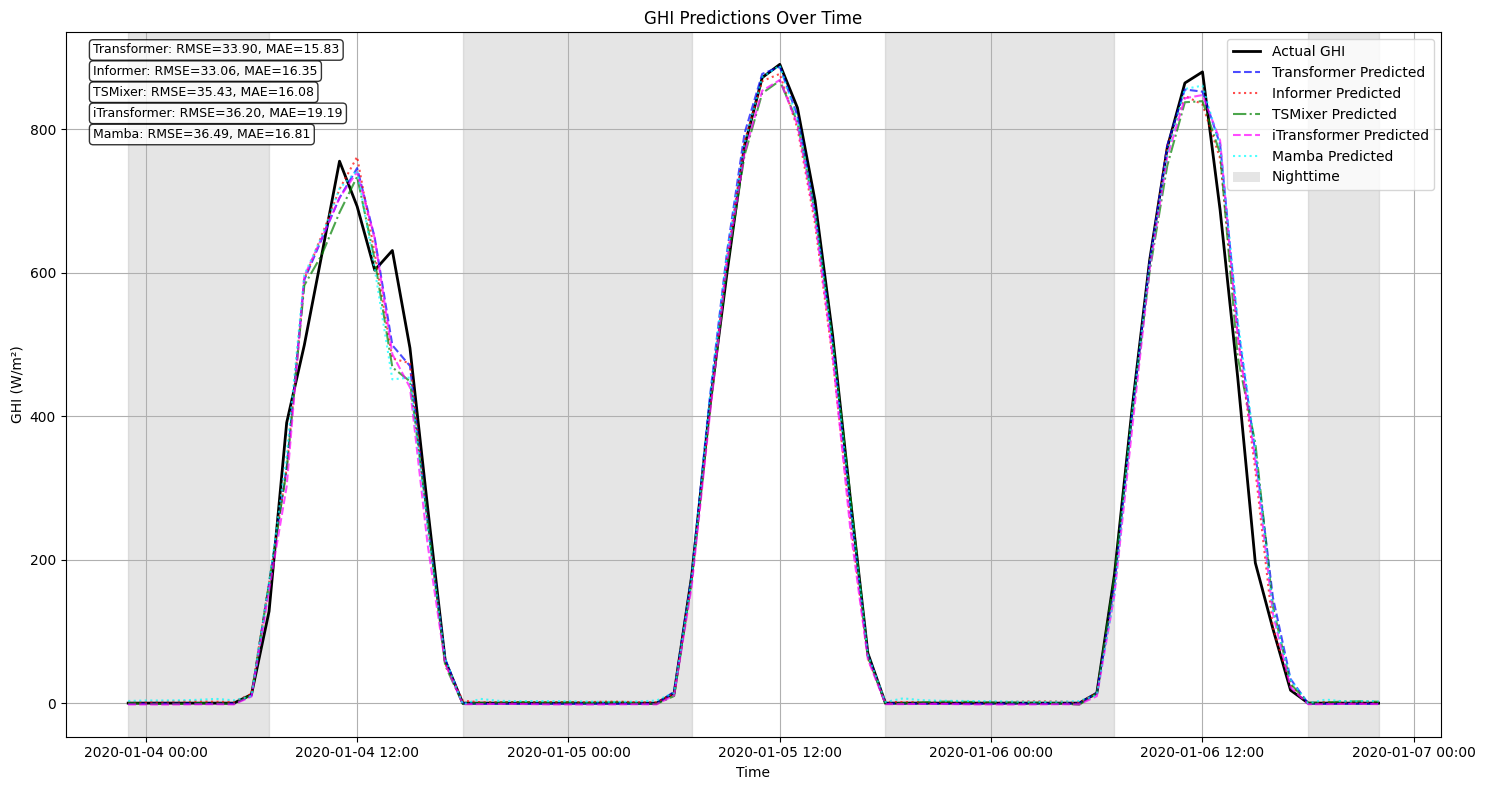
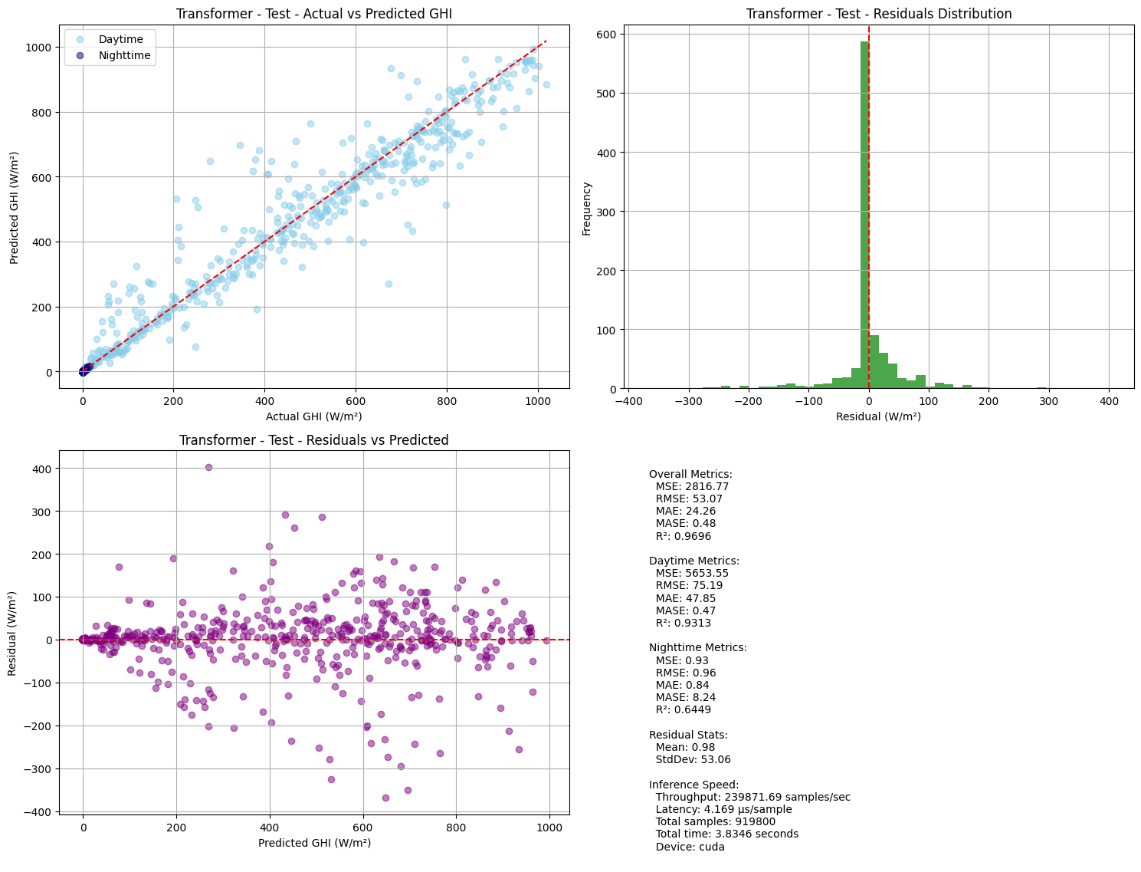
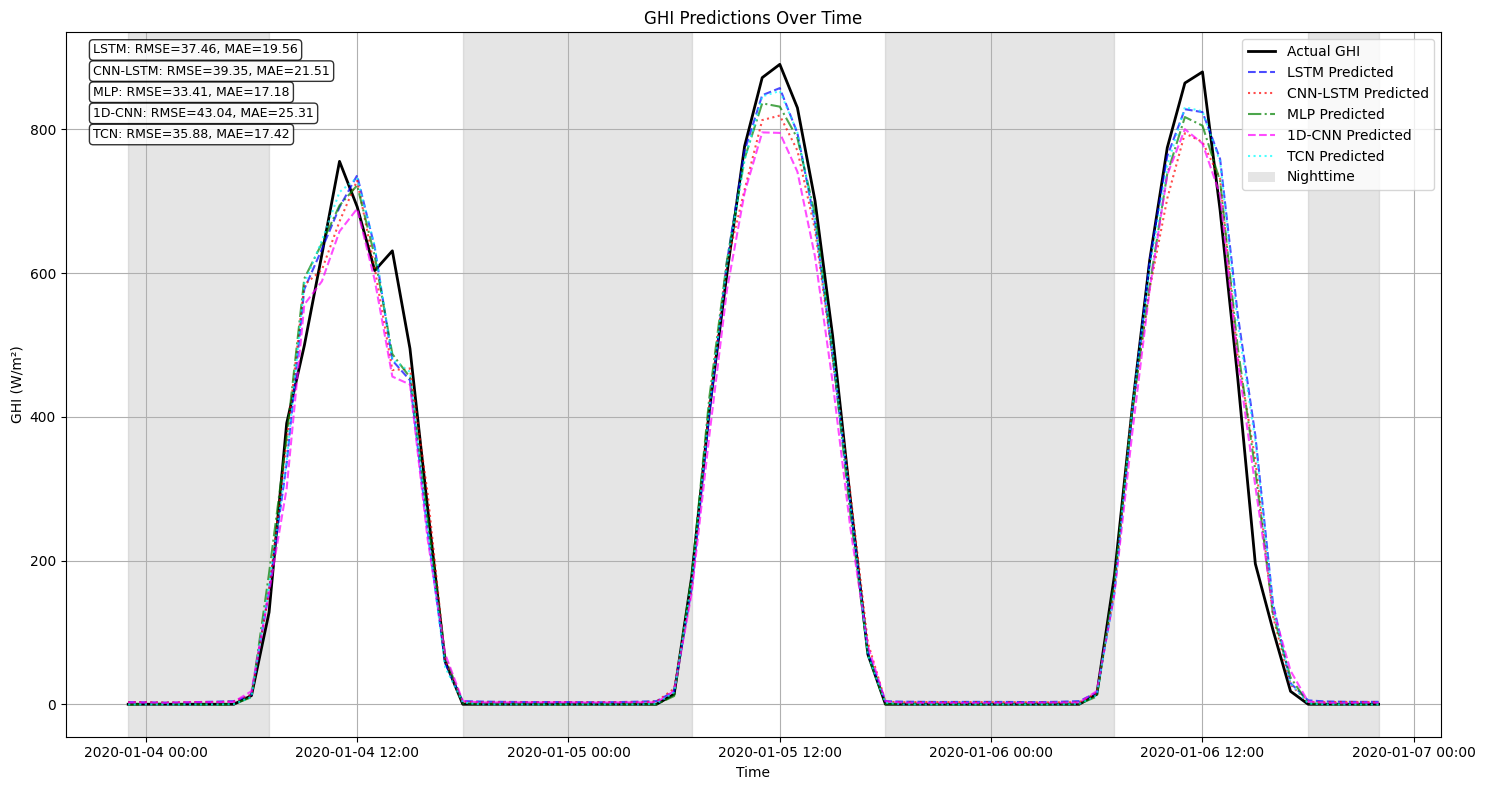
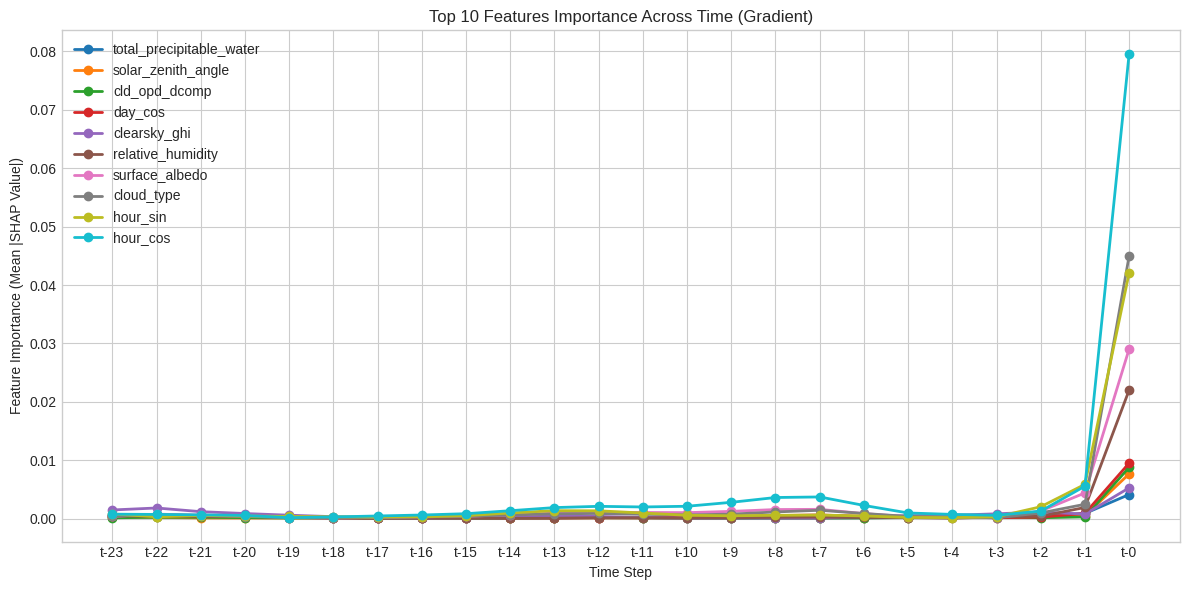
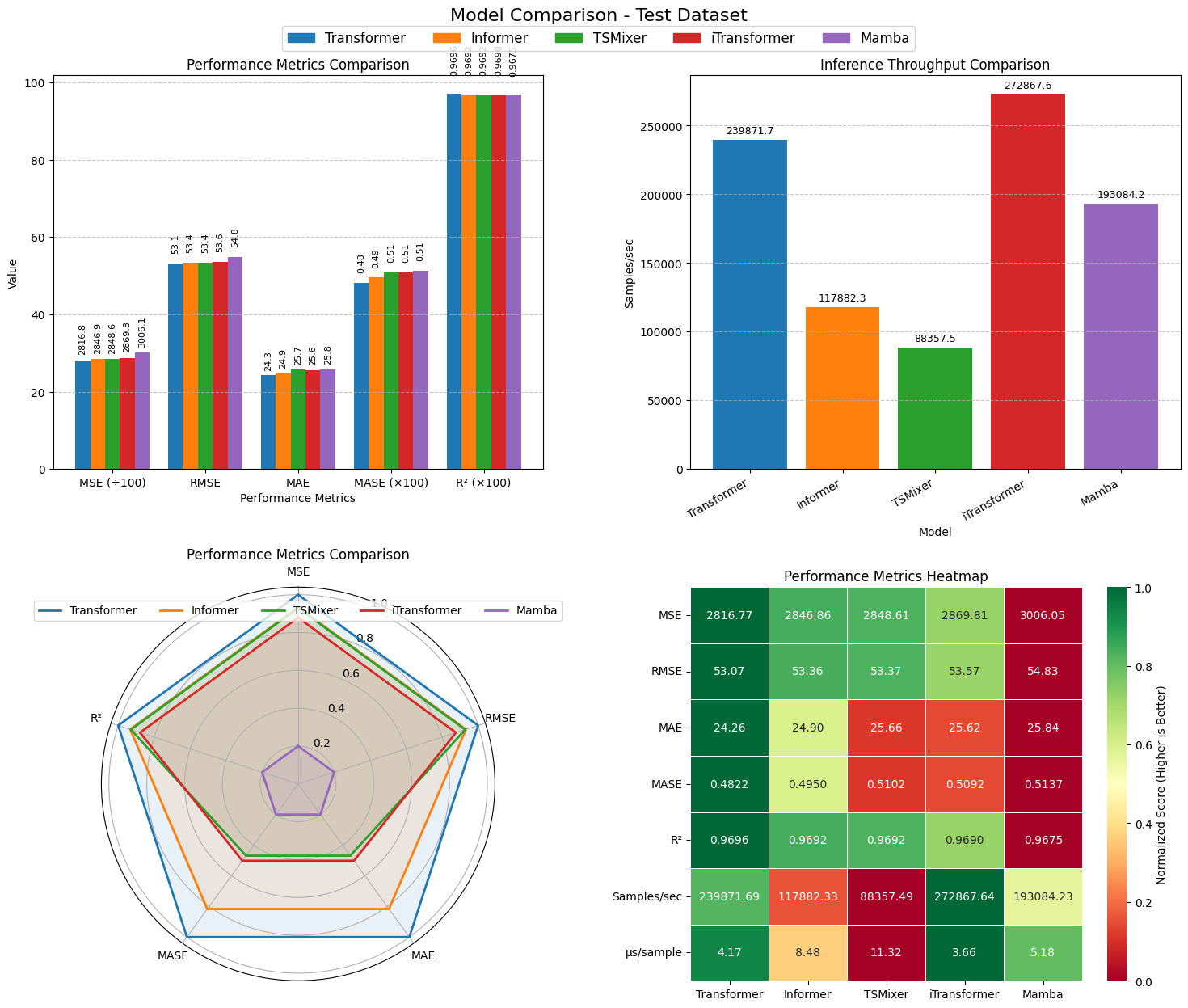
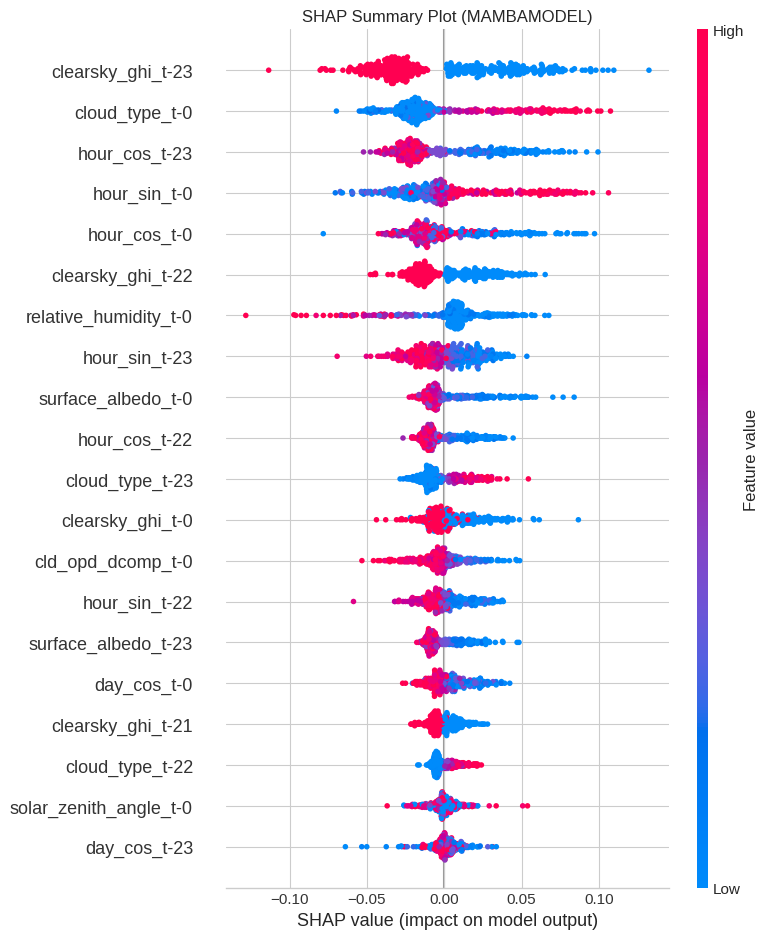
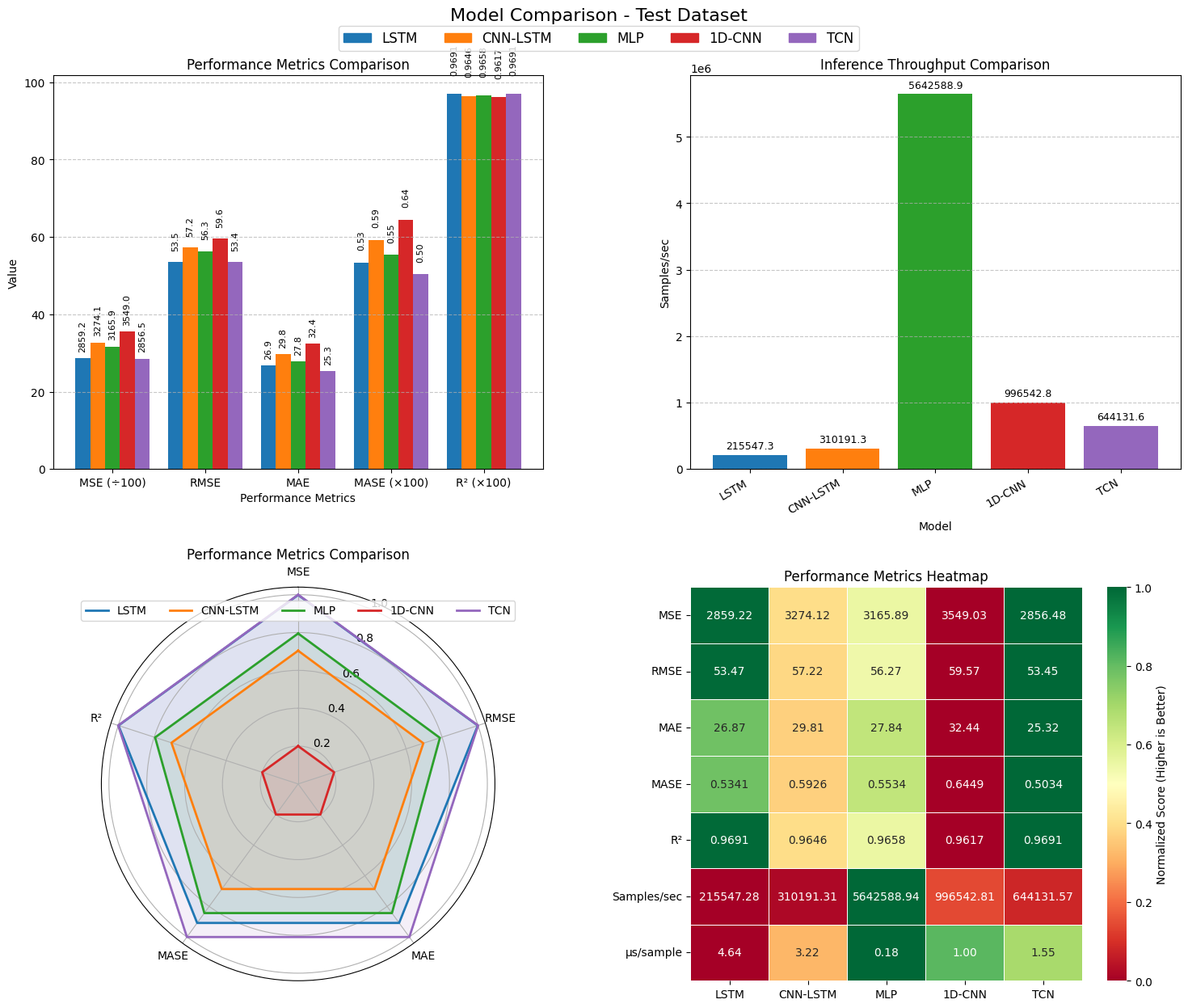
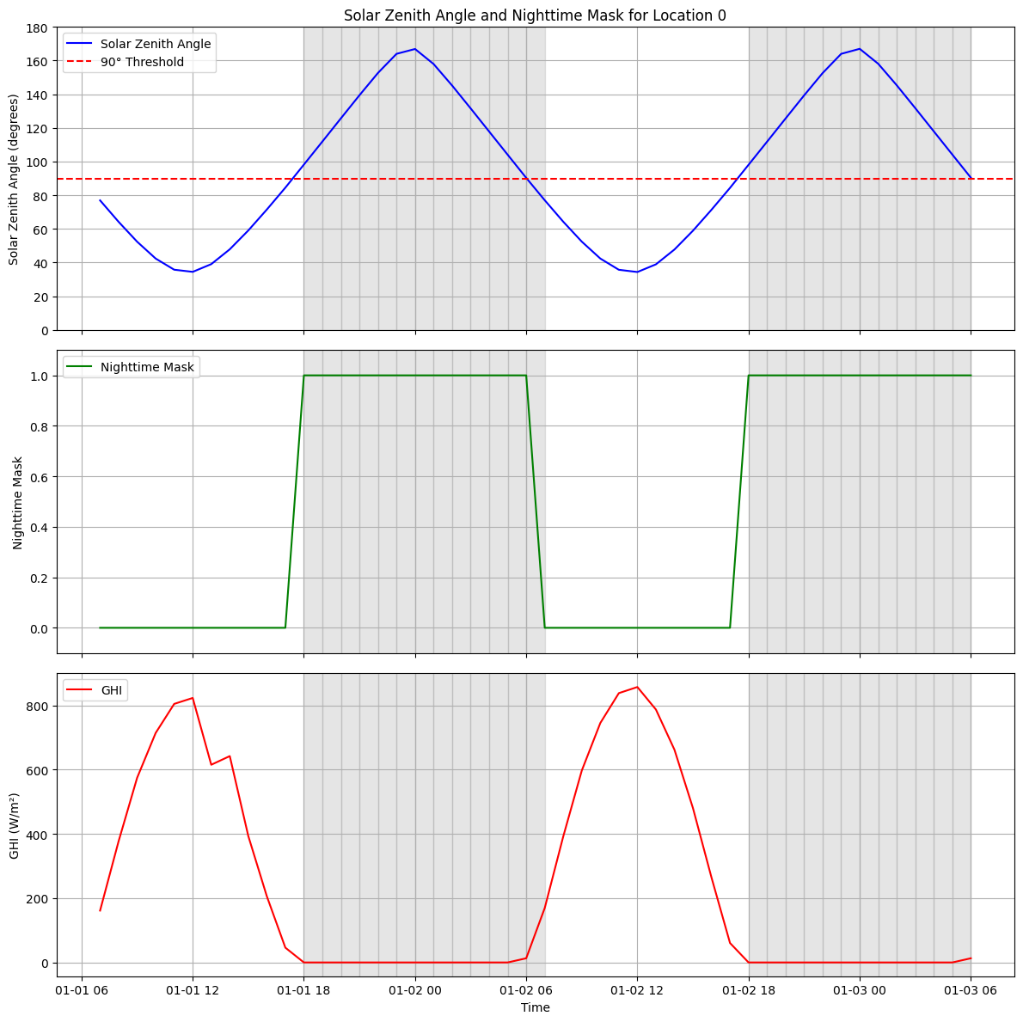
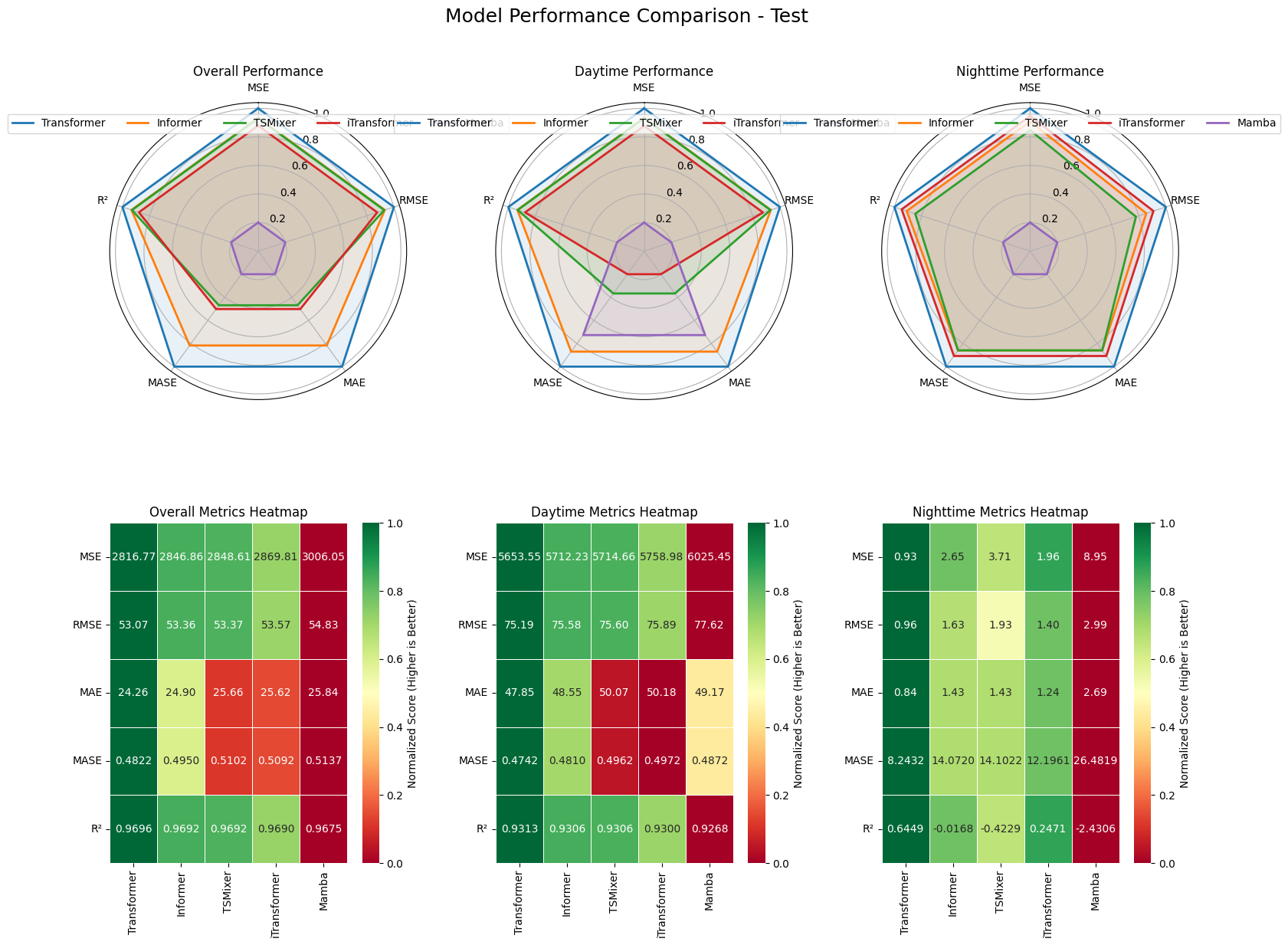
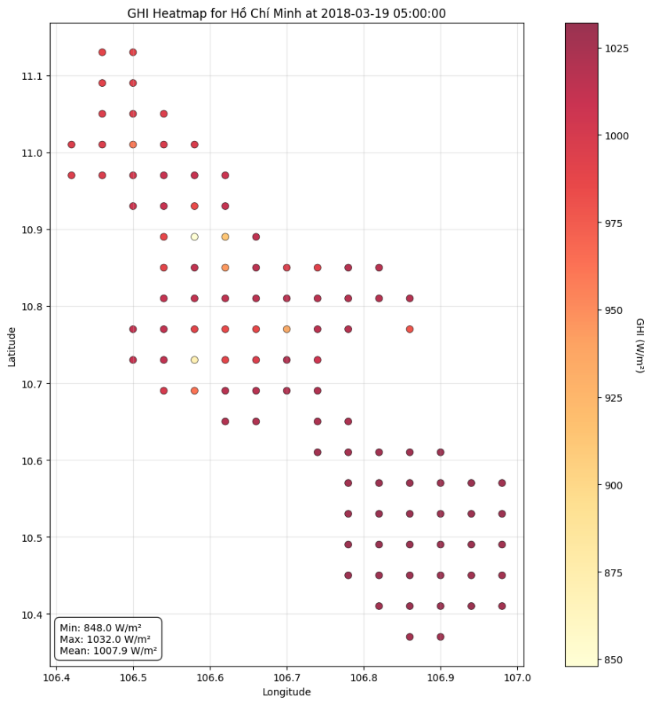
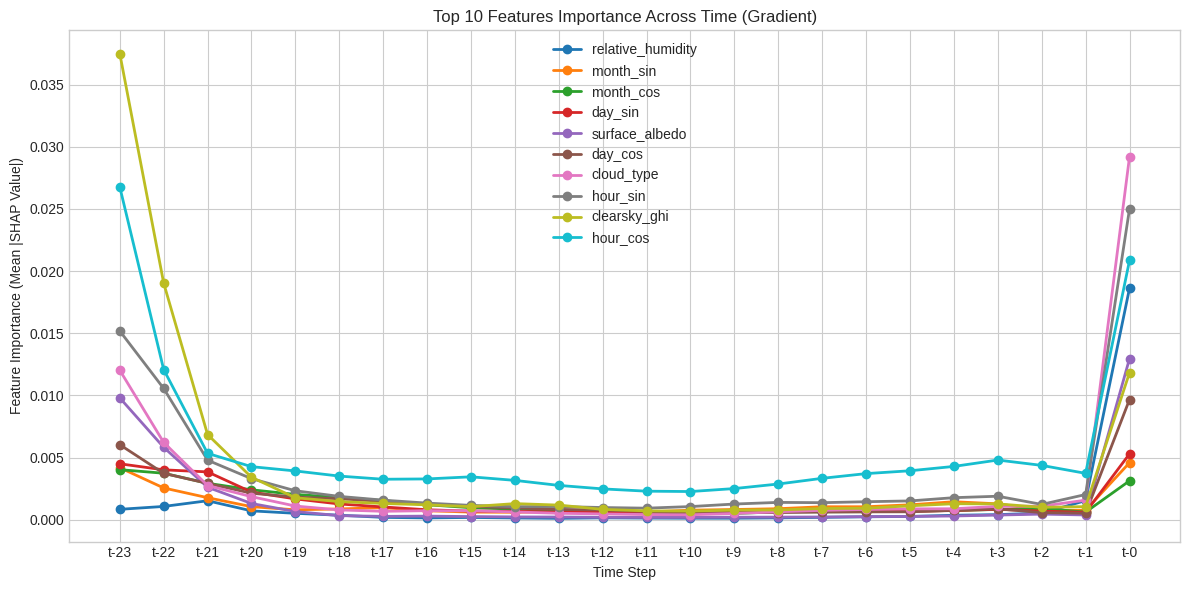
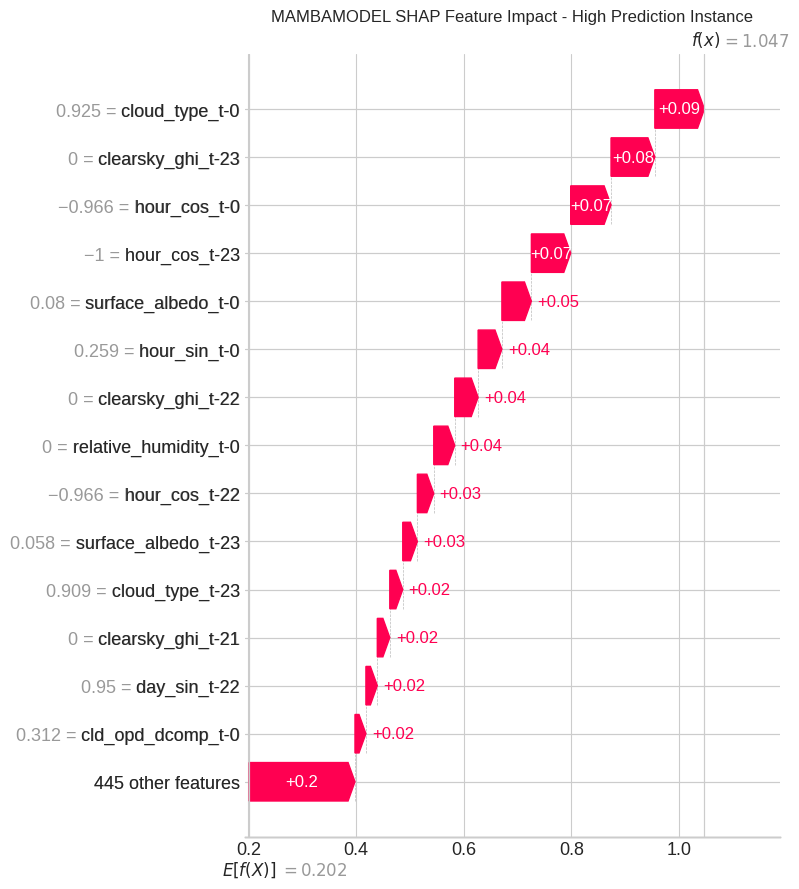
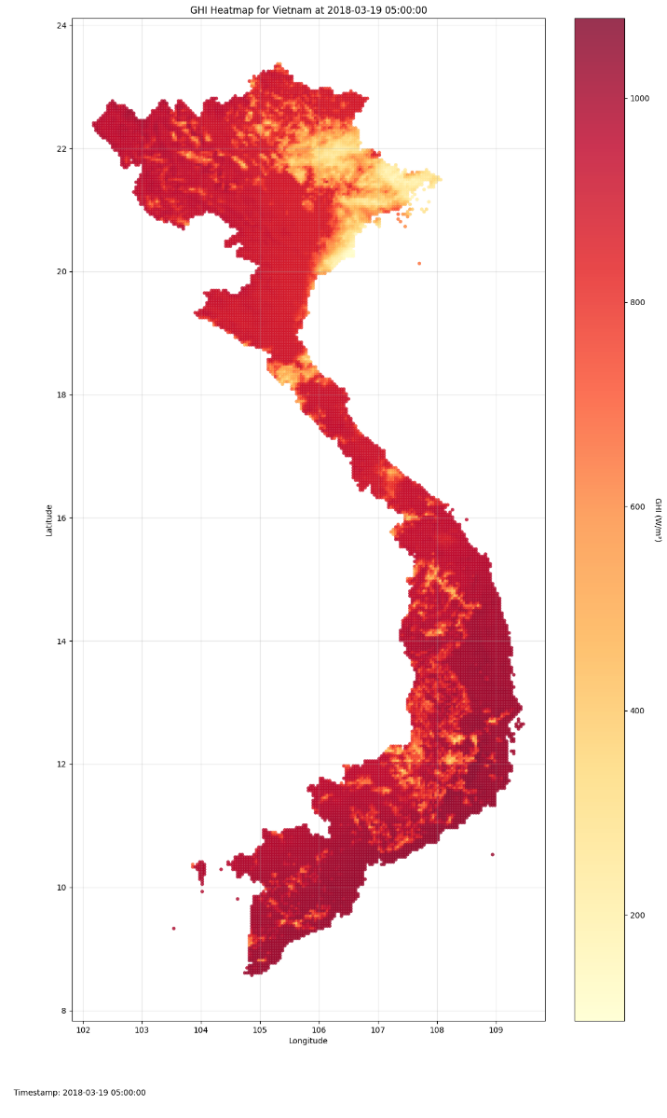
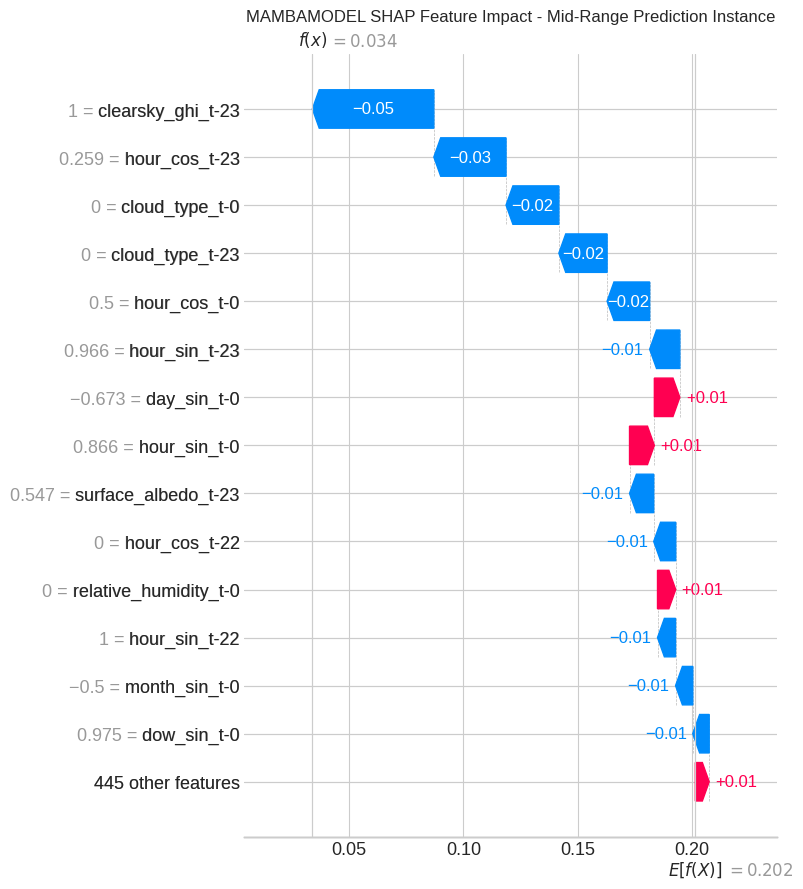
Reliable forecasting of Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) is essential for mitigating the variability of solar energy in power grids. This study presents a comprehensive benchmark of ten deep learning architectures for short-term (1-hour ahead) GHI time series forecasting in Ho Chi Minh City, leveraging high-resolution NSRDB satellite data (2011-2020) to compare established baselines (e.g. LSTM, TCN) against emerging state-of-the-art architectures, including Transformer, Informer, iTransformer, TSMixer, and Mamba. Experimental results identify the Transformer as the superior architecture, achieving the highest predictive accuracy with an R^2 of 0.9696. The study further utilizes SHAP analysis to contrast the temporal reasoning of these architectures, revealing that Transformers exhibit a strong "recency bias" focused on immediate atmospheric conditions, whereas Mamba explicitly leverages 24-hour periodic dependencies to inform predictions. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Knowledge Distillation can compress the high-performance Transformer by 23.5% while surprisingly reducing error (MAE: 23.78 W/m^2), offering a proven pathway for deploying sophisticated, low-latency forecasting on resource-constrained edge devices.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Metaphor:** Deep learning architectures can be likened to cars. Each layer functions as an engine part, and network configurations are akin to the car design. This study determines which designs yield optimal performance. 2. **Simple Explanation:** Through experiments with various datasets, we determined how specific layers and network structures improve natural language processing task performance. 3. **Sci-Tube Style Script:** - [Level 1] "Deep learning helps understand language." - [Level 2] "Network configurations and the number of layers significantly change performance. This study reveals why." - [Level 3] "Higher accuracy, precision, and recall improve natural language processing task quality."📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)