Fighting Multimodal Misinformation with Agent-based Fact-Checking
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Multimodal Fact-Checking An Agent-based Approach- ArXiv ID: 2512.22933
- Date: 2025-12-28
- Authors: Danni Xu, Shaojing Fan, Harry Cheng, Mohan Kankanhalli
📝 Abstract
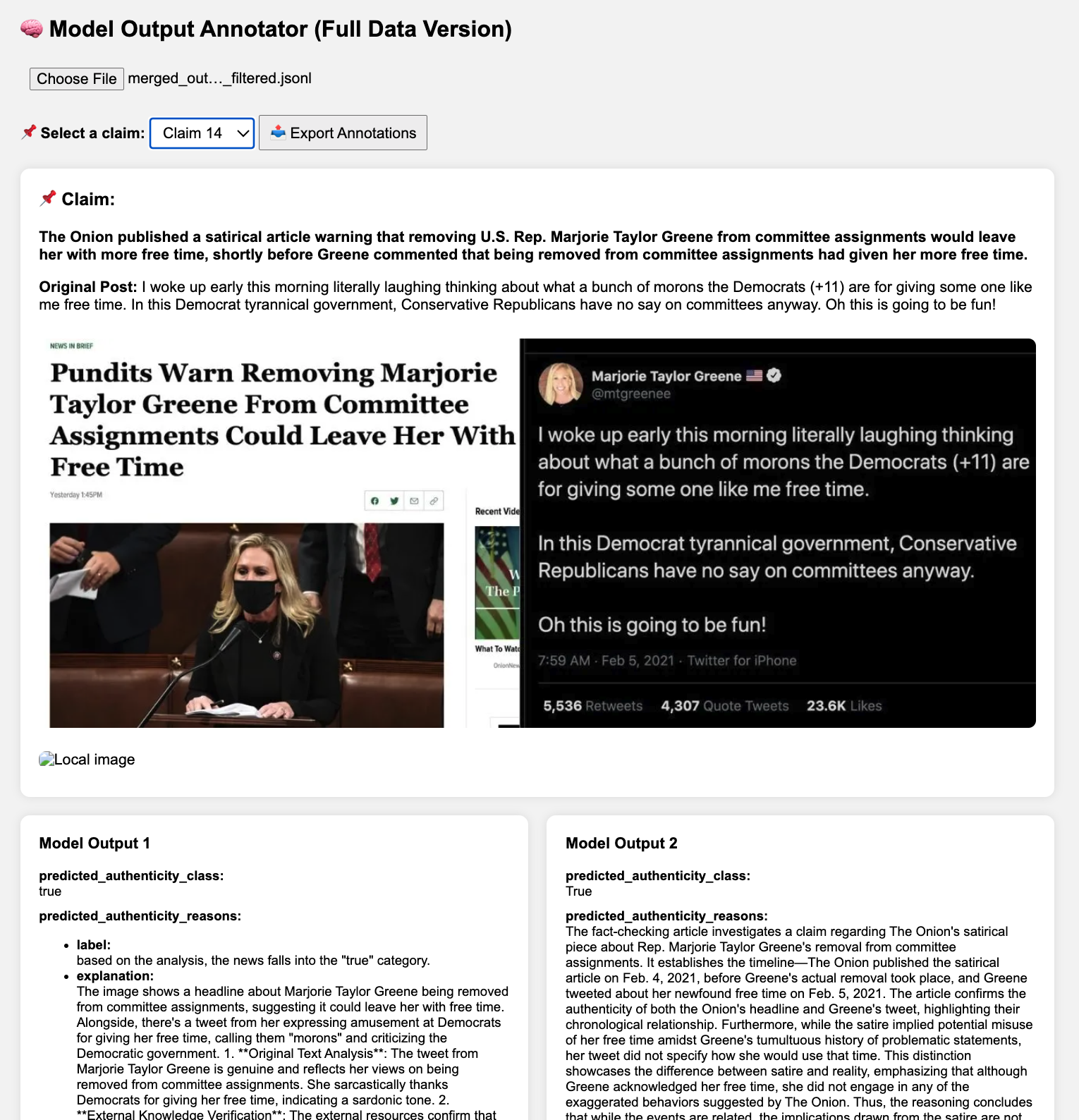
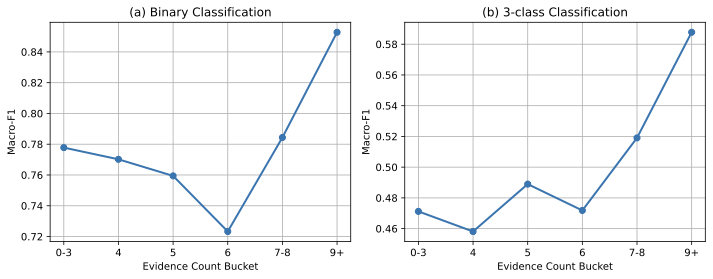
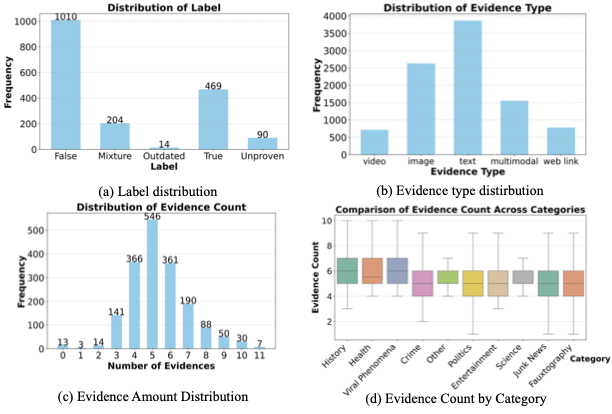
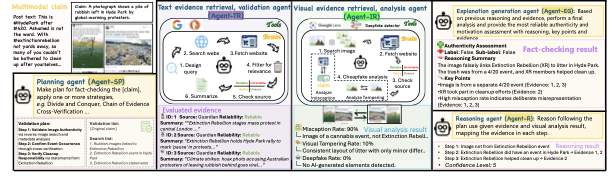
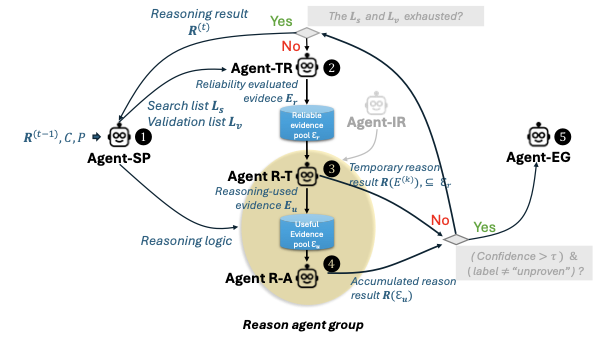
The rapid spread of multimodal misinformation poses a growing challenge for automated fact-checking systems. Existing approaches, including large vision language models (LVLMs) and deep multimodal fusion methods, often fall short due to limited reasoning and shallow evidence utilization. A key bottleneck is the lack of dedicated datasets that provide complete real-world multimodal misinformation instances accompanied by annotated reasoning processes and verifiable evidence. To address this limitation, we introduce RW-Post, a high-quality and explainable dataset for real-world multimodal fact-checking. RW-Post aligns real-world multimodal claims with their original social media posts, preserving the rich contextual information in which the claims are made. In addition, the dataset includes detailed reasoning and explicitly linked evidence, which are derived from human written fact-checking articles via a large language model assisted extraction pipeline, enabling comprehensive verification and explanation. Building upon RW-Post, we propose AgentFact, an agent-based multimodal fact-checking framework designed to emulate the human verification workflow. AgentFact consists of five specialized agents that collaboratively handle key fact-checking subtasks, including strategy planning, high-quality evidence retrieval, visual analysis, reasoning, and explanation generation. These agents are orchestrated through an iterative workflow that alternates between evidence searching and task-aware evidence filtering and reasoning, facilitating strategic decision-making and systematic evidence analysis. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the synergy between RW-Post and AgentFact substantially improves both the accuracy and interpretability of multimodal fact-checking.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Beginner Level**: This research explores various approaches to find the most effective CNN learning method for image recognition. Think of it as training different types of 'eyes' to better recognize images, and comparing which type works best.-
Intermediate Level: The team investigated how initialization methods and transfer learning affect image recognition performance. It’s like using an already well-trained ’eye’ in a new context rather than starting from scratch.
-
Advanced Level: The methodology presented in the research validates the efficiency of CNN models across different datasets, proving that optimization algorithms and initialization strategies play crucial roles.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)