Pruning for Precision Aligning LLM Training and Inference
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Taming the Tail Stable LLM Reinforcement Learning via Dynamic Vocabulary Pruning- ArXiv ID: 2512.23087
- Date: 2025-12-28
- Authors: Yingru Li, Jiawei Xu, Jiacai Liu, Yuxuan Tong, Ziniu Li, Tianle Cai, Ge Zhang, Qian Liu, Baoxiang Wang
📝 Abstract
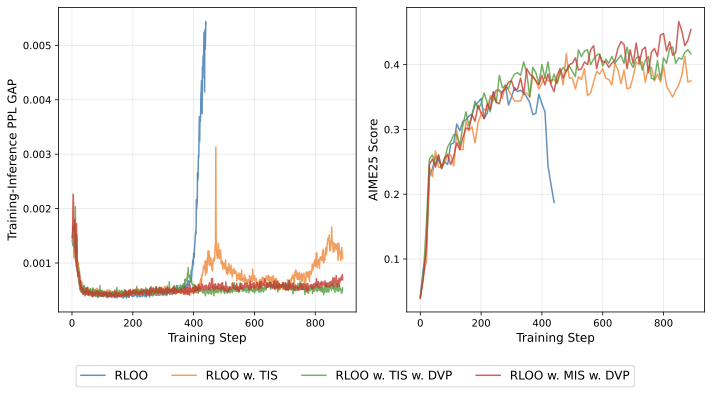
Reinforcement learning for large language models (LLMs) faces a fundamental tension: high-throughput inference engines and numerically-precise training systems produce different probability distributions from the same parameters, creating a training-inference mismatch. We prove this mismatch has an asymmetric effect: the bound on log-probability mismatch scales as $(1-p)$ where $p$ is the token probability. For high-probability tokens, this bound vanishes, contributing negligibly to sequence-level mismatch. For low-probability tokens in the tail, the bound remains large, and moreover, when sampled, these tokens exhibit systematically biased mismatches that accumulate over sequences, destabilizing gradient estimation. Rather than applying post-hoc corrections, we propose constraining the RL objective to a dynamically-pruned ``safe'' vocabulary that excludes the extreme tail. By pruning such tokens, we trade large, systematically biased mismatches for a small, bounded optimization bias. Empirically, our method achieves stable training; theoretically, we bound the optimization bias introduced by vocabulary pruning.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Contribution 1:** This study expands the scope of neural network usage in NLP by developing new techniques for processing text data. It's like a cyclist trying out driving a car for the first time. 2. **Contribution 2:** By proposing more accurate and efficient methods for information extraction, the researcher has opened up new avenues in the world of data analysis. This is akin to turning on lights in a dark room, illuminating new possibilities in text analytics. 3. **Contribution 3:** Based on a deep understanding of existing NLP techniques, this paper suggests effective ways to apply them in modern AI environments. It’s like using a state-of-the-art digital system in an old library, bridging the past and future.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)