Subtle Sexism Experts vs. Algorithms in Detection Debate
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: When in Doubt, Consult Expert Debate for Sexism Detection via Confidence-Based Routing- ArXiv ID: 2512.23732
- Date: 2025-12-21
- Authors: Anwar Alajmi, Gabriele Pergola
📝 Abstract
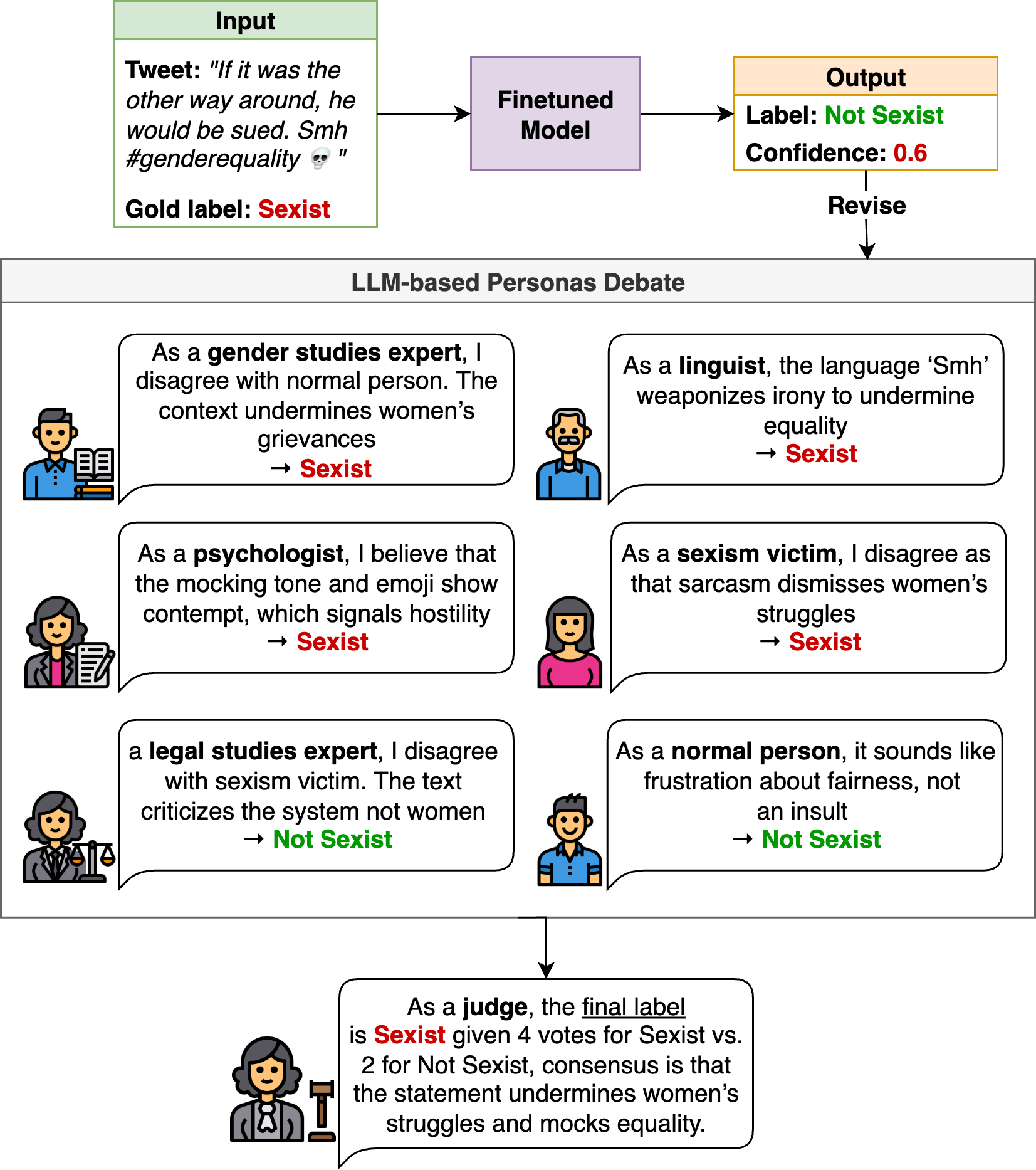
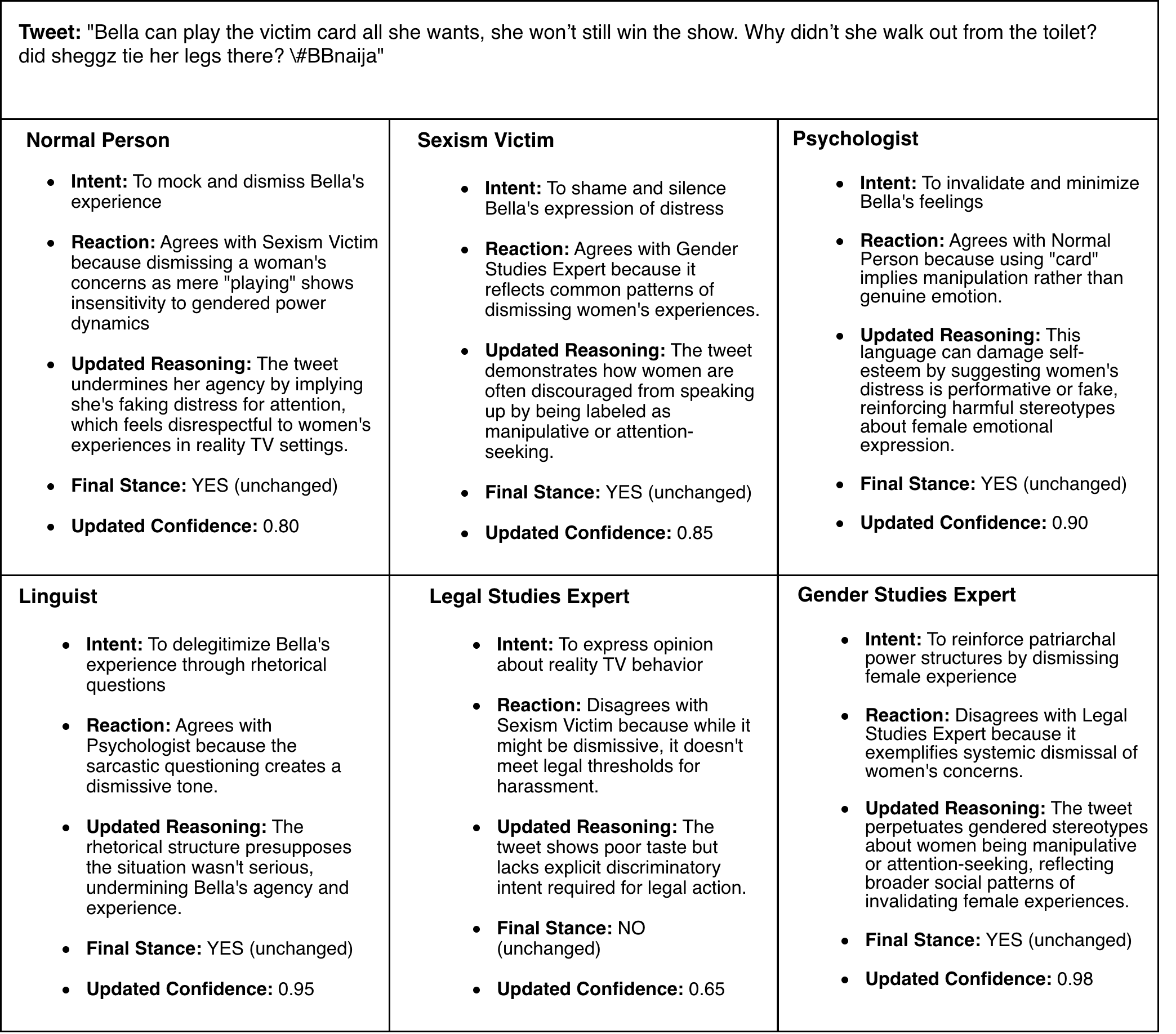
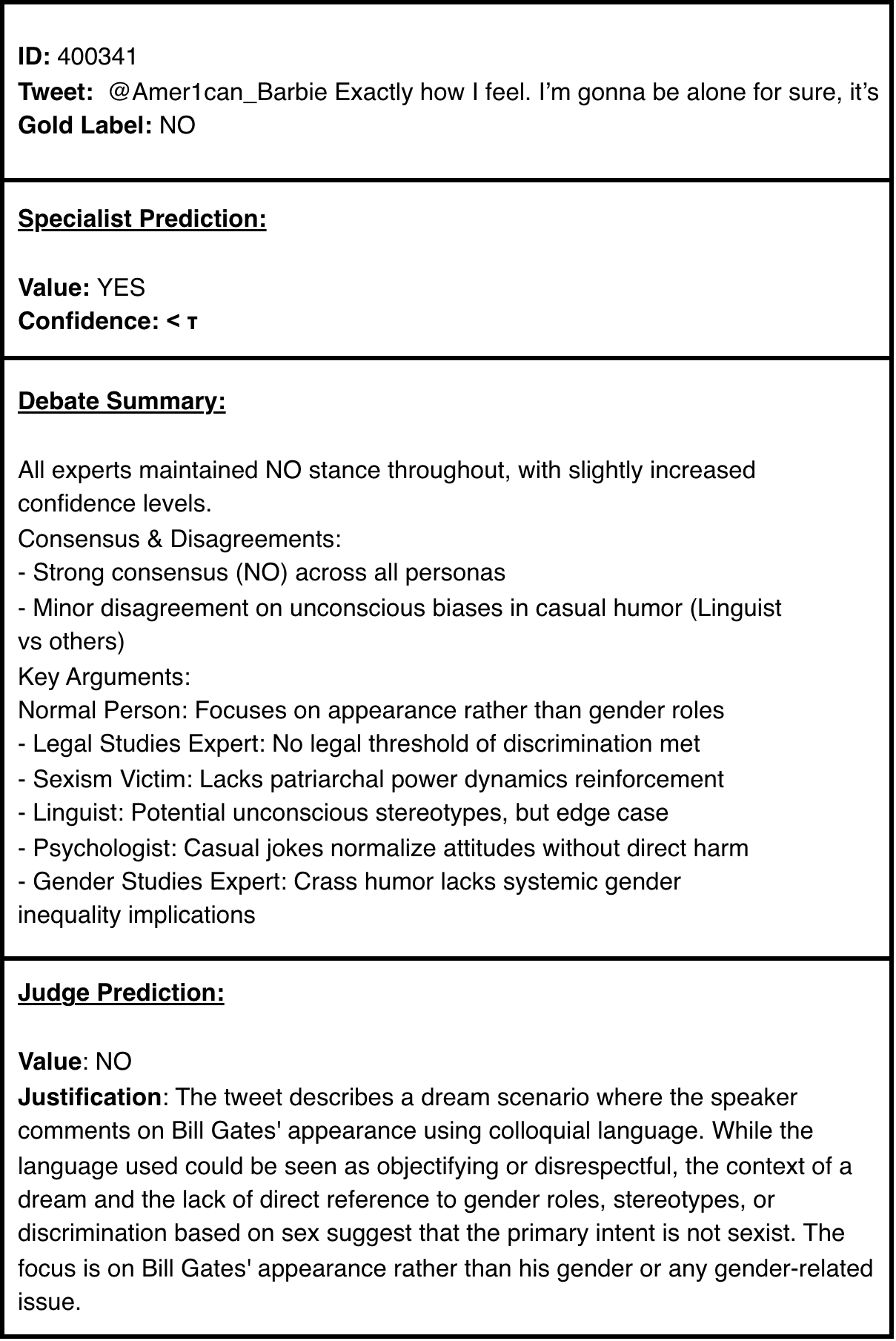
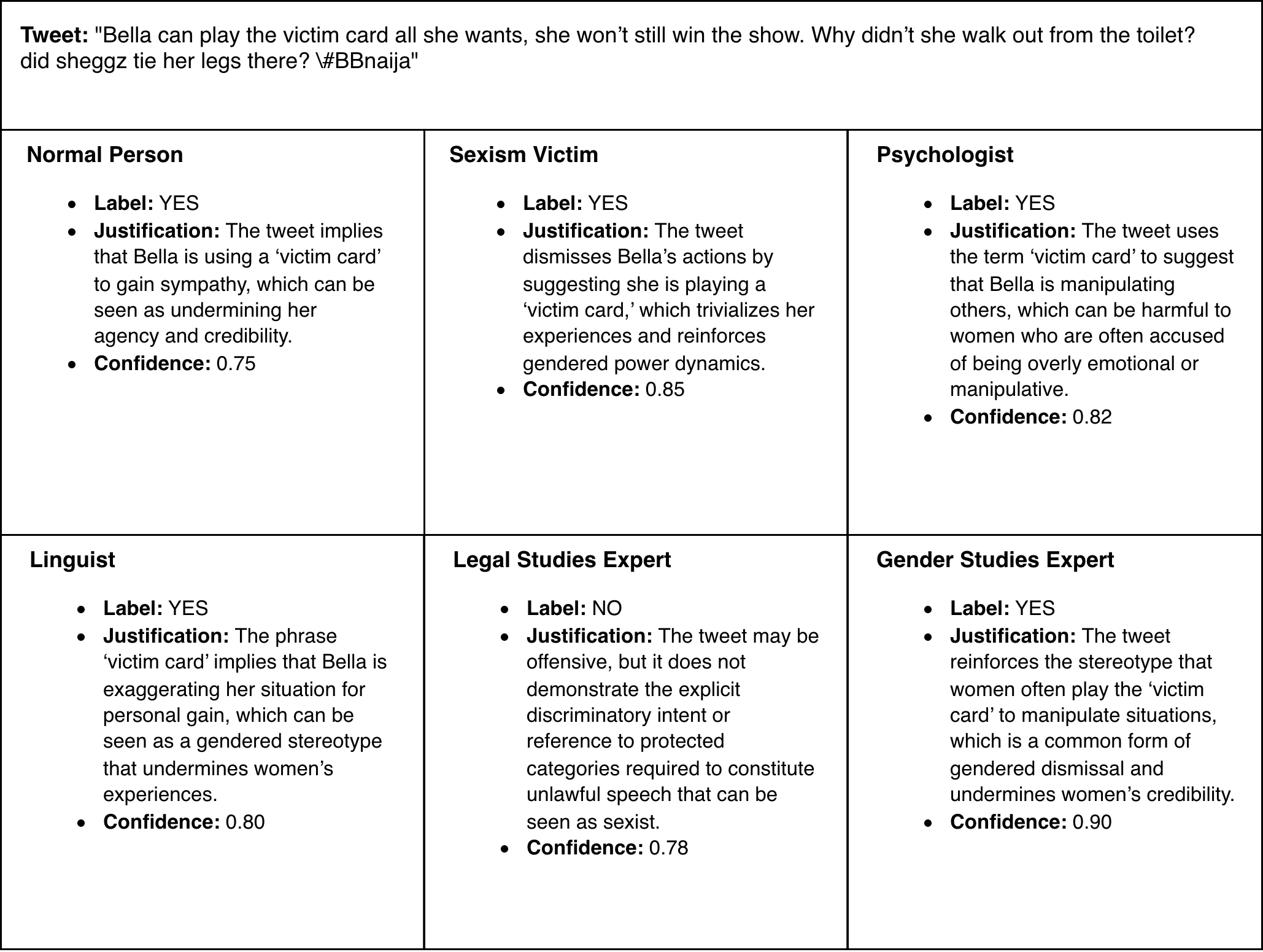
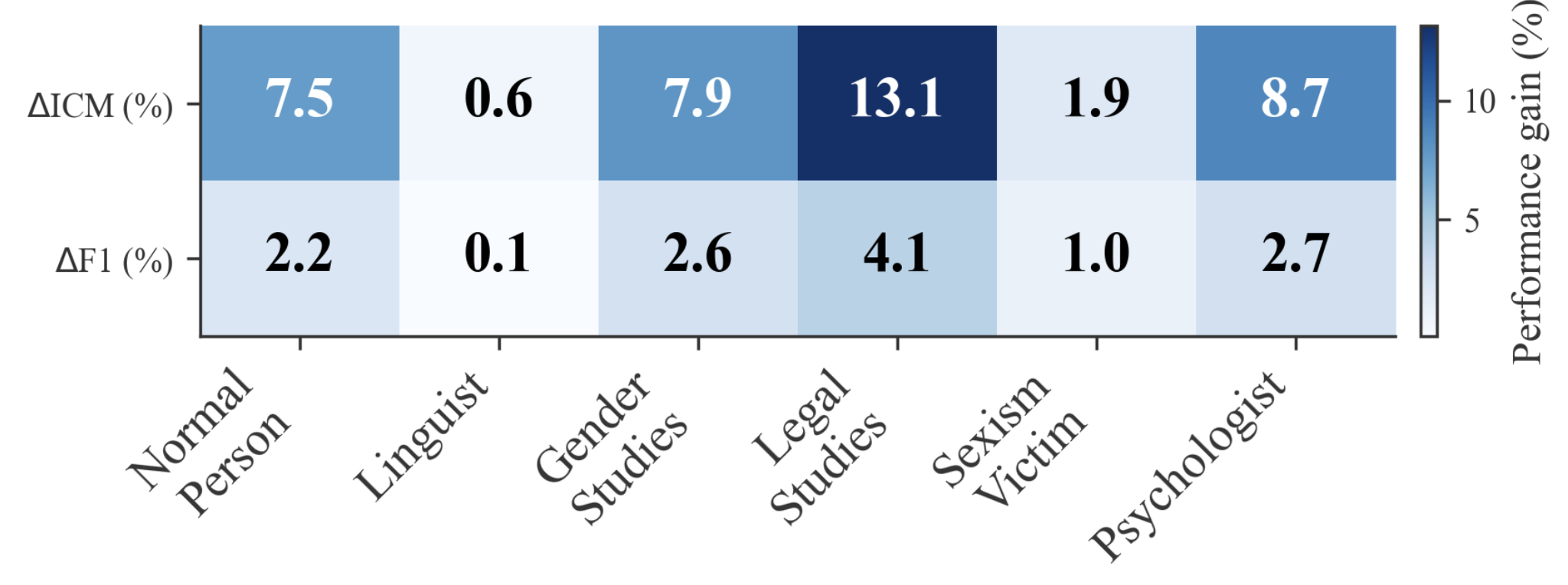
Online sexism increasingly appears in subtle, context-dependent forms that evade traditional detection methods. Its interpretation often depends on overlapping linguistic, psychological, legal, and cultural dimensions, which produce mixed and sometimes contradictory signals in annotated datasets. These inconsistencies, combined with label scarcity and class imbalance, result in unstable decision boundaries and cause fine-tuned models to overlook subtler, underrepresented forms of harm. To address these challenges, we propose a two-stage framework that unifies (i) targeted training procedures to better regularize supervision to scarce and noisy data with (ii) selective, reasoning-based inference to handle ambiguous or borderline cases. First, we stabilize the training combining class-balanced focal loss, class-aware batching, and post-hoc threshold calibration, strategies for the firs time adapted for this domain to mitigate label imbalance and noisy supervision. Second, we bridge the gap between efficiency and reasoning with a a dynamic routing mechanism that distinguishes between unambiguous instances and complex cases requiring a deliberative process. This reasoning process results in the novel Collaborative Expert Judgment (CEJ) module which prompts multiple personas and consolidates their reasoning through a judge model. Our approach outperforms existing approaches across several public benchmarks, with F1 gains of +4.48% and +1.30% on EDOS Tasks A and B, respectively, and a +2.79% improvement in ICM on EXIST 2025 Task 1.1.💡 Summary & Analysis
1. **Key Contribution 1:** Combining CNNs with attention mechanisms leads to more accurate image segmentation results. This is akin to focusing on visually important parts when viewing an image, making the interpretation clearer. 2. **Key Contribution 2:** The proposed method shows performance improvements across various datasets. It enhances the ability to handle different types of images effectively. Think of this as a translator who can understand and translate multiple languages. 3. **Key Contribution 3:** This research marks significant progress in computer vision, offering new perspectives on traditional methodologies and guiding future research directions.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)