From Atomic to Composite: Reinforcement Learning Enables Generalization in Complementary Reasoning
📝 Original Info
- Title: From Atomic to Composite: Reinforcement Learning Enables Generalization in Complementary Reasoning
- ArXiv ID: 2512.01970
- Date: 2025-12-01
- Authors: Sitao Cheng, Xunjian Yin, Ruiwen Zhou, Yuxuan Li, Xinyi Wang, Liangming Pan, William Yang Wang, Victor Zhong
📝 Abstract
Reinforcement Learning (RL) following Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) has become the standard paradigm for post-training Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the mechanism by which RL contributes to reasoning capabilitieswhether it incentivizes the synthesis of new skills or merely amplifies existing behaviors-remains a subject of intense debate. In this work, we investigate this question through the lens of Complementary Reasoning, a complex task that requires integrating internal parametric knowledge with external contextual information. Using a controlled synthetic dataset of human biographies, we strictly decouple this ability into two atomic skills: Parametric Reasoning (relying on internal knowledge encoded in model parameters) and Contextual Reasoning (depending on novel information provided in the context window). To rigorously assess capability boundaries, we evaluate generalization across three distinct levels of difficulty: I.I.D., Composition, and Zero-shot settings. We find that while SFT is sufficient for in-distribution performance, it struggles with out-of-distribution generalization, particularly in Zero-shot settings where relational combinations are novel. Crucially, we identify the SFT Generalization Paradox: Models supervised solely on the composite task achieve near-perfect in-distribution accuracy (90%) but collapse on out-of-distribution generalization (18%), indicating their reliance on rote memorization of path shortcuts. In contrast, we find that RL acts as a reasoning synthesizer rather than a probability amplifier. However, we uncover a strict atomic prerequisite: RL can only synthesize these complex strategies if the base model has first mastered the independent atomic skills (Parametric and Contextual) via SFT. These findings challenge the view of RL as a mere amplifier, suggesting that given sufficient atomic foundations, RL can actively synthesize complex reasoning strategies from learned primitives without explicit supervision on such complex strategies. This indicates that decoupled atomic training followed by RL offers a scalable path to generalization for complex reasoning tasks. Code and data will be at https://github.com/sitaocheng/from atomic to composite.📄 Full Content
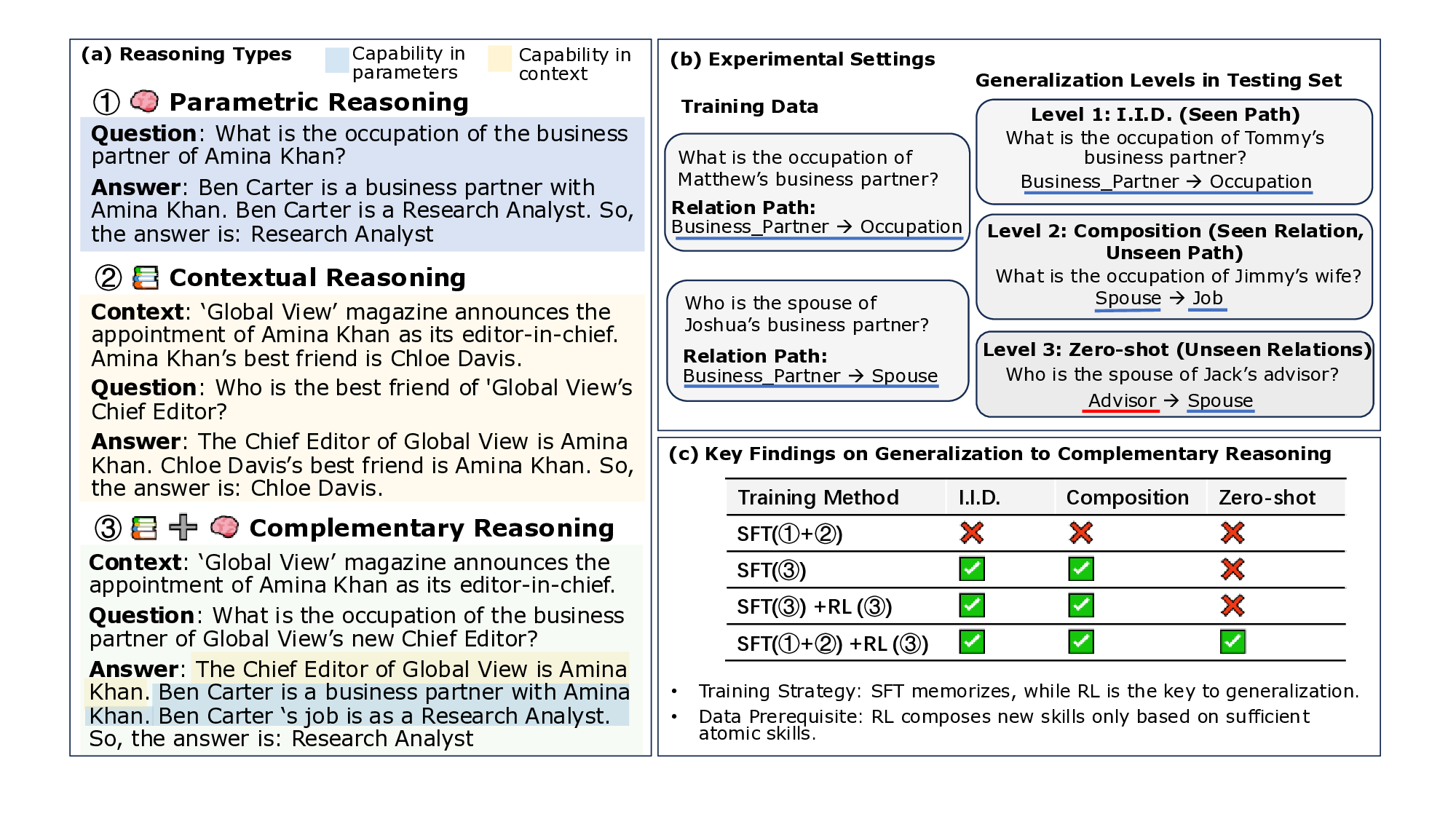
To study the true nature of RL’s contribution, we focus on a common practical task, knowledgeintensive reasoning (Gutiérrez et al., 2025;An et al., 2025;Zhuang et al., 2024). In real-world scenarios, systems often encounter “missing link” failures: for example, in Figure 1(a), a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system might retrieve a document about a “Chief Editor”, but fail to link it to the chief editor’s “business partner” stored in the model’s parametric memory. We define this capability as Complementary Reasoning (COMP): the ability to seamlessly bridge internal parametric knowledge with external contextual information. For example, answering “What is the occupation of the business partner of Global View’s new Chief Editor? " requires the model to seamlessly integrate the external information (e.g., Amina Khan is the Chief…) with the internal knowledge (e.g., Ben Carter is a business partner…). While human intelligence intuitively performs this composition-seamlessly leveraging known facts alongside new context-LLMs often struggle to generalize when required to utilize both parametric and contextual knowledge simultaneously (Cheng et al., 2024a;Yin et al., 2023). While LLMs are known for their fluency in using either parametric or contextual knowledge, Complementary Reasoning serves as an ideal testbed for evaluating how post-training strategies can bridge the generalization gap between the isolated atomic skills and complex, compositional reasoning.
In this paper, we investigate the minimal sufficient conditions required for LLMs to generalize on complementary reasoning. We specifically aim to answer two research questions:
• RQ1: What training strategies are necessary for generalization to Complementary Reasoning?
• RQ2: Can RL synthesize complex reasoning strategies from atomic primitives, or does it merely amplify existing memorization? Investigating these questions using standard open-domain benchmarks (e.g. HotpotQA (Yang et al., 2018) and PopQA (Mallen et al., 2023)) is fundamentally limited by data contamination. In web-scale corpora, it is impossible to rigorously determine whether a model solves a multi-hop query by reasoning over the context or simply by recalling a memorized shortcut connection from pretraining. To address this, we conduct a behavioral study using a controlled synthetic environment where the boundary between Parametric (internal) and Contextual (external) knowledge is strictly enforced (Allen-Zhu & Li, 2023a;b). Specifically, we construct a large-scale dataset of human biographies underpinned by a knowledge graph composed of extensive synthetic entities and relations with real-world meanings. This setup serves as a precise testbed for multi-hop factual task, allowing us to strictly decouple complementary reasoning capabilities into two atomic skills (Figure 1(a)): Parametric Reasoning (MEM), which relies solely on internal knowledge encoded in model parameters, and Contextual Reasoning (CTX), which relies solely on novel facts in the input context.
To rigorously assess the model’s capability boundaries, we evaluate generalization under varying levels of difficulty, shown in Figure 1(b): I.I.D. (seen combinations), Composition (unseen combinations of seen relations), and Zero-shot (combinations involving unseen relations). Based on the strictly controlled knowledge with multi-hop QA pairs for MEM, CTX and COMP, we train models under different combinations and amounts of training data with varying post-training strategies (e.g., SFT, RL). We evaluate the performance on the test set of COMP and study the optimal setting of training method and mix of training data for different levels of generalization.
Our experiments reveal a nuanced relationship between sufficient atomic skills and RL-driven generalization (Figure 1(c)). We demonstrate that simply (SFT) training on complementary data yields high in-distribution performance but fails to generalize to out-of-distribution scenarios with unseen combinations. However, RL serves as a catalyst for generalization under a strong condition that all atomic skills for the comprehensive tasks are captured, particularly in the challenging Zero-shot setting where relation combinations are entirely novel. Our findings challenge the view of RL as merely a probability amplifier. We summarize our key contributions as follows:
• We formally define Complementary Reasoning and introduce a controlled dataset that decouples the complex ability into atomic Parametric and Contextual skills, enabling comprehensive evaluation of generalization levels (i.e., I.I.D., Composition, and Zero-shot). We provide sufficient training data for each skills to facilitate a systematic investigation of training strategies.
• We provide empirical evidence that while Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) is sufficient for memorizing distributions, Reinforcement Learning (RL) is essential for generalization, specifically enabling the model to tackle Zero-shot relational combinations that SFT fails to resolve.
• We uncover a fundamental prerequisite for RL generalization: RL effectively composes new skills only when the base model possesses sufficient atomic capabilities. We show that a model SFT on atomic skills (SFT MEM+CTX ) gains significantly more from subsequent RL on complementary tasks than SFT directly on complementary data (SFT COMP ) regardless of the amount of data.
• We demonstrate that when reaching the prerequisite, RL does not merely amplify existing behaviors but actively composes learned atomic skills into new complex reasoning strategies, challenging the view that RL is solely a probability amplifier.
Our findings suggest a scalable path for training reasoning LLMs: rather than collecting expensive complex reasoning traces for extensive RL, one can focus on efficiently teaching the model sufficient fundamental atomic skills via SFT, and then leverage RL to unlock the generalization required for complex reasoning.
The power of LLMs is unleashed fundamentally through posttraining with an initial Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) stage and a following Reinforcement Learning (RL) stage. While SFT establishes stable output behavior and foundational knowledge, the maximum likelihood estimation inherently favors memorization of the training distribution, leading to diminished robustness and poor generalization (Wang et al., 2025;Chu et al., 2025). In contrast, RL, driven by reward signals, transforms the model’s distribution into goal-oriented, problem-solving strategies (Shao et al., 2024;Schulman et al., 2017). However, a hot debate recently is on whether RL combines new knowledge (Yuan et al., 2025;Liu et al., 2025), or just amplifying from the existing distribution (Wu & Choi, 2025;Yue et al., 2025;Yang et al.;Setlur et al., 2025). Our findings stand for RL incentivizes new skills, but only under some prerequisites.
Knowledge-intensive Reasoning A foundational capability for intelligence is to reason with knowledge. Multi-Hop Reasoning, which requires multiple facts to answer, serves as an ideal testbed (Yang et al., 2018;Ho et al., 2020;Huang et al., 2025). Inherently, this task requires the ability to retrieve knowledge from parametric or external bases and logically compose intermediate facts (Huang et al., 2023b;Cheng et al., 2024b;Huang et al., 2024;Jin et al., 2025). Recent studies identified that LLMs struggle to generalize when using both new and known knowledge for reasoning (Cheng et al., 2024a;Yin et al., 2023). However, relying solely on recent benchmarks risks data contamination, making it hard to distinguish between new and known knowledge. This necessitates moving beyond standard benchmarks to controlled experimental setups.
Behavioral Study with Synthetic Data To address the fundamental challenges of data contamination and memory effects, synthetic data has become essential for LLMs evaluation (Allen-Zhu & Li, 2023a;b). With brand new facts, entities, or entire narratives (such as human biographies), researchers can strictly control the knowledge of the model, the sufficiency of knowledge for a question and the complexity of the task (Yin et al., 2023;Kim et al., 2025;Yuan et al., 2025;Wang et al., 2024). This also allows for rigorous evaluation of the model’s capability under controlled settings. Our study adopts a relational knowledge base with templates to study knowledge-intensive reasoning under varying post-training strategies, where we are able to strictly control the parametric and new knowledge. With the synthetic relational patterns, we can systematically examine how LLMs could generalize to out-of-distribution (O.O.D.) patterns.
We formally define complementary reasoning, and introduce data construction and experiment settings. In real-world scenarios, LLMs can easily tackle multi-hop questions using either parametric or contextual knowledge, both of which are fundamental skills for complementary reasoning. However, acquiring ample data that encompasses both skills is challenging. We try to address these challenges: 1) scheduling of the post-training strategies to generalize beyond the training distribution; 2) recipe of mixing the training data for generalization on complementary reasoning.
Reasoning Types Complementary Reasoning, denoted as COMP, is defined as a multi-hop task requiring both parametric and contextual skills, which complements each other. In addition, we define Parametric and Contextual Reasoning as a task solely requires skills in LLMs’ parameters or the context window, denoted as MEM and CTX, respectively. Formally, we define the capability requirement as a logical conjunction:
This implies that a failure in either atomic skill (C MEM or C CTX ) necessitates a failure in the complementary task. Intuitively, humans find it straightforward to answer a complementary question if the new (unknown) skills are given. However, while capable of parametric and contextual reasoning by post-training with large-scale (Context-)Question-Answer examples, LLMs cannot generalize to complementary reasoning fluently (Cheng et al., 2024a).
In this paper, we study the generalization to complementary reasoning through multi-hop factual tasks. Typically, such question requires the retrieval of relevant knowledge and the capability to link several facts together. Formally, we define the task as traversing a relational path P = (r 1 , r 2 , . . . , r k ) starting from a topic entity to reach the answer. For complementary reasoning, each relation r i in the path falls into either parametric or contextual knowledge, requiring the model to seamlessly integrate both sources. For the example question in Figure 1(a), “What is the occupation of the business partner of Global View’s new Chief Editor?” traverses the path “Global View -Chief Editor -Business Partner -Occupation -Answer”.
Generalization Levels Traditional random data split assumes that testing data follows the same distribution as training data (Independent and Identically Distributed, a.k.a.. I.I.D.). However, this assumption fails to capture the complexity of real-world reasoning. For instance, a web agent often encounters infinite combinations of operations that cannot be exhaustively covered in a finite training set (Deng et al., 2023). To rigorously investigate whether models can transcend rote memorization and generalize to novel scenarios, we evaluate performance across three levels of difficulty based on the novelty of the relational path (i.e., hops) in the question (Gu et al., 2021;Huang et al., 2023a).
Given the relational path P defined above, let P train denote the set of relational paths seen during instruction tuning, and R train denote the set of individual atomic relations observed in those paths. We categorize the generalization levels of difficulty as follows (examples in in Figure 1(b)):
• I.I.D. Generalization evaluates the ability to apply learned patterns to new entities within familiar structures. The relational path in the test question is fully observed during training (P test ∈ P train ). For example, if the model is trained on questions involving the path Business Partner→Job (e.g., “What is the occupation of [X]’s business partner?”), an I.I.D. test query would ask the same question structure for a different entity. Our experiments (Section D) show that SFT is typically sufficient for this level as it merely requires recalling the observed path structure.
Using existing benchmarks presents two fundamental challenges: the risk of data contamination from the model’s pre-training corpus and the difficulty in precisely controlling the parametric and contextual knowledge. To address these, we construct a controlled synthetic dataset of human biographies (Allen-Zhu & Li, 2023a;b), based on which we are able to control the sufficiency of knowledge. We build training and test data for the three reasoning types and generalization levels.
Synthetic Human Profiles with a Knowledge Graph We ground our dataset in a synthetic relational knowledge graph and transform the structured graph into natural language profiles with templates by an LLM (GPT-4o). We define 39 relations including eight symmetric relations (e.g., spouse, sibling), and eight pairs of inverse relations (e.g., child and parent) to mimic real-world complexity. For each relation, we adopt an LLM to construct and validate three natural language templates. We adopt heuristic rules to constrain the tailed entity of the relation (e.g., birthday should be a date). We randomly partition these relations into two disjoint sets to simulate parametric and contextual knowledge sources, respectively. Using the Python Faker Library, we populate the graph with entities (e.g., names, birthday) strictly ensuring that character identities are novel and do not overlap with the model’s pre-training corpus.
We automatically construct 10k biographies for MEM (simulating known facts in the model), and 10k for CTX (simulating new facts), with 5k shared characters to enable bridging between parameters and context (simulating real-world scenarios where new facts can be added to known characters). Refer to Appendix A for more details.
To construct multi-hop questions, we sample relational paths/combinations consisting of 2-5 hops. Note that we ensure the number of hops for each reasoning type is distributed identically. We enforce a constraint where intermediate nodes must be named entities rather than generic values (e.g., dates, emails) to ensure the multi-step dependency. For COMP, we guarantee that the paths incorporate relations from both MEM and CTX. Then, we employ an LLM to generate three linguistically diverse question templates to ensure syntactic variety without relying on repetitive patterns. Crucially, we incorporate Chain-of-Thought (CoT) (Wei et al., 2022) into the target answers for three strategic reasons: 1) to facilitate the decomposition of 2,651 1,910 1,320 453 Complementary 180,919 2,135 1,415 complex multi-hop queries; 2) to facilitate retrieval and application of specific factual knowledge, as suggested by Allen-Zhu & Li (2023a); and 3) to enable precise evaluation of whether the model is retrieving intermediate facts from the parameter or contextual. To form the LLM’s input, we directly query the model for MEM questions. For CTX and COMP, we present the contexts (knowledge documents-biographies) and the question, akin to real-world question answering systems.
Data Split for Generalization Levels To ensure the validity of the generalization levels (Section 3), we implement a rigorous multi-stage splitting protocol at the relational path level prior to natural language generation. Specifically:
-
For I.I.D., we explicitly reserve a subset of relational paths, denoted as P iid . These paths are included in both the training and testing sets. To prevent rote memorization of answers, we ensure that while the relational paths are identical, the entities instantiated in the test set are disjoint from those in the training set.
-
For Zero-shot, from the remaining relational paths (excluding P iid ), we identify the full set of atomic relations and randomly sample a subset, R unseen , to be held out. We then filter the dataset: any path containing at least one relation r ∈ R unseen is exclusively assigned to the testing set. This guarantees that the model never encounters these specific relations during training.
-
For Composition, we randomly partition the remaining paths into two disjoint sets: P train comp (to the training set) and P test comp (to the testing set). Crucially, we verify that the set of atomic relations present in the test split is identical to that in the training split (R test ≡ R train ), ensuring that the difficulty arises solely from the novel combination of known relations.
Through this protocol, we guarantee that I.I.D. tests seen paths, Composition tests unseen paths composed of seen relations, and Zero-shot tests paths with unseen relations. We then construct natural language question and CoT answer pairs by random-walk over the knowledge graph entities. For example, for a relation combination, we sample an entity as the starting point, and walk on the combination over the knowledge graph until we meet the answer. The final answer will then be appended after “So, the answer is:”, which is also used to filter the outcome for evaluation.
Since data generation is scalable, we provide an amount of training samples sufficient for excellent I.I.D. performance, with Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) training for Qwen-2.5-1.5B. Statistics of training and testing set are shown in Table 1a. Refer to Appendix A for more details.
To systematically investigate the research questions (the necessary training strategies and the prerequisite data conditions), we adopt a standard post-training pipeline consisting of Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) followed by Reinforcement Learning (RL). We employ Qwen-2.5-1.5B as our backbone model, as it is widely used in both recent methodologies and analytical works. As mentioned in Section 3, for parametric reasoning (MEM), the model receives only the Question as input. For Contextual (CTX) and Complementary Reasoning (COMP), the model receives both the Question and the Context (new facts). As for training, for SFT, we train models using standard next-token prediction. We also integrate all parametric knowledge documents (biographies) into the SFT process. For RL, we employ Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) (Shao et al., 2024) with a binary outcome reward on the answer (i.e. not on the reasoning chain). The outcome reward and the final evaluation are calculated by the exact match of the ground truth answer. In all experiments, the models are trained until convergence and evaluated on COMP test set.
We first establish the baseline performance of SFT to demonstrate why supervised training alone is insufficient for robust Complementary Reasoning. We analyze the difficulty of the task and the generalization capabilities of two SFT baselines: a model trained on atomic skills (SFT MEM+CTX ) and a model trained directly on the target task (SFT COMP ).
Complementary reasoning is data-hungry and inherently difficult. Table 1a reveals that achieving high in-distribution (I.I.D.) performance on COMP requires significantly more data than atomic tasks (MEM and CTX). The COMP task requires ∼180k samples-nearly double the sum of samples required for MEM (∼88k) and CTX (∼3k) combined. This validates that integrating internal and external knowledge is structurally more complex than applying either skill in isolation.
Atomic skills do not spontaneously compose. A key question is whether teaching a model the necessary components (SFT with MEM and CTX) is sufficient to infer the composite skill. Table 1b shows that SFT MEM+CTX achieves only approximately 24.07-35.18% performance on the COMP test set. While this is non-zero (indicating some transfer), it lags far behind the explicit training baseline (90.26% for I.I.D.), echoing findings in Cheng et al., 2024a;Yin et al., 2023. This suggests that simply possessing the knowledge and retrieval skills does not guarantee the ability to perform complex integration without further guidance. Refer to more analysis in Appendix E.1.
SFT Memorizes rather than Generalizes. Another critical finding is the failure of SFT COMP in out-of-distribution (Zero-shot) settings. While COMP achieves a near-perfect 90.26% on I.I.D., its performance collapses to 26.25% on Zero-shot (Table 1b). This stark contrast indicates that SFT primarily incentivizes the model to memorize specific relational patterns seen during training. When tailored with novel relations where memorization is impossible, the superficial reasoning learned via SFT fails completely.
We have established that SFT alone-whether on atomic skills or target tasks-fails to generalize to complementary reasoning, especially on Zero-shot setting. We hypothesize that generalization is unlocked only through a specific curriculum: establishing sufficient atomic capabilities via SFT, followed by synthesizing these skills via RL. Formally, we propose that the recipe “SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP " is the optimal path to generalization. In this section, we validate the Sufficiency and Necessity of our finding. We first show that this recipe consistently outperforms other data combinations regardless of data scale. Then, we demonstrate that sufficient atomic foundations is strictly required, and that “SFT→RL” is the necessary training strategy for generalization.
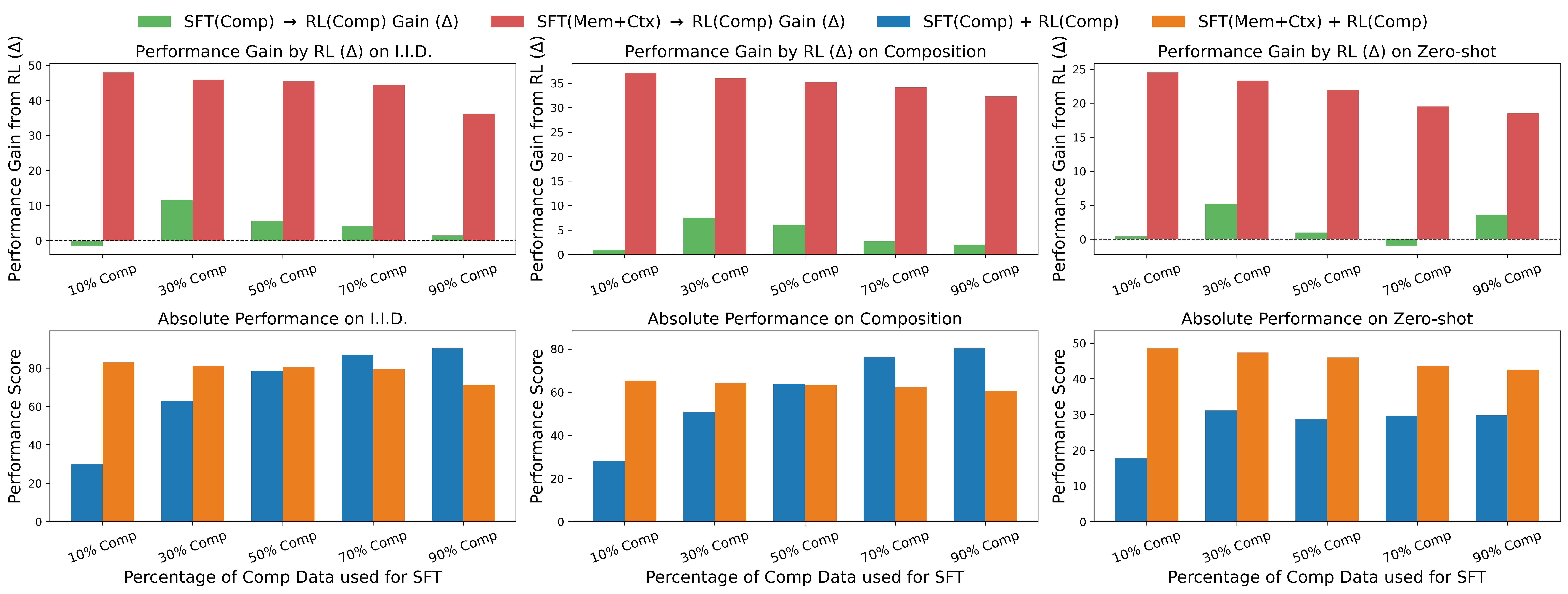
To rigorously test whether our proposed recipe “SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP " consistently yields superior generalization, compared to direct training on the target task, we conduct a controlled experiment by varying the proportion of COMP data. Refer to more comparisons in Appendix D.
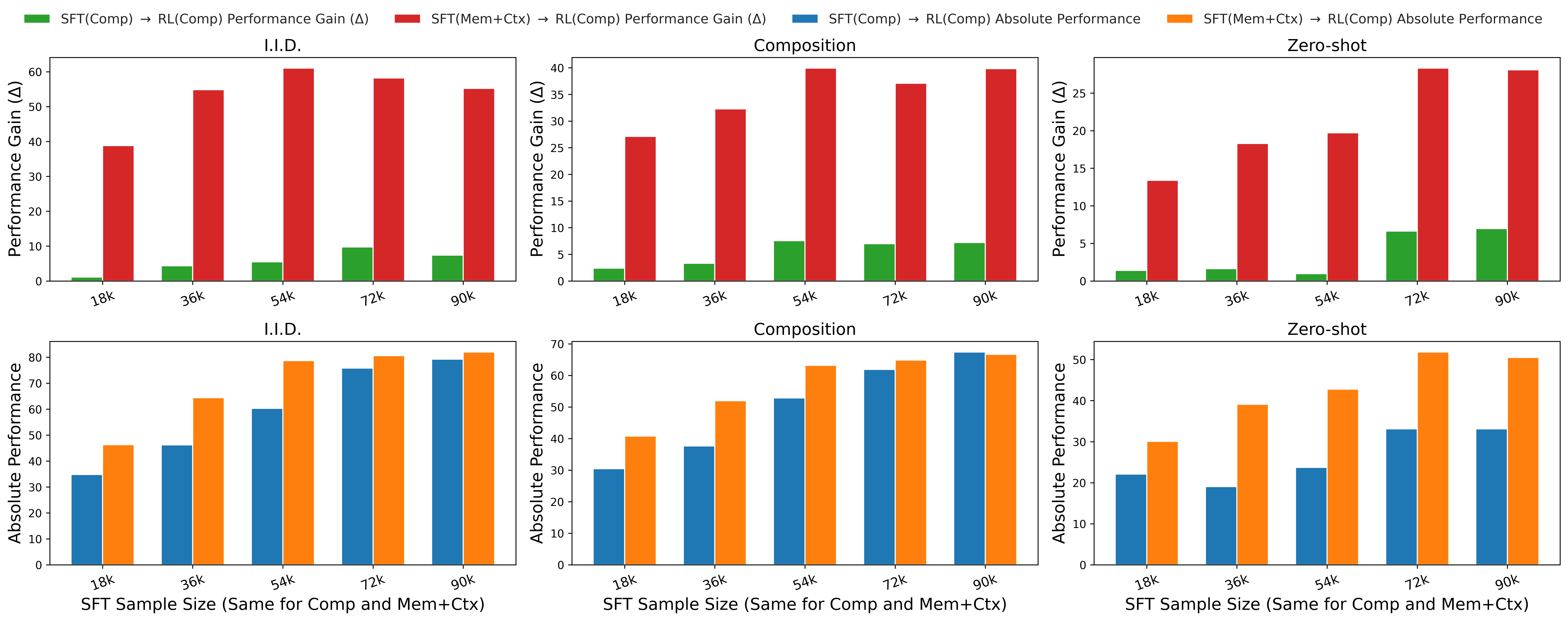
Settings. A common practice for complex tasks is to SFT as a cold-start and then RL over extensive training data (Guo et al., 2025). However, it is unclear how much data is needed to SFT for RL generalization for COMP. To address this, we partition the COMP training data into two subsets: a portion x% used for the SFT stage of the baseline, and the remaining (100 -x)% used for the RL stage. We compare two strategies using strictly identical RL data: 1) SFT COMP →RL COMP : SFT on x% COMP data and then RL on the remaining (100 -x)%; 2) SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP : SFT on all atomic MEM +CTX training data (about 50% of COMP data in amount) and then RL on the same (100 -x)% COMP data. We vary x% from 10% to 90%. Figure 2 illustrates both the relative performance gain on test set of COMP derived specifically from the RL stage (Top Row) and the final absolute performance (Bottom Row).
While Section 5.1 establishes that “SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP " is sufficient for generalization, distinct research questions remain regarding the boundary conditions: 1) Are both parametric and contextual skills strictly necessary, or can the model generalize from partial atomic skills? 2) Is RL specifically required, or can other training strategies (e.g., further SFT) achieve similar results given the same atomic skills?
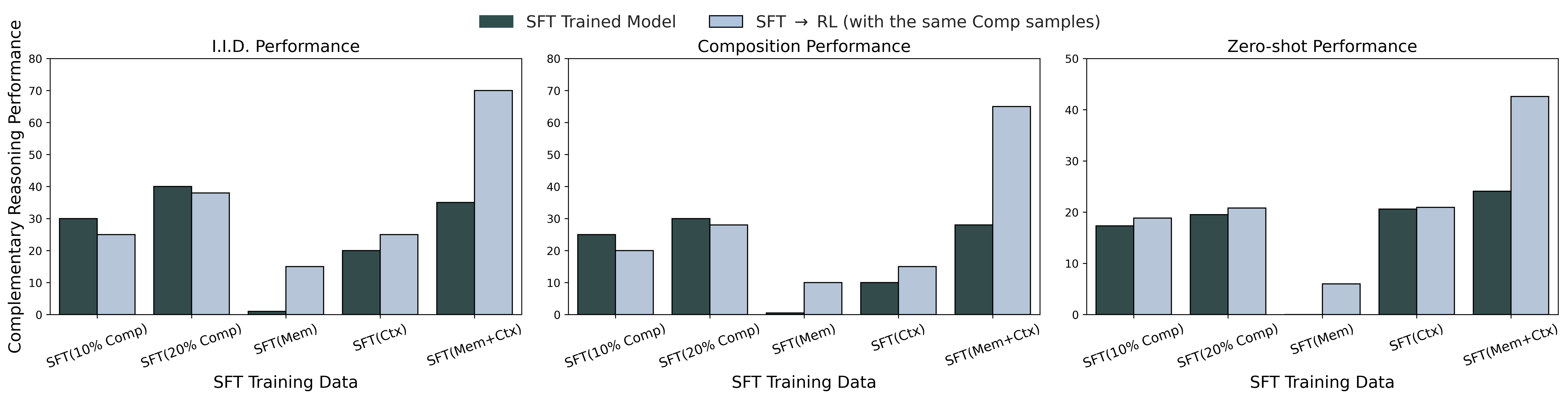
Necessity of Sufficient Atomic Skills (Data Condition). To determine if complete atomic capabilities is a prerequisite for RL-driven generalization, we compare SFT MEM+CTX against three baselines with similar initial performance but deficient atomic foundations: 1) SFT MEM (SFT with MEM only); 2) SFT CTX (SFT with CTX only); 3) SFT 10%COMP and SFT 20%COMP (SFT with COMP data reaching comparable initial performance). We apply identical RL training (using a fixed subset of 12.8k randomly sampled COMP data) to all models. Figure 3 presents the performance on COMP test set before and after RL. We observe two critical findings. First, removing any atomic skill collapses generalization. Models SFTed solely on COMP or CTX fail to generalize significantly after RL, demonstrating that Complementary Reasoning is not merely an additive task but a synthesis requiring the sufficiency of atomic skills. Second, generalization potential is driven by foundational capability, rather than initial metric performance. Notably, SFT 10%COMP and SFT 20%COMP exhibit an initial performance similar to SFT MEM+CTX . However, after RL, their performance gain in all settings is negligible.
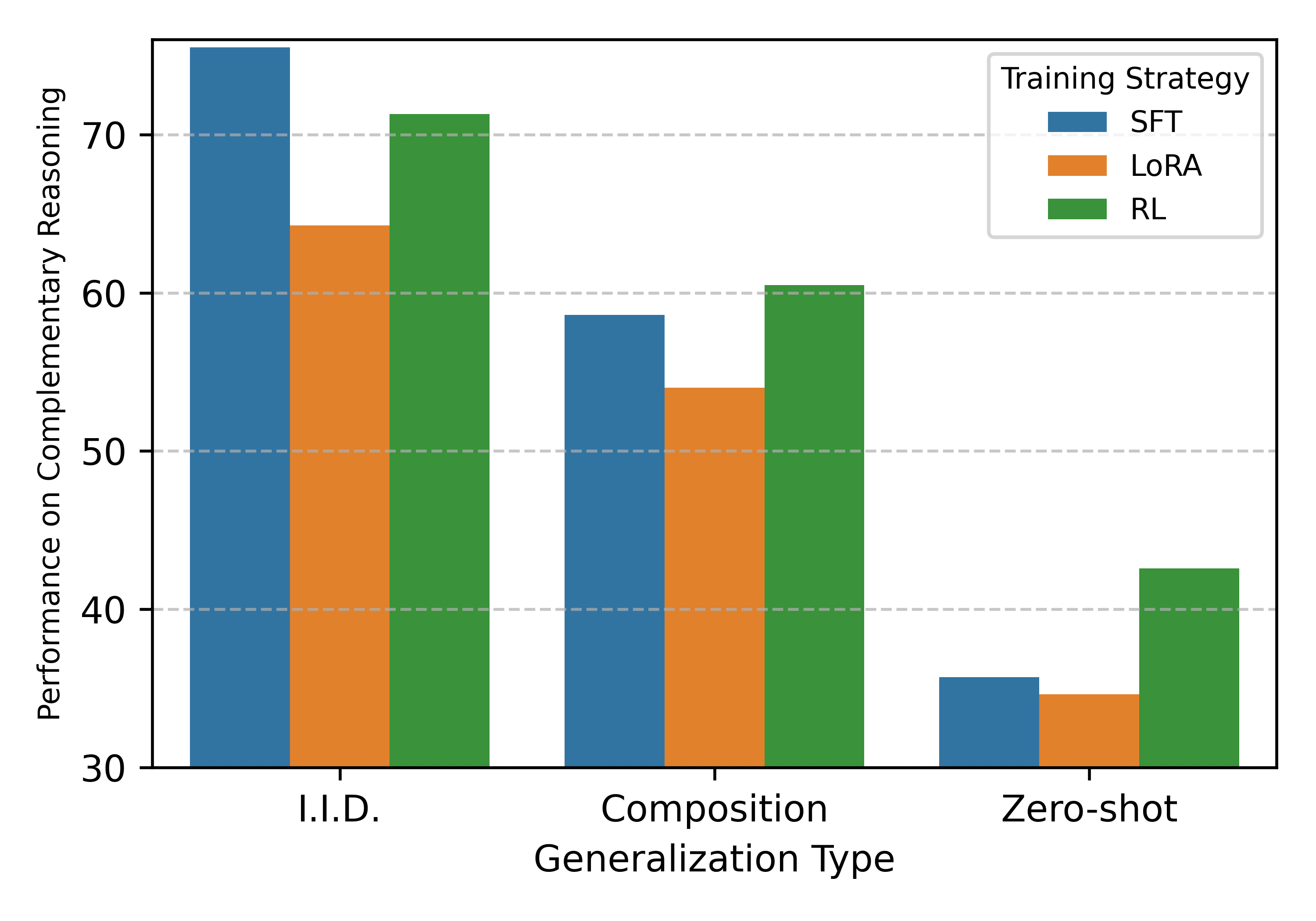
In contrast, SFT MEM+CTX -equipped with the capability of both memory and context processing-achieves substantial gains from RL, nearly doubling the performance in all settings. Also, SFT MEM and SFT CTX , even with very poor initial performance, gain more from RL than the model SFTed with COMP data. This shows that initial test scores before RL are deceptive; the presence of underlying atomic skills is the true predictor of RL success. Figure 4 shows that all training strategies can significantly improve the performance of the model with sufficient atomic skills, demonstrating its strong potential for generalization. However, it reveals a dichotomy between memorization and generalization.
While further SFT (blue bar) yields the highest performance on I.I.D. (indicating strong memorization of seen patterns), it significantly lags behind RL (green bar) in the Zero-shot setting. RL outperforms both SFT and LoRA in unseen relational combinations, confirming that while SFT is superior for pattern matching, RL is uniquely necessary to incentivize the active composition of skills required for out-of-distribution reasoning.
Having established that capturing both the MEM and CTX abilities is the prerequisite for RL-driven generalization, we now analyze the features of base model for RL (i.e., SFT MEM+CTX and SFT COMP ). We investigate from the perspective of sample efficiency and the pass@k performance to see whether RL can compose new skills. We also showcase the training dynamics, the impact of training loss, a PCA analysis of latent space and uncertainty analysis in Appendix E.
We analyze the properties of SFT MEM+CTX by examining whether learning atomic skills induces better sample efficiency compared to learning the composite task directly. We examine this from two perspectives: the data required to prime the base model (SFT efficiency) and the data required to unlock reasoning capabilities (adaptation efficiency).
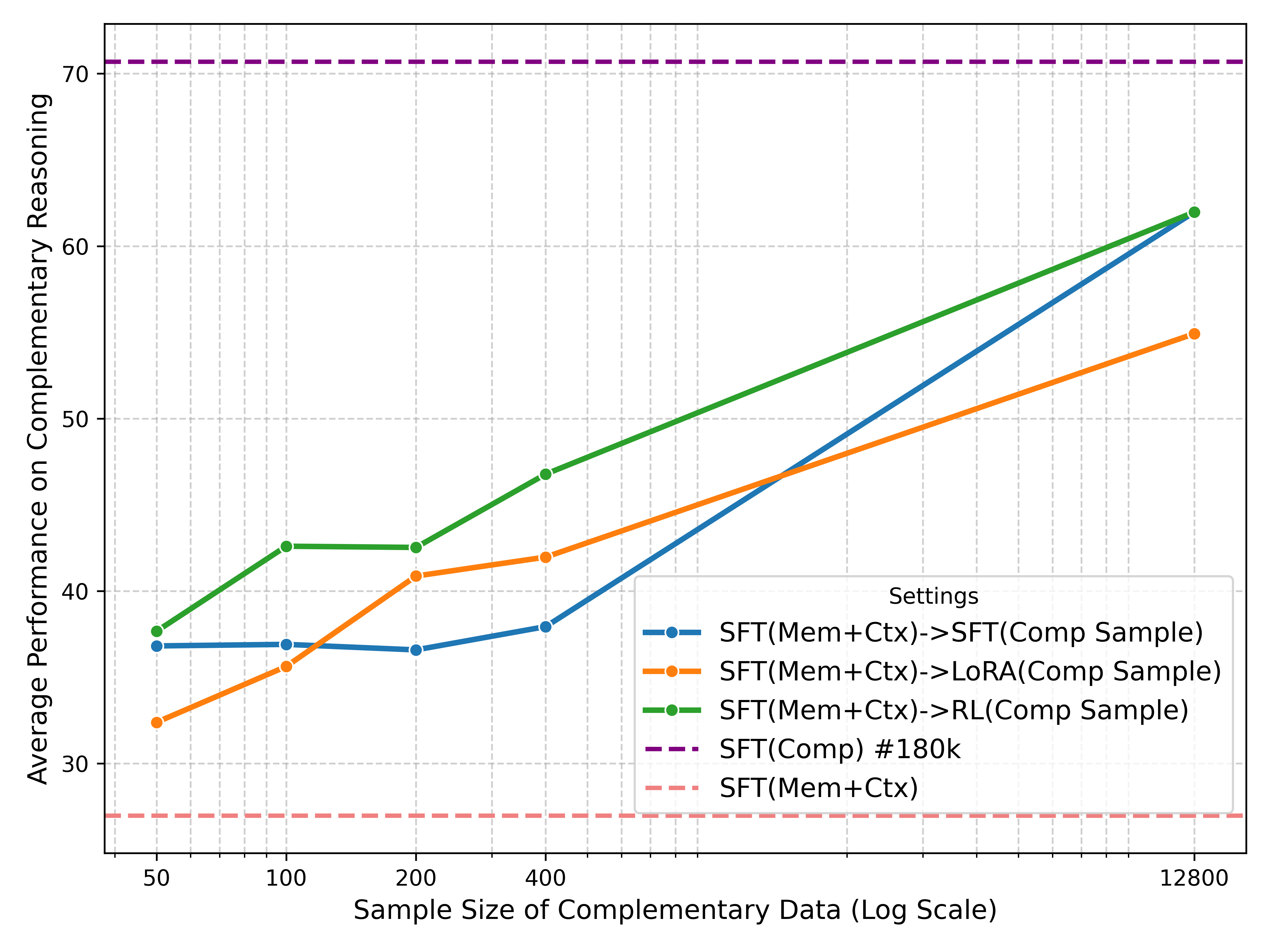
Atomic capability learning requires less SFT data to prime RL generalization. To verify which training paradigm constructs a better foundation for RL with limited data, we conduct a controlled comparison. We first reserve a fixed, large-scale subset (∼90k) of COMP data exclusively for the RL stage. From the remaining data pool, i.e., same amount of (MEM + CTX) and COMP, we create subsets of increasing sizes (20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%) to obtain SFT MEM+CTX and SFT COMP . Crucially, to ensure a fair comparison, we control not just for the number of samples, but also for information content. We strictly enforce that the distribution of reasoning steps (hop counts) is the same across both training data, ensuring that the models are exposed to equivalent reasoning complexities. We then apply RL to all models using the same reserved COMP data. Sufficient atomic skills enable few-shot adaptation. We further investigate how much COMP data is actually needed to “trigger” generalization once sufficient atomic skills are established. Fixing SFT MEM+CTX as the base model, we perform further training using RL, SFT, or LoRA (rank=256) with varying sizes of COMP data, ranging from a “tiny” set (50 samples) to a medium set (12,800 samples, < 10% of the total). We compare this against a skyline baseline: SFT on 100% COMP data (SFT COMP ).
Figure 6 shows the overall performance on COMP test set, from which we observe two key findings. First, rapid adaptation: Even with as few as 50-400 samples, SFT MEM+CTX adapts to the complementary reasoning significantly better than the baseline start, regardless of the training strategy. Second, data efficiency: With less than 10% of COMP data, SFT MEM+CTX effectively matches the performance of the model SFT on the entire dataset (purple dotted line). This demonstrates that once atomic skills are acquired, the cost of “assembling” them into a complex reasoning strategy is extremely low.
There is abundant debate in recent literature: Does RL incentivize the acquisition of genuinely new reasoning capabilities (Synthesis), or merely re-weight the probability of existing skills already present in the base distribution (Amplification) (Setlur et al., 2025)? To distinguish between these roles of RL, we analyze the pass@k performance on the COMP test set before and after RL (Yue et al., 2025). We vary k from 2 0 to 2 9 on a log scale. The logic is as follows: 1) Synthesis Signal: If a significant performance gap persists even at large k (i.e., the curves remain parallel or divergent), it implies that RL has synthesized novel reasoning paths that the SFT model fundamentally cannot discover via sampling. 2) Amplification Signal: If the performance of the SFT model eventually catches up to the RL model as k increases (i.e., the curves merge), it implies that the reasoning paths are latent in the SFT distribution, and RL merely amplifies their generation probability. We compare our SFT MEM+CTX against a strong baseline (SFT COMP trained on 90% data) using identical RL data.
Figure 7 presents the results over different generalization levels.
RL synthesizes new pathways for models with sufficient atomic skills. The top row of Figure 7 reveals a distinct parallel scaling law. For SFT MEM+CTX , the RL performance (orange line) remains significantly higher than the SFT baseline (blue line) even as k increases to 2 9 . The non-convergence of the pass@k curves suggests a fundamental shift in mechanism. If RL were merely amplifying latent behaviors, the SFT model (given enough attempts k) would eventually find the solution.
The persistent gap indicates that RL has synthesized a logic circuit-specifically, the mechanism to bridge context and memory-that is effectively absent from the SFT distribution. This provides empirical evidence that, given sufficient atomic priors, RL creates new capabilities rather than just optimizing old ones. This persistent gap serves as strong empirical evidence that RL is not just re-weighting existing skills. Instead, it is actively synthesizing atomic skills into novel reasoning strategies that are effectively non-existent in the base model’s sampling distribution. Notably, this discovery of “new” capabilities occurs not only for Zero-shot but also on I.I.D. and Compositional settings, suggesting that RL optimizes the logic of combination itself.
RL merely amplifies existing behaviors for models’ composite skills. In stark contrast, the bottom row of Figure 7 shows that for SFT COMP , the curves rapidly converge as k increases. By k = 2 9 , the SFT model nearly matches the RL model’s performance. This indicates that because the model trained on composite data memorized the target distribution during SFT, RL serves primarily as an amplifier-boosting the likelihood of the “best” answer without discovering fundamentally new reasoning paths.
This dichotomy confirms that sufficient atomic skills are the prerequisite for RL to function as a reasoning synthesizer. Without them, RL degenerates into a mere probability amplifier.
Having demonstrated quantitative evidence for SFT MEM+CTX being key to RL generalization. We now qualitatively analyze from specific error cases on the intersection of incorrect samples for the models before and after RL. By aligning the generated CoT with the ground truth, we pinpoint the exact reasoning step where the deviation occurred. We classify these errors based on the required knowledge-parametric (MEM) versus contextual (CTX)-and calculate the progress (the normalized position of the failure step within the reasoning path). Table 2 shows distinct error patterns among the models.
Although we have validated our conclusion that only “SFT MEM+CTX → RL COMP " generalizes, which well addresses the research questions, we still have some limitations: 1) Although we show from several distinct angles that our finding holds, we only test on Qwen models. While evaluated on the Qwen family, our decomposition of reasoning into atomic priors suggests these findings are likely architecture-agnostic. 2) As we investigate from the sample efficiency, the pass@k performance, the training dynamic, the embedding distributions and case study, it is still difficult to find the mechanisms that enable the SFT MEM+CTX model to outperform. Future work should investigate the mechanistic interpretability of how RL circuits recruit atomic attention heads. 3) While our study relies on synthetic biographies, this was a necessary design choice to strictly enforce the boundary between Parametric (known) and Contextual (new) information-a boundary that is impossible to guarantee in web-scale corpora due to pre-training contamination. Future work should validate these findings on controlled splits of real-time benchmarks (e.g., news QA) where the “new” information is strictly dated post-training. Moreover, future work should study how to mix COMP data with MEM and CTX data to improve the overall I.I.D., Composition and Zero-shot performance. 4) It would be interesting to adapt our findings into real-world knowledge-intensive benchmarks, especially to check the O.O.D. testing performance. After we split the relation combinations based on the generalization levels 3, we can synthesize human biographies based on the knowledge graph. We firstly conduct random walk over the knowledge graph entities, and then translate the obtained dict-formed biographies into natural language paragraphs with the relation templates. Table 5 shows an example of the biography dict and corresponding natural language paragraph.
As discussed in Section 4.1, we are able to synthesize as much data as needed. However, in realworld scenarios, while LLMs can easily handle either Parametric or Contextual Reasoning, probably through post-training with sufficient data, they struggles in Complementary Reasoning task, where it is hard to collect ample data. We show in Table 1a that Complementary Reasoning is data-hungry and most difficult compared to parametric and contextual reasoning. Here we show empirical results training with SFT and evaluating on the corresponding testing set in Table 6.
It further shows that Contextual Reasoning is the easiest. While LLMs learns to adopt new knowledge during SFT training, they manage to handle most of the unseen knowledge in the context window. We hypothesize that this ability is essential for further generalization to new reasoning patterns. Moreover, SFT training involving parametric knowledge would be hard to generalize on Zero-shot settings. Both parametric and complementary reasoning, while performing well on I.I.D. setting, drop significantly on Composition and almost fail on Zero-shot setting.
This further highlights our motivations: we try to figure out the recipe of training strategies and mix of training data required for generalization to complementary reasoning on all difficulty levels. Table 5: An example of human biography in the form of Python Dict and Natural Language Document.
Python Dictionary Natural Language Document “Allison Hill”: { “name”: “Allison Hill”, “birth date”: “1942-04-29”, “occupation”: “Civil engineer, consulting”, “email”: “garzaanthony@example.org”, “phone”: “538.990.8386”, “new”: true, “died on”: “2024-11-01”, “child”: “Donald Marsh”, “pet”: “Whiskers”, “wrote”: “Baby administration”, “influenced by”: “Matthew Cooper”, “mentoring”: “Daniel Watkins”, “hobby”: “painting”, “classmate”: “Adam Villanueva”, “first language”: “Finnish”, “roommate”: “Shannon Krause”, “university”: “University of Chicago”, “service”: “Habitat for Humanity”, “known for”: “painting”, “died in”: “Brownbury”, “boss”: “Lindsey Johnson”, “favorite food”: “tacos” } Allison Hill has a pet named Whiskers. Allison Hill spoke Finnish as their first language. A favorite activity of Allison Hill is painting. Lindsey Johnson is the boss of Allison Hill.
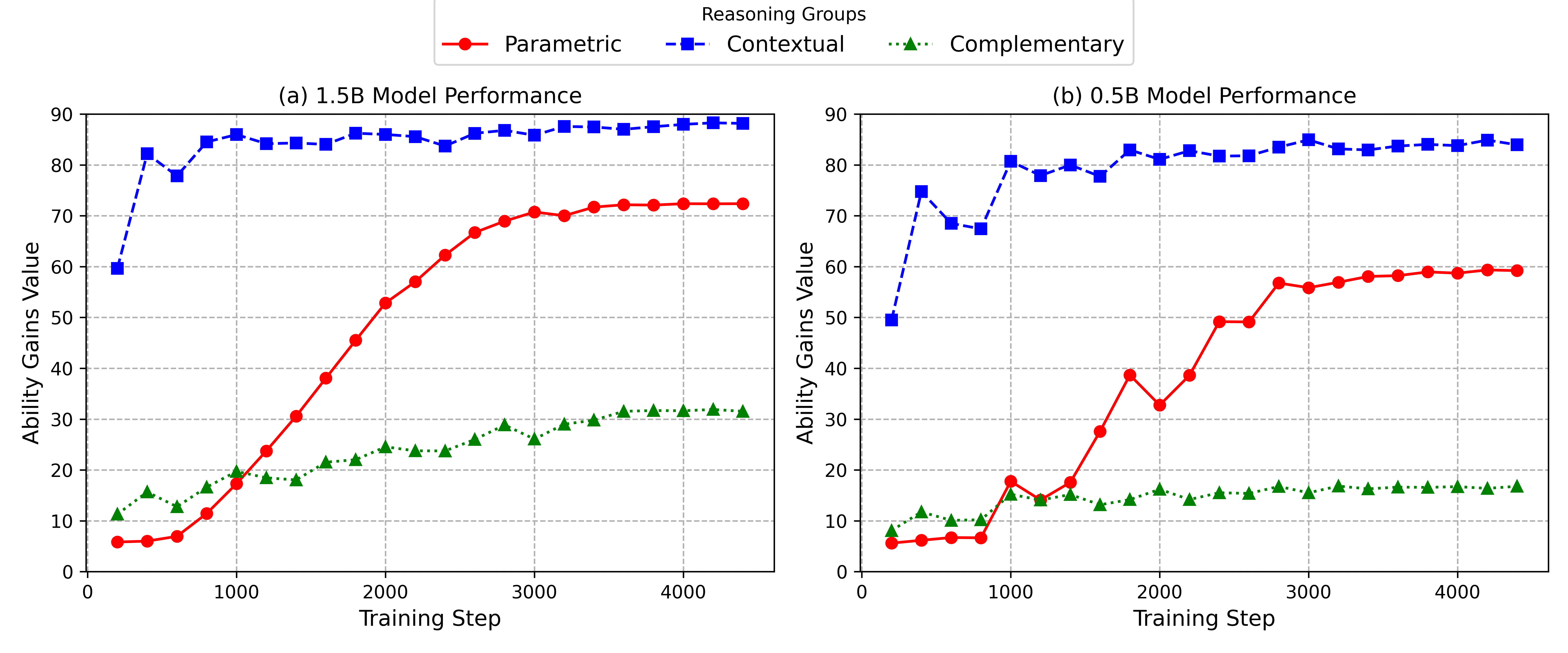
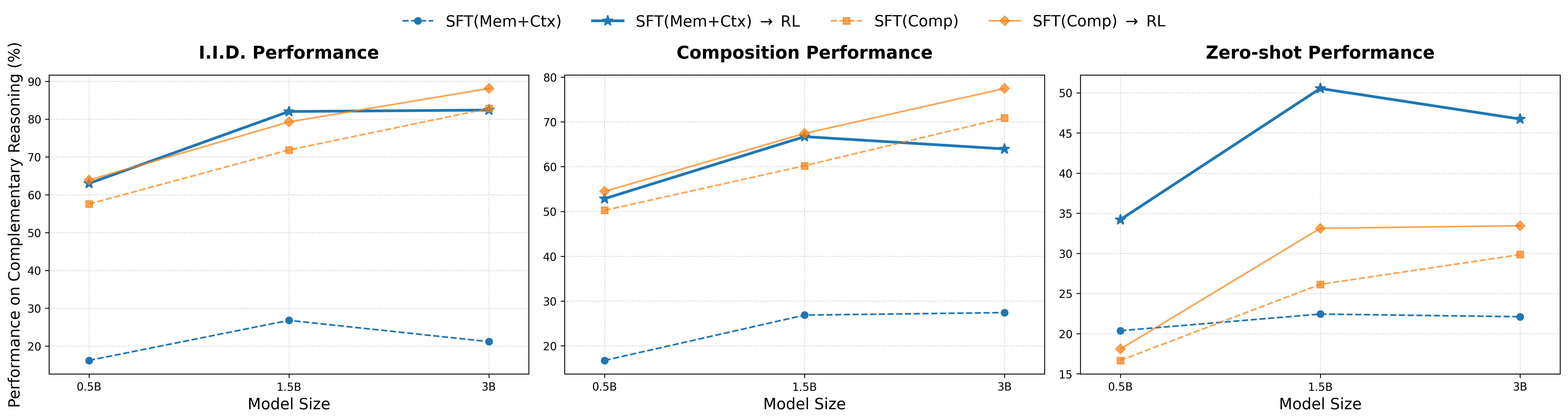
We study whether our findings that “RL enables generalization in Complementary Reasoning from sufficient atomic skills” persist as models scale. We compare Qwen-2.5-0.5B, Qwen-2.5-1.5B and Qwen-2.5-3B due to limited compute. Figure 8 illustrates the performance trends across model sizes.
We observe consistent behaviors that strongly support the effectiveness of our proposed recipe.
As shown by the blue lines, SFT MEM+CTX leads to substantial performance jumps after RL COMP . This improvement is particularly pronounced in the Zero-shot setting, indicating that the model with sufficient atomic skills successfully generalizes the reasoning capabilities acquired during RL. In contrast, SFT COMP (orange dashed line), while starting with decent performance, exhibits limited growth after RL training (orange solid line). The gap between the pre-RL and post-RL performance is marginal, suggesting that SFT with composite data may limit the model’s potential for further generalization.
There are many factors affecting models’performance or generalizability. We showcase the sample efficiency and pass@k performance as some features to see why the model with atomic skills are essentials for RL generalization in composite tasks. Here, we investigate from the perspective of training dynamics of SFT MEM+CTX , the impact of training loss of the base model for RL, the embedding distributions of the SFT and RL model and the uncertainty of the model. The ability of complementary reasoning emerges to some extent with the progress of both parametric and contextual reasoning. Figure 9 shows the training dynamic over training steps. First, it shows that as the SFT training with both MEM and CTX data progresses, the ability of COMP somehow emerges with MEM and CTX to some extent. Second, the conclusion is consistent over different model sizes, with larger models generalizes better to COMP with MEM and CTX data. Third, it further demonstrates that contextual reasoning is the easiest (learned from relatively early stage), while the parametric and complementary reasoning is relatively difficult.
We investigate a critical question regarding the interplay between Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL): Does the degree of SFT convergence dictate the model’s potential for RL-based generalization? Specifically, we aim to determine if a “grokking-like” phenomenon exists-where continuous optimization of SFT loss, even after apparent metric saturation, further unlocks the model’s reasoning capabilities during the RL stage. Also, we study at which checkpoint (i.e., training loss) may the model emerge the ability of generalization. We take four intermediate checkpoints of SFT MEM+CTX to further conduct RL COMP and evaluate the performance on three levels of generalization.
Figure 10 illustrates the performance trajectories across SFT checkpoints (1k to 4k steps), revealing three distinct phases of capability emergence:
• Insufficient Representation. At the early stage (i.e., 1k steps, Training Loss ≈ 0.44), the model has not yet internalized the necessary reasoning patterns. Consequently, it fails to generalize effectively during the RL stage, resulting in suboptimal performance across all metrics (e.g., Zero-shot accuracy is significantly lower compared to later stages).
• Emergence of Capabilities. As the SFT loss decreases to approximately 0.16 (i.e., 2k steps), we observe a sharp “phase transition” in downstream RL performance. While the base SFT model’s direct performance (dashed lines) shows only moderate improvements, its latent potential for RL adaptation increases dramatically. This suggests that the critical structures required for reasoning generalization are established during this interval.
• Saturation and Robustness. Performance peaks around 3k steps (Loss ≈ 0.05). Interestingly, further extending training to 4k steps-where the model nearly memorizes the training data (Loss ≈ 0.0004)-does not yield further significant gains, nor does it lead to performance degradation. This indicates that while “grokking” (delayed generalization) effectively occurs between 1k and 3k steps, the benefit saturates once the loss drops below a certain threshold (< 0.05). The model becomes robust, maintaining its high plasticity for RL even when deeply fitted to the SFT distribution.
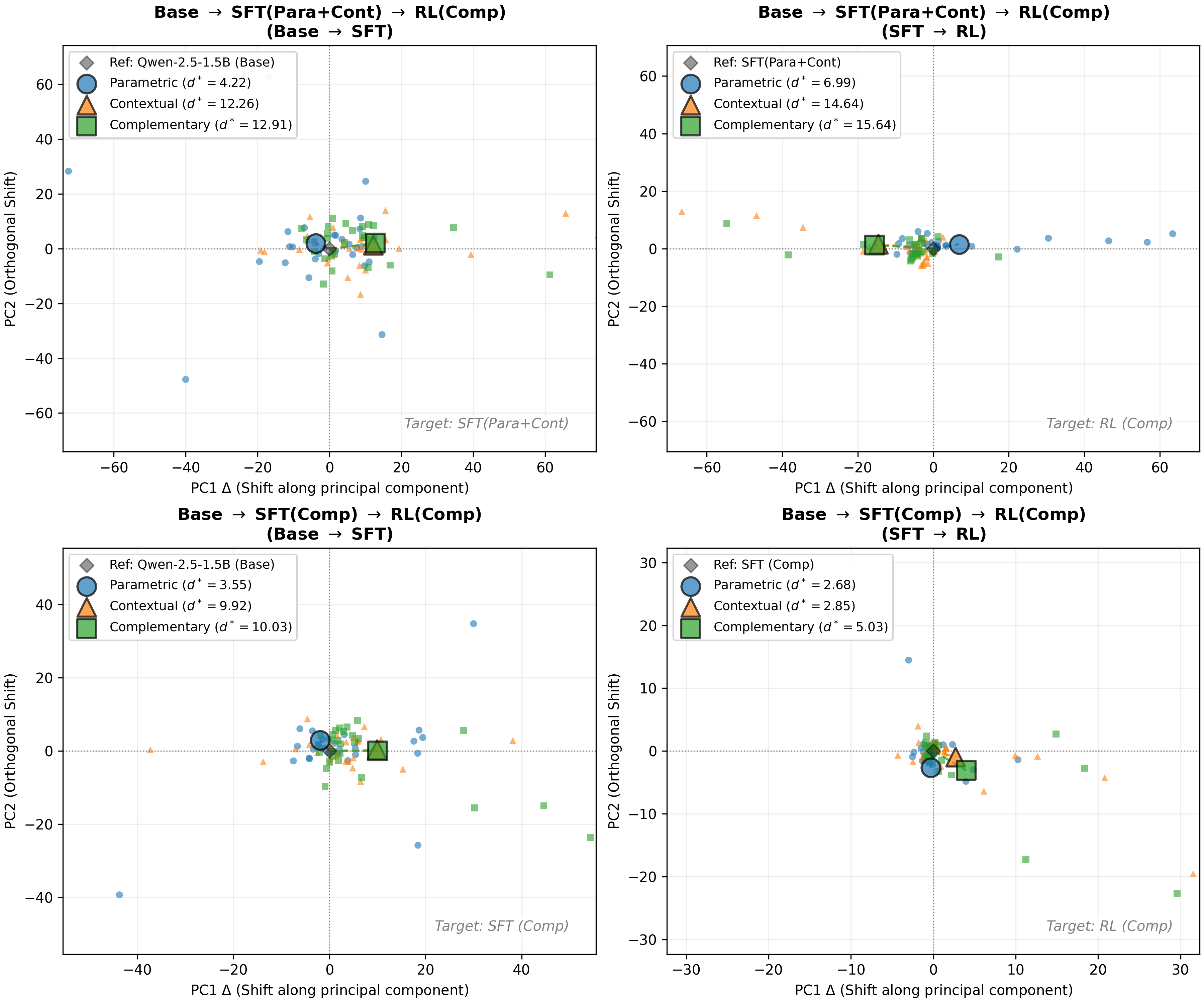
In conclusion, minimizing SFT loss is crucial up to a point. The generalization capability for RL does not scale infinitely with lower loss but requires a sufficient “incubation” period (up to 3k steps in our setting) to fully emerge. Formally, for a given model pair (Anchor Model M anc and Target Model M tgt ) and a specific layer l, we extract the hidden states corresponding to the last token of the input queries. Let H anc l ∈ R N ×D and H tgt l ∈ R N ×D denote the hidden state matrices for N queries at layer l, where D is the hidden dimension. To capture the relative shift induced by training, we fit the PCA transformation on M anc ’s states H anc l , which defines a 2D coordinate system based on the principal variations of the reference model. We then project M tgt ’s states H tgt l into this fixed coordinate system. The shift vector for layer l is calculated as the difference between the centroids of the projected target states and the anchor states. This process is repeated for all layers. Figure 11 shows the layer-wise shifts by scatter points. The large markers represent the global centroid shift (z * ) for each Reasoning type.
Disentanglement of atomic skills in SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP As shown in the top-left panel of Figure 11, SFT MEM+CTX exhibits a significant “disentanglement” of atomic reasoning types. The centroid for MEM data (Blue Circle) and CTX data (Orange Triangle) move in distinct directions and magnitudes within the principal component space. This suggests that the SFT MEM+CTX stage effectively separates the internal representations required for parametric recall versus contextual reasoning. Furthermore, in the subsequent RL stage (top-right panel), this separation is maintained and refined. Notably, the COMP data (Green Square) aligns closely with the established distributions of MEM and CTX data. This indicates that the model can effectively generalize the logic learned from MEM and CTX data to the composite COMP tasks.
Entanglement of skills in SFT COMP →RL COMP . In contrast, the bottom row reveals a phenomenon of “representation entanglement”. Please note that the scale of the axis for the bottom row is lower than that for the top row. For the model trained only on COMP data, the embeddings for MEM, CTX, and COMP queries remain tightly clustered together, after both the SFT stage (bottomleft) and the RL stage (bottom-right). The centroids for all three data types are located close to the origin with overlapping distributions. This lack of separation implies that SFT COMP fails to distin- guish between the underlying mechanisms of parametric and contextual reasoning, instead learning a coupled representation.
We hypothesize that the superior generalization capability of SFT MEM+CTX → RL(Comp) stems from this structural disentanglement. By explicitly separating the latent representations of parametric and contextual capabilities during the SFT stage, the model establishes a robust basis that facilitates better adaptation during the RL phase. Conversely, the coupled representations in SFT COMP limit the model’s ability to distinctly apply these capabilities, leading to suboptimal performance.
We investigate the evolution of model uncertainty (quantified by the average prediction entropy ×100) to understand the underlying dynamics of RL generalization. Table 8 presents the entropy metrics across I.I.D., Compositional, and Zero-shot subsets.
Uncertainty is correlated with SFT convergence, not necessarily RL potential. We first address whether high uncertainty is a prerequisite for effective RL exploration. Comparing the SFT MEM+CTX checkpoints, the uncertainty drops significantly from 3k steps (12.92) to 4k steps (7.13) as the loss minimizes. Despite this lower starting entropy, we previously observed that the 4k-step model sustains high performance after RL. This indicates that a “calibrated” and confident SFT model (lower entropy) does not hinder subsequent RL generalization. Task Difficulty Indicator. Consistently across all settings, the uncertainty is highest in the Zeroshot subset (e.g., 12.96 for 10% SFT(G3)). This aligns with intuition, as the model exhibits lower confidence on unseen distributions.
SFT MEM+CTX Facilitates Efficient RL Adaptation. A key insight emerges when comparing the post-RL behaviors. In the 30% data setting, 30% SFT COMP (7.18) and SFT MEM+CTX (7.13) start at remarkably similar uncertainty levels. However, after applying identical RL training, SFT COMP →RL COMP shows minimal entropy reduction (7.18 → 6.11), suggesting the model struggles to find a more optimal, confident policy. In contrast, our recipe SFT MEM+CTX →RL COMP achieves a drastic reduction in uncertainty (7.13 → 2.90). This demonstrates that the model with sufficient atomic skills does not merely provide “randomness” for exploration; rather, it structures the latent space (see Figure 11) in a way that allows RL to efficiently converge to a high-confidence, correct solution.
F TERMINOLOGIES
While current LLMs are proficient in multi-hop reasoning with either parametric or contextual knowledge, they struggle to handle questions that require the integration of both knowledge sources. In this paper, we study how LLMs can generalize to Complementary Reasoning with post-training strategies (i.e., SFT and RL). We conduct strictly controlled experiments with our synthetic human biographies based on a relational knowledge graph, constructing QA pairs for atomic skills (i.e., Parametric and Contextual Reasoning) and the compound skill (i.e., Complementary Reasoning). We also split the dataset into different levels of generalization difficulties I.I.D., Composition and Zero-shot. Based on this, we study the effect of training strategies and find that only by firstly SFT with sufficient atomic skills can LLMs generalize via RL. This finding suggests a scalable path for training reasoning LLMs: focusing on teaching the model sufficient fundamental atomic skills via SFT, and then leveraging RL for generalization to O.O.D. complex tasks.
- {e2} is {e1}’s brother/sister. {e2} is the boss of {e3}. {e3} received guidance from {e4}. {e5} is {e4}’s closest friend. So, the answer is: {e5}
📸 Image Gallery