An Electrocardiogram Multi-task Benchmark with Comprehensive Evaluations and Insightful Findings
Reading time: 2 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: An Electrocardiogram Multi-task Benchmark with Comprehensive Evaluations and Insightful Findings
- ArXiv ID: 2512.08954
- Date: 2025-11-28
- Authors: Yuhao Xu, Jiaying Lu, Sirui Ding, Defu Cao, Xiao Hu, Carl Yang
📝 Abstract
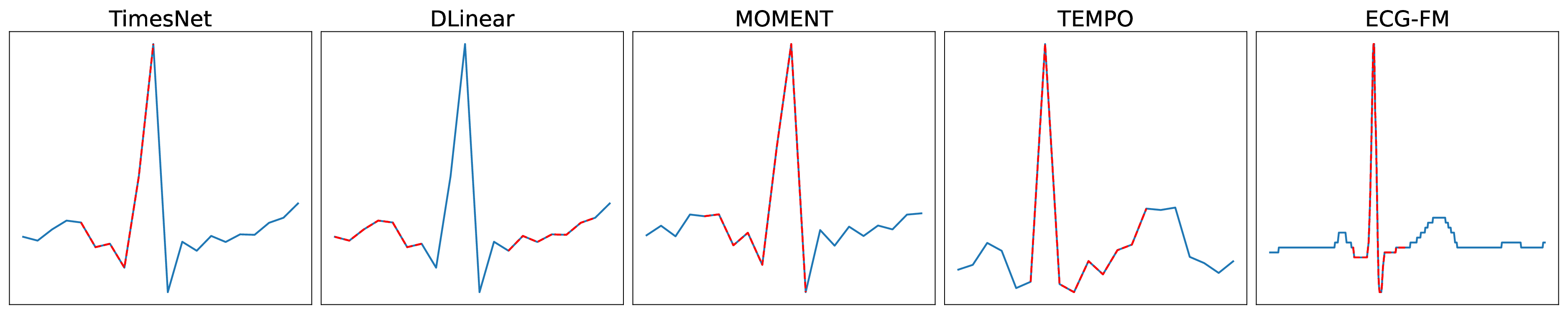
In the process of patient diagnosis, non-invasive measurements are widely used due to their low risks and quick results. Electrocardiogram (ECG), as a noninvasive method to collect heart activities, is used to diagnose cardiac conditions. Analyzing the ECG typically requires domain expertise, which is a roadblock to applying artificial intelligence (AI) for healthcare. Through advances in self-supervised learning and foundation models, AI systems can now acquire and leverage domain knowledge without relying solely on human expertise. However, there is a lack of comprehensive analyses over the foundation models' performance on ECG. This study aims to answer the research question: "Are Foundation Models Useful for ECG Analysis?" To address it...📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery
Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.