Large-Scale Traffic Signal Control with a New Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Large-Scale Traffic Signal Control Using a Novel Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning- ArXiv ID: 1908.03761
- Date: 2021-09-14
- Authors: Xiaoqiang Wang, Liangjun Ke, Zhimin Qiao, and Xinghua Chai
📝 Abstract
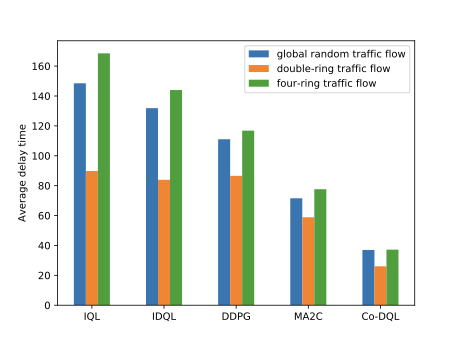
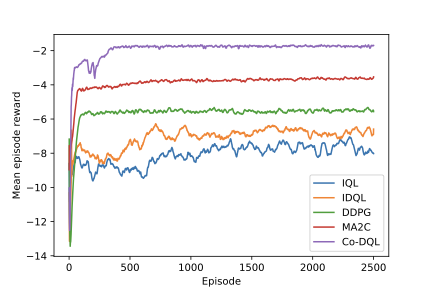
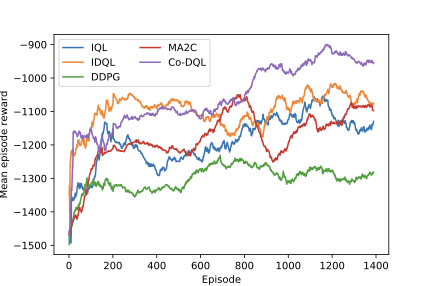
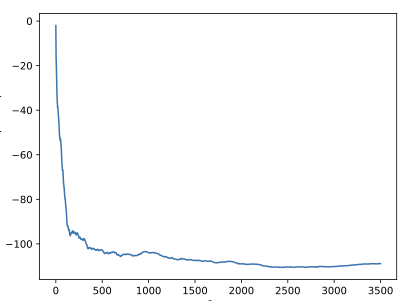
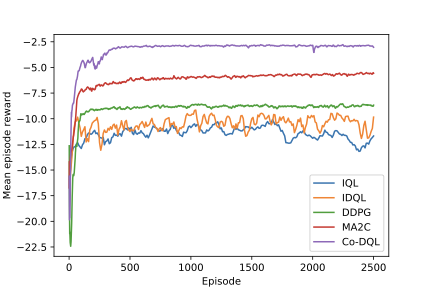
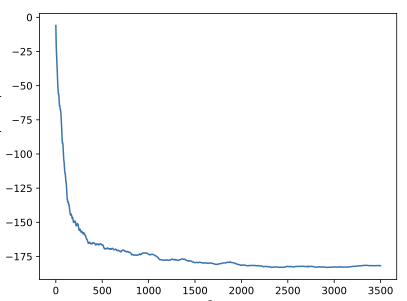
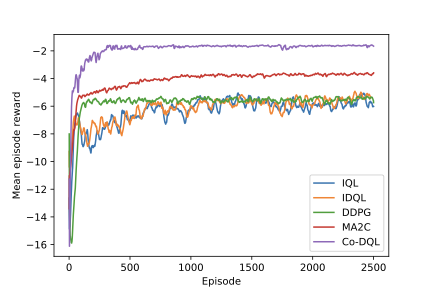
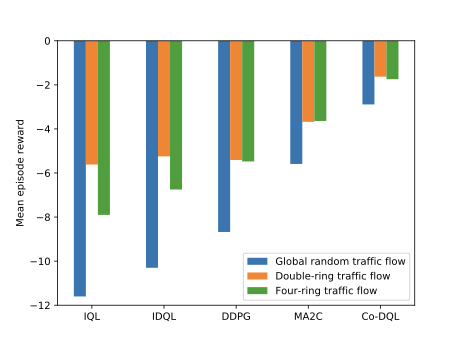
Finding the optimal signal timing strategy is a difficult task for the problem of large-scale traffic signal control (TSC). Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) is a promising method to solve this problem. However, there is still room for improvement in extending to large-scale problems and modeling the behaviors of other agents for each individual agent. In this paper, a new MARL, called Cooperative double Q-learning (Co-DQL), is proposed, which has several prominent features. It uses a highly scalable independent double Q-learning method based on double estimators and the UCB policy, which can eliminate the over-estimation problem existing in traditional independent Q-learning while ensuring exploration. It uses mean field approximation to model the interaction among agents, thereby making agents learn a better cooperative strategy. In order to improve the stability and robustness of the learning process, we introduce a new reward allocation mechanism and a local state sharing method. In addition, we analyze the convergence properties of the proposed algorithm. Co-DQL is applied on TSC and tested on a multi-traffic signal simulator. According to the results obtained on several traffic scenarios, Co- DQL outperforms several state-of-the-art decentralized MARL algorithms. It can effectively shorten the average waiting time of the vehicles in the whole road system.💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper introduces a new Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) method called Cooperative double Q-learning (Co-DQL), which aims to address the challenge of large-scale traffic signal control. The problem being tackled is optimizing vehicle waiting times in urban road systems, an area where traditional reinforcement learning methods have limitations due to scalability and modeling interactions between agents. Co-DQL incorporates several key features: it uses independent double Q-learning with multiple estimators and UCB policy, which prevents over-estimation while ensuring exploration; employs mean field approximation for better cooperative strategy learning among agents; introduces new reward allocation mechanisms and local state sharing methods to improve stability and robustness in the learning process. The results show that Co-DQL outperforms several state-of-the-art decentralized MARL algorithms in various traffic scenarios, significantly reducing average vehicle waiting times across the entire road system. This method is significant as it offers a powerful solution for traffic signal control, which could be applied to real-world urban traffic management systems.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)