Pipelined Repair Techniques for Erasure-Coded Storage Algorithms and Analysis
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Repair Pipelining for Erasure-Coded Storage Algorithms and Evaluation- ArXiv ID: 1908.01527
- Date: 2020-11-23
- Authors: Xiaolu Li, Zuoru Yang, Jinhong Li, Runhui Li, Patrick P. C. Lee, Qun Huang, Yuchong Hu
📝 Abstract
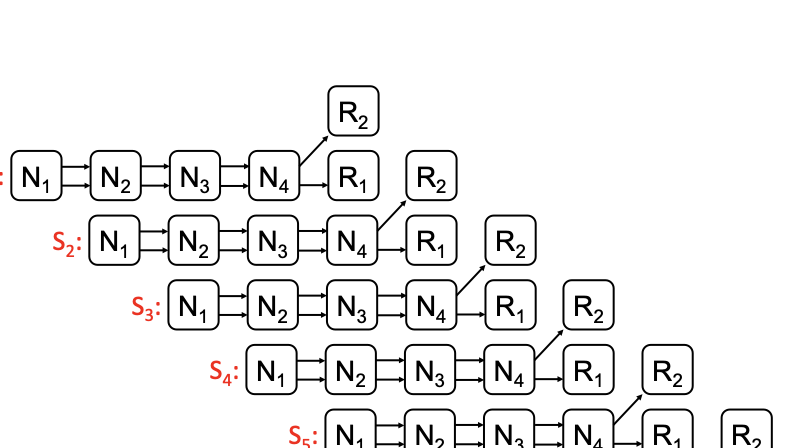
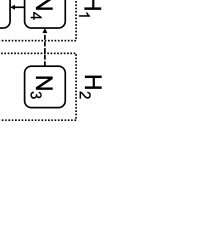
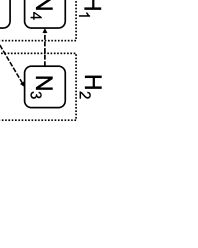
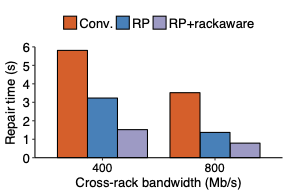
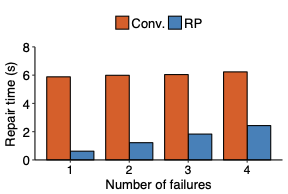
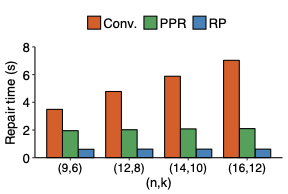
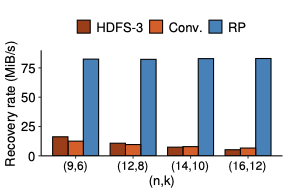
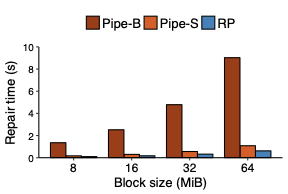
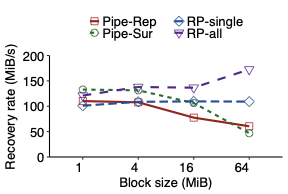
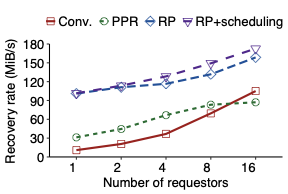
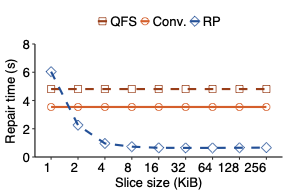
We propose repair pipelining, a technique that speeds up the repair performance in general erasure-coded storage. By carefully scheduling the repair of failed data in small-size units across storage nodes in a pipelined manner, repair pipelining reduces the single-block repair time to approximately the same as the normal read time for a single block in homogeneous environments. We further design different extensions of repair pipelining algorithms for heterogeneous environments and multi-block repair operations. We implement a repair pipelining prototype, called ECPipe, and integrate it as a middleware system into two versions of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) (namely HDFS-RAID and HDFS-3) as well as Quantcast File System (QFS). Experiments on a local testbed and Amazon EC2 show that repair pipelining significantly improves the performance of degraded reads and full-node recovery over existing repair techniques.💡 Summary & Analysis
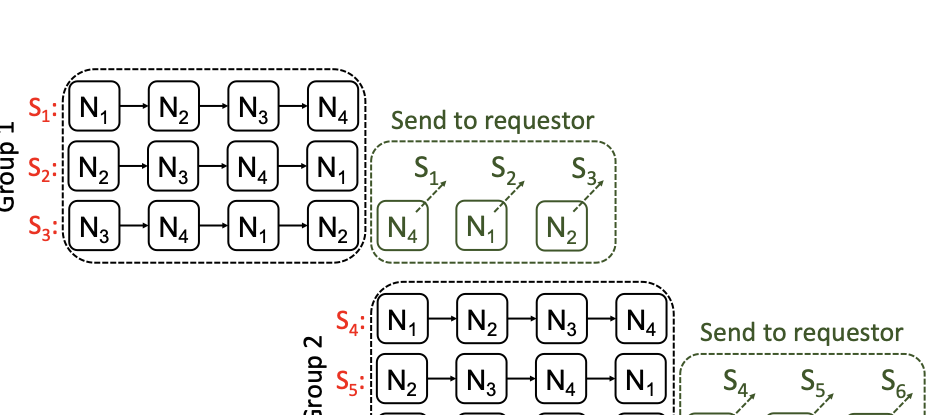
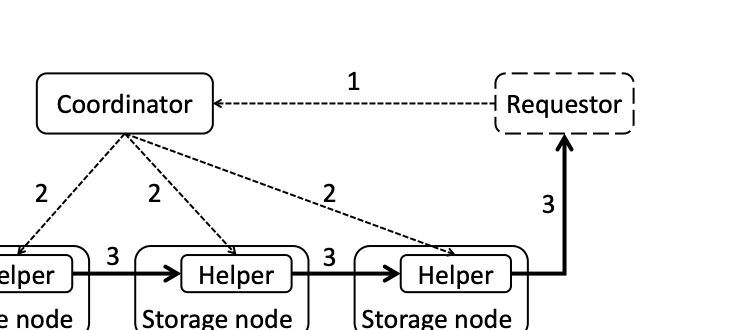
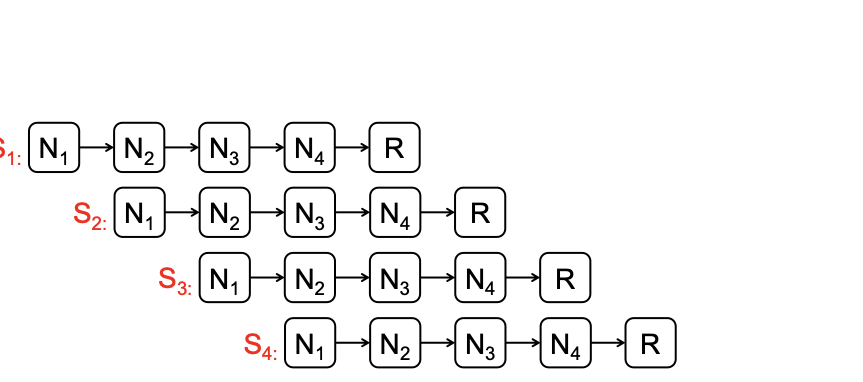
The paper discusses a new technique called "repair pipelining" aimed at enhancing the repair efficiency in erasure-coded storage systems. This method addresses a critical challenge faced by distributed file systems where node failures necessitate time-consuming and resource-intensive recovery processes, often leading to reduced overall system performance. Repair pipelining works by breaking down the damaged data into small units and scheduling their restoration across multiple nodes in a parallel fashion. The result is that the repair time for each block becomes comparable to normal read times, significantly improving efficiency.The authors extended this approach to handle heterogeneous environments and multi-block repairs, ensuring robust performance across different conditions. They implemented a prototype called ECPipe, integrating it into various versions of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Quantcast File System (QFS). Through experiments conducted on local testbeds and Amazon EC2, they demonstrated that repair pipelining outperforms traditional recovery methods in terms of degraded read performance and full-node recovery. This work is crucial for enhancing the efficiency of distributed storage systems, particularly beneficial in large-scale cloud environments where data integrity and rapid recovery are paramount.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)