Computer Science / Systems and Control
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science / Systems and Control
A Local Direct Method for Identifying Modules in Dynamic Networks with Correlated Noise
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: A local direct method for module identification in dynamic networks with correlated noise- ArXiv ID: 1908.00976
- Date: 2020-11-03
- Authors: Karthik R. Ramaswamy and Paul M.J. Van den Hof
📝 Abstract
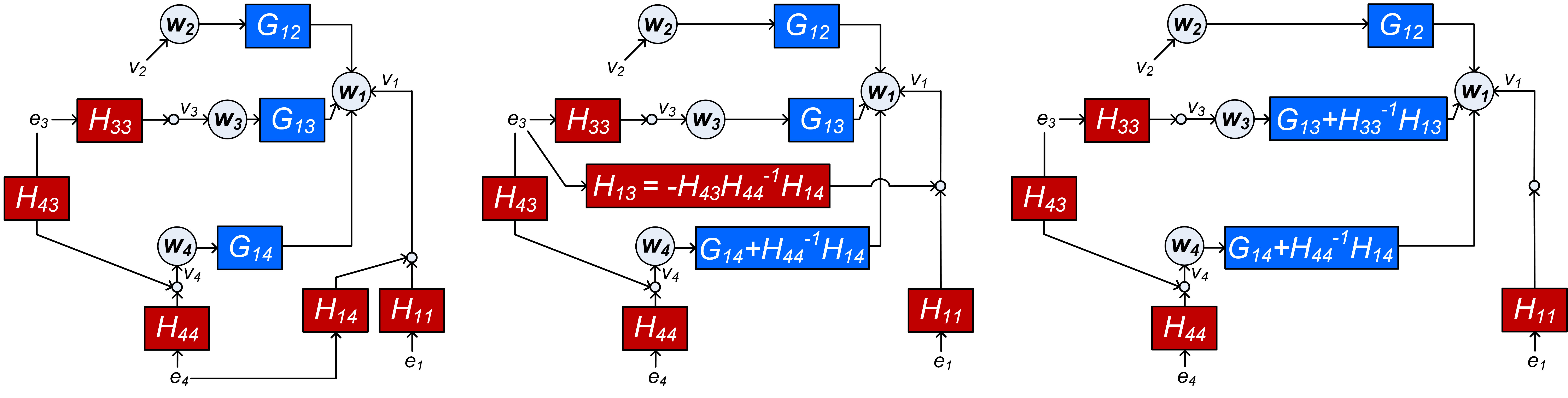
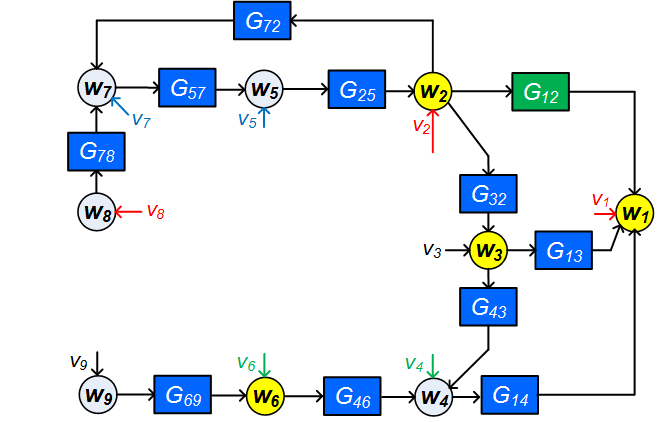
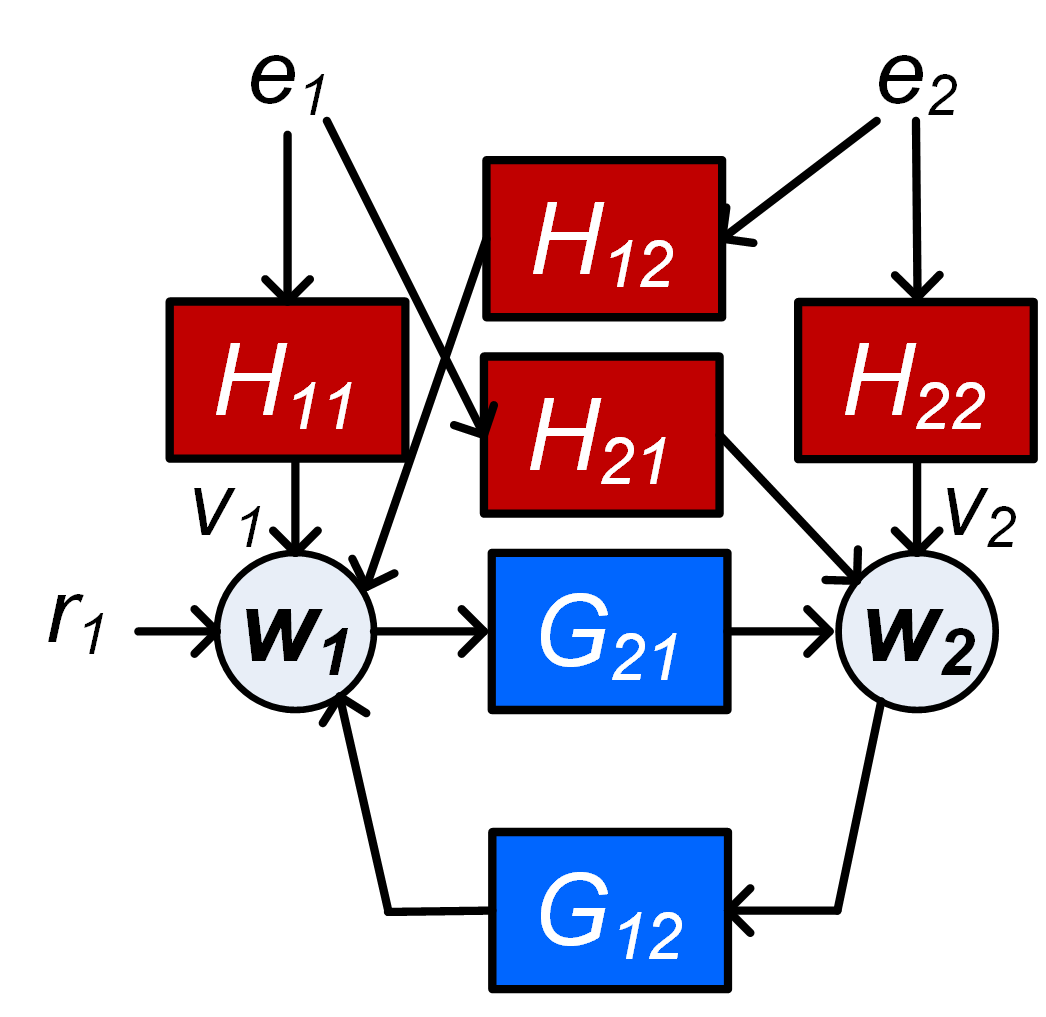
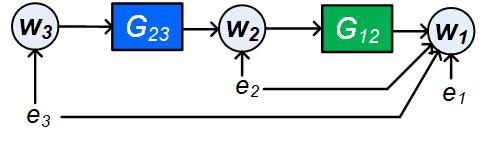
The identification of local modules in dynamic networks with known topology has recently been addressed by formulating conditions for arriving at consistent estimates of the module dynamics, under the assumption of having disturbances that are uncorrelated over the different nodes. The conditions typically reflect the selection of a set of node signals that are taken as predictor inputs in a MISO identification setup. In this paper an extension is made to arrive at an identification setup for the situation that process noises on the different node signals can be correlated with each other. In this situation the local module may need to be embedded in a MIMO identification setup for arriving at a consistent estimate with maximum likelihood properties. This requires the proper treatment of confounding variables. The result is a set of algorithms that, based on the given network topology and disturbance correlation structure, selects an appropriate set of node signals as predictor inputs and outputs in a MISO or MIMO identification setup. Three algorithms are presented that differ in their approach of selecting measured node signals. Either a maximum or a minimum number of measured node signals can be considered, as well as a preselected set of measured nodes.💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper presents a new methodology for identifying modules in dynamic networks where the signals between different nodes may be correlated. Traditionally, methods for module identification assumed that disturbances across nodes were uncorrelated, which often does not hold true in real-world scenarios. The authors address this limitation by developing algorithms that can handle situations with correlated process noises. They propose three distinct algorithms that select appropriate node signals as inputs and outputs in either a MISO (Multiple Input-Single Output) or MIMO (Multiple Input-Multiple Output) identification setup, taking into account the network topology and disturbance correlation structure. This approach not only improves the accuracy of module estimation but also enhances our ability to handle complex real-world networks where nodes are often interconnected through correlated signals.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)