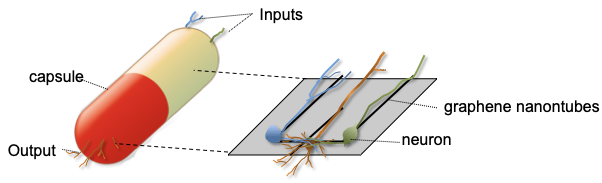
Using Engineered Neurons in Digital Logic Circuits A Molecular Communications Analysis
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Utilizing Neurons for Digital Logic Circuits A Molecular Communications Analysis- ArXiv ID: 1909.02833
- Date: 2020-03-31
- Authors: Geoflly L. Adonias, Anastasia Yastrebova, Michael Taynnan Barros, Yevgeni Koucheryavy, Frances Cleary, Sasitharan Balasubramaniam
📝 Abstract
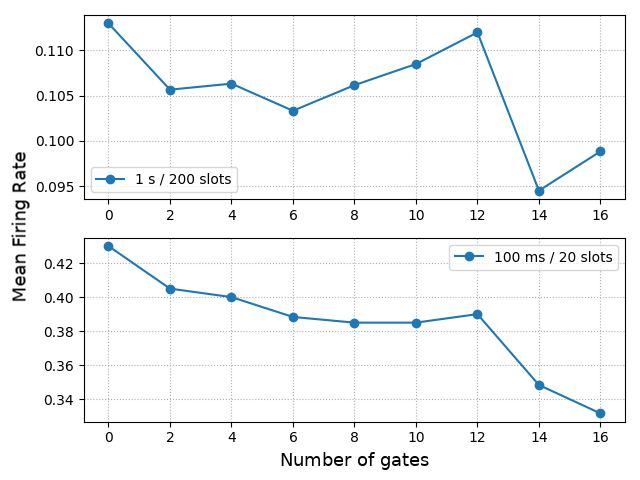
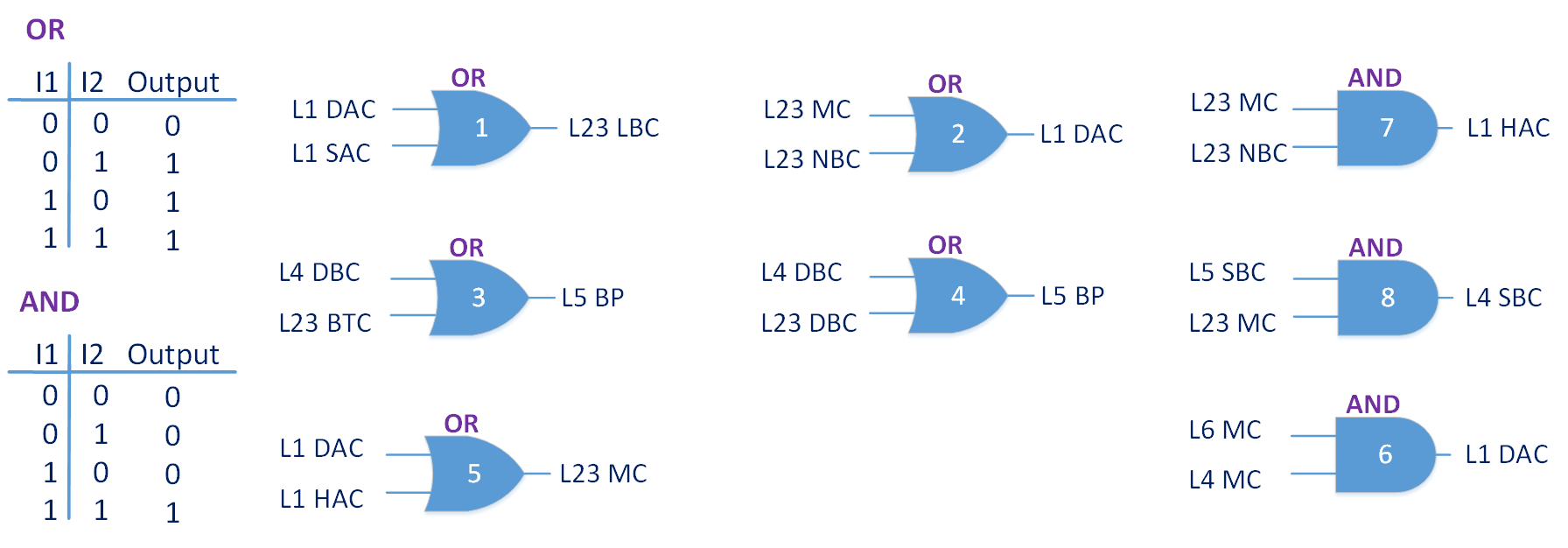
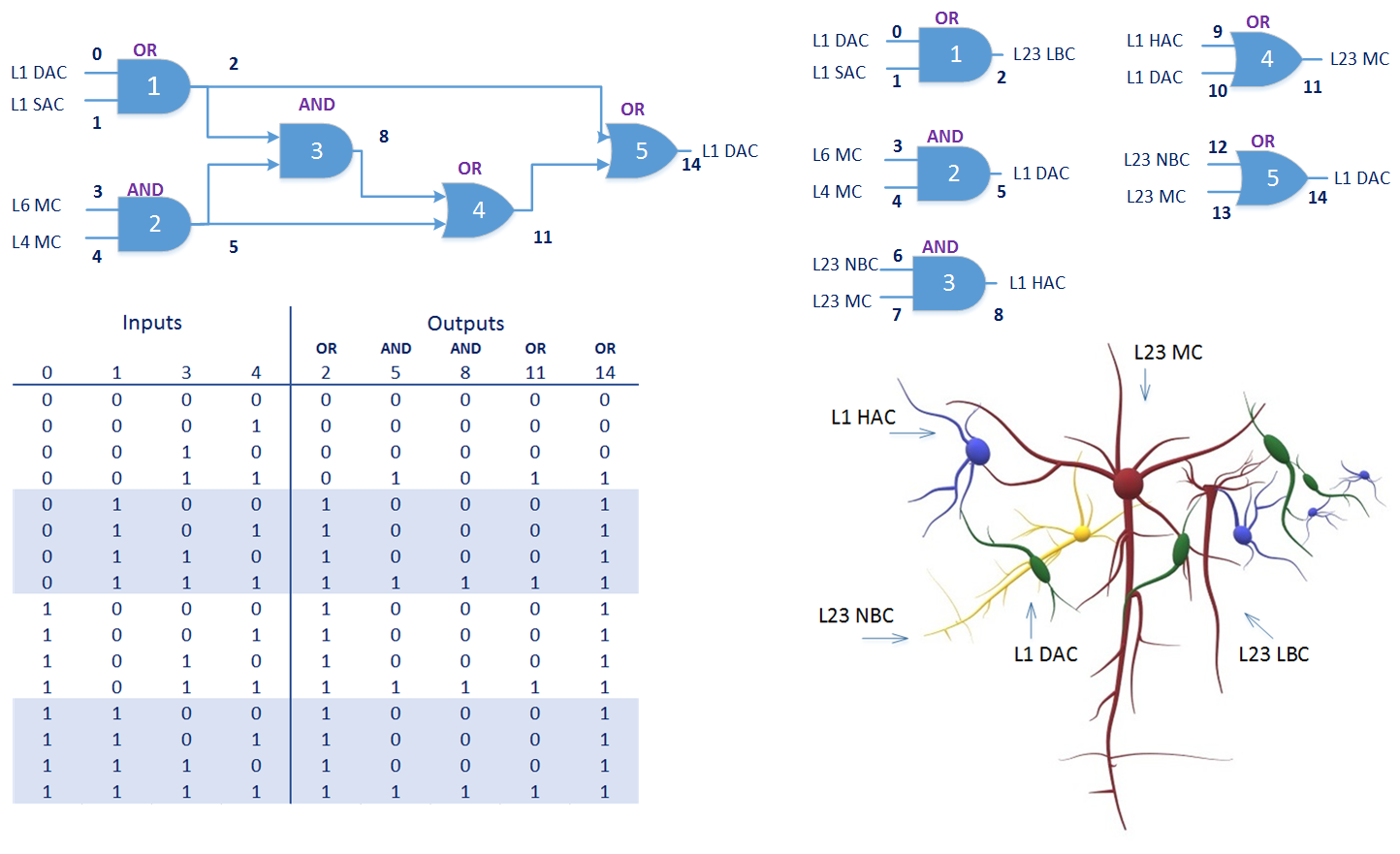
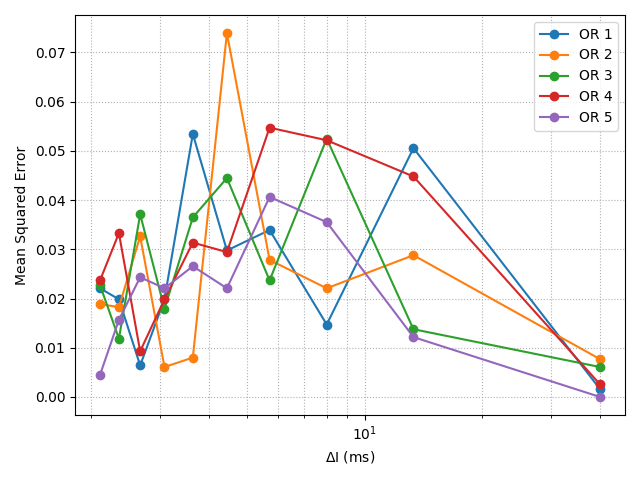
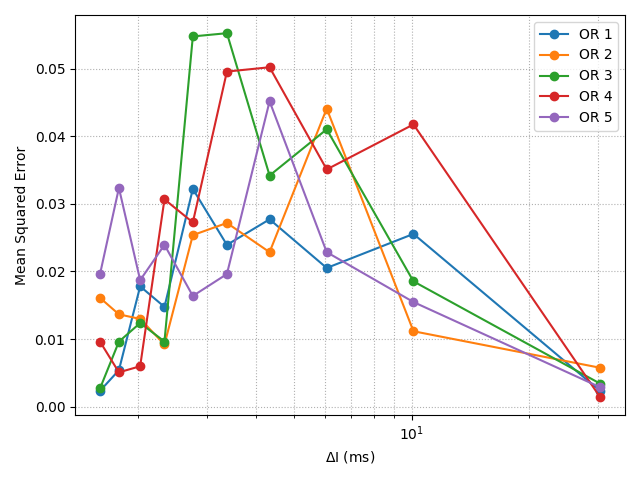
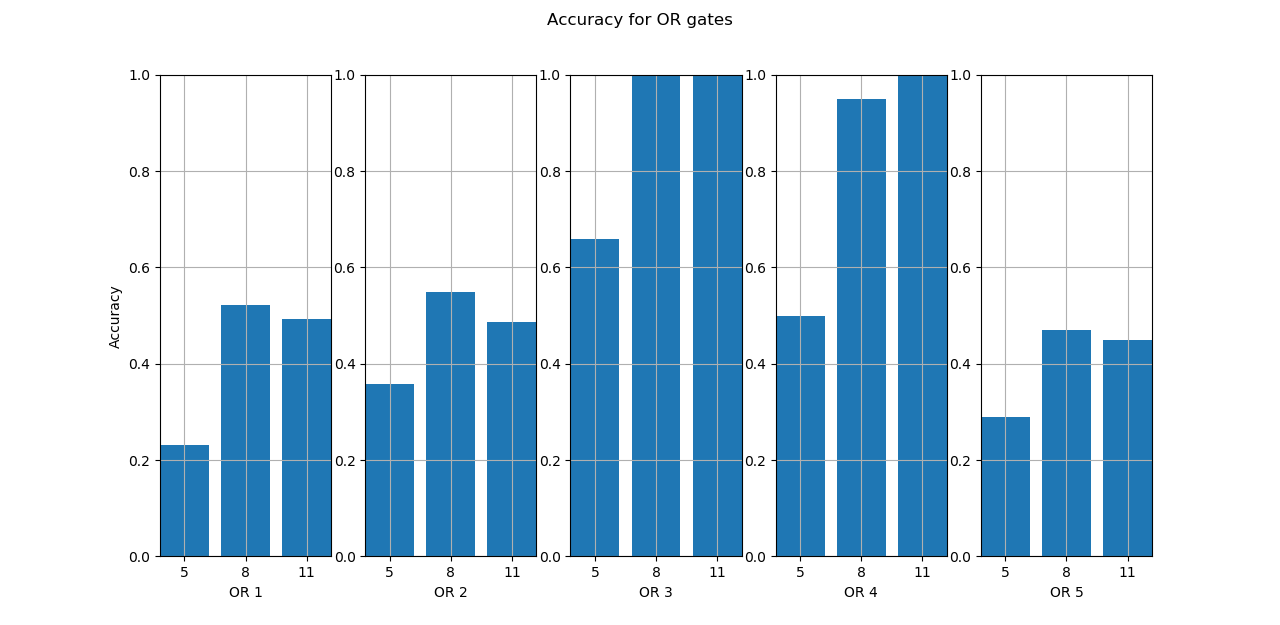
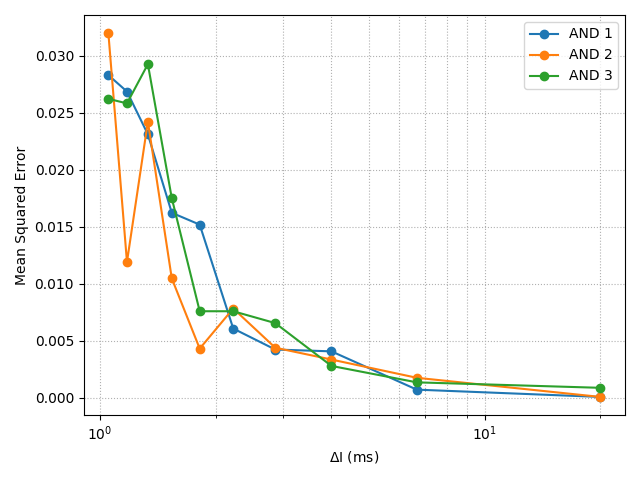
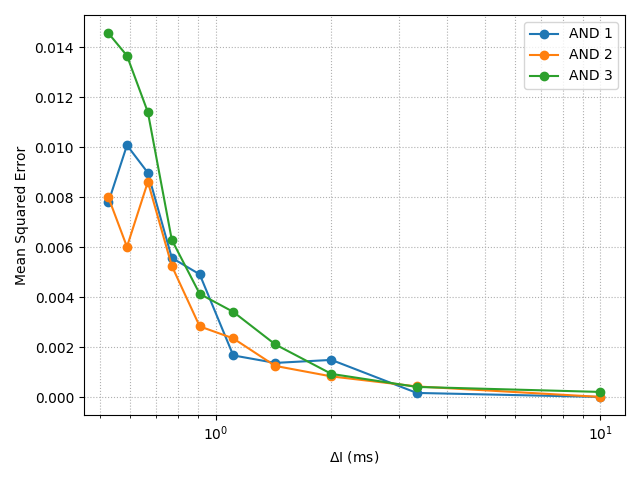
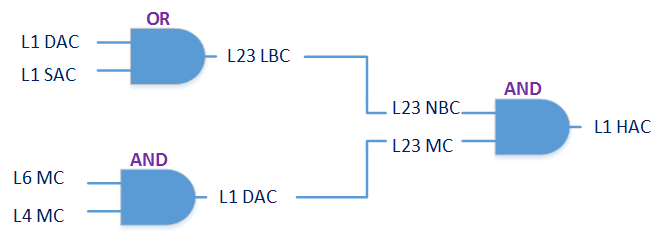
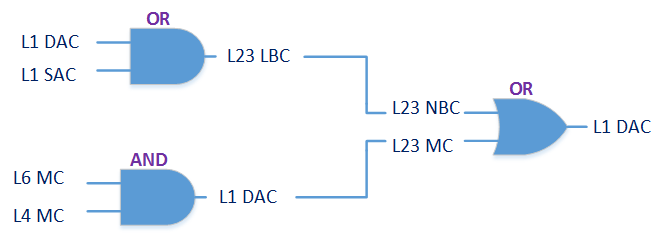
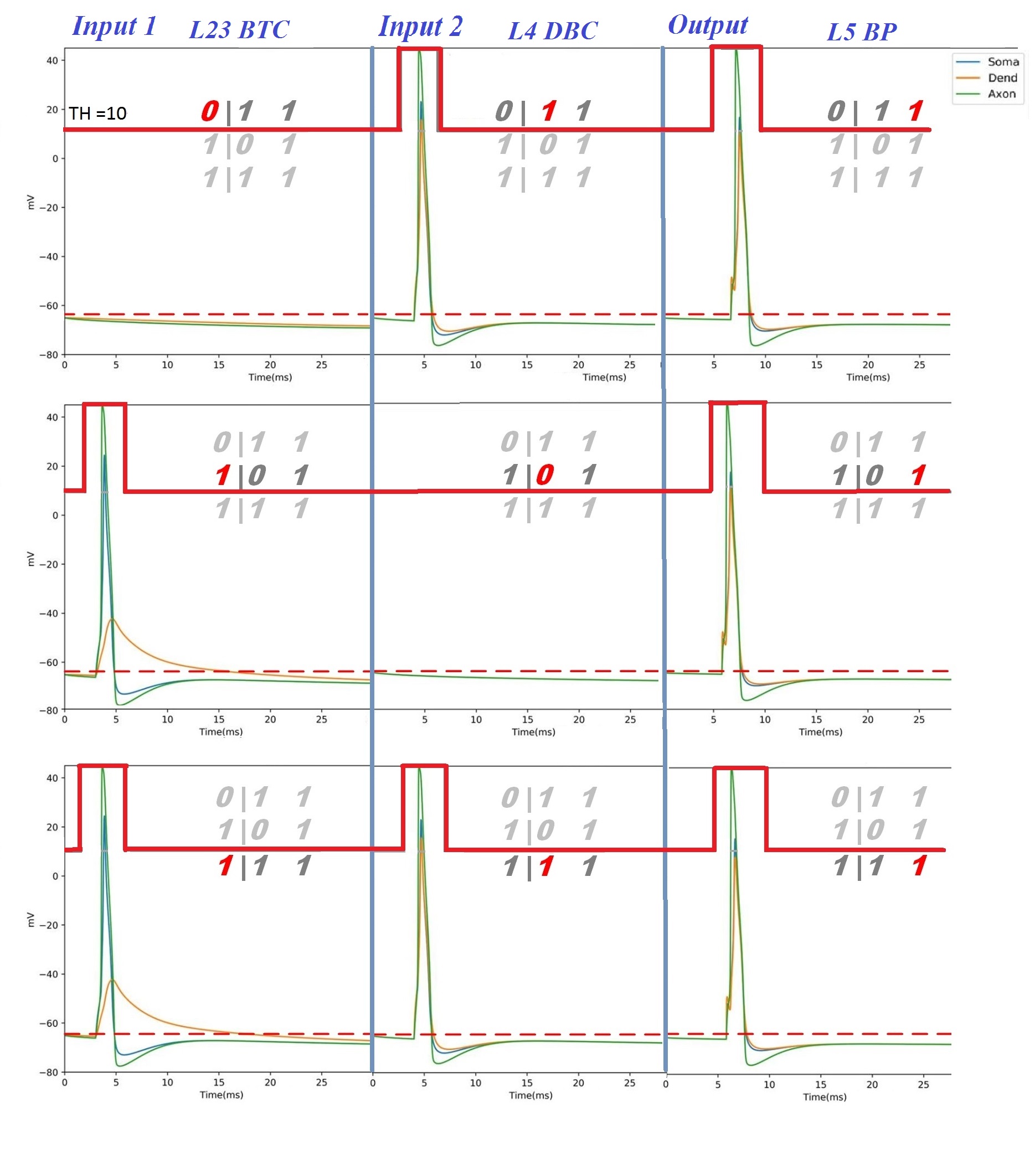
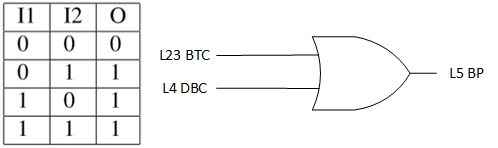
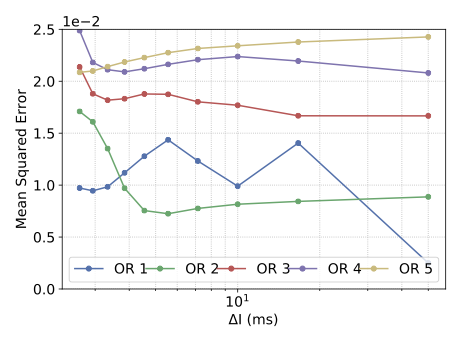
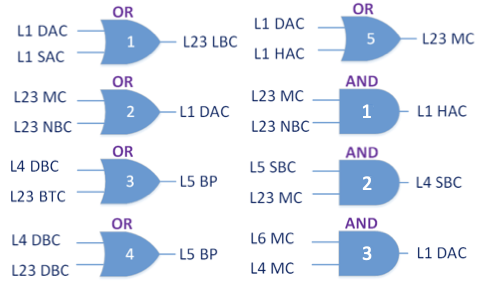
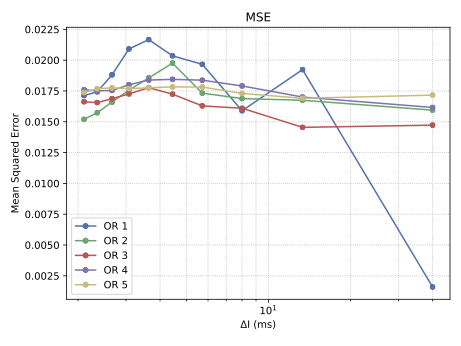
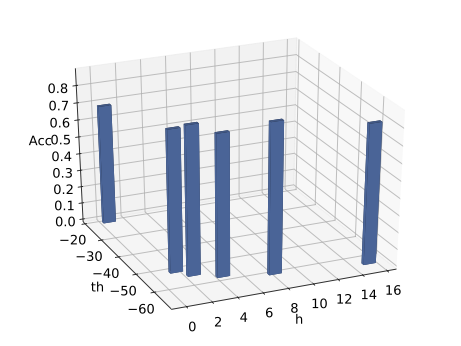
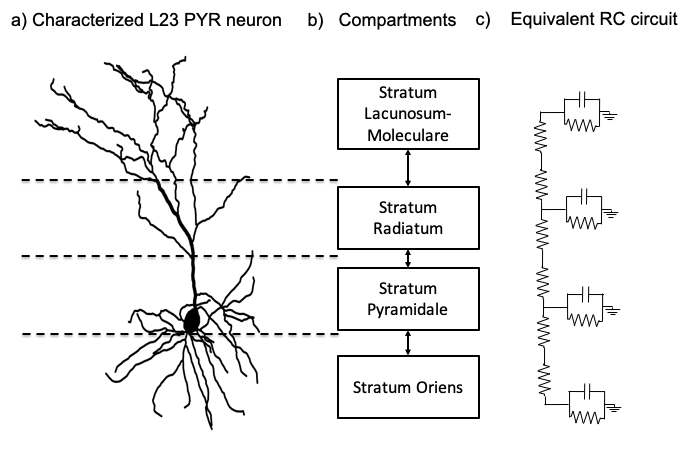
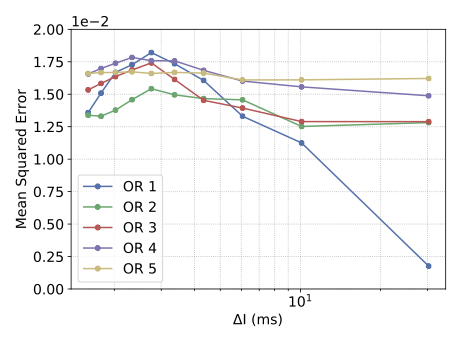
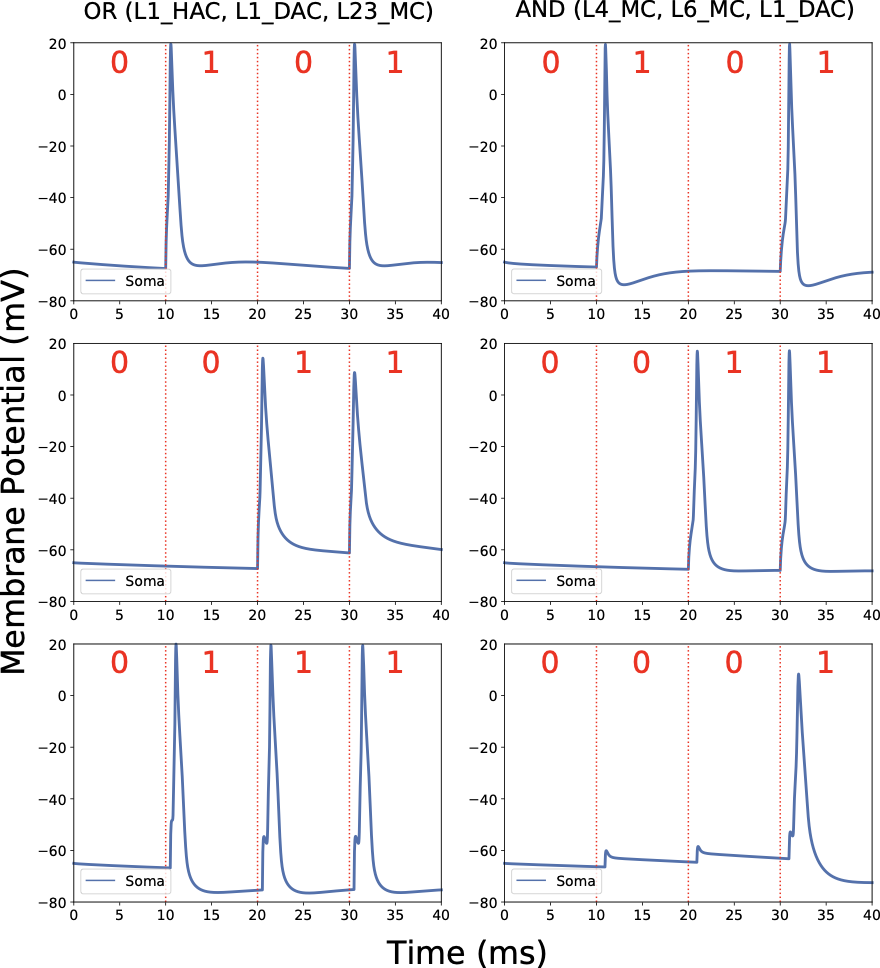
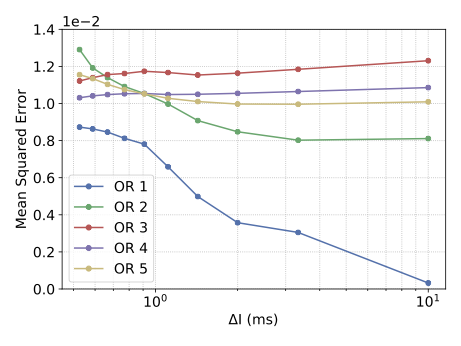
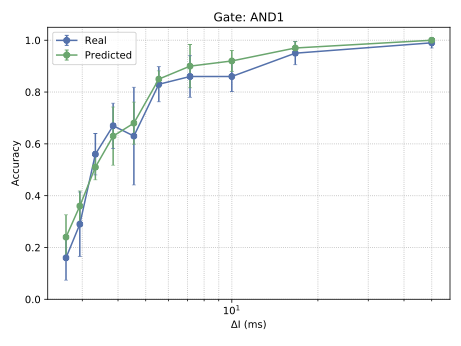
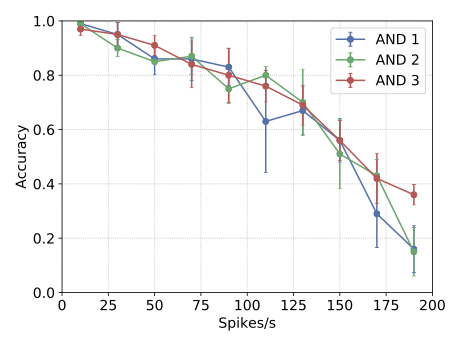
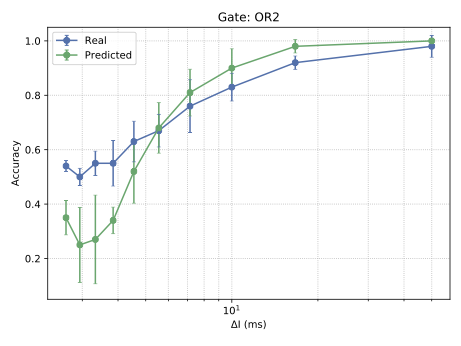
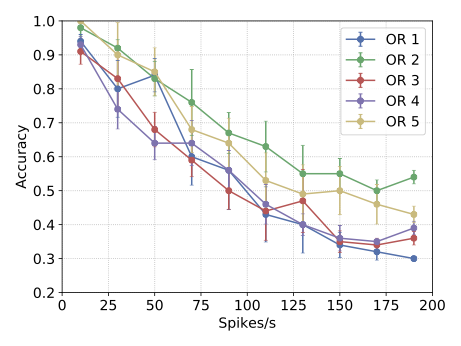
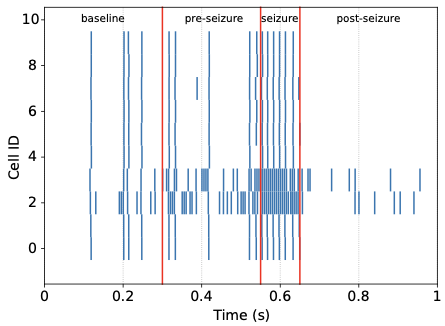
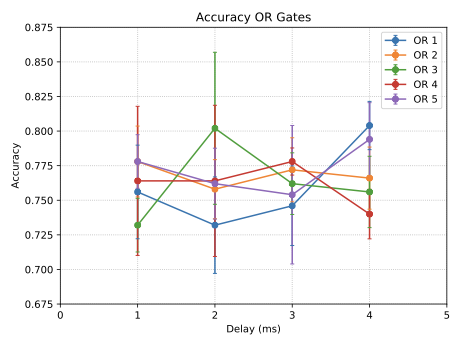
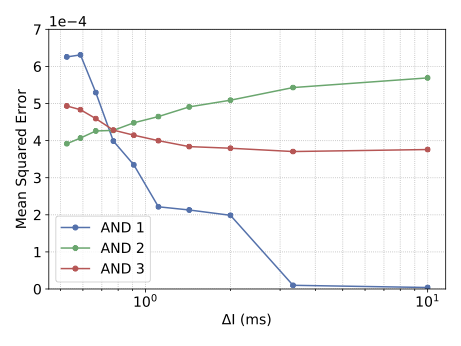
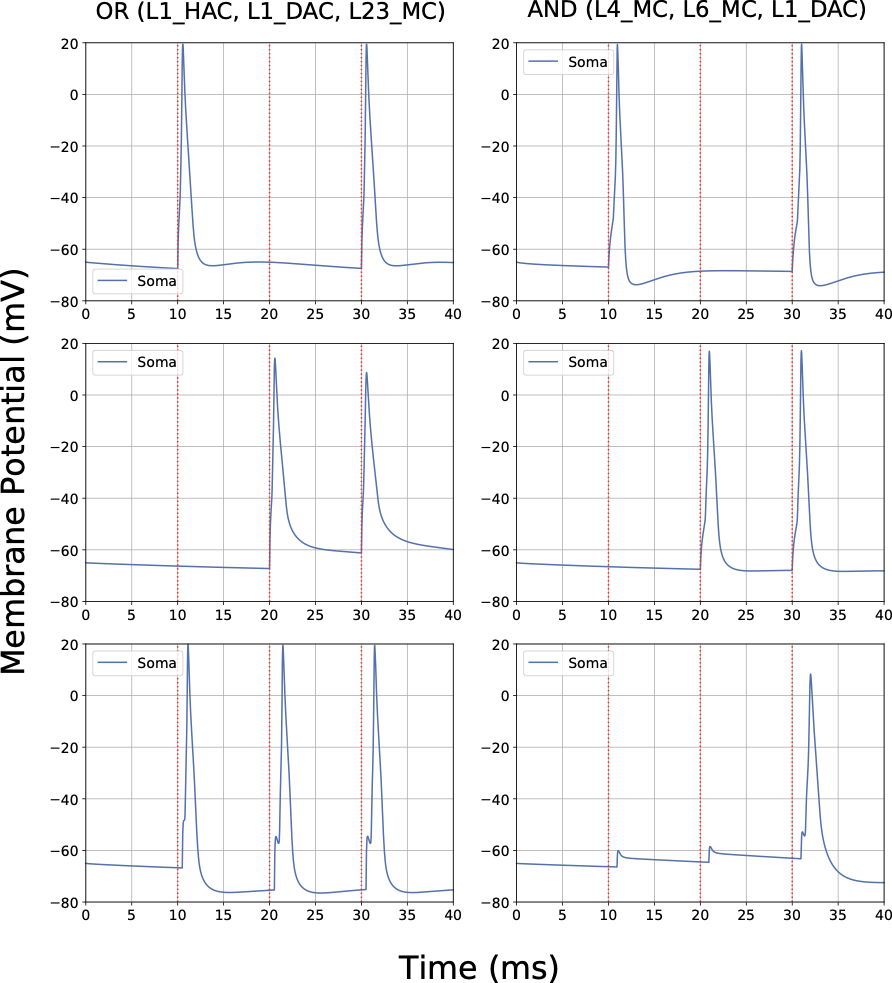
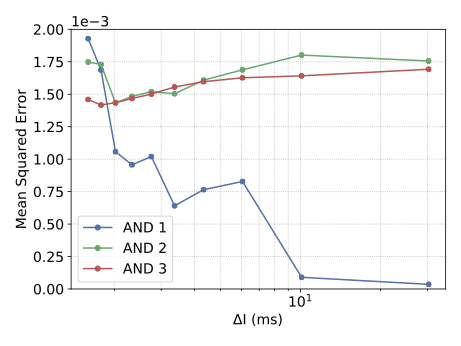
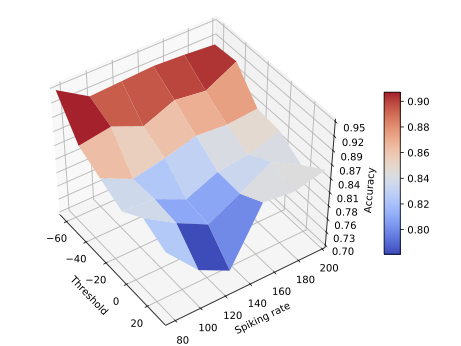
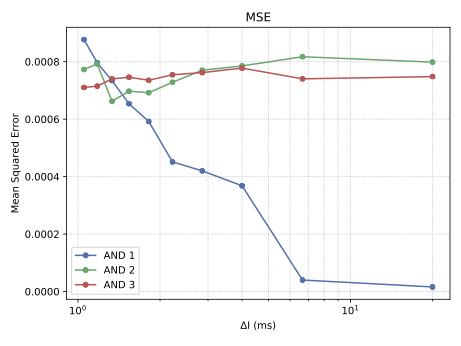
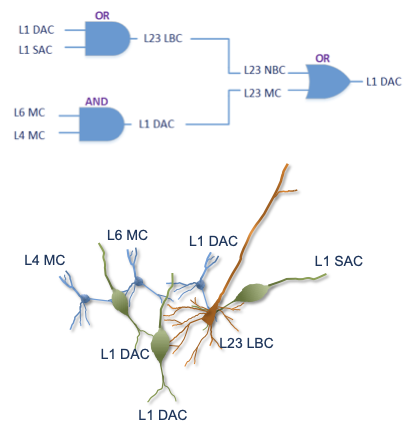
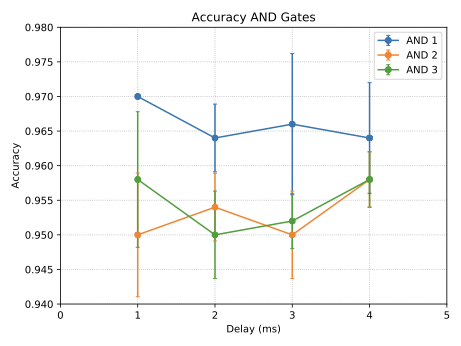
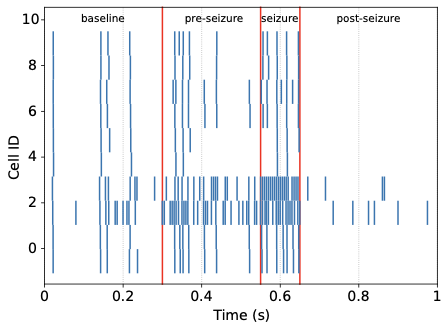
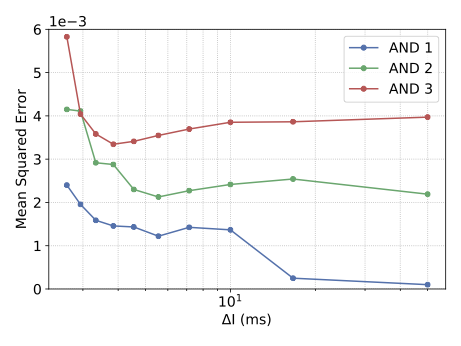
With the advancement of synthetic biology, several new tools have been conceptualized over the years as alternative treatments for current medical procedures. Most of those applications are applied to various chronic diseases. This work investigates how synthetically engineered neurons can operate as digital logic gates that can be used towards bio-computing for the brain. We quantify the accuracy of logic gates under high firing rates amid a network of neurons and by how much it can smooth out uncontrolled neuronal firings. To test the efficacy of our method, simulations composed of computational models of neurons connected in a structure that represents a logic gate are performed. The simulations demonstrated the accuracy of performing the correct logic operation, and how specific properties such as the firing rate can play an important role in the accuracy. As part of the analysis, the Mean squared error is used to quantify the quality of our proposed model and predicting the accurate operation of a gate based on different sampling frequencies. As an application, the logic gates were used to trap epileptic seizures in a neuronal network, where the results demonstrated the effectiveness of reducing the firing rate. Our proposed system has the potential for computing numerous neurological conditions of the brain.💡 Summary & Analysis
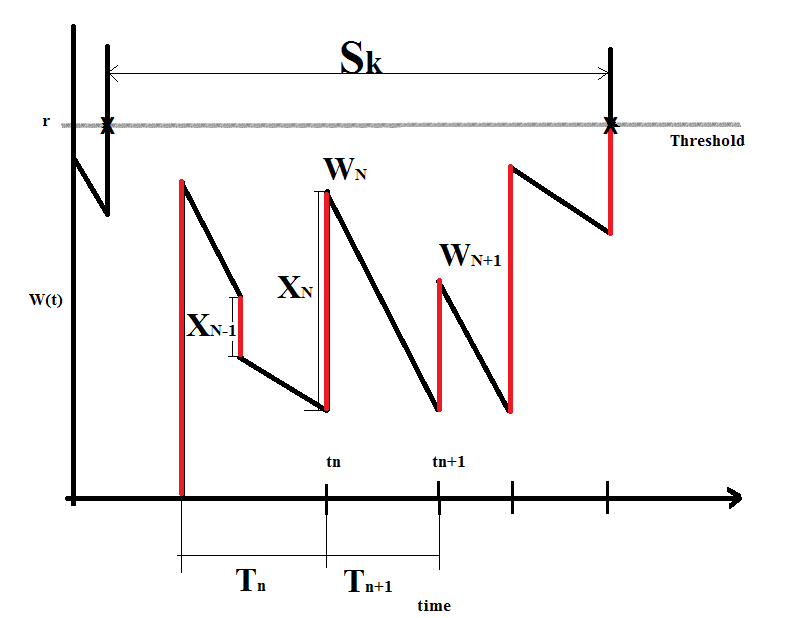
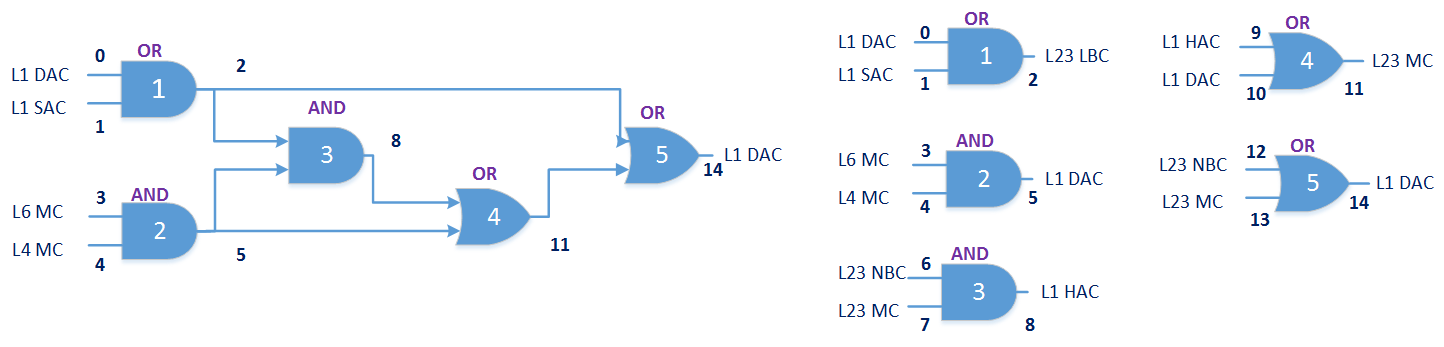
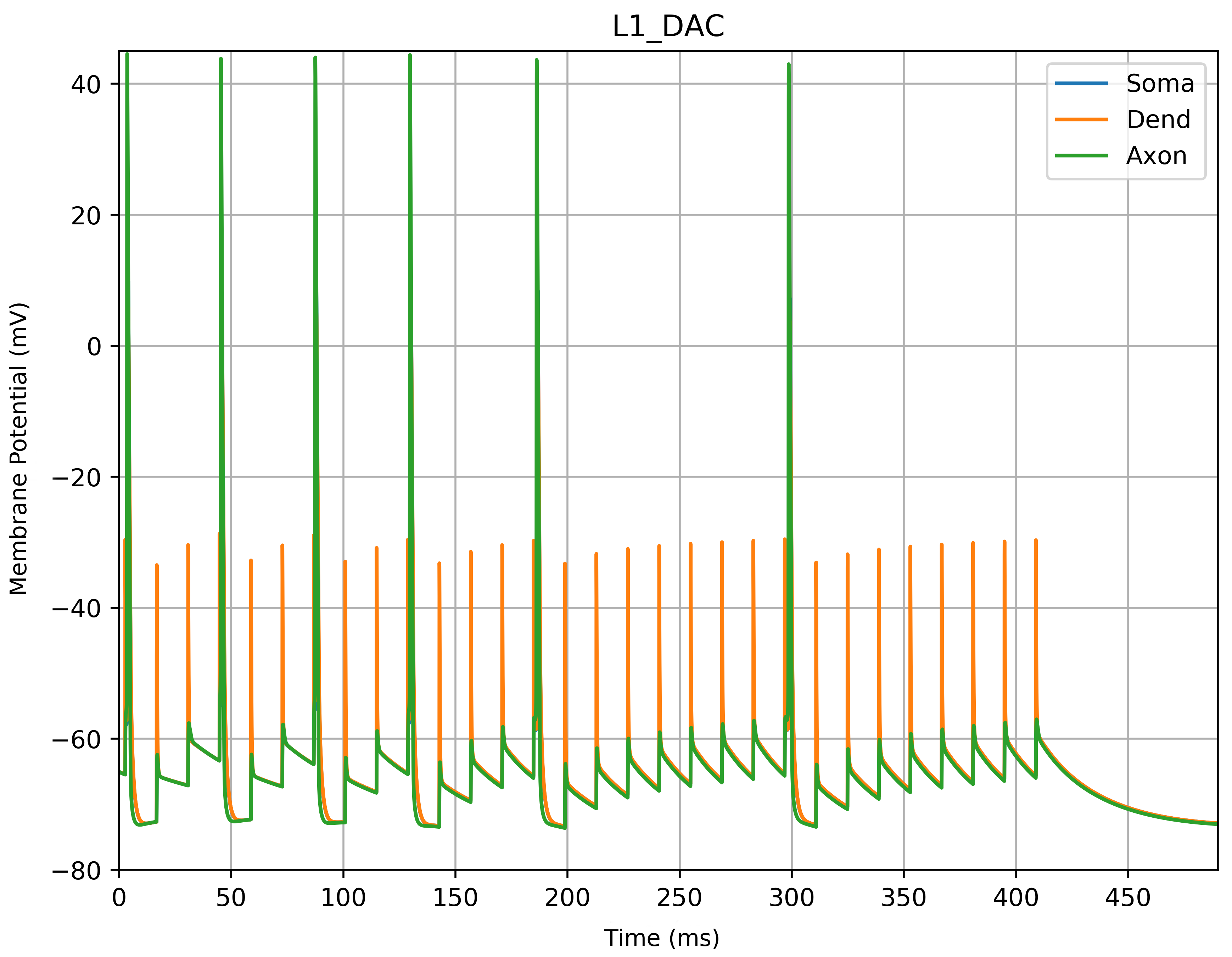
This paper explores the possibility of using synthetically engineered neurons to act as digital logic gates, which could be a significant step in bio-computing for brain-related conditions. It investigates how these logic gates can accurately perform operations within high firing rates among interconnected neurons and how they can help control uncontrolled neuronal firings. The researchers used computational models of neurons connected in a manner that simulates the function of logic gates, performing simulations to test their method's efficacy. They found that specific properties like the firing rate play a critical role in ensuring accurate logical operations. This research also uses mean squared error to quantify the quality of the proposed model and predict the correct operation based on different sampling frequencies. As an application, these logic gates were used to trap epileptic seizures within a neuronal network, demonstrating their effectiveness in reducing firing rates. The proposed system has potential for managing various neurological conditions through bio-computing.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)