Computer Science / Neural and Evolutionary Computing
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science / Systems and Control
Computer Science / Systems and Control
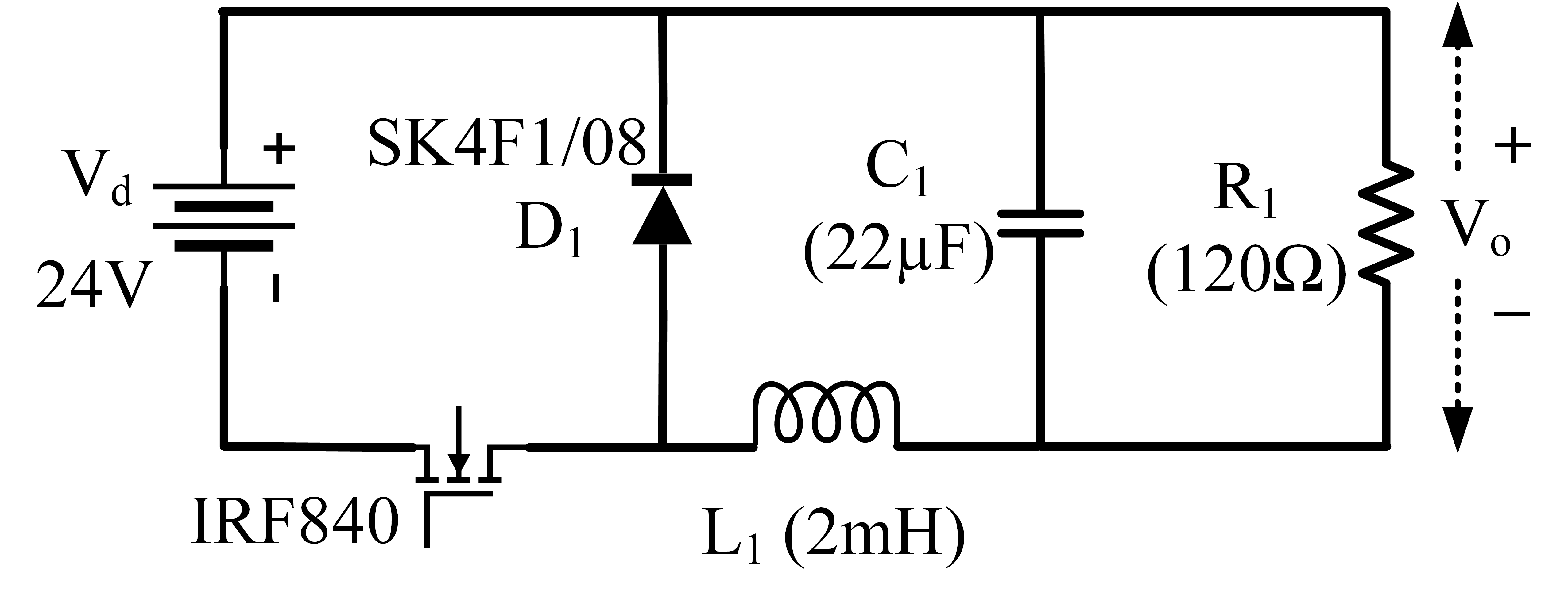
A Multi-Objective Evolutionary Approach for Grey-Box Modeling of a Buck Converter
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Multi-objective Evolutionary Approach to Grey-Box Identification of Buck Converter- ArXiv ID: 1909.04320
- Date: 2020-02-21
- Authors: Faizal Hafiz and Akshya Swain and Eduardo M.A.M. Mendes and Luis Aguirre
📝 Abstract
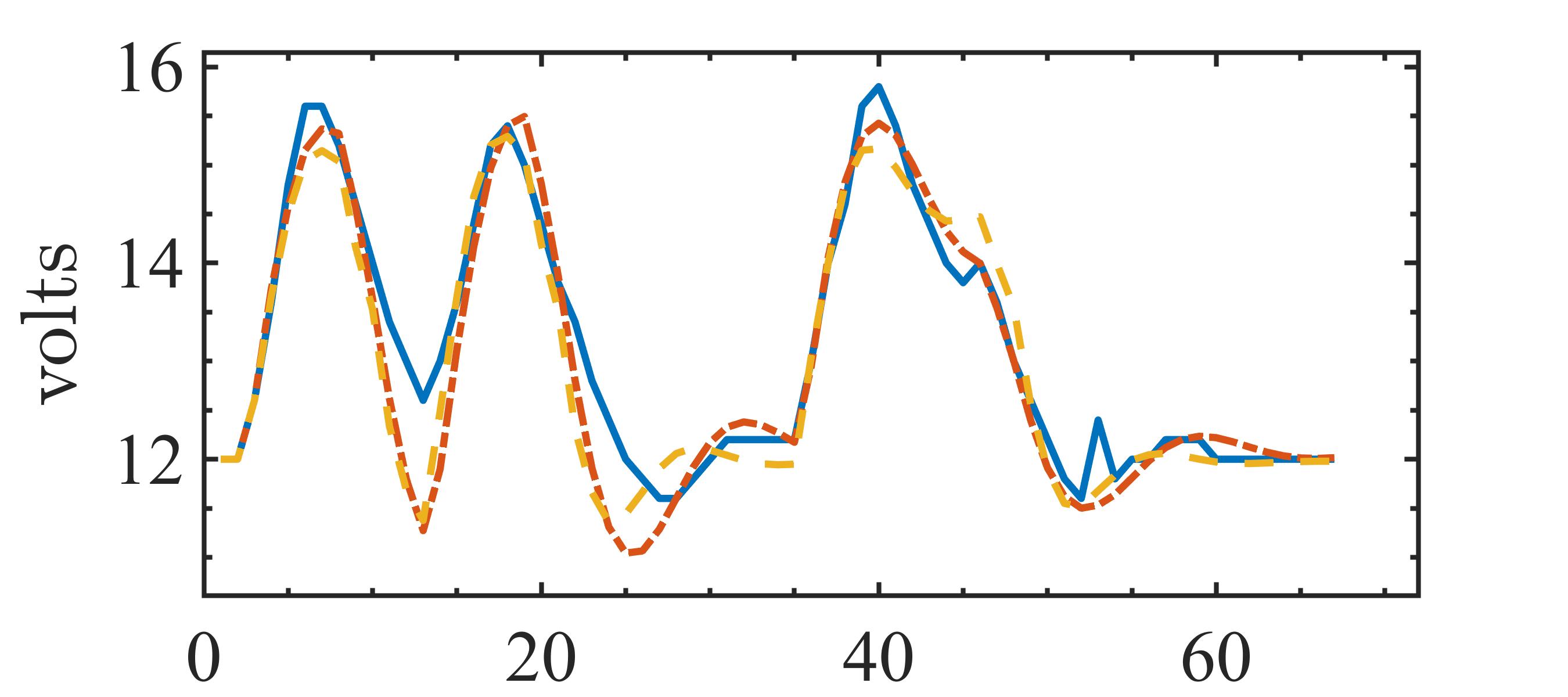
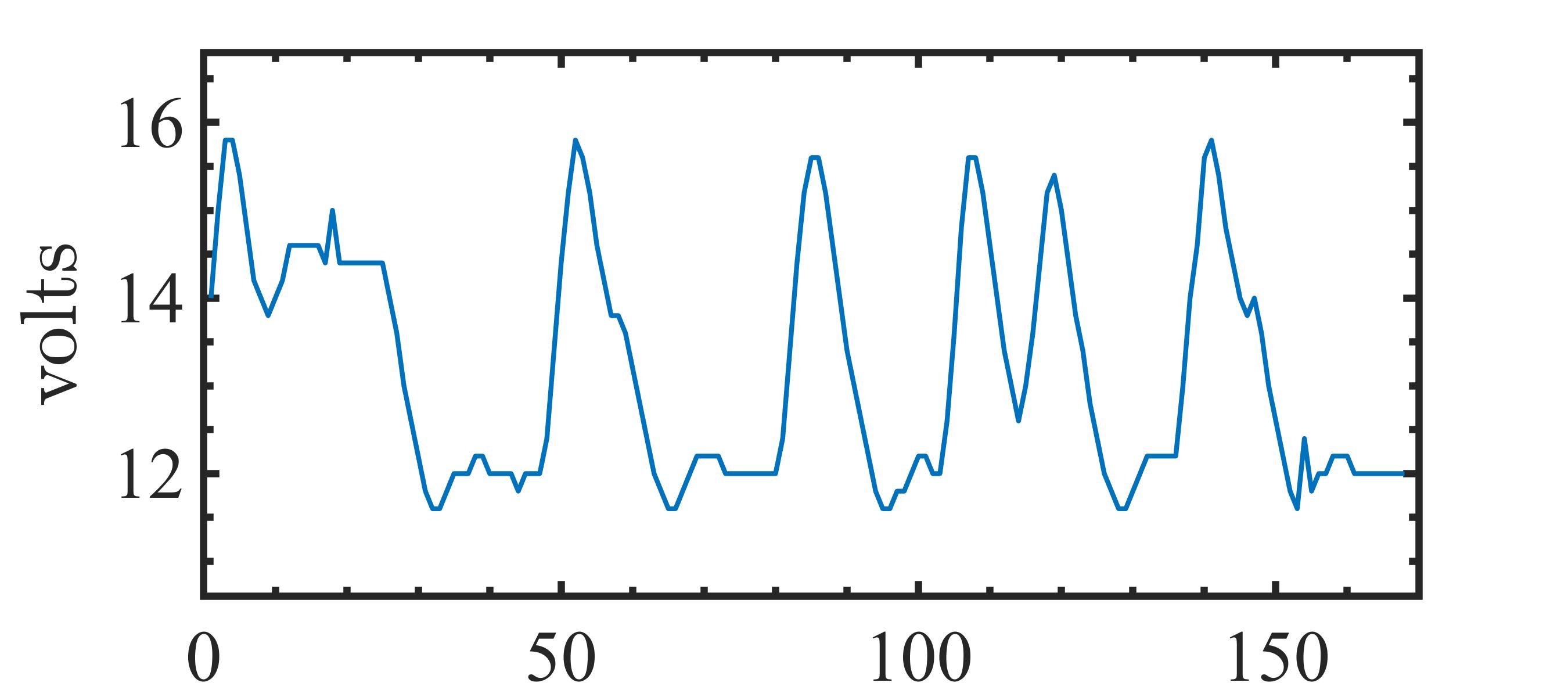
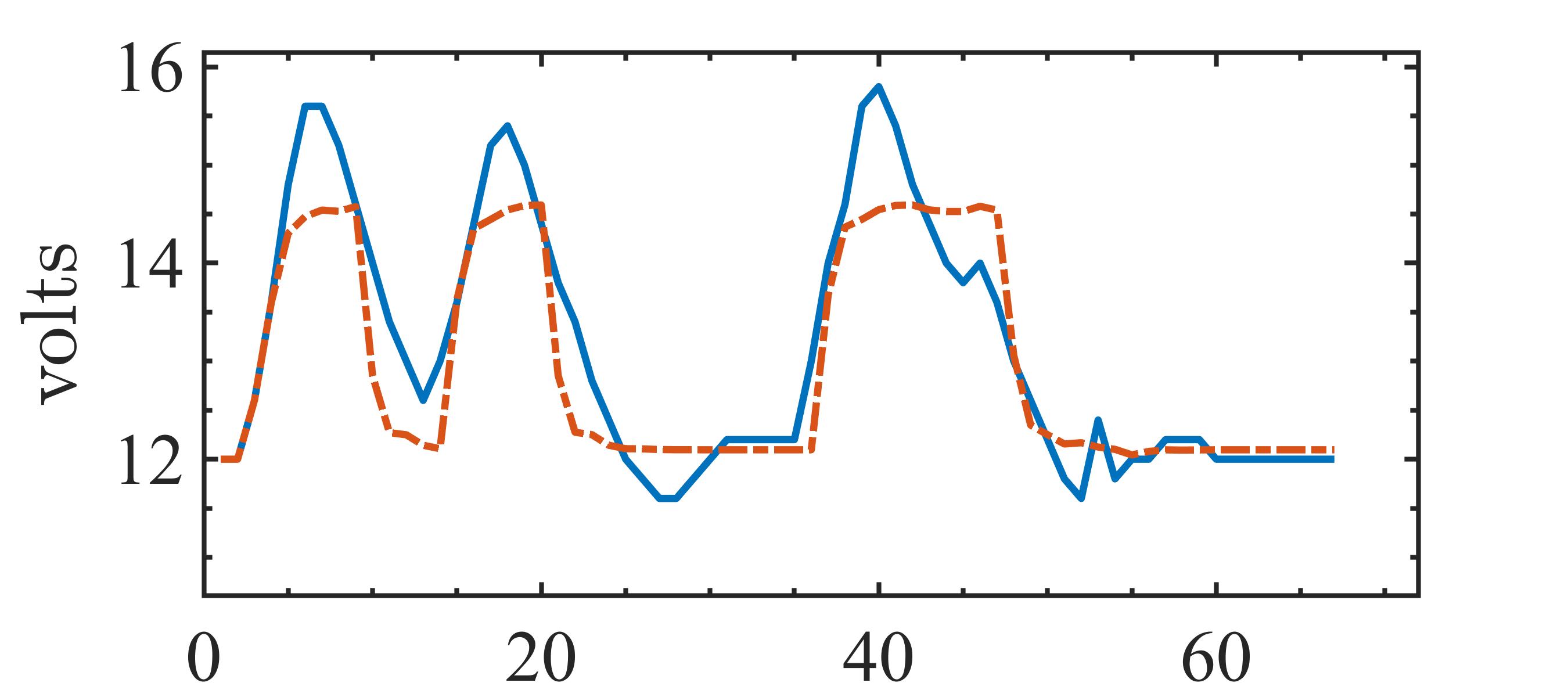
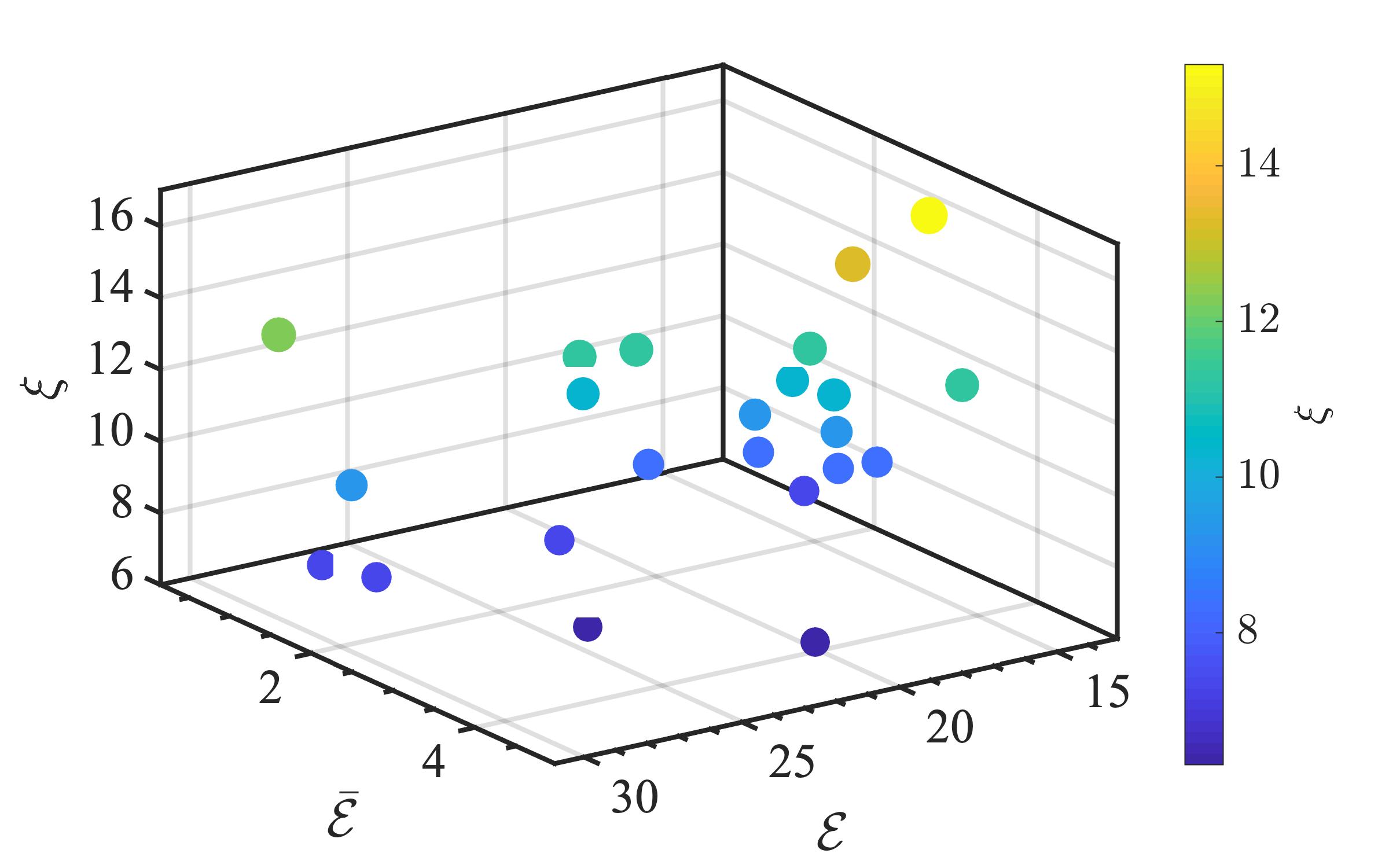
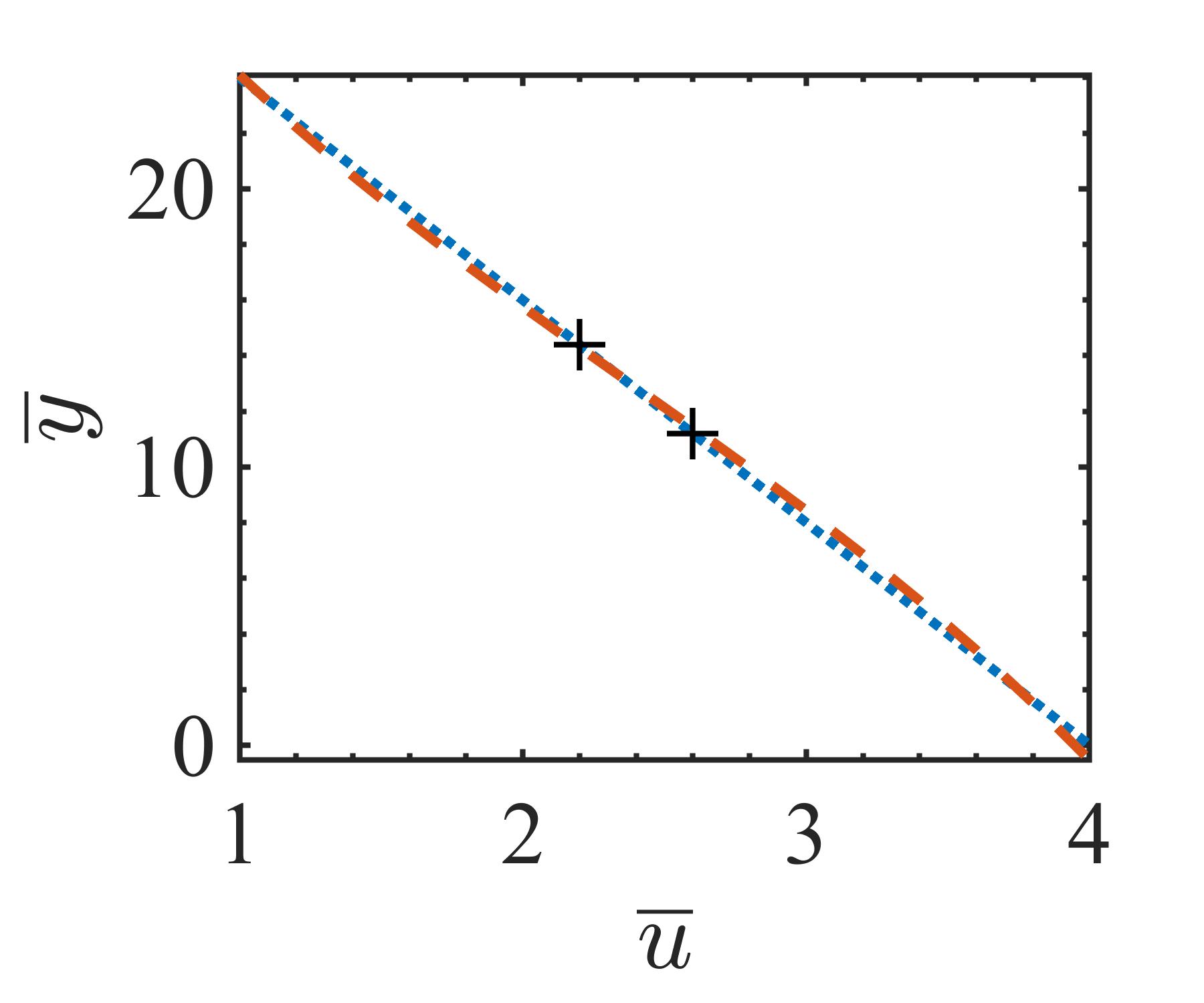
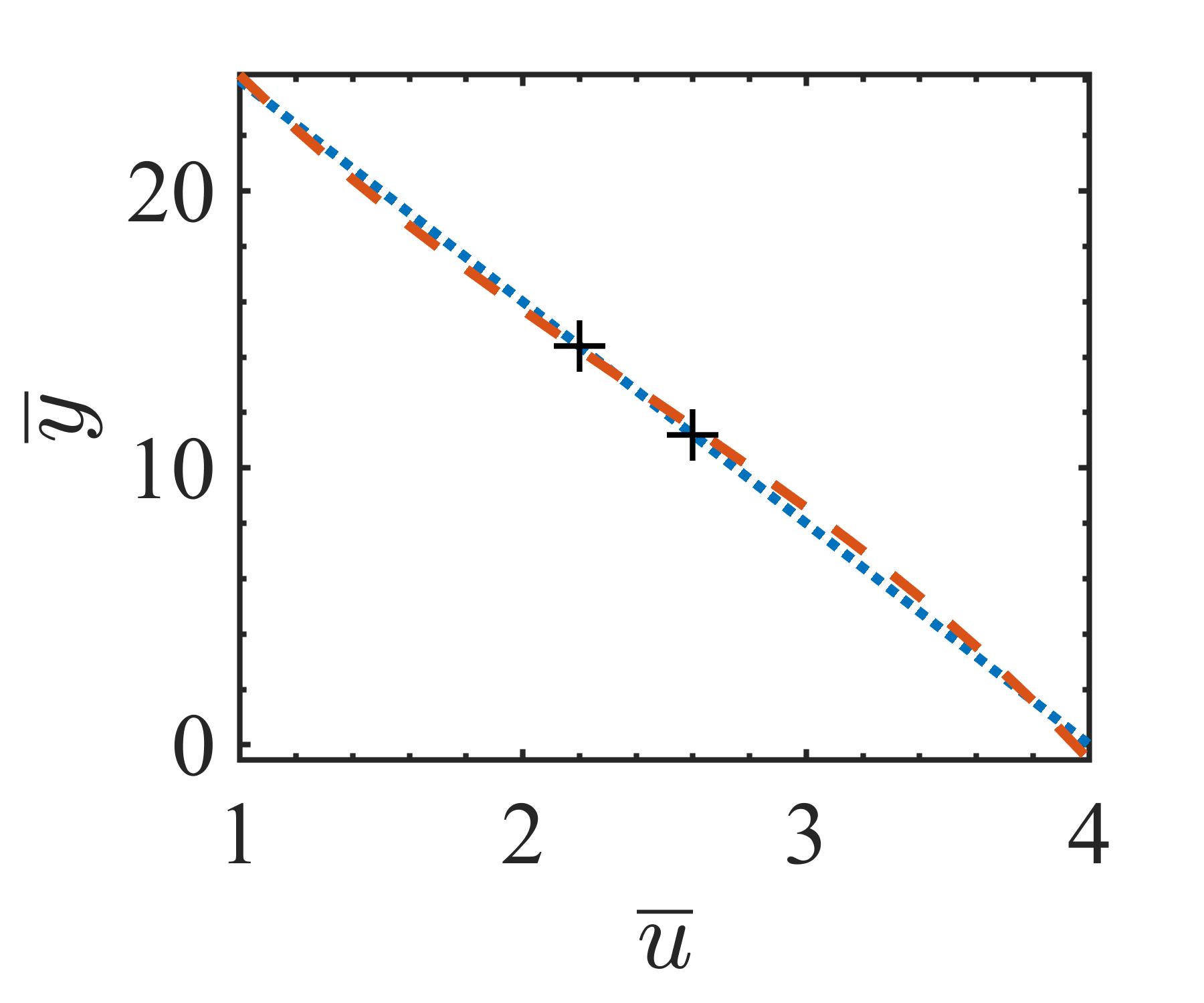
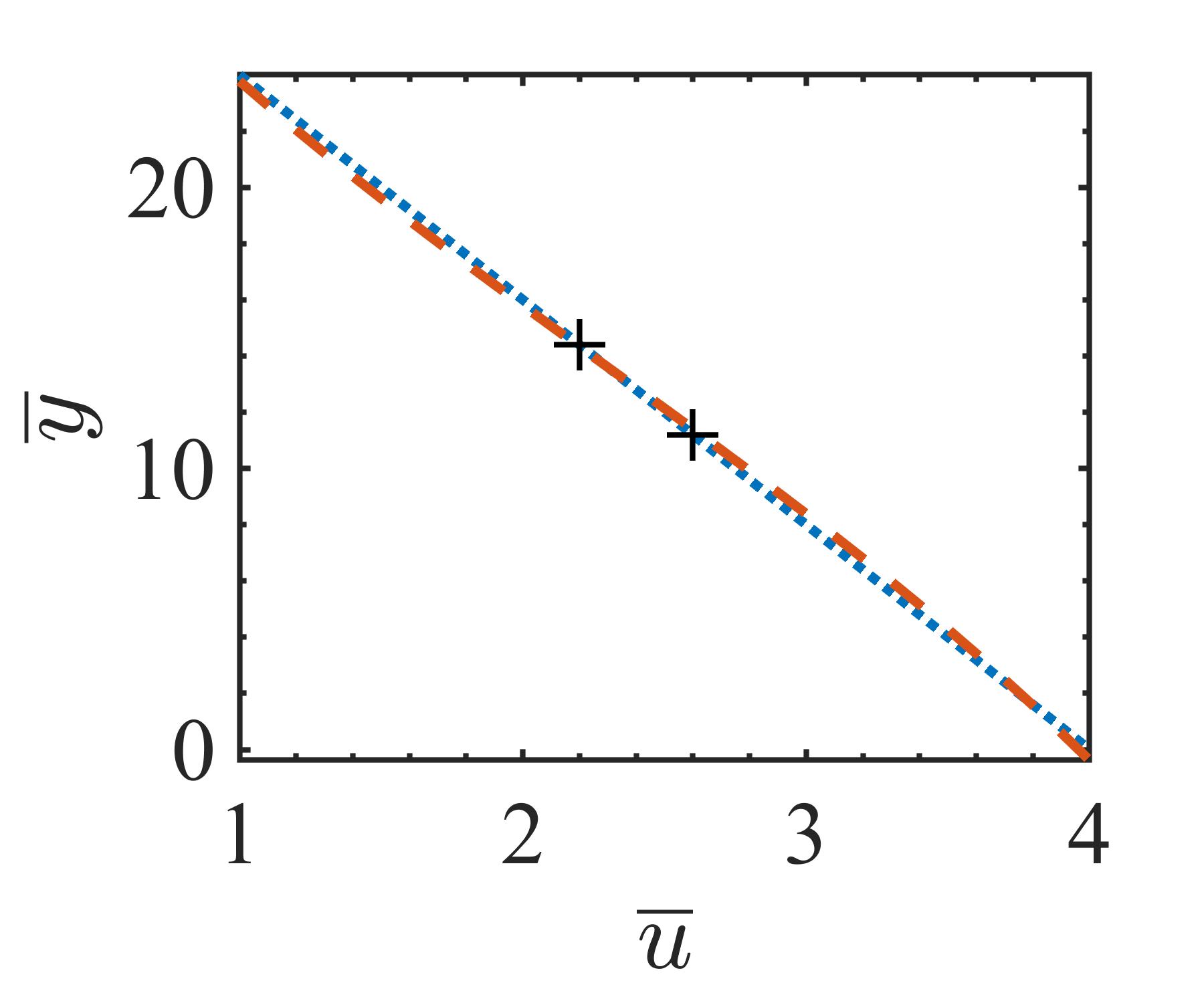
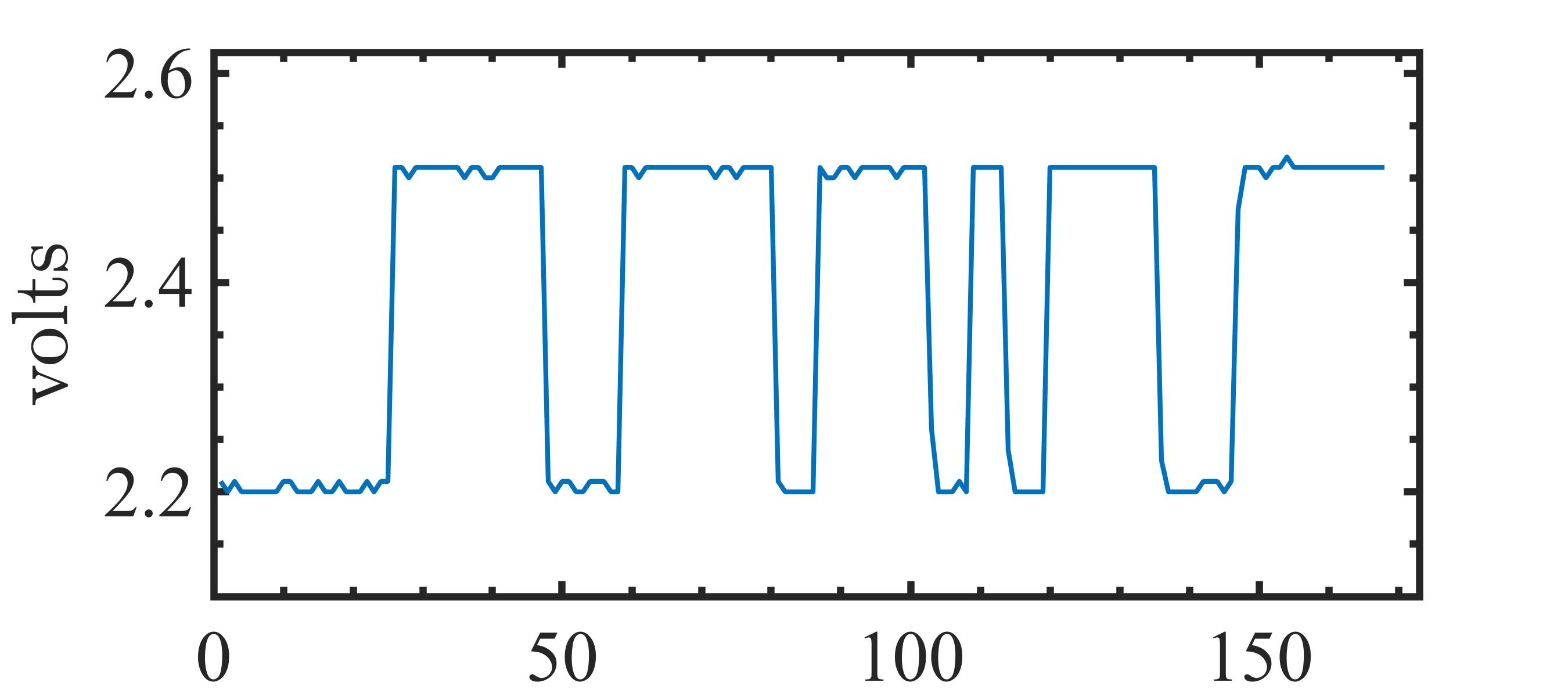
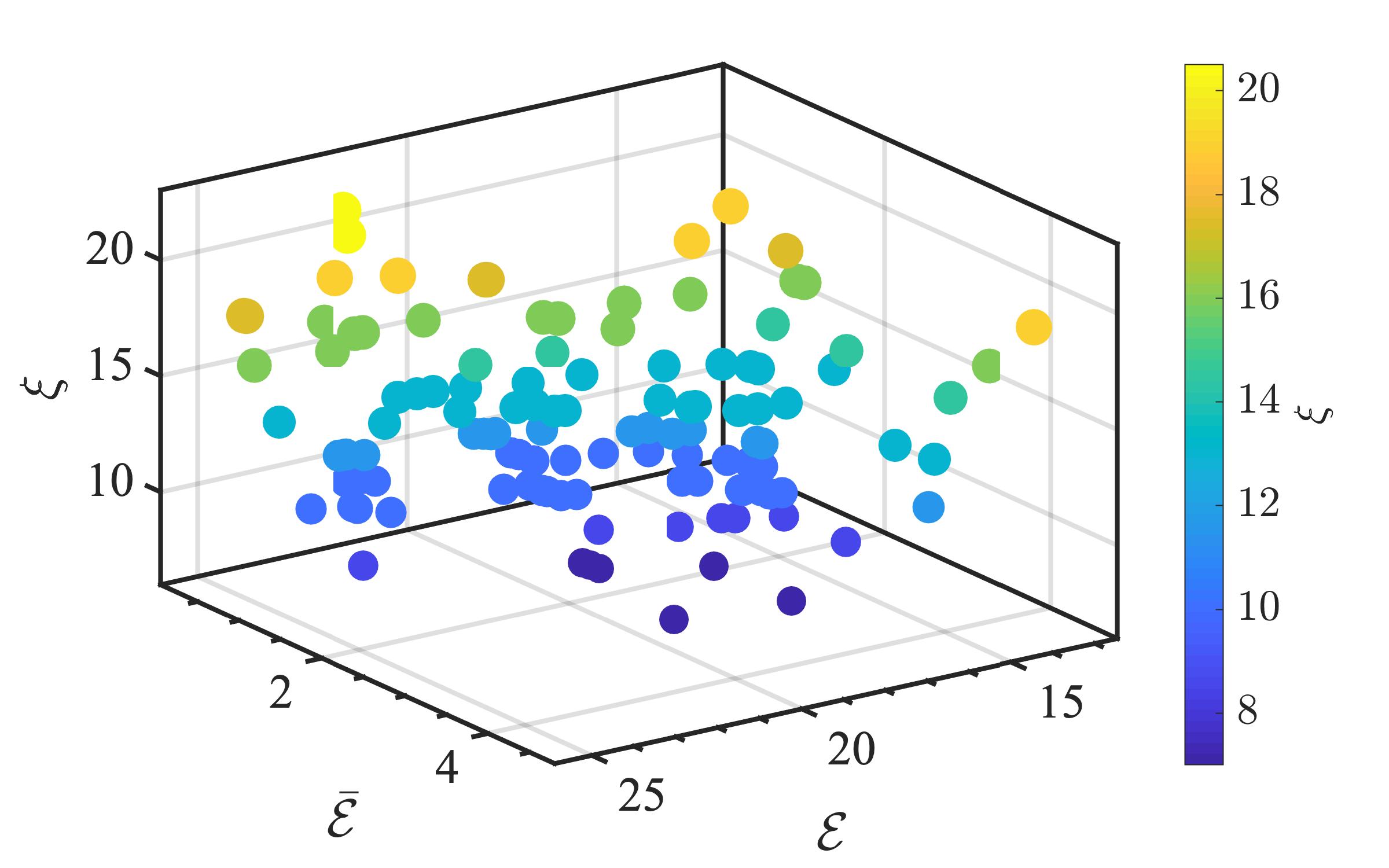
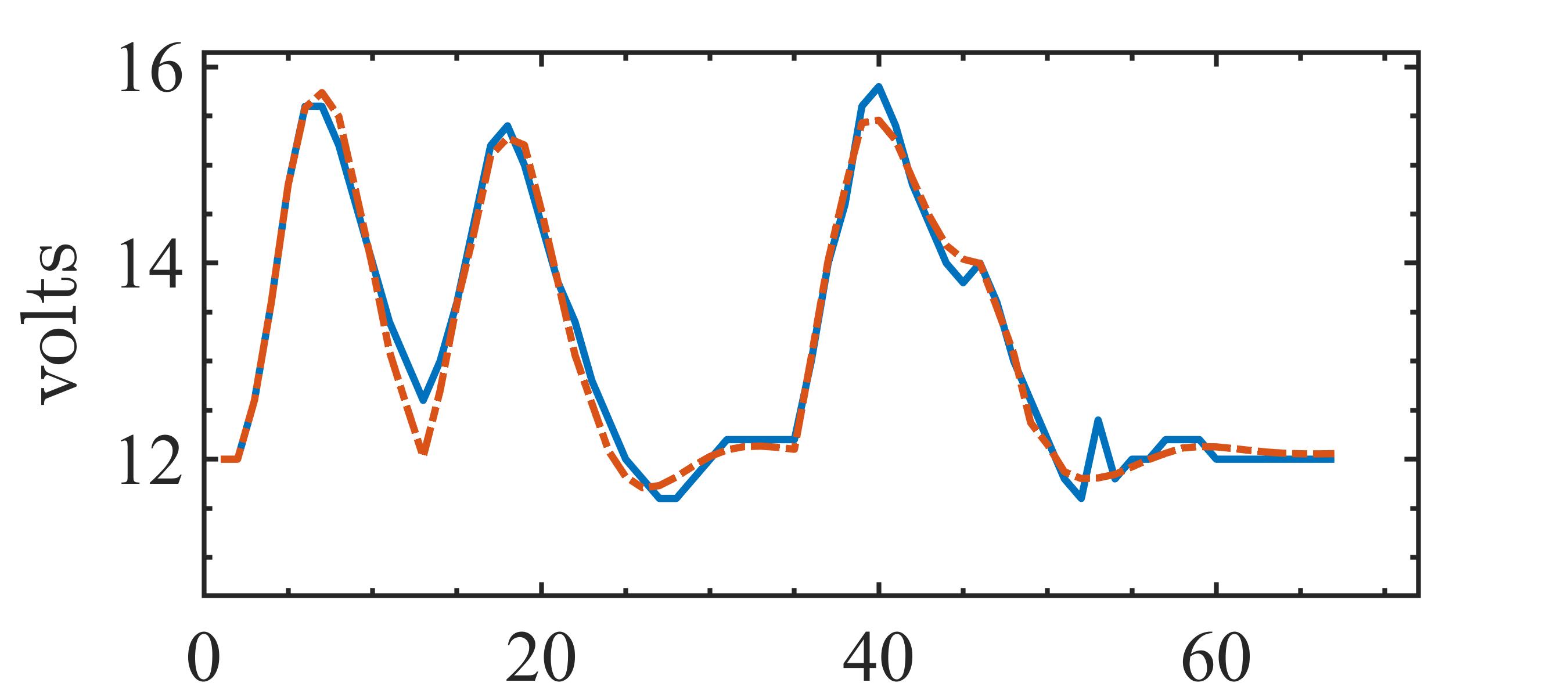
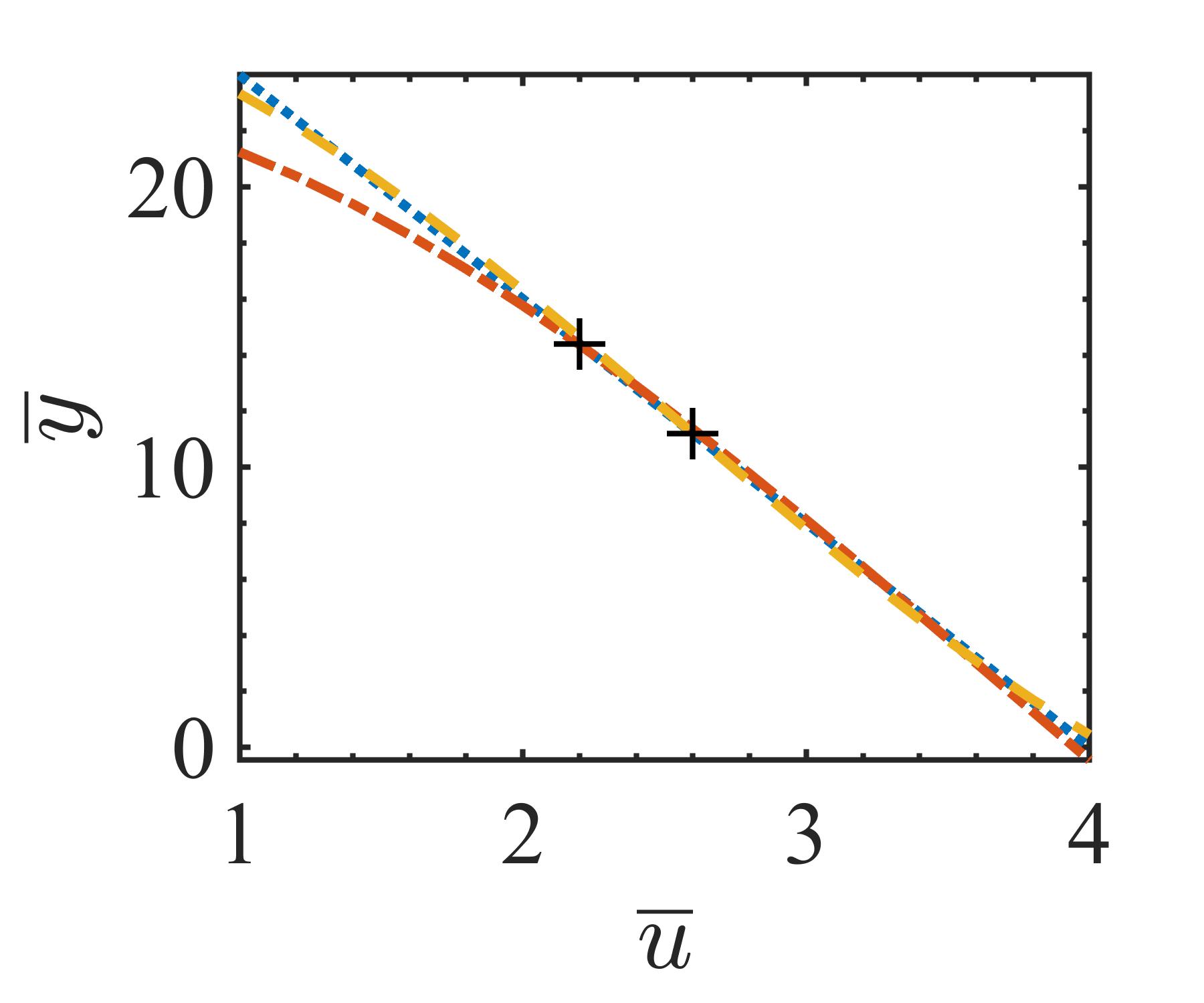
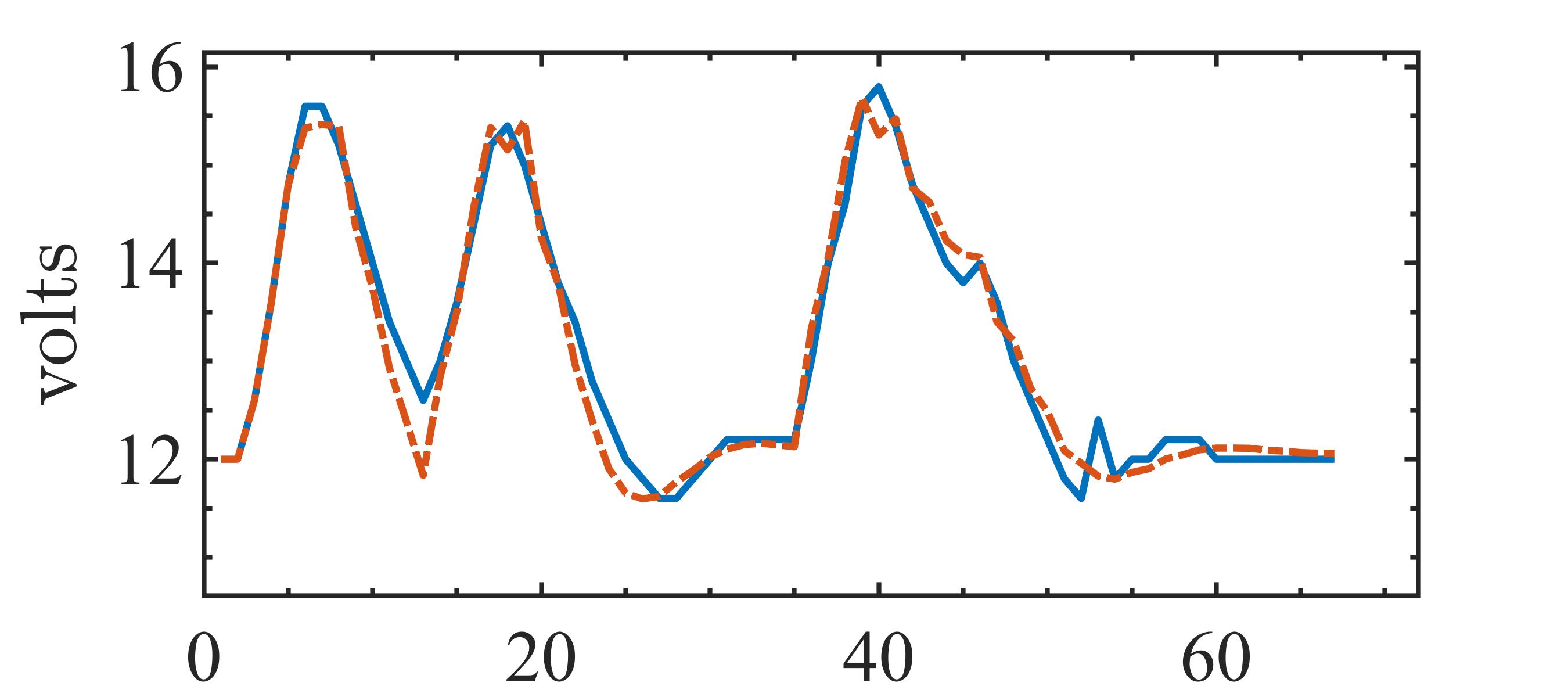
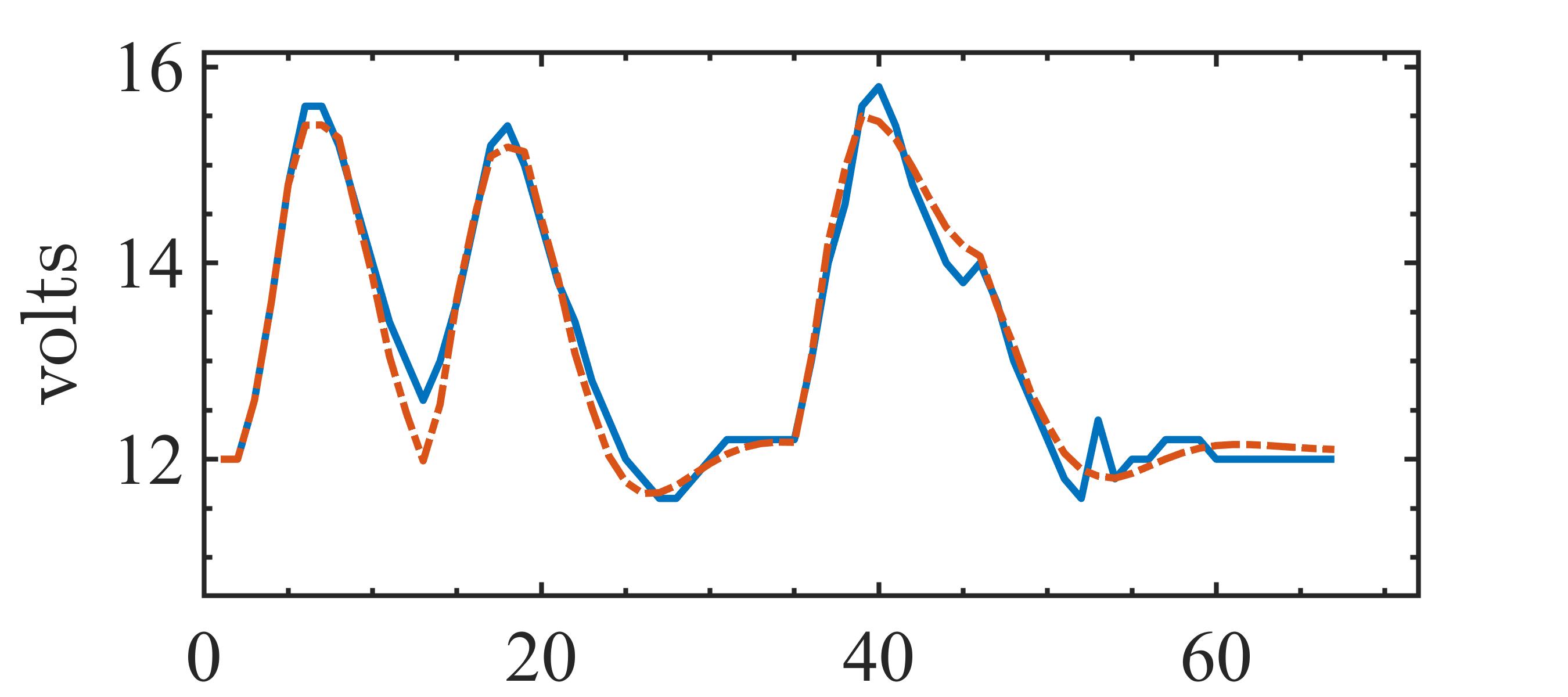
The present study proposes a simple grey-box identification approach to model a real DC-DC buck converter operating in continuous conduction mode. The problem associated with the information void in the observed dynamical data, which is often obtained over a relatively narrow input range, is alleviated by exploiting the known static behavior of buck converter as a priori knowledge. A simple method is developed based on the concept of term clusters to determine the static response of the candidate models. The error in the static behavior is then directly embedded into the multi-objective framework for structure selection. In essence, the proposed approach casts grey-box identification problem into a multi-objective framework to balance bias-variance dilemma of model building while explicitly integrating a priori knowledge into the structure selection process. The results of the investigation, considering the case of practical buck converter, demonstrate that it is possible to identify parsimonious models which can capture both the dynamic and static behavior of the system over a wide input range.💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper proposes a straightforward grey-box identification approach for modeling a DC-DC buck converter operating in continuous conduction mode. The challenge lies in accurately understanding the system from dynamic data obtained over a narrow input range, which often fails to capture the full behavior of the system. The proposed method mitigates this issue by leveraging known static characteristics of the buck converter. Using term clusters to determine the static response of candidate models and integrating these errors into a multi-objective framework for structure selection helps balance the bias-variance trade-off in model building while incorporating prior knowledge explicitly. The results show that it is possible to identify parsimonious models capable of capturing both dynamic and static behavior over a wide input range, thus providing deeper insights into system operations.📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)