Achieving State Synchronization in Homogeneous Networks of Non-Introspective Agents with Input Saturation A Scale-Free Protocol Design Approach
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: State Synchronization for Homogeneous Networks of Non-introspective Agents in Presence of Input Saturation -A Scale-free Protocol Design- ArXiv ID: 1908.06535
- Date: 2020-01-06
- Authors: Zhenwei Liu, Ali Saberi, Anton A. Stoorvogel, and Donya Nojavanzadeh
📝 Abstract
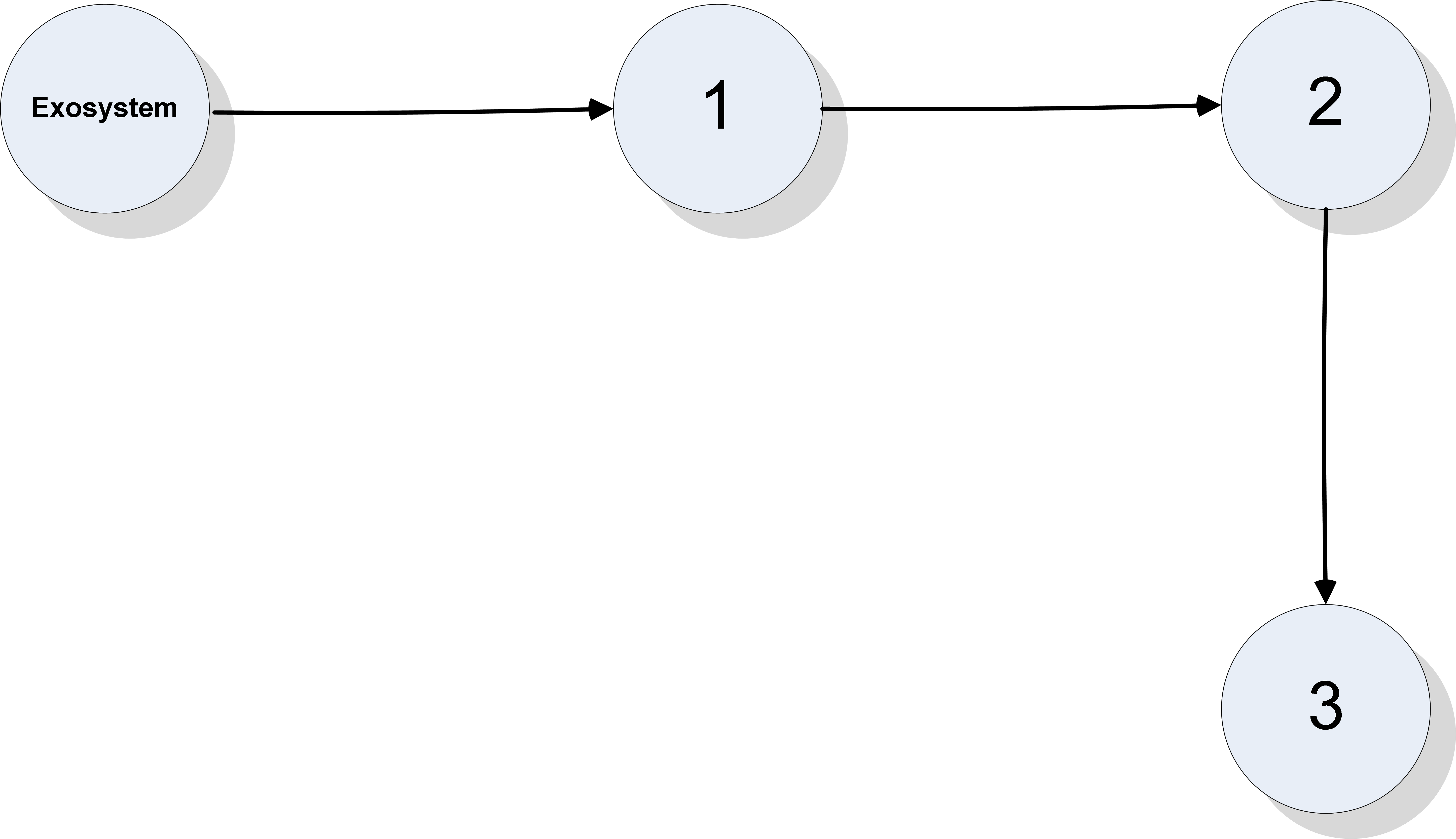
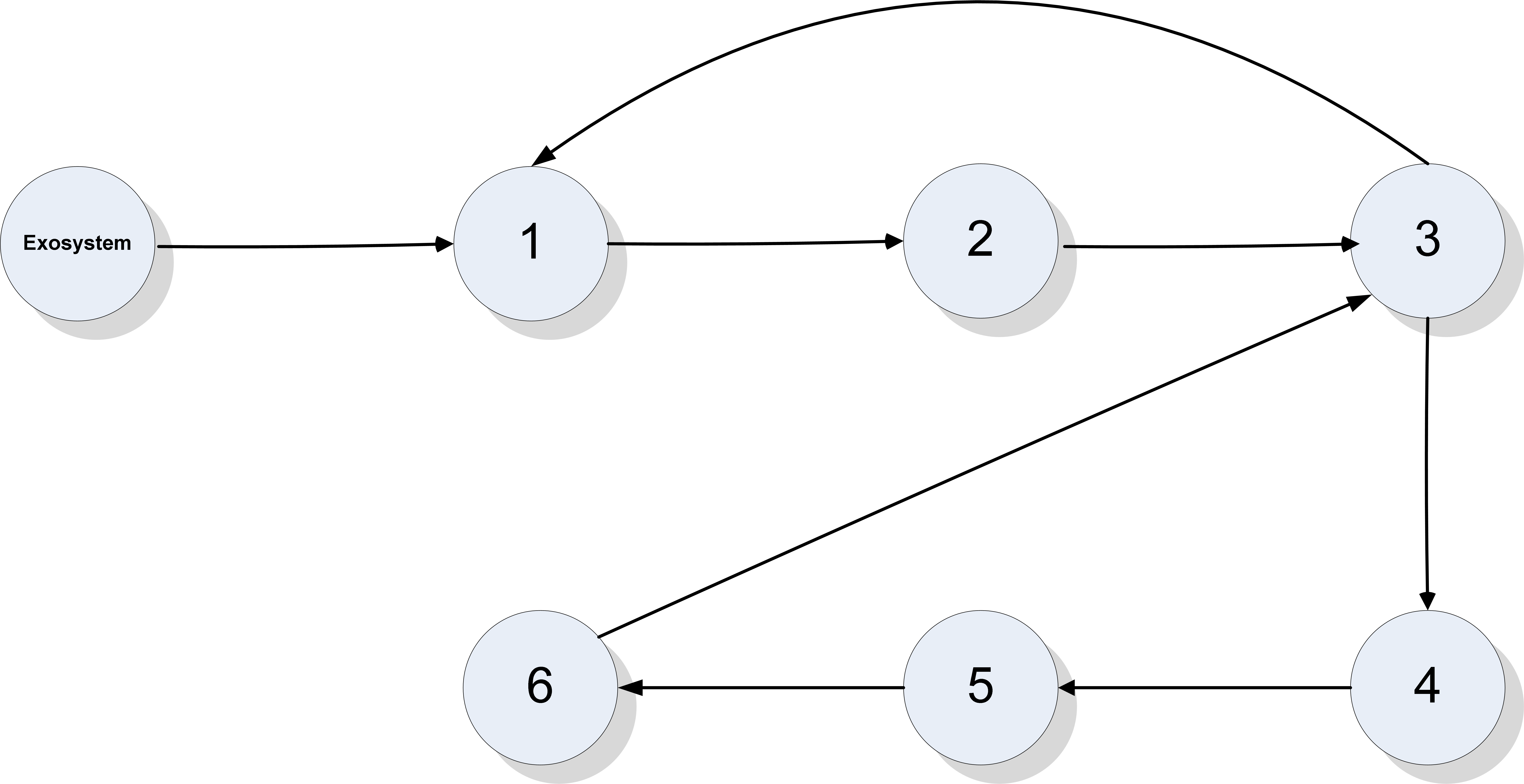
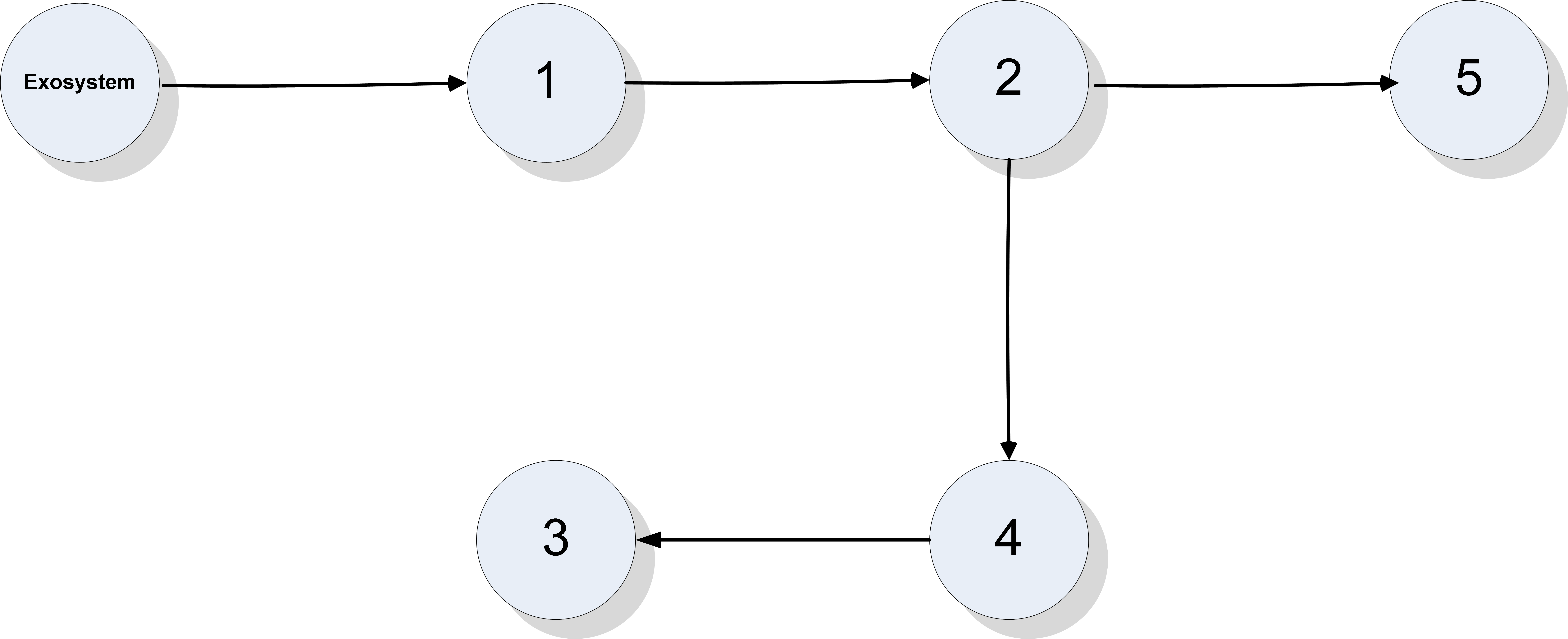
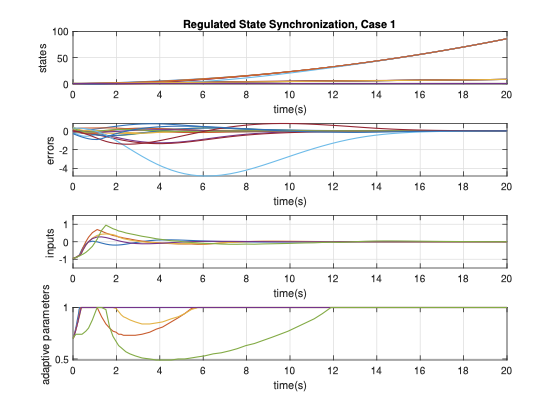
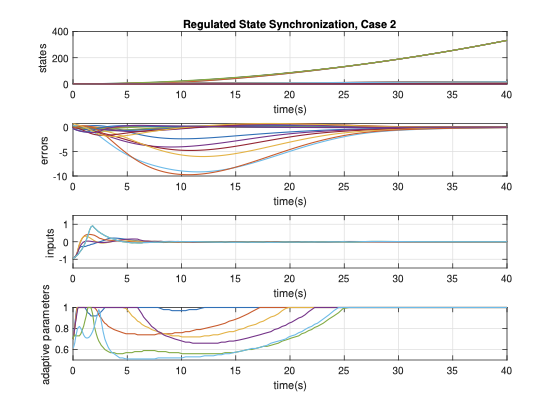
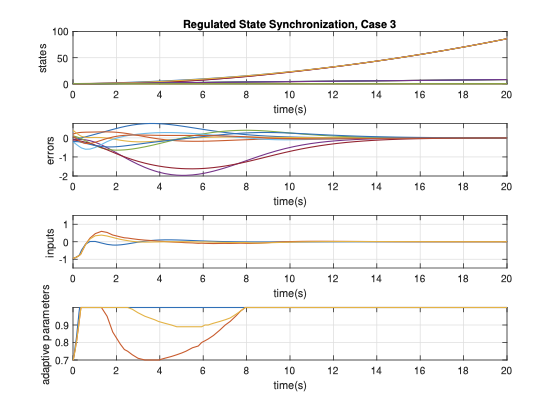
This paper studies global and semi-global regulated state synchronization of homogeneous networks of non-introspective agents in presence of input saturation based on additional information exchange where the reference trajectory is given by a so-called exosystem which is assumed to be globally reachable. Our protocol design methodology does not need any knowledge of the directed network topology and the spectrum of the associated Laplacian matrix. Moreover, the proposed protocol is scalable and achieves synchronization for any arbitrary number of agents.💡 Summary & Analysis
**Summary**: This paper focuses on synchronizing the states of agents within a network to follow a common trajectory even when faced with input saturation. The goal is to ensure that all agents in a homogeneous network can synchronize their states without needing complete information about the network's structure or its Laplacian matrix.Problem Statement: In networks, each agent may operate at different speeds and states, making it challenging to synchronize them. This problem becomes more complex when there are limitations on how much information can be exchanged between agents. Additionally, achieving synchronization requires precise knowledge of the network’s topology and specific parameters, which might not always be available.
Solution: The research team has developed a protocol that allows agents to follow a reference trajectory provided by an exosystem without needing detailed topological or spectral data about the network. This approach is designed to work even under conditions of input saturation, meaning it can handle situations where the system’s inputs are limited.
Key Achievements: The proposed protocol is scalable and can achieve synchronization regardless of the number of agents in the network. This means that as networks grow larger, they can still effectively synchronize their states using this method, ensuring robust performance across varying scales.
Significance & Applications: By providing a solution for state synchronization under complex conditions, this research opens up possibilities for effective information exchange and coordination in diverse fields such as autonomous vehicles, drones, and other systems where synchronized operation is critical.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)