Stability of User Equilibria in Heterogeneous Routing Games
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: On stability of users equilibria in heterogeneous routing games- ArXiv ID: 1912.02007
- Date: 2019-12-05
- Authors: Leonardo Cianfanelli and Giacomo Como
📝 Abstract
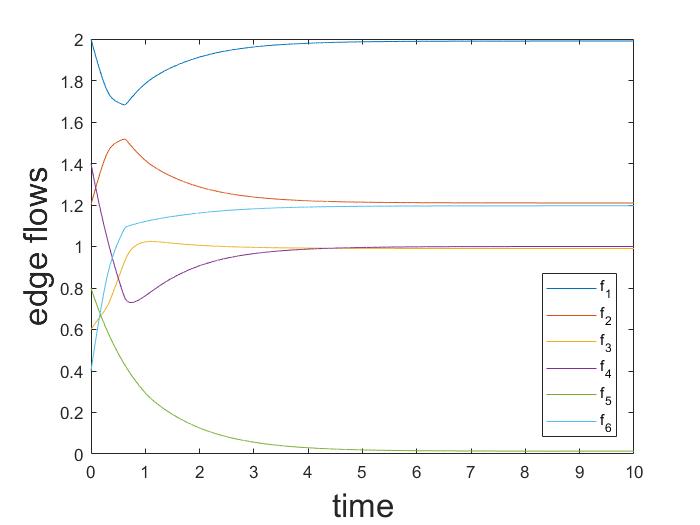
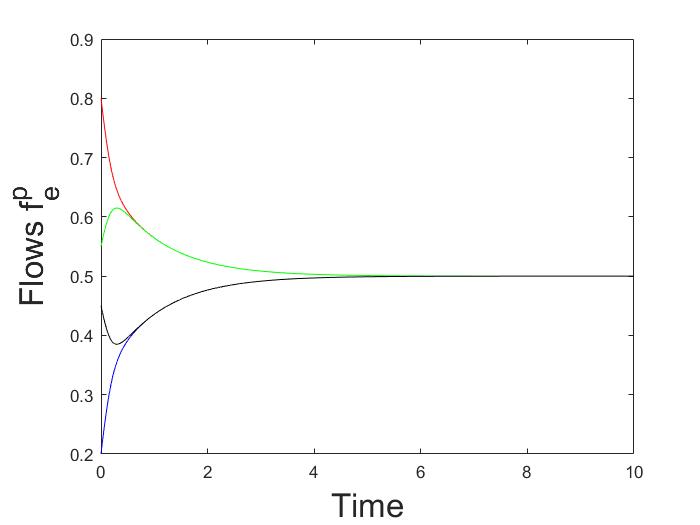
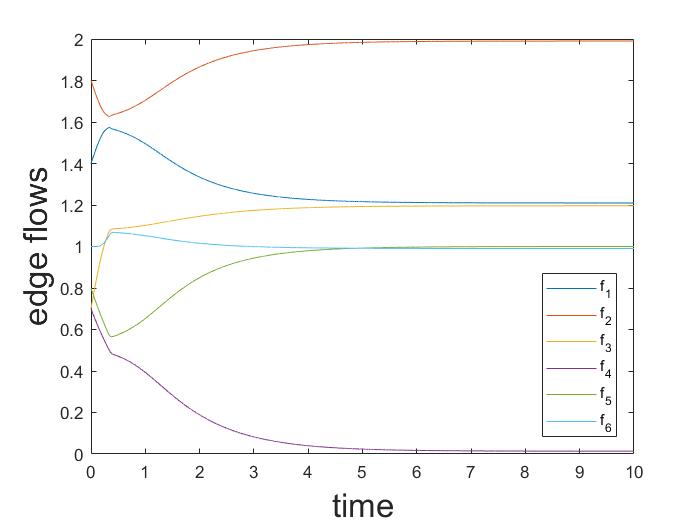
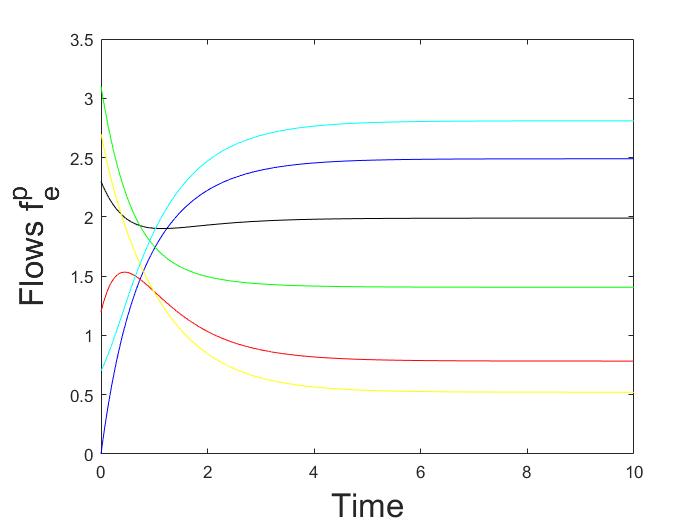
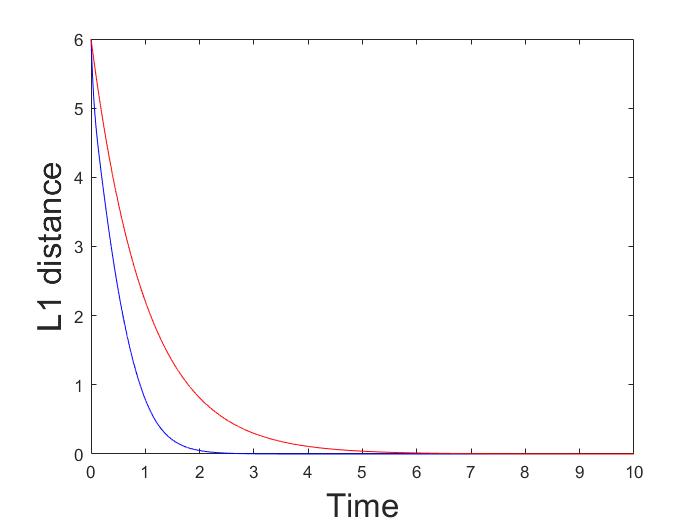
The asymptotic behaviour of deterministic logit dynamics in heterogeneous routing games is analyzed. It is proved that in directed multigraphs with parallel routes, and in series composition of such multigraphs, the dynamics admits a globally asymptotically stable fixed point. Moreover, the unique fixed point of the dynamics approaches the set of Wardrop equilibria, as the noise vanishes. The result relies on the fact that the dynamics of aggregate flows is monotone, and its Jacobian is strictly diagonally dominant by columns.💡 Summary & Analysis
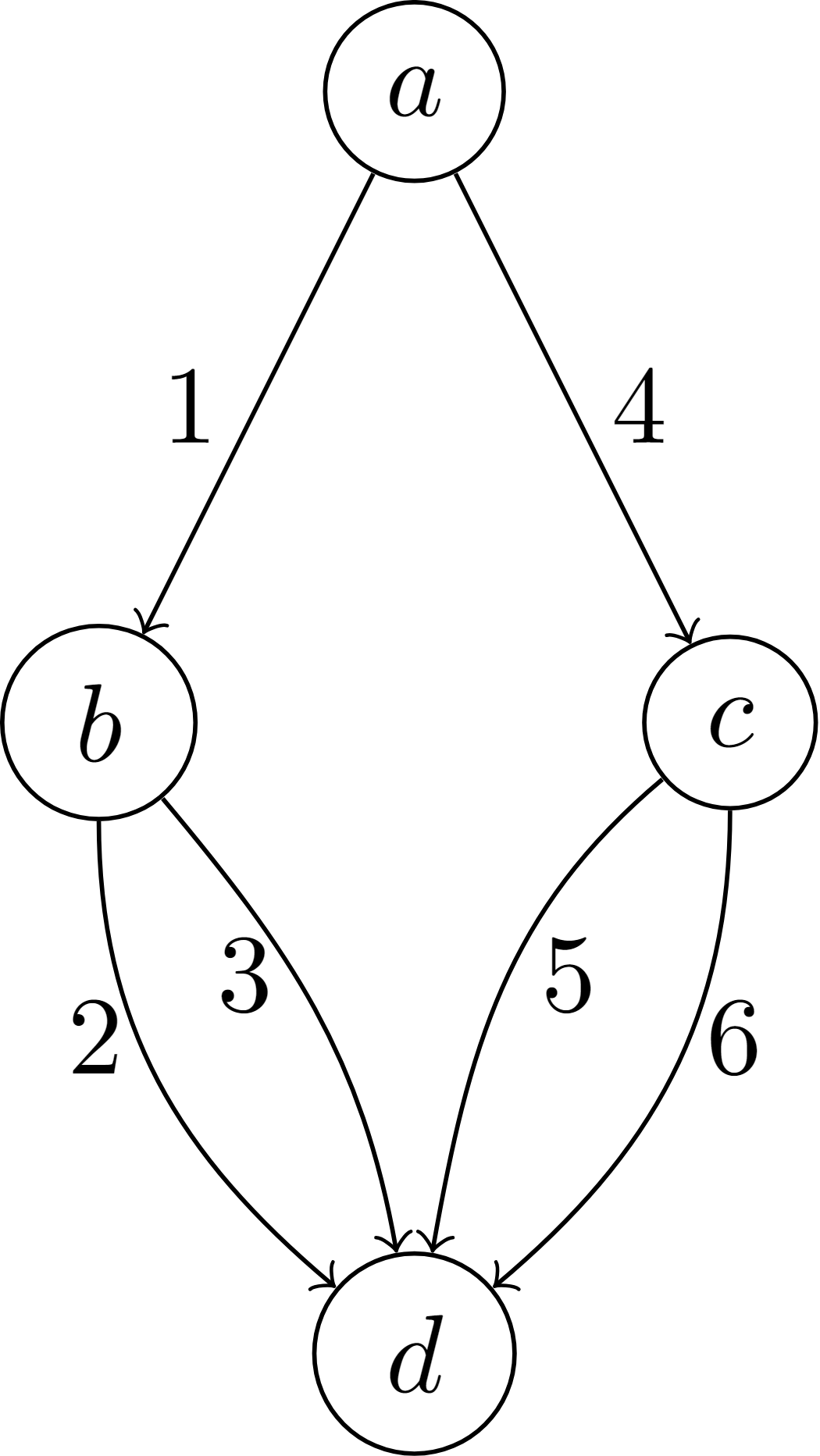
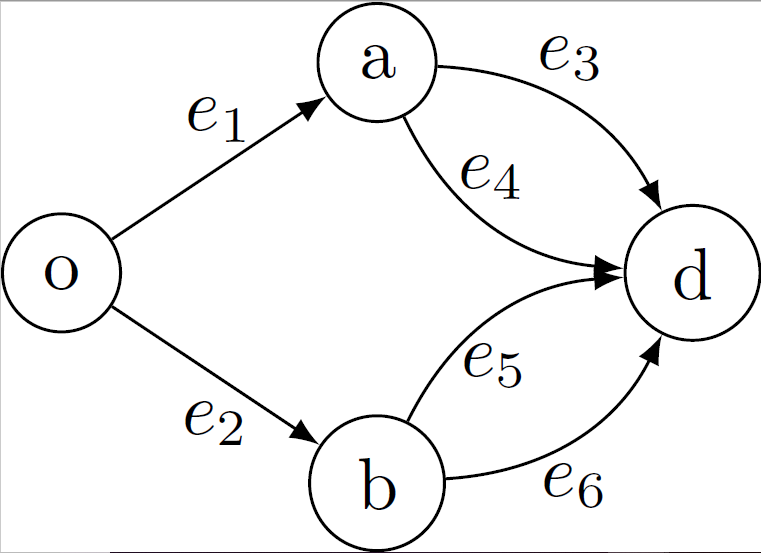
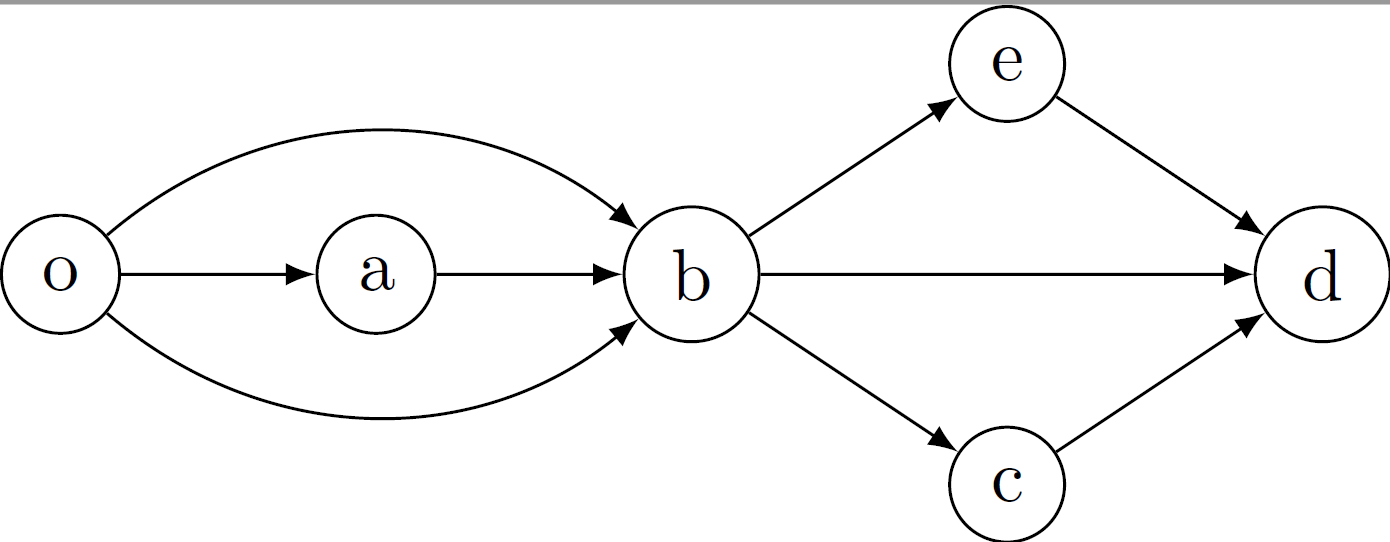
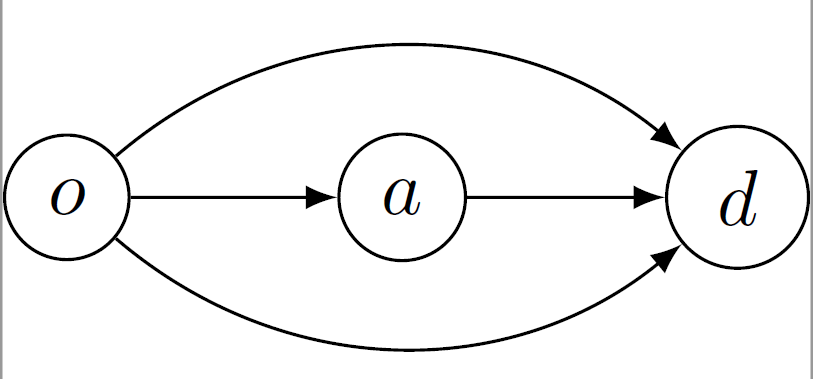
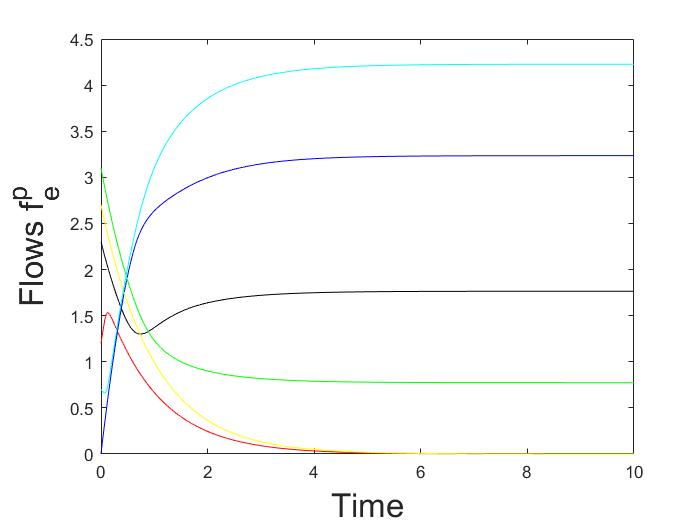
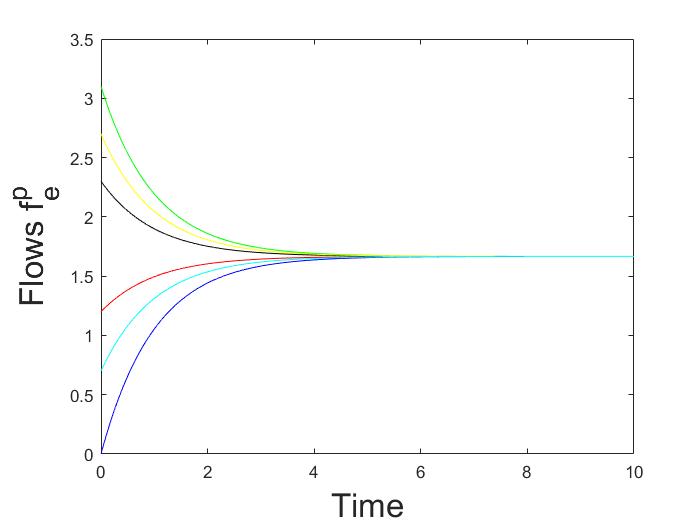
This paper focuses on the analysis of deterministic logit dynamics in heterogeneous routing games, which are systems where users choose among multiple routes with varying costs. The study aims to understand how these choices stabilize into a balanced state over time. Specifically, it examines scenarios involving directed multigraphs with parallel routes and their series compositions.The research employs deterministic logit dynamics to model user behavior: the probability of choosing a route depends on its cost. Through this framework, the authors prove that under certain conditions, such as in networks composed of directed multigraphs with parallel routes or their series combinations, the system reaches a globally asymptotically stable fixed point. This means the network stabilizes into an equilibrium where no user has an incentive to deviate from their chosen route.
The study also shows that as noise decreases (i.e., when choices become more deterministic), these equilibria converge towards Wardrop equilibria, which are states where all users face equal marginal costs for their chosen routes. This finding is significant because it provides a theoretical foundation for understanding and predicting how complex network systems can reach stable states under various conditions.
**
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)