Approximate Query Processing using Deep Generative Models
📝 Original Info
- Title: Approximate Query Processing using Deep Generative Models
- ArXiv ID: 1903.10000
- Date: 2019-11-20
- Authors: Saravanan Thirumuruganathan, Shohedul Hasan, Nick Koudas, Gautam Das
📝 Abstract
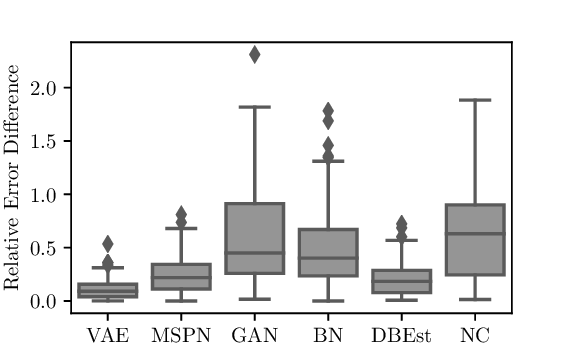
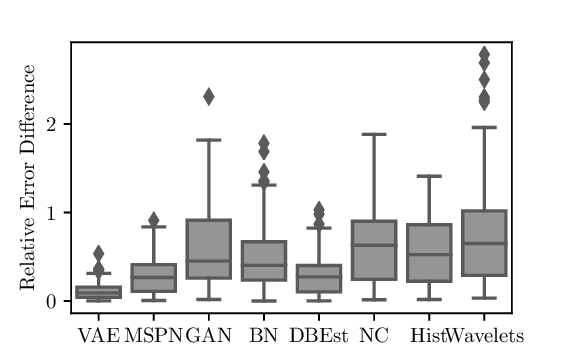
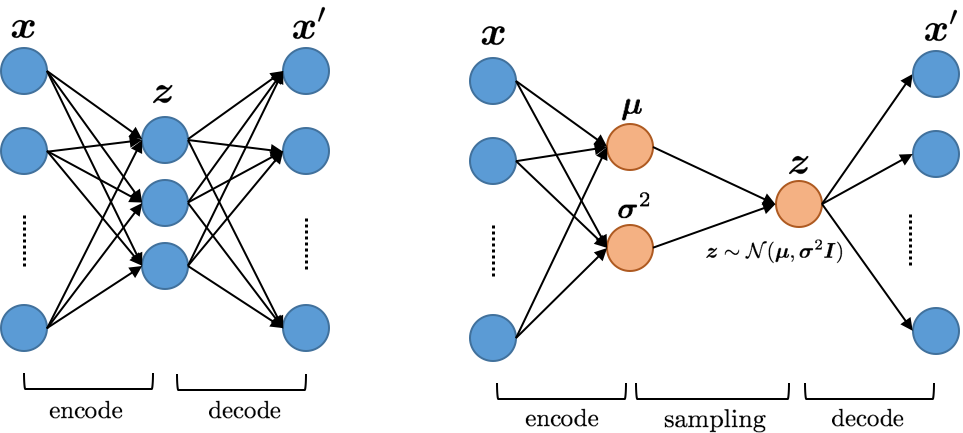
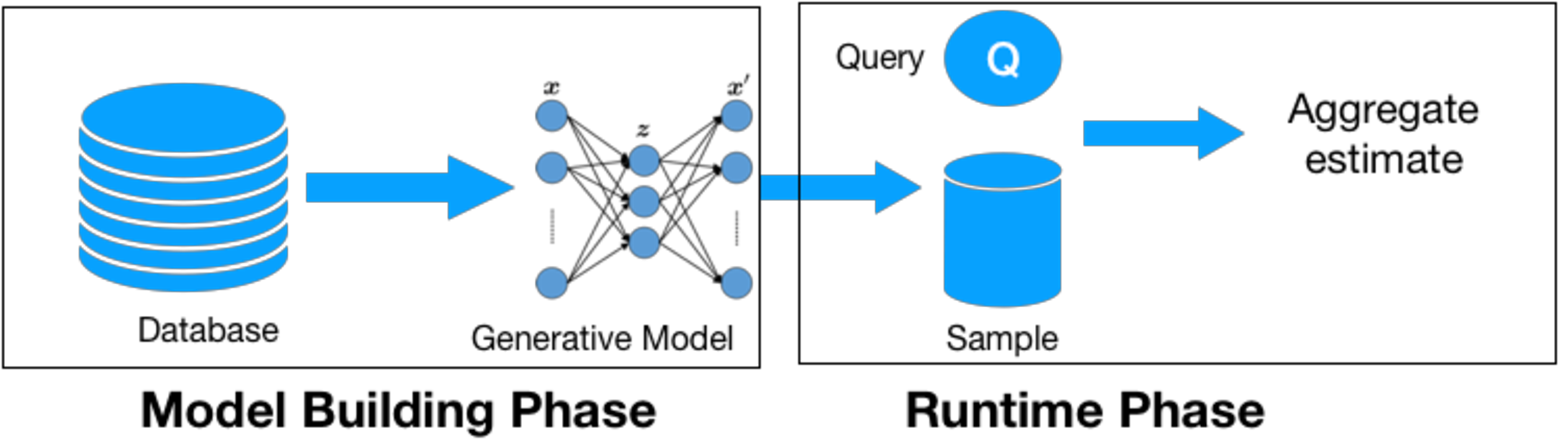
Data is generated at an unprecedented rate surpassing our ability to analyze them. The database community has pioneered many novel techniques for Approximate Query Processing (AQP) that could give approximate results in a fraction of time needed for computing exact results. In this work, we explore the usage of deep learning (DL) for answering aggregate queries specifically for interactive applications such as data exploration and visualization. We use deep generative models, an unsupervised learning based approach, to learn the data distribution faithfully such that aggregate queries could be answered approximately by generating samples from the learned model. The model is often compact - few hundred KBs - so that arbitrary AQP queries could be answered on the client side without contacting the database server. Our other contributions include identifying model bias and minimizing it through a rejection sampling based approach and an algorithm to build model ensembles for AQP for improved accuracy. Our extensive experiments show that our proposed approach can provide answers with high accuracy and low latency.📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery














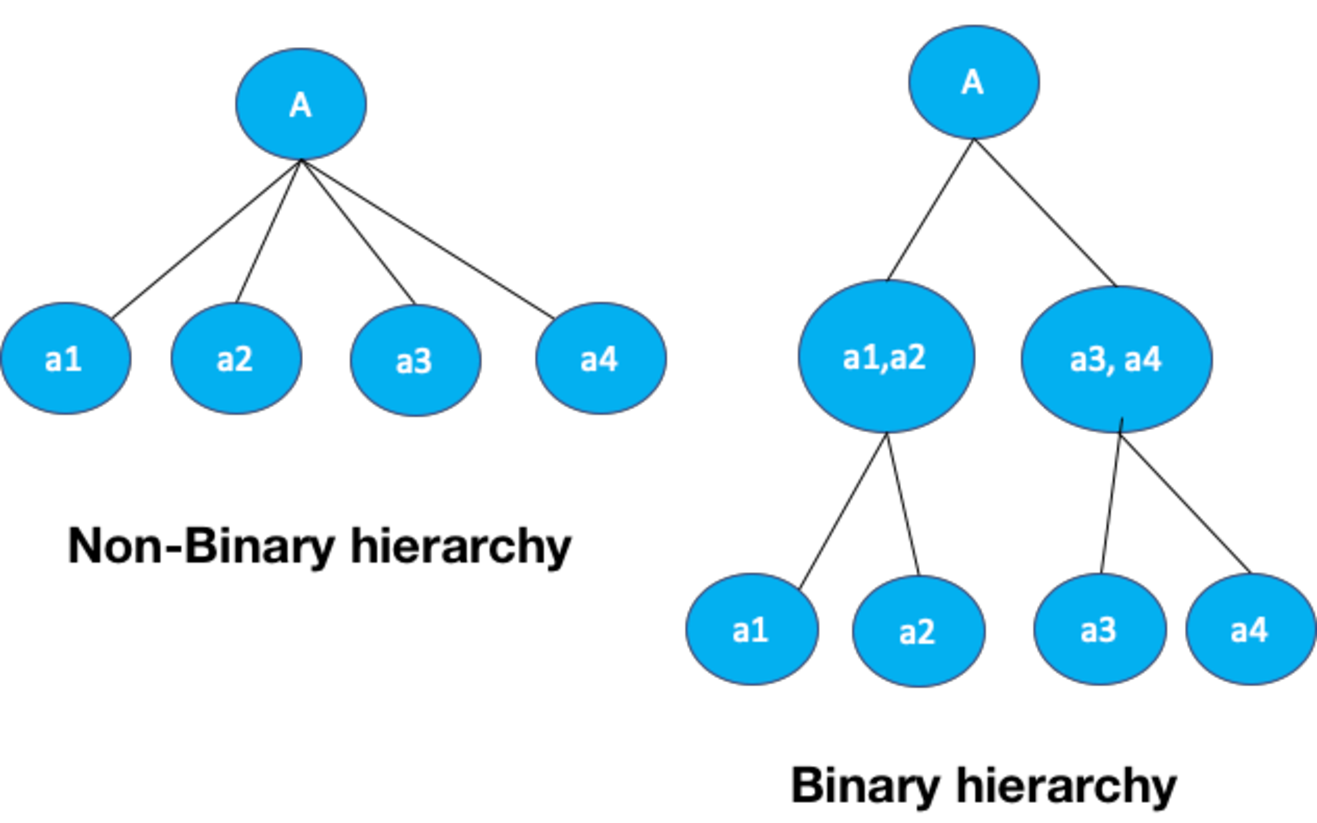
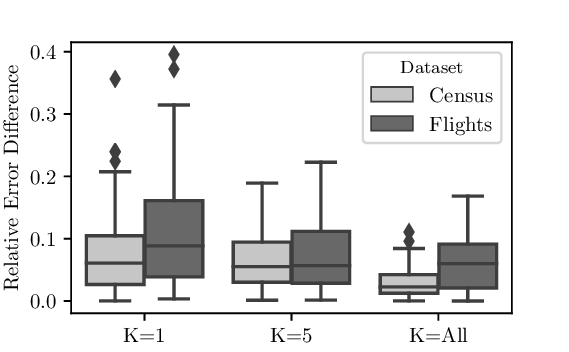
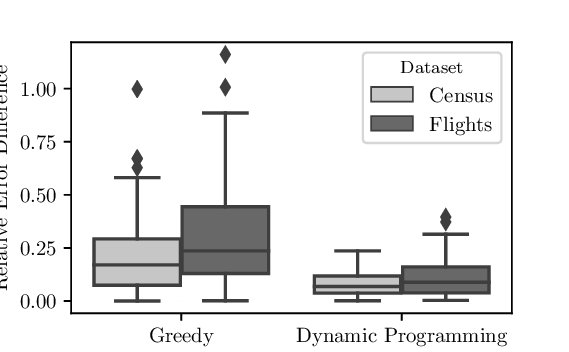
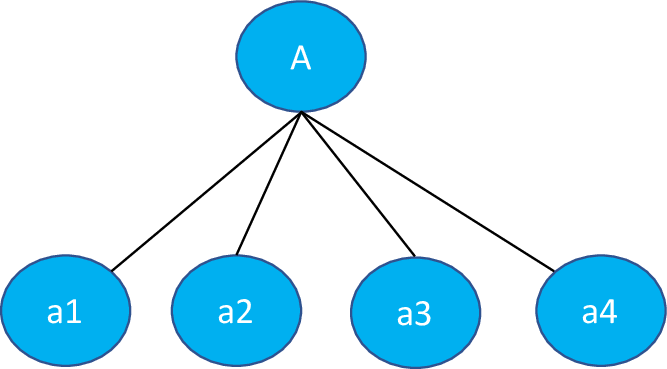





Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.